-
In the process of rumor propagation, people who know the truth or judge the truth can spread true information about rumors. Therefore, on the rumor propagation, it is significant to introduce the spreaders who spread true information in the rumor propagation. But the previous studies did not take into consideration the influence of true information spreading on the rumor propagation. In this paper, the susceptible-infective-true-removed (SITR) rumor propagation model with the true information spreader and the forgetting factor of rumors is established. The threshold K0 is obtained by using the method of the next generation matrix. If K0 < 1, the balance between no rumor and no true information spreader is locally asymptotically stable. The existence and stability of two boundary balance (that is, there are rumor spreaders but no true information spreaders, and there are no rumor spreaders but true information spreaders) are proved. The bistable region of two-boundary balance is given. Further, under different conditions we obtain the existence and locally asymptotical stability of positive balance (rumor spreaders and true information spreaders coexist). Finally, the theoretical results are verified by numerical simulations. We find that the initial value of the true information spreaders affects the peak value of the rumor spreaders and the duration of the rumor. The bigger the initial value of the true information spreaders, the smaller the peak value of the rumor spreaders is and the shorter the duration of the rumor is. The initial value of the rumor spreaders affects the peak value of the rumor spreaders, and the time when the rumor spreaders reach the peak value. The larger the initial value of the rumor spreaders, the larger the peak value of the rumor spreaders is and the earlier the peak value appears. But the initial value of the rumor spreaders does not affect the duration of the rumor. Therefore, in the process of rumor propagation, according to mathematical analysis of the rumor propagation model, we find that the rumor spread is a very complicated process. The results of mathematical analysis can provide theoretical basis to control the rumor propagation and reduce the negative effects of rumors.
-
Keywords:
- rumor propagation /
- true information /
- threshold /
- equilibrium
[1] Daley D J, Kendall D G 1964 Nature 204 1118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sudbury A 1985 J. Appl. Prob. 22 443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zanette D H 2001 Phys. Rev. E 64 050901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zanette D H 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 041908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Nekovee M, Moreno Y, Bianconi G, Marsili M 2007 Physica A 374 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Moreno Y, Nekovee M, Pacheco A F 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 066130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhao L J, Wang J J, Chen Y C, Wang Q, Cheng J J, Cui H X 2012 Physica A 391 2444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhao L J, Wang Q, Cheng J J, Chen Y C, Wang J J, Huang W 2011 Physica A 390 2619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Deng S F, Li W 2017 Phys. Rev. E 95 042306
[10] Zan Y L, Wu J L, Li P, Yu Q L 2014 Physica A 405 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Y Q, Yang X Y, Han Y L, Wang X A 2013 Commun. Theor. Phys. 59 510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang L X, Zang T R, Yang X F, Wu Y B, Tang Y Y 2017 arXiv: 1705.10618v1 [cs.SI]
[13] He Z B, Cai Z P, Yu J G, Wang X M, Sun Y C, Li Y S 2017 IEEE. T. Veh. Technol. 66 2789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Huo, Liang’an, Wang L, Song N X, Ma C Y, He B 2017 Physica A 468 855
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang Y H, Zhu J J 2018 Physica A 503 862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xiao Y P, Chen D Q, Wei S H, Li Q, Wang H H, Xu M 2019 Nonlinear Dyn. 95 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 顾亦然, 夏玲玲 2012 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y R, Xia L L 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王辉, 韩江洪, 邓林, 程克勤 2013 62 110505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Han J H, Deng L, Cheng K Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 110505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张亚明, 苏妍嫄, 刘海鸥 2017 系统科学与数学 37 1960
Zhang Y M, Su Y Y, Liu H O 2017 J. Sys. Sci. Math. Scis. 37 1960
[20] 万贻平, 张东戈, 任清辉 2015 64 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan Y P, Zhang D G, Ren Q H 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 冉茂洁, 刘超, 黄贤英, 刘小洋, 杨宏雨, 张光建 2018 计算机应用 38 3312
Ran M J, Liu C, Huang X Y, Liu X Y, Yang H Y, Zhang G J 2018 J. Comput. Appl. 38 3312
[22] 赵敏, 陈文霞, 宋乾坤 2018 应用数学和力学 39 1400
Zhao M, Chen W X, Song Q K 2018 Appl. Math. Mech. 39 1400
[23] Driessche P, Watmough J 2002 Math. Biosci. 180 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Routh E J 1877 A Streatis on the Stability of Given State of Motion (London: Macmillan) pp3−21
[25] Jin Z, Sun G Q, Zhu H P 2014 Math. Biosci. Eng. 11 1295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yao Y R, Zhang J P 2016 J. Biol. Syst. 24 577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jing W J, Jin Z, Zhang J P 2018 J. Biol. Dynam. 12 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3
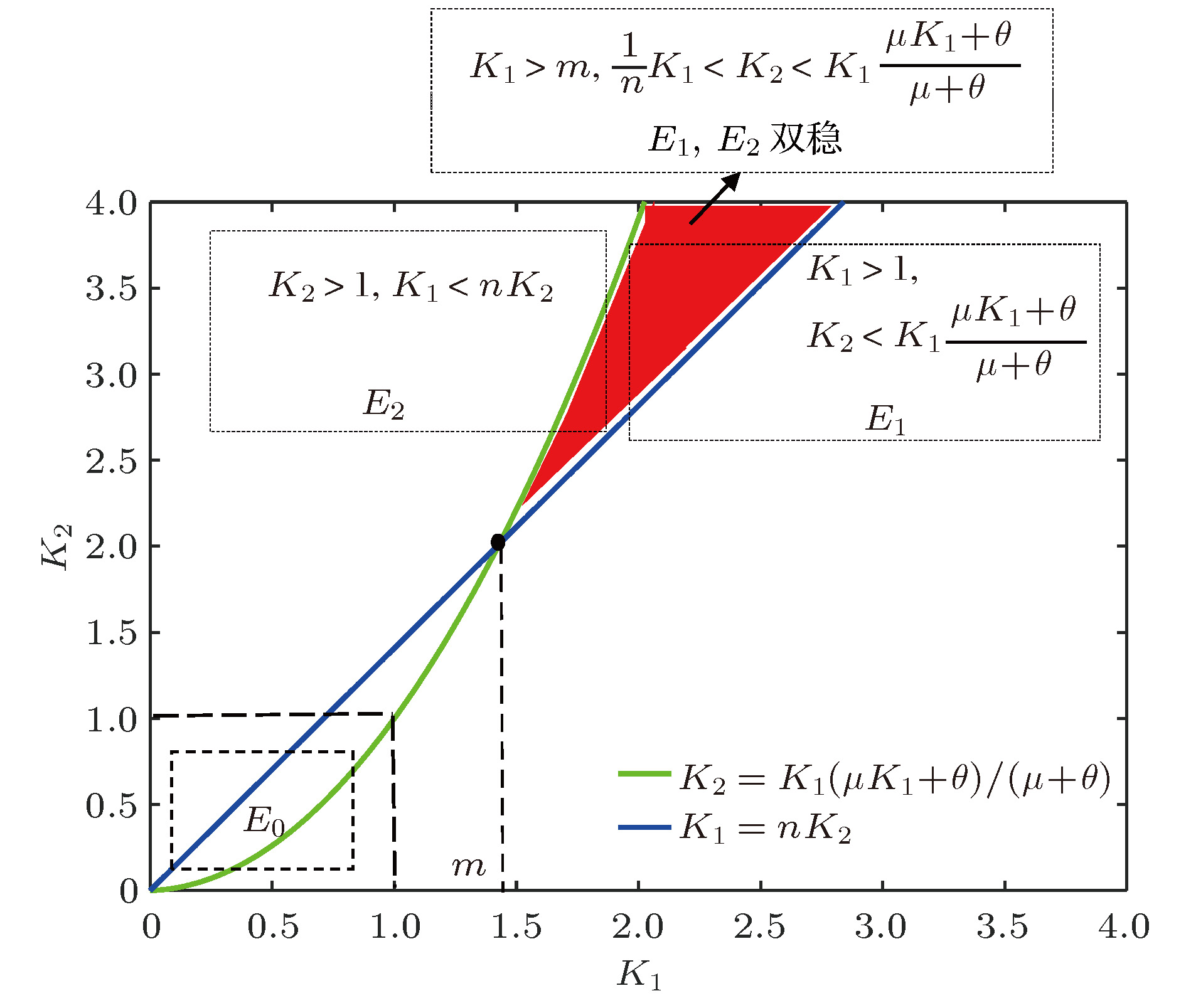
$K_1$ 与$K_2$ 关系图($\alpha_1=0.7, \beta=0.9, A=0.2,\ \mu=$ $0.2,\; \theta=0.01)$ (a)$\epsilon=0.01$ ,$\epsilon<(1-\alpha_1)\beta$ ; (b)$\epsilon=0.3$ ,$\epsilon>(1-\alpha_1)\beta$ Figure 3. Diagram of
$K_1$ and$K_2$ ($\alpha_1\!= 0.7,\; \beta\!=0.9,\; A\!=0.2,$ $\mu=0.2,\; \theta=0.01$ ): (a)$\epsilon=0.01$ ,$\epsilon<(1-\alpha_1)\beta$ ; (b)$\epsilon=$ $0.3,\; \epsilon > (1-\alpha_1)\beta$ 图 4
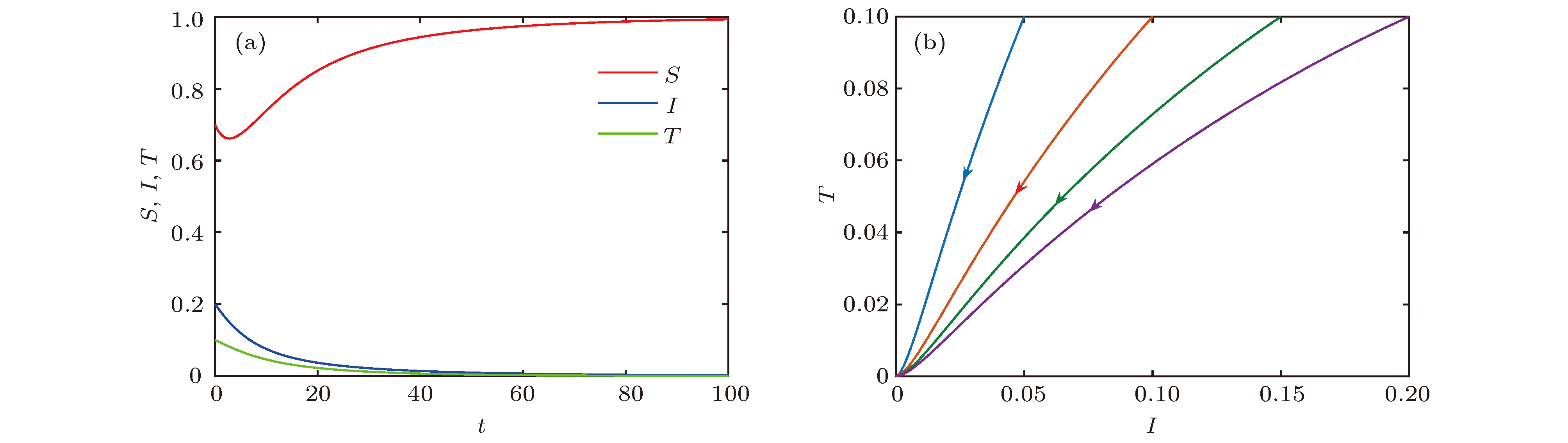
$\alpha_1 = 0.3,\;\beta = 0.6,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.15$ 时, (a) S, I, T的时间序列图和(b) I-T相平面图Figure 4. When
$\alpha_1 = 0.3,\;\beta = 0.6,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.15$ , (a) time series graph of S, I, and T; (b) phase plan of I-T.图 5
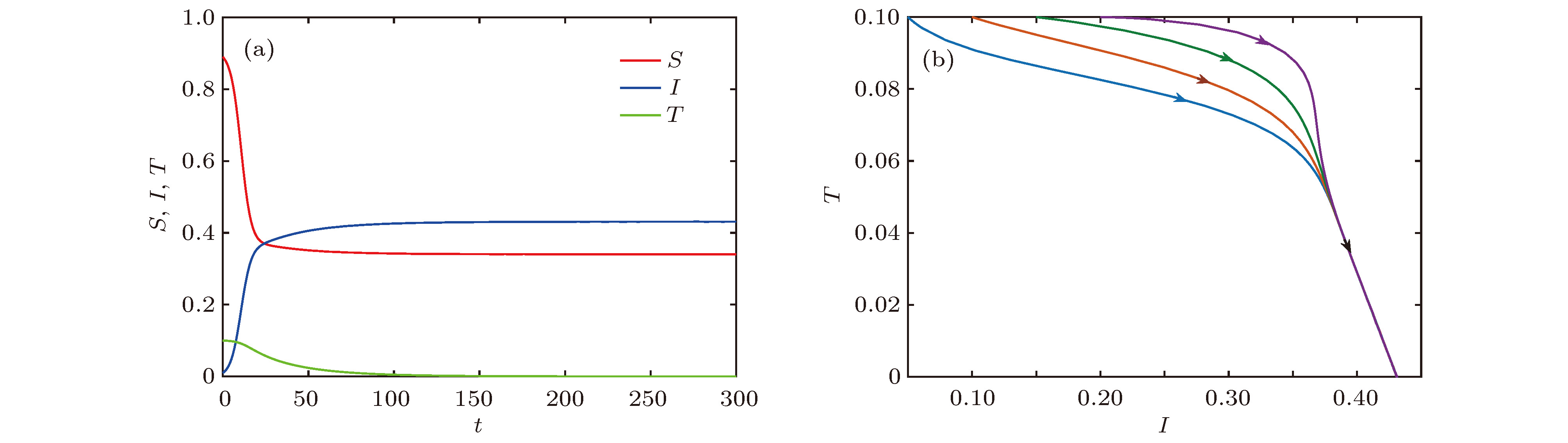
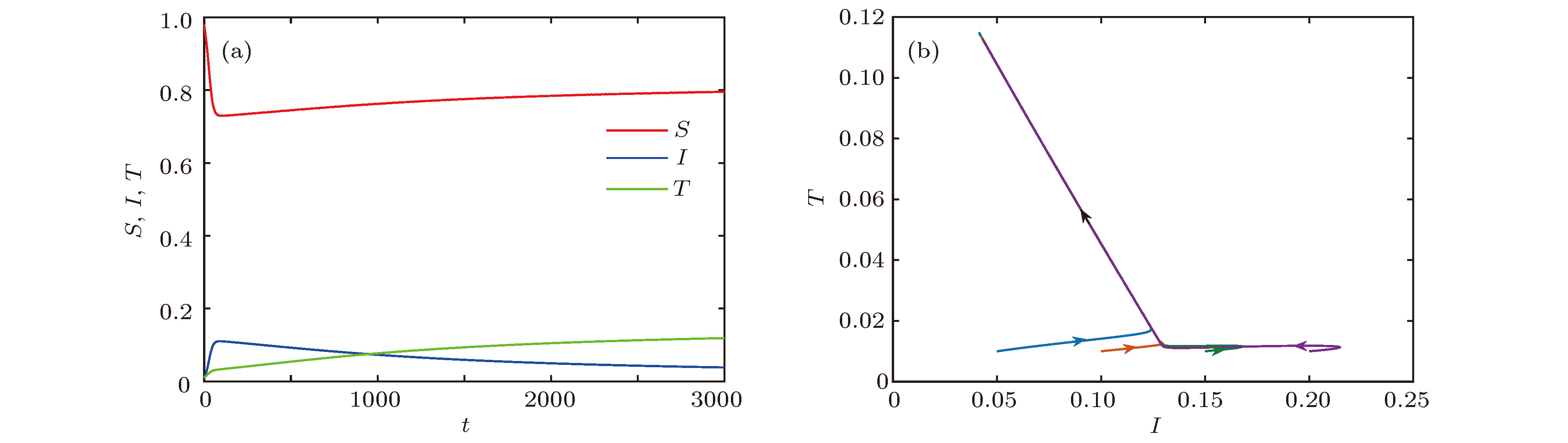
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.36$ 时, (a) S, I, T的时间序列图和(b) I-T相平面图Figure 5. When
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.36$ , (a) time series graph of S, I, and T; (b) phase plan of I-T.图 6
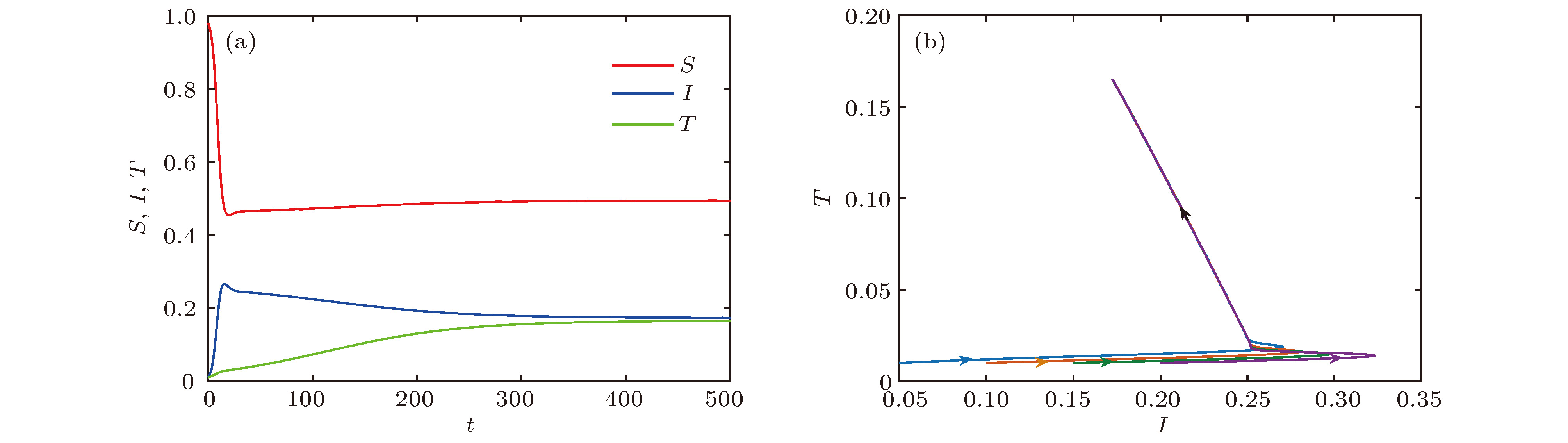
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.22$ 时, (a) S, I, T的时间序列图和(b) I-T相平面图Figure 6. When
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.22$ , (a) time series graph of S, I, and T; (b) phase plan of I-T.图 8
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.3 $ 时, (a) S, I, T的时间序列图和(b) I-T相平面图Figure 8. When
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.3 $ , (a) time series graph of S, I, and T; (b) phase plan of I-T.图 9
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.3,\;\delta = 0.3 $ 时, (a) S, I, T的时间序列图和(b) I-T相平面图Figure 9. When
$\alpha_1 = 0.7,\;\beta = 0.9,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.3,\;\delta = 0.3 $ , (a) time series graph of S, I, and T; (b) phase plan of I-T.图 10
$ \alpha_1 = 0.5,\;\beta = 0.6,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.24 $ 时, (a) S, I, T的时间序列图和(b) I-T相平面图Figure 10. When
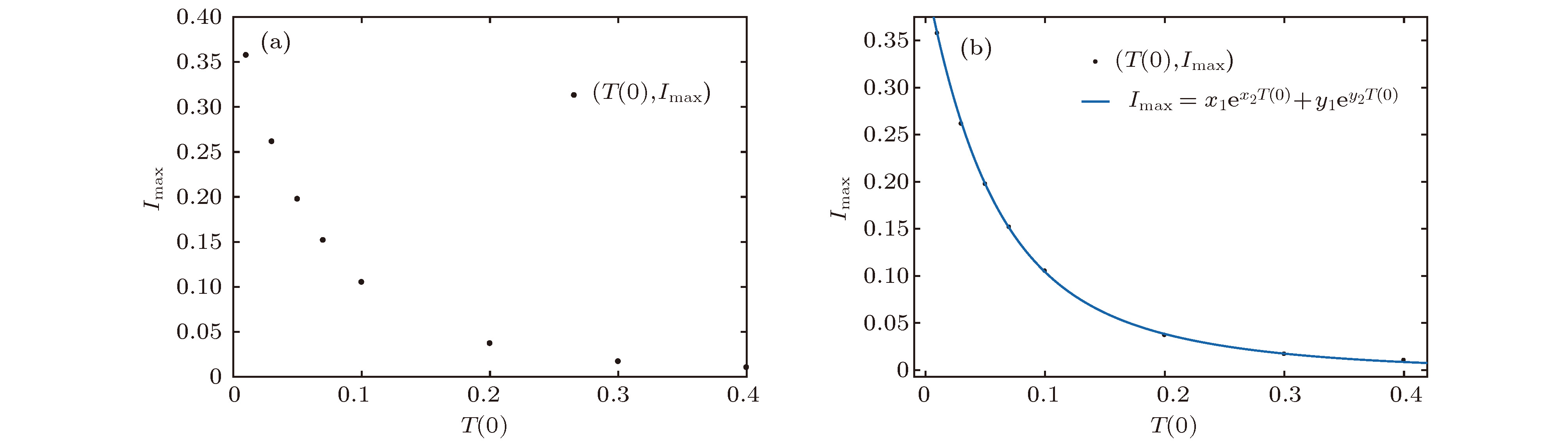
$\alpha_1 = 0.5,\;\beta = 0.6,\; A = 0.2,\;\mu =0.2,\;\theta = 0.01,\;\epsilon = 0.01,\;\delta = 0.24 $ , (a) time series graph of S, I, and T; (b) phase plan of I-T.图 11 (a)不同真实信息传播者的初始值对谣言传播的影响; (b)不同谣言传播者的初始值对谣言传播的影响; 参数取值
$\alpha_1=0.7$ ,$\beta=0.9$ ,$\delta=0.36$ ,$A=0.2$ ,$\mu=0.2$ ,$\theta=0.01$ ,$\epsilon=0.01$ Figure 11. (a) Influence of different initial values of true information spreaders; (b) influence of different initial values of rumor spreaders on the rumor propagation. The parameter values are
$\alpha_1=0.7$ ,$\beta=0.9$ ,$\delta=0.36$ ,$A=0.2$ ,$\mu=0.2$ ,$\theta=0.01$ ,$\epsilon=0.01$ .系统(2)的平衡点 $ \epsilon< \left( {1 - {\alpha _1}} \right){\rm{\beta }}$ ${K_2} > {K_1}$ ${K_2} > \dfrac{{{K_1}\left( {\mu {R_1} + \theta } \right)}}{{\mu + \theta }}$ ${K_2} < 1$ 图3(a)中黄色区域${E_0},\;E_1^*$ ${K_2} > 1 > {K_1}$ 图3(a)中绿色区域${E_0},\;{E_2},\;E_1^*$ ${K_1} > 1$ 图3(a)中紫色区域${E_0},\;{E_1},\;{E_2},\;E_1^*$ ${K_2} < \dfrac{{{K_1}\left( {\mu {K_1} + \theta } \right)}}{{\mu + \theta }}$ $\epsilon < \left( {1 - 2{\alpha _1} } \right)\beta + \dfrac{ {\delta \theta } }{\mu },{\varDelta _1} \geqslant 0$ 图3(a)中蓝色区域${E_0},\;{E_1},\;{E_2},\;E_6^*,\;E_7^*$ ${K_2} < {K_1}$ ${K_1} < 1$ 图3(a)中橙色区域$E_0$ ${K_1} > 1 > {K_2}$ 图3(a)中红色区域$E_0,\;E_1$ ${K_1} > {K_2} > 1$ 图3(a)中空白区域$E_0,\;E_1,\;E_2$ $\epsilon > \left( {1 - {\alpha _1}} \right){\rm{\beta }}$ ${K_2} > {K_{1,}}$ ${K_2} > \dfrac{{{K_1}\left( {\mu {K_1} + \theta } \right)}}{{\mu + \theta }}$ ${K_2} < 1$ 图3(b)中黄色区域$E_0,\;E_2^*$ ${K_2} > 1 > {K_1}$ 图3(b)中绿色区域$E_0,\;E_2,\;E_2^*$ ${K_1} > 1$ 图3(b)中紫色区域$E_0,\;E_1,\;E_2,\;E_2^*$ $K_2<K_1$ $K_1<1$ 图3(b)中橙色区域$E_0$ $K_1>1>K_2$ 图3(b)中红色区域$E_0,\;E_1$ $1 < {K_2} < \dfrac{{{K_1}\left( {\mu {K_1} + \theta } \right)}}{{\mu + \theta }}$ 图3(b)中空白区域$E_0,\;E_1,\;E_2$ -
[1] Daley D J, Kendall D G 1964 Nature 204 1118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sudbury A 1985 J. Appl. Prob. 22 443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zanette D H 2001 Phys. Rev. E 64 050901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zanette D H 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 041908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Nekovee M, Moreno Y, Bianconi G, Marsili M 2007 Physica A 374 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Moreno Y, Nekovee M, Pacheco A F 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 066130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhao L J, Wang J J, Chen Y C, Wang Q, Cheng J J, Cui H X 2012 Physica A 391 2444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhao L J, Wang Q, Cheng J J, Chen Y C, Wang J J, Huang W 2011 Physica A 390 2619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Deng S F, Li W 2017 Phys. Rev. E 95 042306
[10] Zan Y L, Wu J L, Li P, Yu Q L 2014 Physica A 405 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Y Q, Yang X Y, Han Y L, Wang X A 2013 Commun. Theor. Phys. 59 510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang L X, Zang T R, Yang X F, Wu Y B, Tang Y Y 2017 arXiv: 1705.10618v1 [cs.SI]
[13] He Z B, Cai Z P, Yu J G, Wang X M, Sun Y C, Li Y S 2017 IEEE. T. Veh. Technol. 66 2789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Huo, Liang’an, Wang L, Song N X, Ma C Y, He B 2017 Physica A 468 855
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang Y H, Zhu J J 2018 Physica A 503 862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xiao Y P, Chen D Q, Wei S H, Li Q, Wang H H, Xu M 2019 Nonlinear Dyn. 95 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 顾亦然, 夏玲玲 2012 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y R, Xia L L 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王辉, 韩江洪, 邓林, 程克勤 2013 62 110505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Han J H, Deng L, Cheng K Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 110505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张亚明, 苏妍嫄, 刘海鸥 2017 系统科学与数学 37 1960
Zhang Y M, Su Y Y, Liu H O 2017 J. Sys. Sci. Math. Scis. 37 1960
[20] 万贻平, 张东戈, 任清辉 2015 64 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan Y P, Zhang D G, Ren Q H 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 240501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 冉茂洁, 刘超, 黄贤英, 刘小洋, 杨宏雨, 张光建 2018 计算机应用 38 3312
Ran M J, Liu C, Huang X Y, Liu X Y, Yang H Y, Zhang G J 2018 J. Comput. Appl. 38 3312
[22] 赵敏, 陈文霞, 宋乾坤 2018 应用数学和力学 39 1400
Zhao M, Chen W X, Song Q K 2018 Appl. Math. Mech. 39 1400
[23] Driessche P, Watmough J 2002 Math. Biosci. 180 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Routh E J 1877 A Streatis on the Stability of Given State of Motion (London: Macmillan) pp3−21
[25] Jin Z, Sun G Q, Zhu H P 2014 Math. Biosci. Eng. 11 1295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yao Y R, Zhang J P 2016 J. Biol. Syst. 24 577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Jing W J, Jin Z, Zhang J P 2018 J. Biol. Dynam. 12 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 18657
- PDF Downloads: 321
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: