-
提出了一个考虑空间扩散与发酵期时滞的社交网络谣言传播模型, 重点研究了扩散与时滞对在线社交网络中谣言时空传播的影响. 首先, 分析了谣言传播平衡点的存在性, 并得到了基本再生数
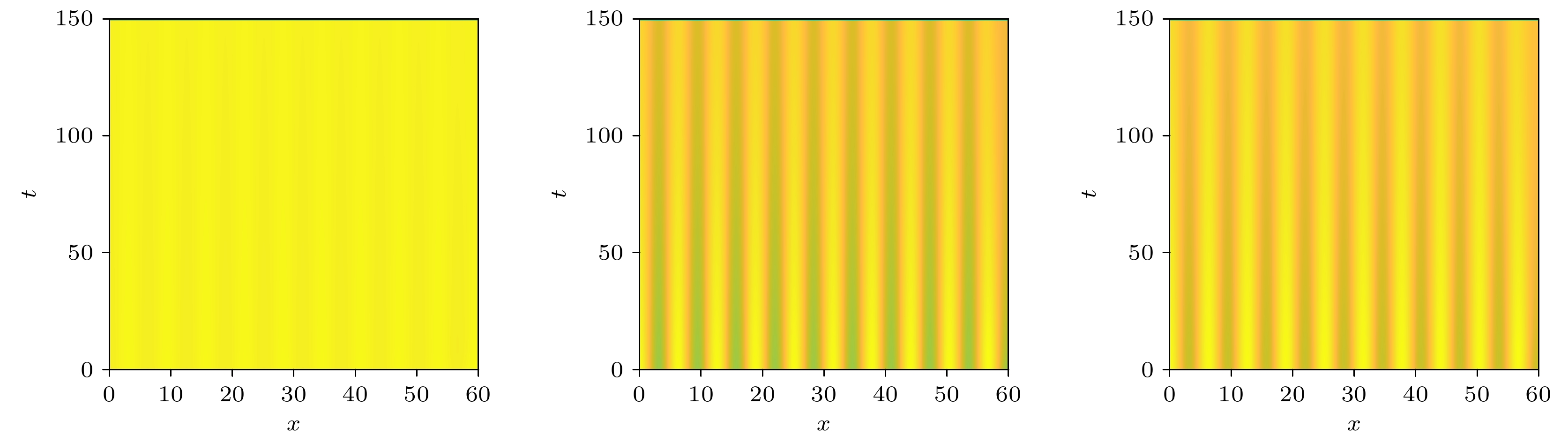
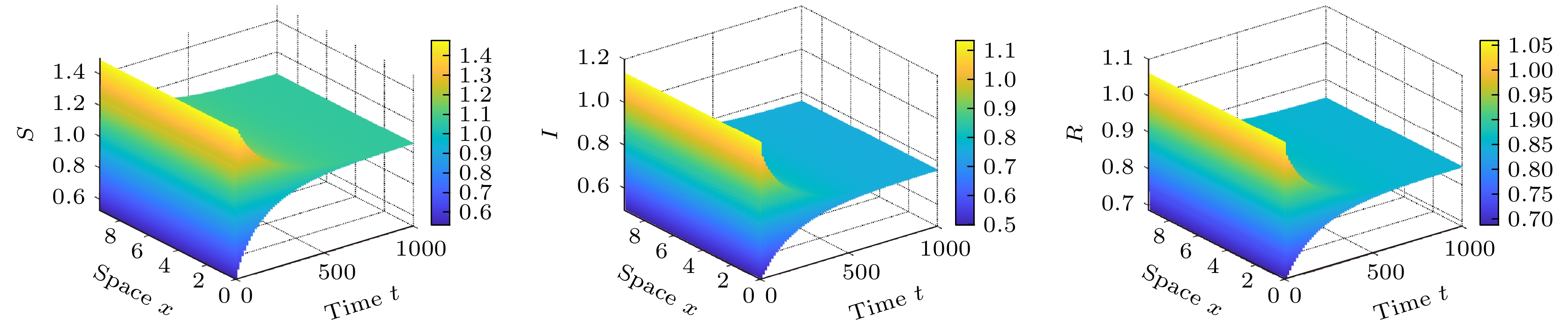
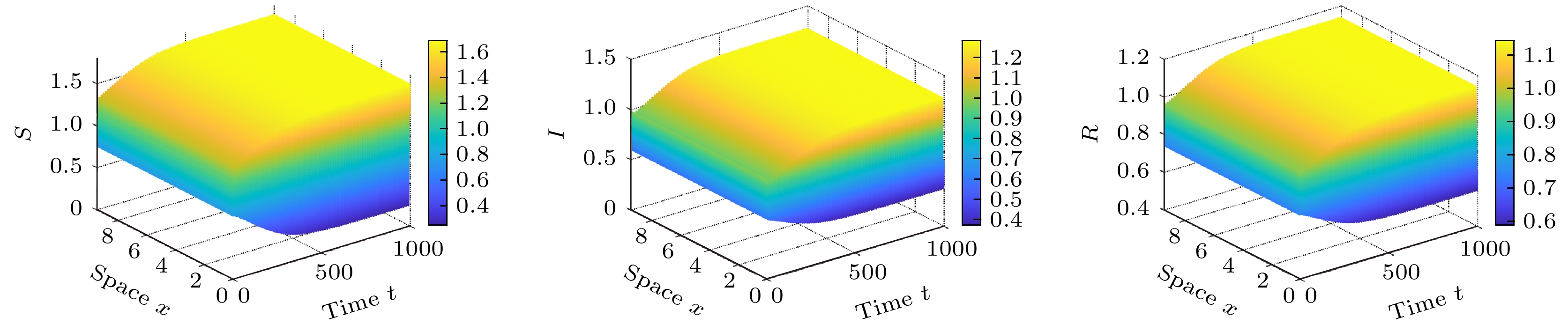
$R_{0}$ ; 其次, 运用Roth-Hurwitz稳定判据分析了谣言传播平衡点的局部稳定性, 并讨论了扩散诱导的Turing不稳定; 最后, 选取时滞为分岔参数, 建立了谣言传播模型的Hopf 分岔条件. 数值仿真结果表明, 扩散和时滞的出现都能使得谣言传播模型的稳定性发生根本性改变. 本文从时间和空间两个维度扩展了传统谣言传播动力学仅考虑时间演化的局限, 更加真实地模拟了谣言在现实社会中的时空传播规律, 为谣言传播的治理提供了全新的角度和思路.Rumors in social networks are often referred to as infectious diseases of the Internet, because rumors spreading in networks feature strong concealment, fast transmission speed and wide spread. With the development of mobile devices, online rumors nowadays are far more harmful than before. Rumors in social networks show completely different spatiotemporal dynamics from traditional rumor spreading dynamics. A social network rumor spreading model with considering both reaction diffusion and fermentation time delay is proposed in this paper. The effects of spatial diffusion and time delay on rumor spreading in online social networks are studied. Firstly, the existence of equilibrium point of the reaction-diffusion rumor spreading model is analyzed, and the basic regeneration number$R_{0}$ is calculated. When$R_{0} < 1$ , the rumor stops spreading and disappears in social networks; when$R_{0}>1$ , the rumor persists in social networks. Secondly, the local stability of the rumor spreading equilibrium is investigated by using the Roth-Hurwitz stability criterion, and the influence of diffusion on the system stability is discussed. When the diffusion is introduced into a stable rumor spreading model without time delay, the model becomes unstable, indicating that the Turing instability is caused by diffusion. Thirdly, the Hopf bifurcation condition of the rumor spreading model is established by selecting the time delay τ as the bifurcation parameter, and the expression of bifurcation threshold$\tau_{0}$ is given. When$\tau < \tau_{0}$ , the rumor propagation model with diffusion term is stable; when$\tau>\tau_{0}$ , the model loses the stability and the Hopf bifurcation occurs. The numerical simulation results show that both diffusion and time delay play an important role in the dynamic evolution of rumor spreading. At the same time, the influence of the crowding degree of spreaders on rumor propagation is also simulated. As the crowding gets worse and worse, the rumor refuting effect weakens, the bifurcation threshold$\tau_{0}$ decreases, and the propagation peak increases. Therefore, it is important to build an excellent social network environment to supervise the rumors that are still in the fermentation stage, improve the timeliness of the release of rumor refuting information, and strengthen the refuting of rumors among key groups. This paper breaks through the limitation considering only the time evolution, explores the spatiotemporal spreading law of rumor in real society, and provides a new perspective and idea for governing the rumor spreading.-
Keywords:
- rumor propagation /
- reaction diffusion /
- Hopf bifurcation /
- Turing instability
[1] Liu X, Li T, Xu H, Liu W 2019 Physica A 514 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hui H, Zhou C, Lu X, Li J 2020 Nonlinear Dyn. 101 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王祁月, 刘润然, 贾春晓 2021 70 068902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Y, Liu R R, Jia C X 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 068902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhou D, Han W, Wang Y 2015 J. Comput. Res. Dev. 52 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Youssef B, Gregory Z, Judicael R, Bruno V 2019 Simulation 95 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李瑾颉, 吴联仁, 齐佳音, 闫强 2017 电子与信息学报 39 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J J, Wu L R, Qi J Y, Yan Q 2017 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 39 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Junior V V, Rodriguez P M, Speroto A 2021 J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp. 12 123403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张菊平, 郭昊明, 荆文君, 靳祯 2019 68 150501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J P, Guo H M, Jing W J, Jin Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 150501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhu L, Wang B 2020 Inf. Sci. 526 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jia P, Wang C, Zhang G, Ma J 2019 Physica A 524 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huo L, Chen S, Zhao L 2021 Physica A 571 125828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zanette D H 2001 Phys. Rev. E 64 050901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Moreno Y, Pacheco A F, Nekovee M 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 066130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou J, Liu Z H, Li B M 2007 Phys. Lett. A 368 458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张芳, 司光亚, 罗批 2009 复杂系统与复杂性科学 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F, Si G Y, Luo P 2009 Complex Systems and Complexity Science 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhao L J, Wang Q, Cheng J J, Chen Y C, Wang J J, Huang W 2011 Physica A 390 2619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 顾亦然, 夏玲玲 2012 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y R, Xia L L 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 万佑红, 王小初 2016 计算机应用 36 2381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan Y H, Wang X C 2016 Journal of Computer Applications 36 2381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 朱霖河, 李玲 2020 69 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu L H, Li L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ruan Z Y, Yu B, Shu X C, Zhang Q P, Xuan Q 2020 Chaos 30 083101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen X L, Wang N 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ahmed N, Korkamaz A, Rehman M A, Rafiq M, Ali M, Ahmad M O 2020 Int. J. Comput. Math. 98 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hattaf K, Yousfi N 2016 Comput. Math. Appl. 72 2741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 赵洪涌, 朱霖河 2015 南京航空航天大学学报 47 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H Y, Zhu L H 2015 Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics 47 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhu L, Huang X, Liu Y, Zhang Z 2021 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 493 124539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Tan W, Yu W W, Hayat T, Alsaadi F, Fardoun H M 2018 Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos 28 1830029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Peter F P, John F, Jakob H 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 022302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Van D D, Watmough J 2002 Math. Biosci. 180 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同α对应的平衡点与分岔阈值
Table 1. Equilibrium point and bifurcation threshold for different α
饱和因子α 平衡点$(S^{\ast}, I^{\ast}, R^{\ast})$ 分岔阈值$\tau_{0}$ 0.1 (1.1615, 0.6479, 0.8572) 2.8331 0.3 (1.1074, 0.7040, 0.8552) 2.7589 0.5 (1.0596, 0.7584, 0.8487) 2.7048 0.7 (1.0182, 0.8094, 0.8390) 2.6436 0.9 (0.9833, 0.8560, 0.8274) 2.5143 -
[1] Liu X, Li T, Xu H, Liu W 2019 Physica A 514 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hui H, Zhou C, Lu X, Li J 2020 Nonlinear Dyn. 101 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王祁月, 刘润然, 贾春晓 2021 70 068902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Y, Liu R R, Jia C X 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 068902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhou D, Han W, Wang Y 2015 J. Comput. Res. Dev. 52 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Youssef B, Gregory Z, Judicael R, Bruno V 2019 Simulation 95 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李瑾颉, 吴联仁, 齐佳音, 闫强 2017 电子与信息学报 39 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J J, Wu L R, Qi J Y, Yan Q 2017 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 39 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Junior V V, Rodriguez P M, Speroto A 2021 J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp. 12 123403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张菊平, 郭昊明, 荆文君, 靳祯 2019 68 150501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J P, Guo H M, Jing W J, Jin Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 150501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhu L, Wang B 2020 Inf. Sci. 526 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jia P, Wang C, Zhang G, Ma J 2019 Physica A 524 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huo L, Chen S, Zhao L 2021 Physica A 571 125828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zanette D H 2001 Phys. Rev. E 64 050901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Moreno Y, Pacheco A F, Nekovee M 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 066130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou J, Liu Z H, Li B M 2007 Phys. Lett. A 368 458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张芳, 司光亚, 罗批 2009 复杂系统与复杂性科学 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F, Si G Y, Luo P 2009 Complex Systems and Complexity Science 6 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhao L J, Wang Q, Cheng J J, Chen Y C, Wang J J, Huang W 2011 Physica A 390 2619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 顾亦然, 夏玲玲 2012 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y R, Xia L L 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 238701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 万佑红, 王小初 2016 计算机应用 36 2381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan Y H, Wang X C 2016 Journal of Computer Applications 36 2381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 朱霖河, 李玲 2020 69 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu L H, Li L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 020501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ruan Z Y, Yu B, Shu X C, Zhang Q P, Xuan Q 2020 Chaos 30 083101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen X L, Wang N 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ahmed N, Korkamaz A, Rehman M A, Rafiq M, Ali M, Ahmad M O 2020 Int. J. Comput. Math. 98 517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hattaf K, Yousfi N 2016 Comput. Math. Appl. 72 2741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 赵洪涌, 朱霖河 2015 南京航空航天大学学报 47 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H Y, Zhu L H 2015 Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics 47 332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhu L, Huang X, Liu Y, Zhang Z 2021 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 493 124539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Tan W, Yu W W, Hayat T, Alsaadi F, Fardoun H M 2018 Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos 28 1830029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Peter F P, John F, Jakob H 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 022302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Van D D, Watmough J 2002 Math. Biosci. 180 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6456
- PDF下载量: 152
- 被引次数: 0

























 下载:
下载: