-
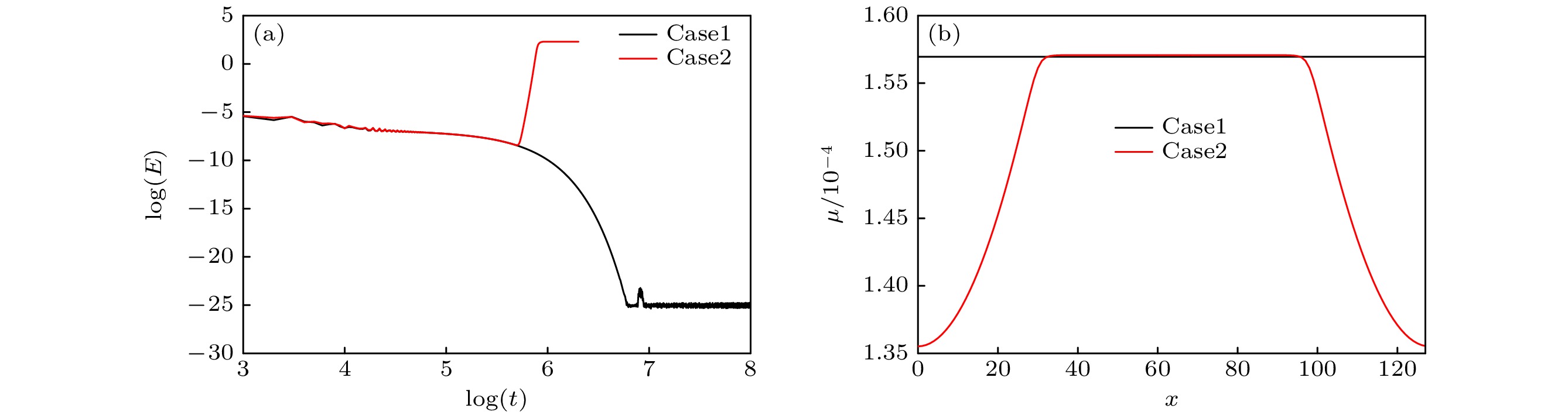
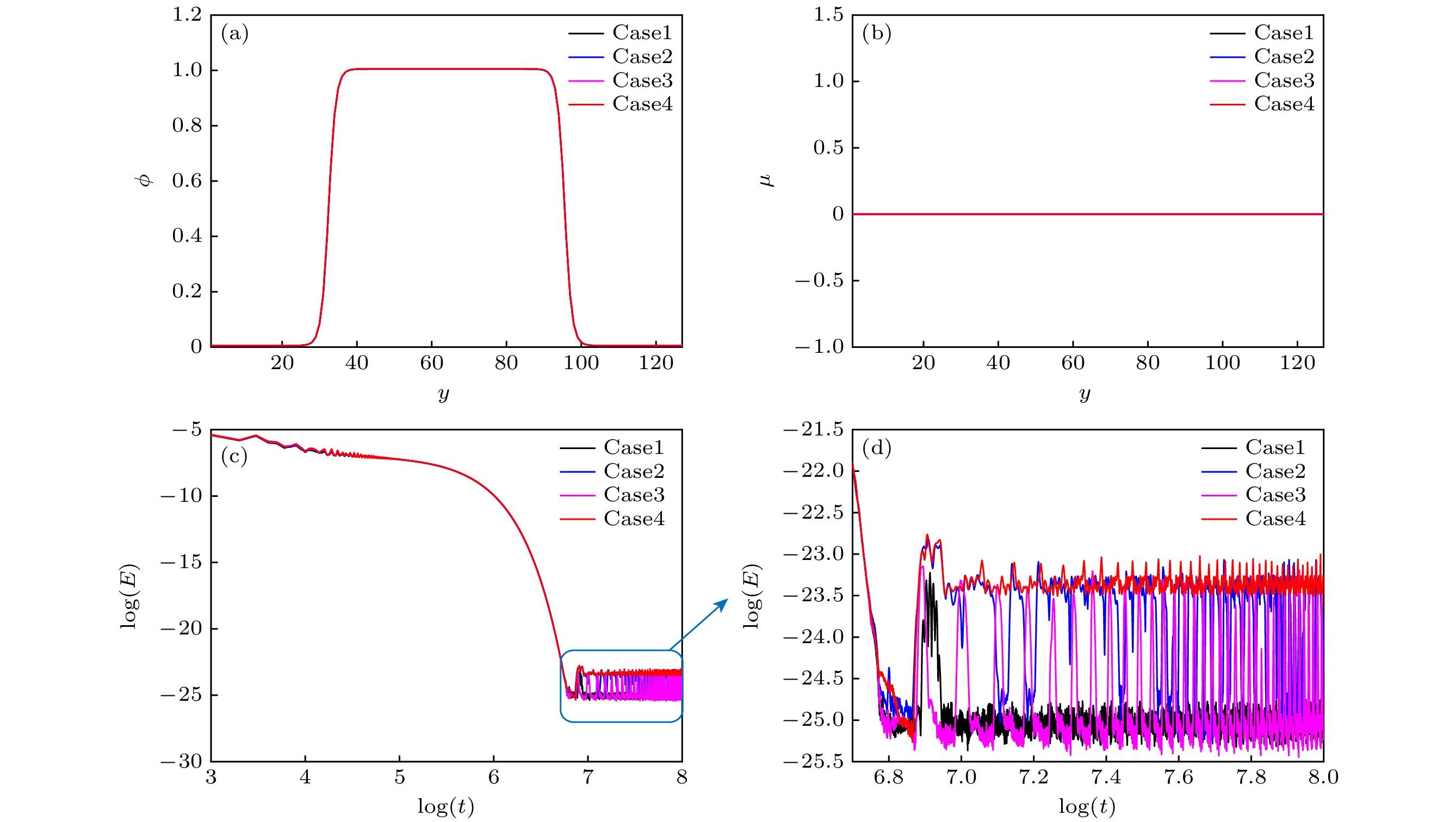
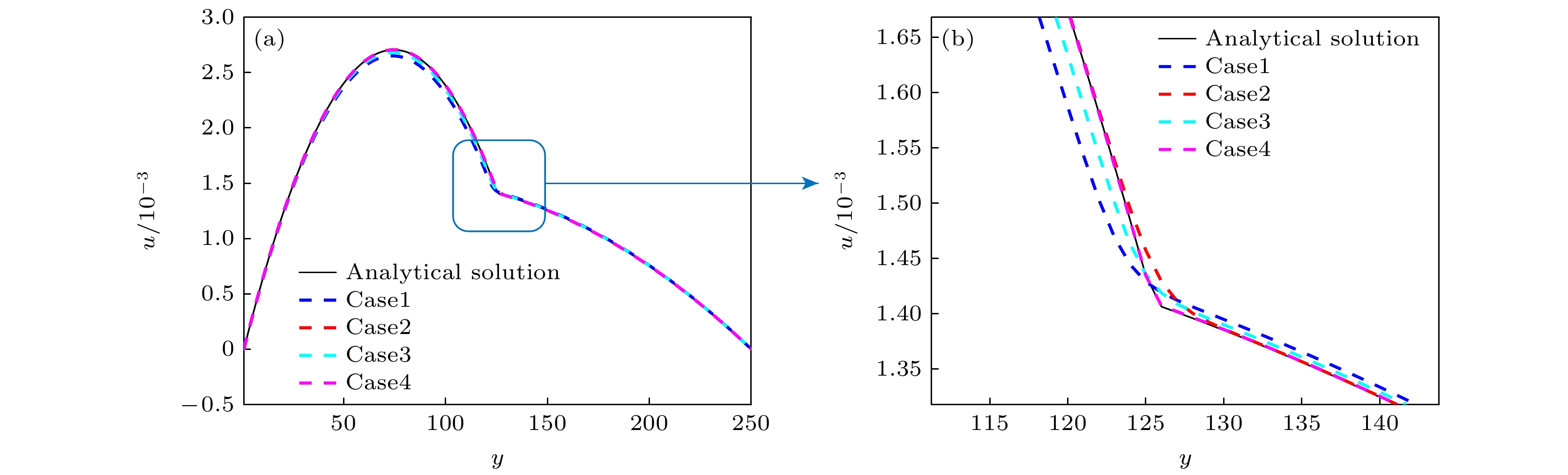
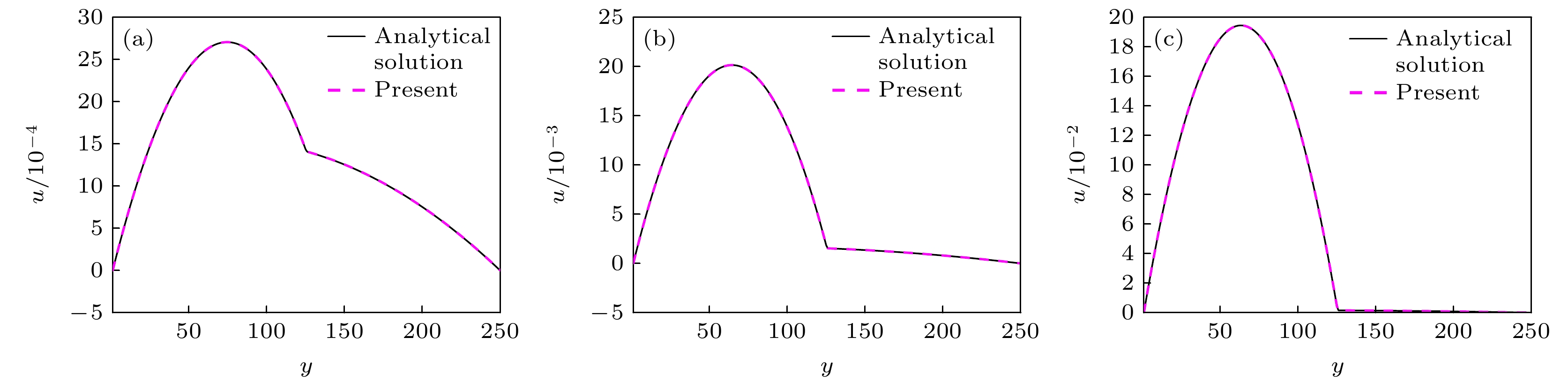
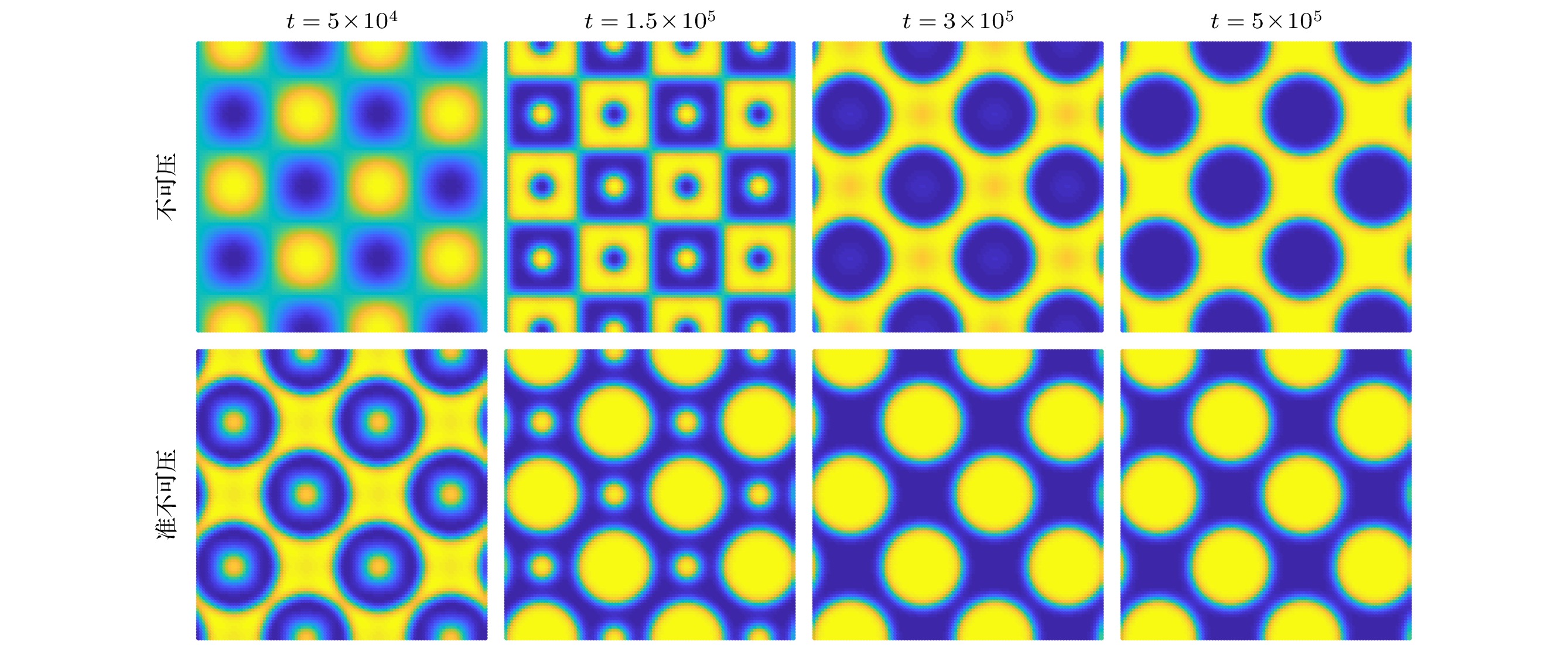
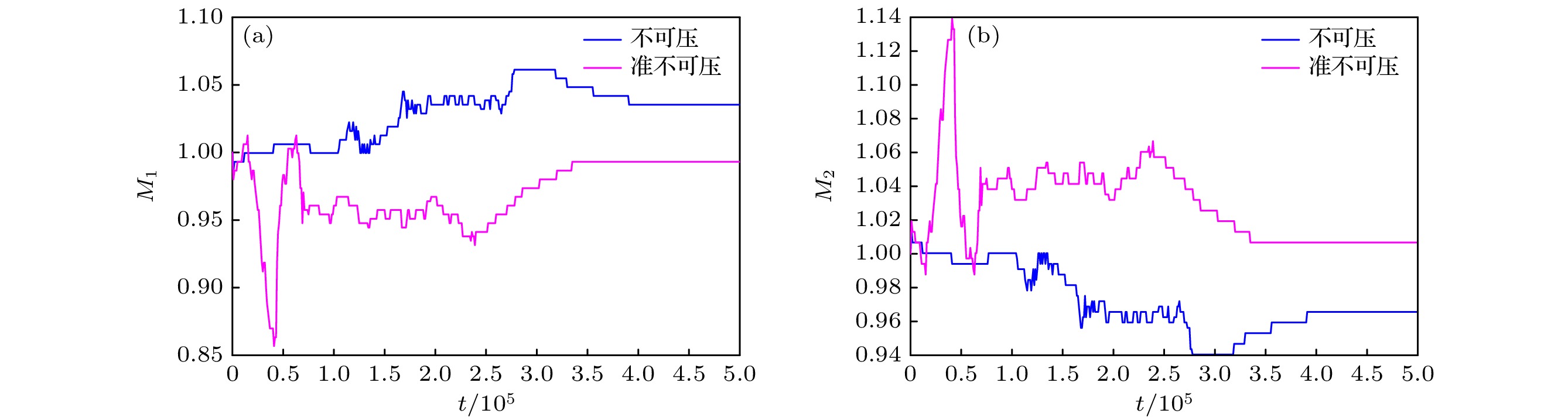
相比于基于不可压相场的两相格子Boltzmann方程(LBE)模型, 基于准不可压相场理论的LBE模型能够严格保证局部质量守恒. 然而, 以往准不可压相场LBE模型不具有精准平衡性质, 两相界面附近存在虚假速度且界面分布不满足热力学平衡 . 针对这一问题, 本文通过重新设计求解相场方程的平衡态分布函数和源项, 实现了离散尺度的精准平衡, 建立了准不可压相场理论的精准两相LBE模型. 对平界面问题和稳态液滴问题的数值模拟表明, 该模型能消除虚假速度, 具有良好的平衡性能. 对分层泊肃叶流的数值模拟证明了该模型模拟动态问题及大黏度比问题的准确性. 此外还比较了不同表面张力和不同黏度混合规则对模型的影响, 结果表明, 使用$ {\boldsymbol{F}}_{s}=\mu {{\nabla}} \phi $计算表面张力无法消除虚假速度; 模拟动态问题时, 使用阶跃混合规则计算混合黏度可以得到更准确的结果. 最后, 对相分离问题的数值模拟表明, 该模型可以严格保证局部质量守恒.
-
关键词:
- 两相流 /
- 格子Boltzmann方法 /
- 准不可压相场模型
Compared with the lattice Boltzmann equation (LBE) model based on incompressible phase field theory, the LBE based on quasi-incompressible phase field theory has the advantage of local mass conservation. However, previous quasi-incompressible phase-field-based LBE model does not satisfy the well-balanced property, resulting in spurious velocities in the vicinity of interface and density profiles inconsistent with those from thermodynamics. To address this problem, a novel LBE model is developed based on the quasi-incompressible phase-field theory. First, numerical artifacts in the original LBE for the Cahn-Hilliard are analyzed. Based on this analysis, the equilibrium distribution function and source term are reformulated to eliminate the numerical artifacts, enabling the new LBE to realize the well-balanced characteristics at a discrete level. The performance of the proposed LBE model is tested by simulating a number of typical two-phase systems. The numerical results of the planar interface and static droplet problems demonstrate that the present model can eliminate spurious velocities and achieve well-balanced state. Numerical results of the layered Poiseuille flow demonstrate the accuracy of the present model in simulating dynamic two-phase flow problems. The well-balanced properties of the LBE model with two different formulations of surface tension ($ {\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{s}}}=-\phi {{\nabla}} \mu$ and ${\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{s}}}=\mu {{\nabla}} \phi $) are also investigated. It is found that the formulation of $ {\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{s}}}=\mu {{\nabla}} \phi $ cannot eliminate the spurious velocities, while the formulation of $ {\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{s}}}=\mu {{\nabla}} \phi $ can achieve the well-balanced state. The influences of viscosity formulations of the fluid mixture are also compared. Particularly, four mixing rules are considered. It is shown that the use of step mixing rule gives more accurate results for the layered Poiseuille flow. Finally, we compare the performance of the present quasi-incompressible LBE model with that of the original fully incompressible LBE model by simulating the phase separation problem, and the results show that the present model can ensure the local mass conservation, while the fully incompressible LBE can yield quite different predictions.[1] Guo Z L, Shu C 2013 Lattice Boltzmann Method and its Application in Engineering (Vol. 3) (Singapore: World Scientific Publishing
[2] Huang H B, Sukop M, Lu X Y 2015 Multiphase Lattice Boltzmann Methods: Theory and Application (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell
[3] Yang K, Guo Z L 2016 Phys. Rev. E 93 043303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang C H, Guo Z L, Liang H 2021 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 93 2225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Connington K, Lee T 2012 J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26 3857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gong J M, Oshima N, Tabe Y 2019 Comput. Math. Appl. 78 1166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Huang H B, Krafczyk M, Lu X Y 2011 Phys. Rev. E 84 046710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhai Q L, Zheng L, Zheng S 2017 Phys. Rev. E 95 023313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Siebert D, Philippi P, Mattila K 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 053310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Cristea A, Sofonea V 2003 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 14 1251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wagner A J 2003 Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 17 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shan X 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 047701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sbragaglia M, Benzi R, Biferale L, Succi S, Sugiyama K, Toschi F 2007 Phys. Rev. E 75 026702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Guo Z L, Zheng C G, Shi B C 2011 Phys. Rev. E 83 036707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Guo Z L 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 031709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang C H, Guo Z L, Wang L P 2022 Phys. Fluids 34 012110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zheng L, Zheng S, Zhai Q L 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 092102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ju L, Liu P Y, Yan B C, Bao J, Sun S Y, Guo Z L 2023 arXiv: 2311.10827v1 [physics. flu-dyn]
[19] Lowengrub J, Truskinovsky L 1998 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 454 2617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shen J, Yang X F, Wang Q 2013 Commun. Comput. Phys. 13 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jacqmin D 1999 Commun. Comput. Phys. 155 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng B, Shi B C, Wang G C 2005 Chin. Phys. Lett. 22 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
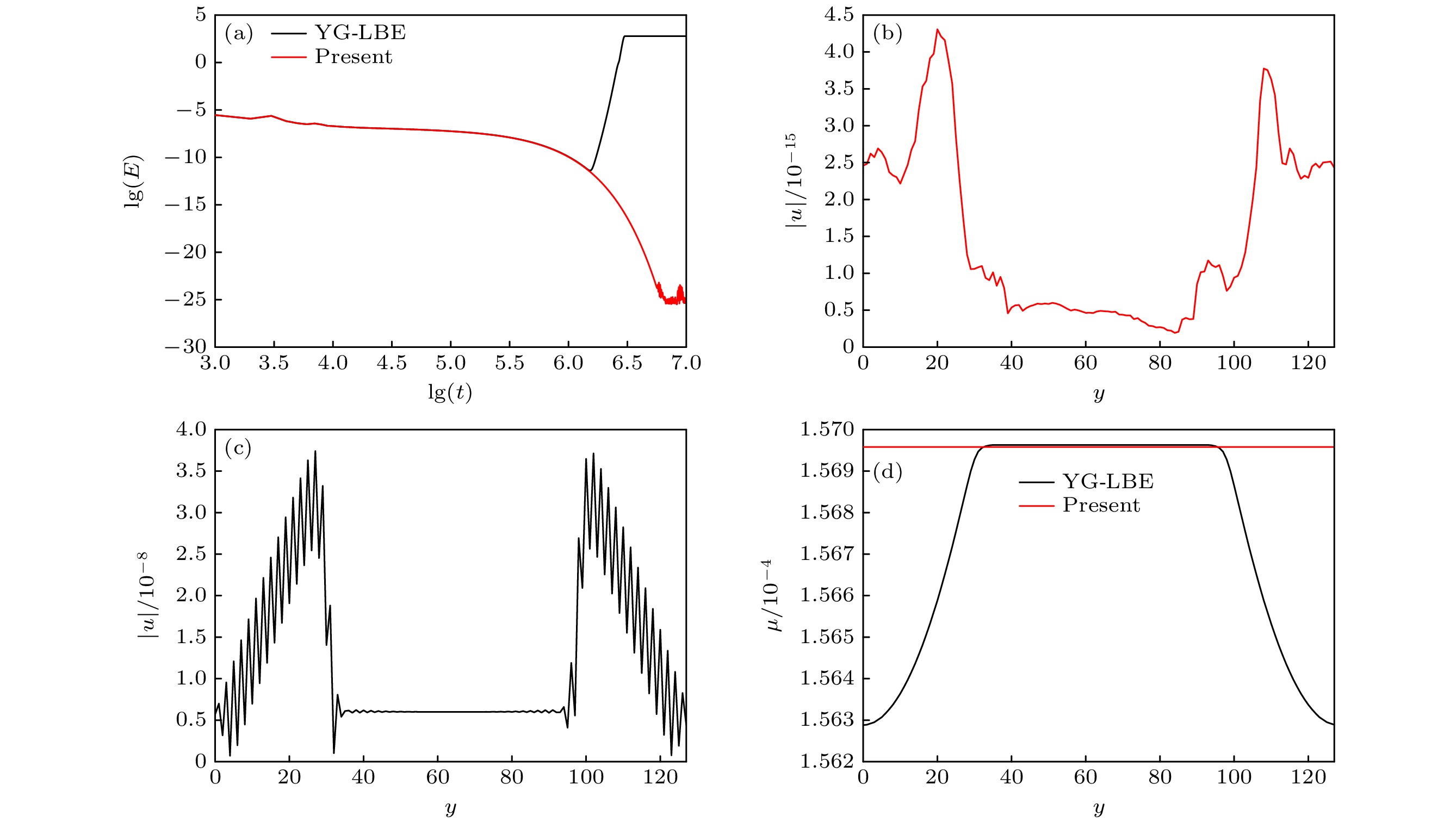
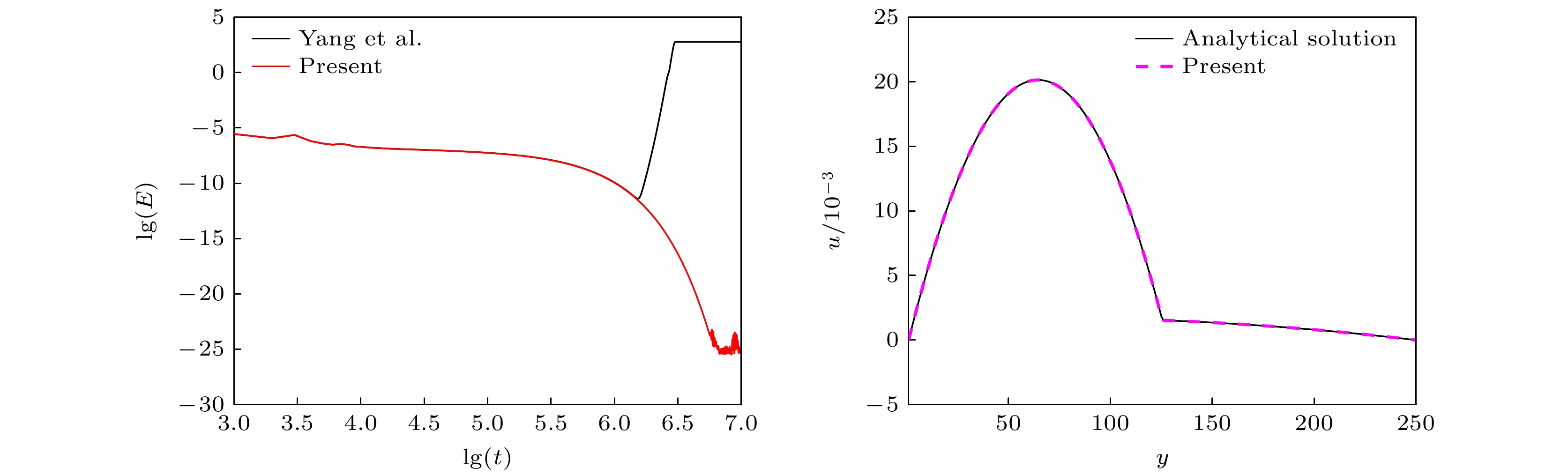
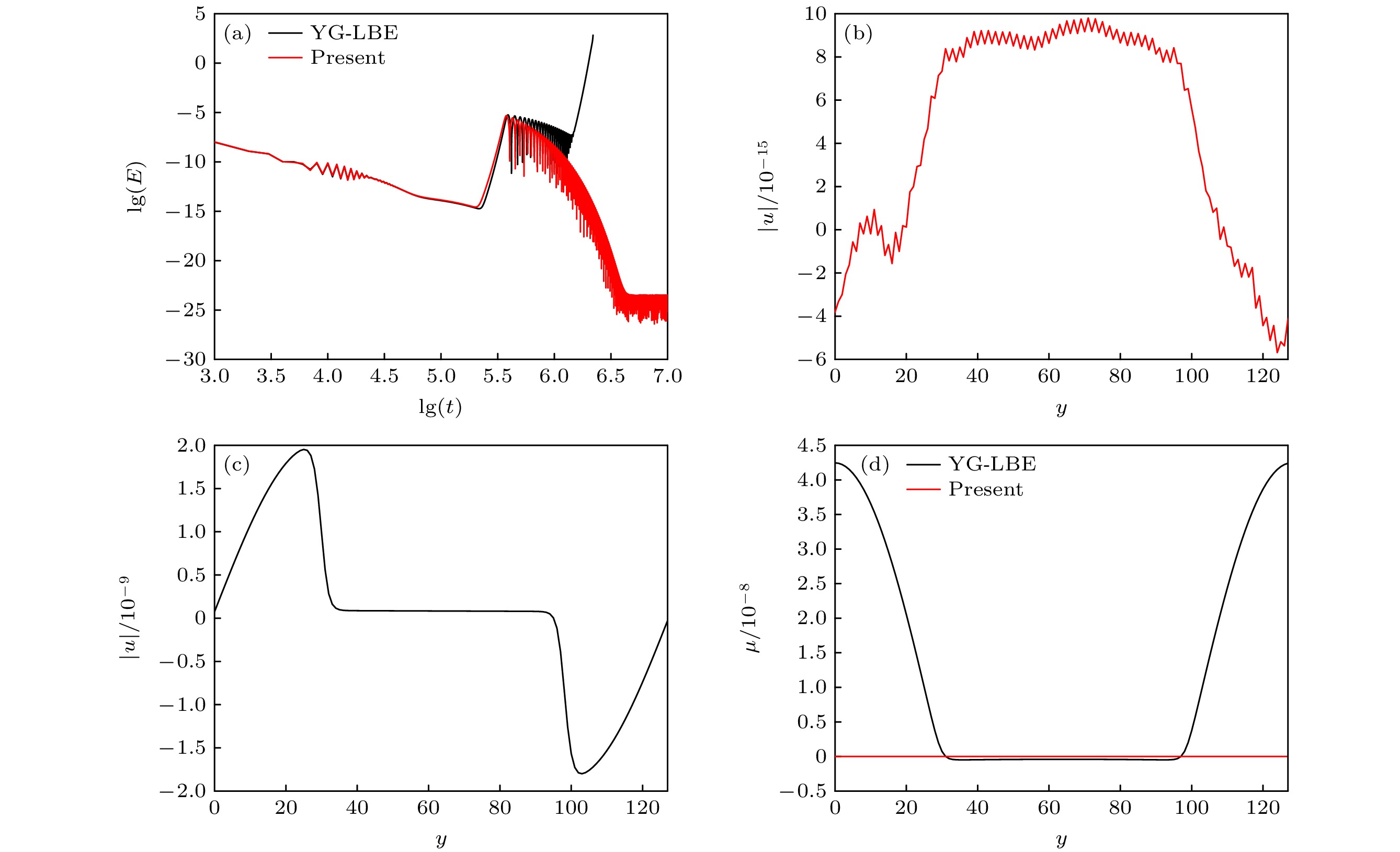
图 1 本文WB-LBE模型与YG-LBE模型模拟平界面问题的结果 (a)总动能随时间的演化过程; (b)稳态时WB-LBE计算的流动速度分布; (c)稳态时YG-LBE模型计算的流动速度分布; (d)化学势分布
Fig. 1. Numerical results of the WB-LBE and YG-LBE models for the planar interface: (a) Time evolution of the total kinetic energy; (b) distribution of velocity obtained by the WB-LBE model at steady state; (c) distribution of velocity obtained by the YG-LBE model at steady state; (d) distributions of chemical potential.
图 2 本文WB-LBE模型与YG-LBE模型模拟稳态液滴问题的结果 (a)总动能随时间的演化过程; (b)稳态时WB-LBE计算的流动速度分布; (c)稳态时YG-LBE计算的流动速度分布; (d)化学势分布
Fig. 2. Results of the WB-LBE and YG-LBE models for the steady-state droplet problem: (a) Time evolution of the total kinetic energy; (b) velocity distribution obtained by the WB-LBE model; (c) velocity distribution obtained by the YG-LBE model; (d) distributions of chemical potential.
-
[1] Guo Z L, Shu C 2013 Lattice Boltzmann Method and its Application in Engineering (Vol. 3) (Singapore: World Scientific Publishing
[2] Huang H B, Sukop M, Lu X Y 2015 Multiphase Lattice Boltzmann Methods: Theory and Application (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell
[3] Yang K, Guo Z L 2016 Phys. Rev. E 93 043303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang C H, Guo Z L, Liang H 2021 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 93 2225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Connington K, Lee T 2012 J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26 3857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gong J M, Oshima N, Tabe Y 2019 Comput. Math. Appl. 78 1166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Huang H B, Krafczyk M, Lu X Y 2011 Phys. Rev. E 84 046710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhai Q L, Zheng L, Zheng S 2017 Phys. Rev. E 95 023313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Siebert D, Philippi P, Mattila K 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 053310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Cristea A, Sofonea V 2003 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 14 1251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wagner A J 2003 Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 17 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shan X 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 047701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sbragaglia M, Benzi R, Biferale L, Succi S, Sugiyama K, Toschi F 2007 Phys. Rev. E 75 026702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Guo Z L, Zheng C G, Shi B C 2011 Phys. Rev. E 83 036707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Guo Z L 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 031709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang C H, Guo Z L, Wang L P 2022 Phys. Fluids 34 012110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zheng L, Zheng S, Zhai Q L 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 092102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ju L, Liu P Y, Yan B C, Bao J, Sun S Y, Guo Z L 2023 arXiv: 2311.10827v1 [physics. flu-dyn]
[19] Lowengrub J, Truskinovsky L 1998 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 454 2617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shen J, Yang X F, Wang Q 2013 Commun. Comput. Phys. 13 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jacqmin D 1999 Commun. Comput. Phys. 155 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng B, Shi B C, Wang G C 2005 Chin. Phys. Lett. 22 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2947
- PDF下载量: 103
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: