-
When ultrashort pulse laser interacts with near-critical-density plasma, extremely strong transient electromagnetic field will generate a great variety of nonlinear phenomena, such as efficient pulse absorption, magnetic self-channeling, nonlinear coherent structure, and electron and ion acceleration. It is of great significance to make a profound study of these physical processes for studying the laser-plasma interaction. Here in this work, we investigate the near-critical-density plasma structure and its temporal evolution by using proton radiography. The plasma is generated by the interaction of ultra-intense femtosecond laser (I
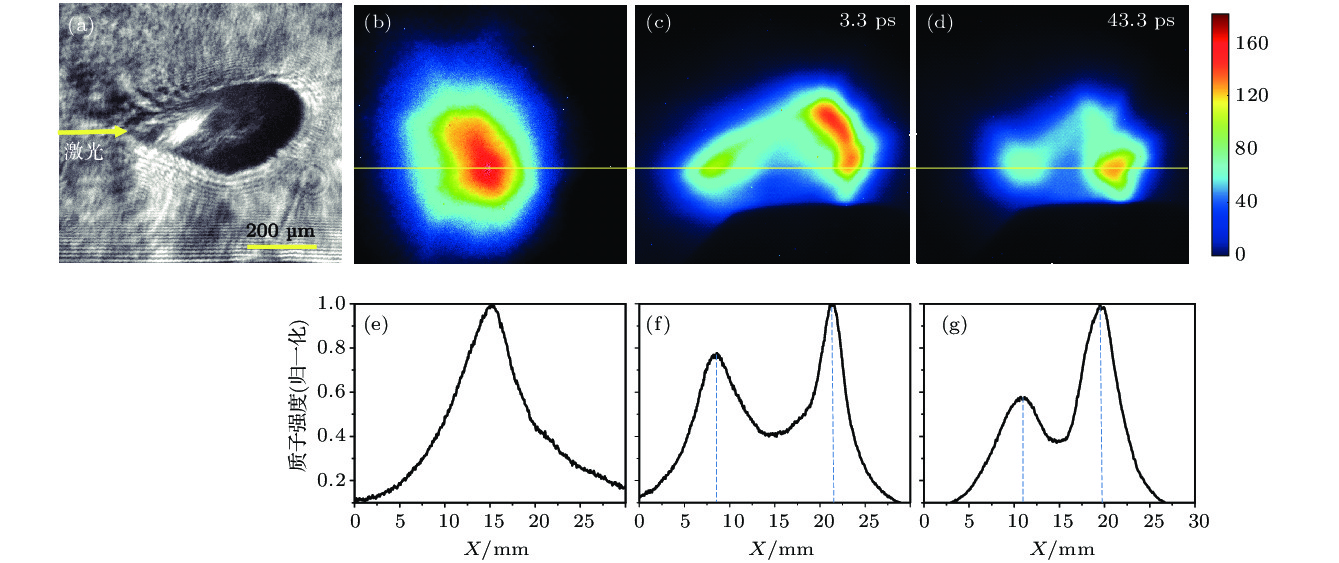
$\sim $ 3.6 × 1018 W/cm2) with high-density gas-jet target, which can produce plasma with electron density ne$ \sim$ 0.7nc (here, nc is the near-critical-density) for 800 nm laser. The proton beam is produced by the interaction of another ultra-intense femtosecond laser with stainless steel foil target. In the experiment, the proton beam is split into two asymmetric spots. On the one hand, the distance between two spots first increases rapidly and decreases slowly as time goes by. On the other hand, the size of proton beam spot on the right side is obviously lager than the one on the left side. The modification of proton beam profile indicates that a transient electric field with a maximum amplitude of 109 V/m is produced when ultrashort laser pulse interacts with the plasma. Besides, the electric field in the direction of laser propagation axis is stronger than that in the opposite direction. When the proton beam goes through the laser-plasma interaction area, most of the protons enter into the electric field in the direction of laser propagation axis, only a small number of protons enter into the electric field in the opposite direction, resulting in the fact that the proton beam is split into two asymmetric spots. The space-charge field in the plasma is induced by the laser ponderomotive force which expels the electrons piled up into a step-like profile. This field can be sustained for a long time, as the ions expand slowly because of the coulomb repulsion between ions, and the hot electrons continue to move forward with energy of a few MeV. At the end, these expanded ions gradually recombine with the reflowed electrons, causing the space-charge field to weaken until it disappears eventually. As a result, the deflection of the proton beam by the electric field in the plasma is also weakened, so the distance between proton beam splitting spots is correspondingly reduced. The hypothesis is justified by the particle-in-cell simulations. The results may have important implications in laser wake-field electron acceleration, ion acceleration and fast ignition scheme to inertial confinement fusion.-
Keywords:
- ultra-intense laser /
- near-critical-density /
- plasma /
- proton radiography
[1] Wilks S C, Kruer W, Tabak M, Langdon A 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 1383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pukhov A, Meyer-ter-Vehn J 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 3975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bulanov S V, Lontano M, Esirkepov T, Pegoraro F, Pukhov A 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 3562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bulanov S V, Esirkepov T, Naumova N, Pegoraro F, Vshivkov V 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 3440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Esirkepov T, Nishihara K, Bulanov S, Pegoraro F 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 275002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mori W B, Joshi C, Dawson J, Forslund D, Kindel J 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 60 1298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li G, Yan R, Ren C, Wang T L, Tonge J, Mori W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nakamura T, Mima K 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 205006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shaw J L, Lemos N, Amorim L D, Vafaeinajafabadi N, Marsh K A, Tsung F S 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 064801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王剑, 蔡达锋, 赵宗清, 谷渝秋 2017 66 075203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Cai D F, Zhao Z Q, Gu Y Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 075203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nakamura T, Bulanov S, Esirkepov T, Kando M 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 135002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bulanov S V, Esirkepov T Z, Khoroshkov V S, Kunetsov A V, Pegoraro F 2002 Phys. Lett. A 299 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 师绍猛, 陈荣昌, 薛艳玲, 任玉琦, 杜国浩, 邓彪, 谢红兰, 肖体乔 2008 57 6319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi S M, Chen R C, Xue Y L, Ren Y Q, Du G H, Deng B, Xie H L, Xiao T Q 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Borghesi M, Schiavi A, Campbell D H, Haines M G, Willi O, MacKinnon A J, Gizzi L A, Galimberti M, Clarke R J, Ruhl H 2001 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 43 A267
[15] Borghesi M, Sarri G, Cecchetti C A, Kourakis I, Hoarty D, Stevenson R M, James S, Brown C D, Hobbs P, Lockyear J, Morton J, Willi O, Jung R, Dieckmann M E 2010 Laser Part. Beams 28 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Borghesi M, MacKinnon A, Barringer L, Gaillard R, Gizzi L, Meyer C, Willi O, Pukhov A, Meyer-ter-Vehn J 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yogo A, Daido H, Bulanov S V, Nemoto K, Oishi Y, Nayuki T, Fujii T, Ogura K, Orimo S, Sagisaka A, Ma J L, Esirkepov T Zh, Mori M, Nishiuchi M, Pirozhkov A S, Nakamura S, Noda A, Nagatomo H, Kimura T, Tajima T 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 016401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Willingale L, Nagel S R, Thomas A G, Bellei C, Clarke R J, Dangor A E, Heathcote R, Kaluza M C, Kamperidis C, Kneip S, Krushelnick K, Lopes N, Mangles S P, Nazarov W, Nilson P M, Najmudin Z 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Okihara S, Esirkepov T Zh, Nagai K, Shimizu S, Sato F, Hashida M, Iida T, Nishihara K, Norimatsu T, Izawa Y, Sakabe S 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 026401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Palmer C A, Dover N P, Pogorelsky I, Babzien M, Dudnikova G I, Ispiriyan M, Polyanskiy M N, Schreiber J, Shkolnikov P, Yakimenko V, Najmudin Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 014801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Haberberger D, Tochitsky S, Fiuza F, Gong C, Fonseca R A, Silva L O, Mori W B, Joshi C 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 95
[22] Sylla F, Flacco A, Kahaly S, Veltcheva M, Lifschitz A, Malka V, d'Humières E, Andriyash I, Tikhonchuk V 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 085001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen S N, Vranic M, Gangolf T, Boella E, Antici P, Bailly-Grandvaux M, Loiseau P, Pepin H, Revet G, Santos J J, Schroer A M, Starodubtsev M, Willi O, Silva L O, d'Humieres E, Fuchs J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 13505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Mackinnon A J, Patel P K, Town R P, Edwards M J, Phillips T, Lerner S C, Price D W, Hicks D, Key M H, Hatchett S 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 3531
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Romagnani L, Borghesi M, Cecchetti C A, Kar S, Antici P, Audebert P, Bandhoupadjay S, Ceccherini F, Cowan T, Fuchs J 2008 Laser Part. Beams 26 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Romagnani L, Bulanov S V, Borghesi M, Audebert P, Gauthier J C, Löwenbruck K, Mackinnon A J, Patel P, Pretzler G, Toncian T, Willi O 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 025004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li C K, Séguin F H, Frenje J A, Manuel M, Casey D, Sinenian N, Petrasso R D, Amendt P A, Landen O L, Rygg J R, Town R P J, Betti R, Delettrez J, Knauer J P, Marshall F, Meyerhofer D D, Sangster T C, Shvarts D, Smalyuk V A, Soures J M, Back C A, Kilkenny J D, Nikroo A 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 056304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Borghesi M, Mackinnon A J, Gaillard R, Willi O, Pukhov A, Meyer-ter-Vehn J 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 5137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Smyth A G, Sarri G, Vranic M, Amano Y, Doria D, Guillaume E, Habara H, Heathcote R, Hicks G, Najmudin Z, Nakamura H, Norreys P A, Kar S, Silva L O, Tanaka K A, Vieira J, Borghesi M 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 063121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Li C K, Seguin F H, Frenje J A, Rygg J R, Petrasso R D, Town R P, Amendt P A, Hatchett S P, Landen O L, Mackinnon A J, Patel P K, Smalyuk V A, Sangster T C, Knauer J P 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 135003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Li G, Li S, Ain Q, Gao K, Mirzaie M, Hafz N A M 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 022306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fonseca R A, Silva L O, Tsung F S, Decyk V K, Lu W, Ren C 2002 Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2331 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 光学探针与质子探针结果(激光自左向右入射) (a)光学阴影成像; (b)原始质子束斑; (c)打靶3.3 ps后的质子束斑; (d)打靶43.3 ps后的质子束斑; (e)−(g)打靶高度处对应的质子强度图(黄线)
Figure 2. Raw images of optical probe and proton probe: (a) Optical probe result; proton beam spot for (b) no gas, (c) 3.3 ps after interaction, (d) 43.3 ps after interaction; (e)−(g) the corresponding lineout intensity profiles.
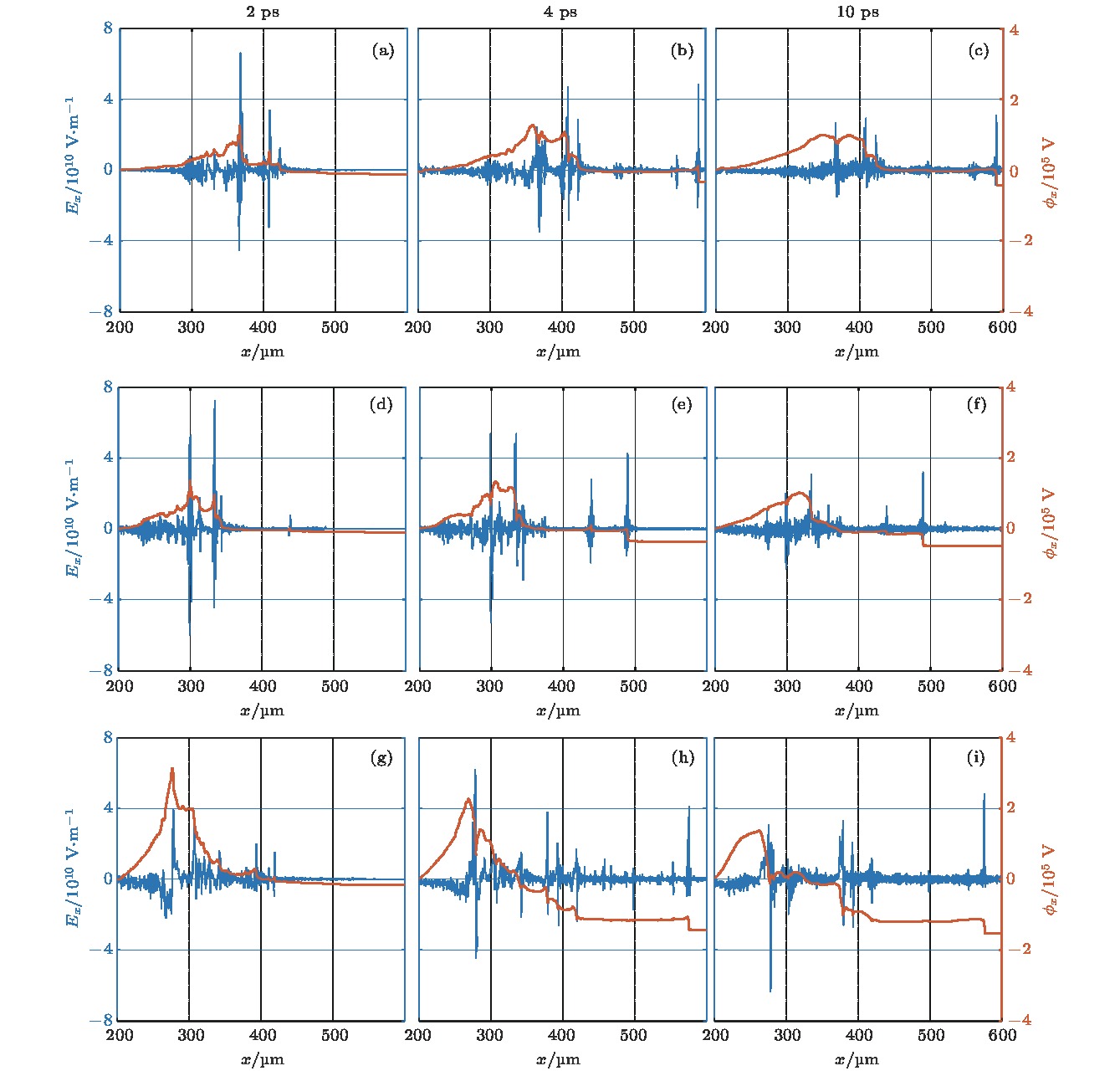
图 6 不同密度等离子体中不同时刻的时间平均的纵向电场强度和电势分布 (a)−(c)最高密度为0.8 × 1021 cm–3; (d)−(f)最高密度为1.2 × 1021 cm–3; (g)−(i)最高密度为1.2 × 1021 cm–3
Figure 6. Averaged longitudinal electric field and potential distributions with times of plasma with different density: (a)−(c) The highest plasma density is 0.8 × 1021 cm–3; (d)−(f) the highest plasma density is 1.0 × 1021 cm–3; (g)−(i) the highest plasma density is 1.2 × 1021 cm–3.
-
[1] Wilks S C, Kruer W, Tabak M, Langdon A 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 1383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pukhov A, Meyer-ter-Vehn J 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 3975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bulanov S V, Lontano M, Esirkepov T, Pegoraro F, Pukhov A 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 3562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bulanov S V, Esirkepov T, Naumova N, Pegoraro F, Vshivkov V 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 3440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Esirkepov T, Nishihara K, Bulanov S, Pegoraro F 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 275002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mori W B, Joshi C, Dawson J, Forslund D, Kindel J 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 60 1298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li G, Yan R, Ren C, Wang T L, Tonge J, Mori W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nakamura T, Mima K 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 205006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shaw J L, Lemos N, Amorim L D, Vafaeinajafabadi N, Marsh K A, Tsung F S 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 064801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王剑, 蔡达锋, 赵宗清, 谷渝秋 2017 66 075203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Cai D F, Zhao Z Q, Gu Y Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 075203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nakamura T, Bulanov S, Esirkepov T, Kando M 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 135002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bulanov S V, Esirkepov T Z, Khoroshkov V S, Kunetsov A V, Pegoraro F 2002 Phys. Lett. A 299 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 师绍猛, 陈荣昌, 薛艳玲, 任玉琦, 杜国浩, 邓彪, 谢红兰, 肖体乔 2008 57 6319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi S M, Chen R C, Xue Y L, Ren Y Q, Du G H, Deng B, Xie H L, Xiao T Q 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Borghesi M, Schiavi A, Campbell D H, Haines M G, Willi O, MacKinnon A J, Gizzi L A, Galimberti M, Clarke R J, Ruhl H 2001 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 43 A267
[15] Borghesi M, Sarri G, Cecchetti C A, Kourakis I, Hoarty D, Stevenson R M, James S, Brown C D, Hobbs P, Lockyear J, Morton J, Willi O, Jung R, Dieckmann M E 2010 Laser Part. Beams 28 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Borghesi M, MacKinnon A, Barringer L, Gaillard R, Gizzi L, Meyer C, Willi O, Pukhov A, Meyer-ter-Vehn J 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yogo A, Daido H, Bulanov S V, Nemoto K, Oishi Y, Nayuki T, Fujii T, Ogura K, Orimo S, Sagisaka A, Ma J L, Esirkepov T Zh, Mori M, Nishiuchi M, Pirozhkov A S, Nakamura S, Noda A, Nagatomo H, Kimura T, Tajima T 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 016401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Willingale L, Nagel S R, Thomas A G, Bellei C, Clarke R J, Dangor A E, Heathcote R, Kaluza M C, Kamperidis C, Kneip S, Krushelnick K, Lopes N, Mangles S P, Nazarov W, Nilson P M, Najmudin Z 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Okihara S, Esirkepov T Zh, Nagai K, Shimizu S, Sato F, Hashida M, Iida T, Nishihara K, Norimatsu T, Izawa Y, Sakabe S 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 026401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Palmer C A, Dover N P, Pogorelsky I, Babzien M, Dudnikova G I, Ispiriyan M, Polyanskiy M N, Schreiber J, Shkolnikov P, Yakimenko V, Najmudin Z 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 014801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Haberberger D, Tochitsky S, Fiuza F, Gong C, Fonseca R A, Silva L O, Mori W B, Joshi C 2012 Nat. Phys. 8 95
[22] Sylla F, Flacco A, Kahaly S, Veltcheva M, Lifschitz A, Malka V, d'Humières E, Andriyash I, Tikhonchuk V 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 085001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen S N, Vranic M, Gangolf T, Boella E, Antici P, Bailly-Grandvaux M, Loiseau P, Pepin H, Revet G, Santos J J, Schroer A M, Starodubtsev M, Willi O, Silva L O, d'Humieres E, Fuchs J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 13505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Mackinnon A J, Patel P K, Town R P, Edwards M J, Phillips T, Lerner S C, Price D W, Hicks D, Key M H, Hatchett S 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 3531
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Romagnani L, Borghesi M, Cecchetti C A, Kar S, Antici P, Audebert P, Bandhoupadjay S, Ceccherini F, Cowan T, Fuchs J 2008 Laser Part. Beams 26 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Romagnani L, Bulanov S V, Borghesi M, Audebert P, Gauthier J C, Löwenbruck K, Mackinnon A J, Patel P, Pretzler G, Toncian T, Willi O 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 025004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li C K, Séguin F H, Frenje J A, Manuel M, Casey D, Sinenian N, Petrasso R D, Amendt P A, Landen O L, Rygg J R, Town R P J, Betti R, Delettrez J, Knauer J P, Marshall F, Meyerhofer D D, Sangster T C, Shvarts D, Smalyuk V A, Soures J M, Back C A, Kilkenny J D, Nikroo A 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 056304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Borghesi M, Mackinnon A J, Gaillard R, Willi O, Pukhov A, Meyer-ter-Vehn J 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 5137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Smyth A G, Sarri G, Vranic M, Amano Y, Doria D, Guillaume E, Habara H, Heathcote R, Hicks G, Najmudin Z, Nakamura H, Norreys P A, Kar S, Silva L O, Tanaka K A, Vieira J, Borghesi M 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 063121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Li C K, Seguin F H, Frenje J A, Rygg J R, Petrasso R D, Town R P, Amendt P A, Hatchett S P, Landen O L, Mackinnon A J, Patel P K, Smalyuk V A, Sangster T C, Knauer J P 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 135003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Li G, Li S, Ain Q, Gao K, Mirzaie M, Hafz N A M 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 022306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fonseca R A, Silva L O, Tsung F S, Decyk V K, Lu W, Ren C 2002 Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2331 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11662
- PDF Downloads: 187
- Cited By: 0

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: