-
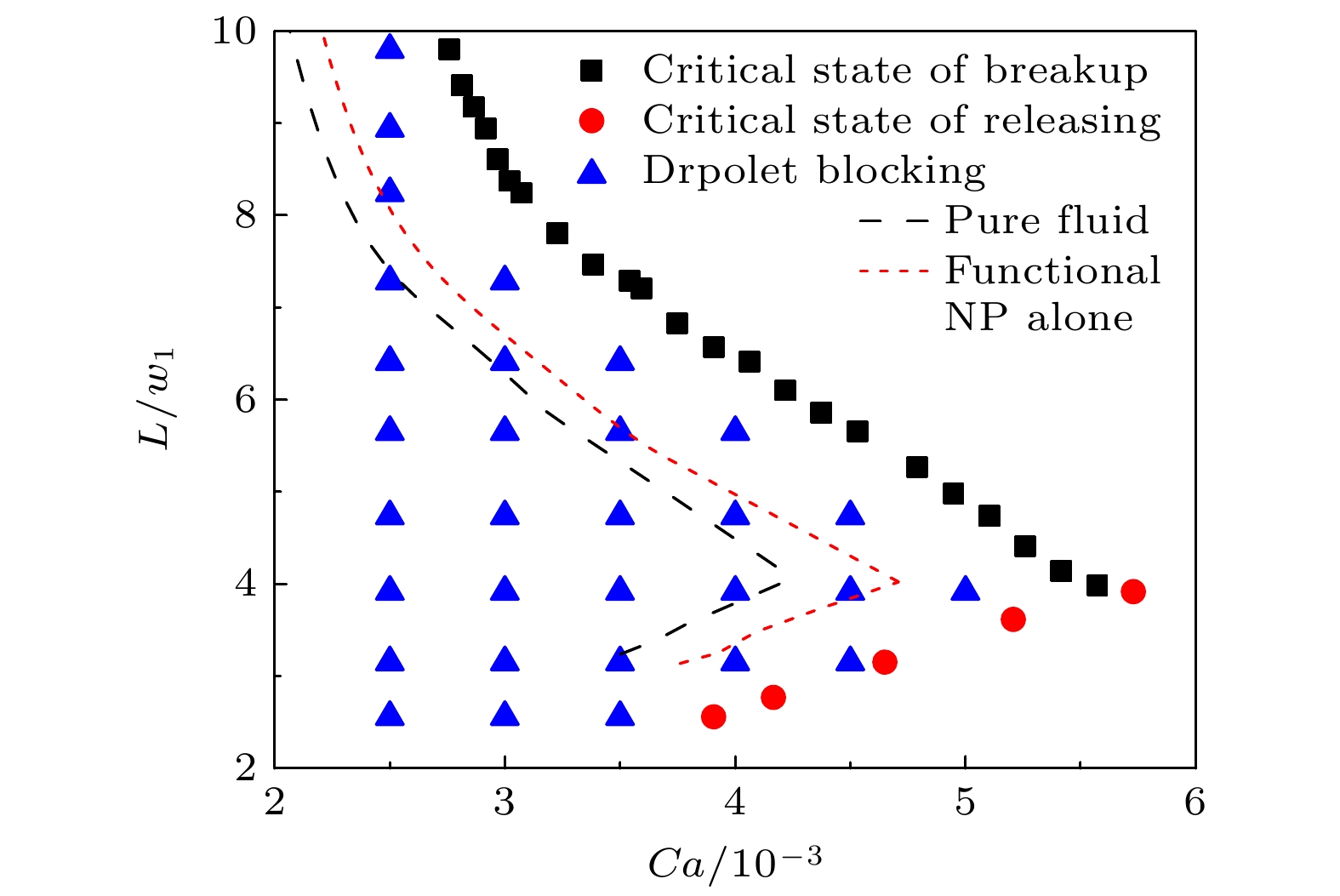
微孔喉结构内束缚液滴释放是提高原油采收率的关键. 纳米颗粒表面活性剂能够增强纳米颗粒在油水界面上的吸附稳定性, 进而显著影响束缚液滴的释放过程, 对于发展纳米驱提采技术具有重要意义. 本文通过微流控可视化实验与荧光技术, 系统研究了纳米颗粒表面活性剂对微孔喉中束缚液滴释放行为的影响. 在纳米颗粒表面活性剂作用下, 微孔喉结构中束缚液滴存在破碎释放与直接释放两种释放状态; 获得了微孔喉内束缚液滴释放状态相图, 结合液滴受力分析建立了束缚液滴释放状态的临界转变理论模型; 通过对比分析液滴长度随液滴释放的临界流量与毛细数的变化, 获得了纳米颗粒表面活性剂对液滴释放行为的影响规律; 结合荧光实验进一步阐明了纳米颗粒表面活性剂诱发界面黏弹性而抑制微孔喉内束缚液滴释放的作用机制.The release of trapped droplets in pore-throat structures is of great significance to study multiphase flow in porous media. In this paper, the effects of nanoparticle surfactants on the release behavior of trapped droplets in micro-pore throat are investigated using microfluidic visualization system and fluorescence techniques. We demonstrate a droplet control technique in microchannel and observe the release states of trapped droplets in pore-throat. We obtain the phase diagram of droplet states and establish mathematical models describing the critical transition condition by mechanism analysis. Based on the analysis of force on the trapped droplets, the breakup mechanism and the release mechanism are also obtained when droplets move through the pore-throat. The breakup of droplets is dominated by capillary pressure, with the critical capillary number of breakup being negatively correlated with droplet size. Conversely, the release of droplets is controlled by capillary pressure and hydrostatic pressure, with the critical capillary number of release exhibiting a positive correlation with droplet size. In addition, this research reveals the effect of nanoparticle surfactants on droplet release behavior by analyzing the variation of droplet length with flow velocity and capillary number. Nanoparticle surfactant reduces the critical flow velocity of droplet release but significantly increases the critical capillary number, and this phenomenon becomes more pronounced with the increase of concentrations of nanoparticle surfactants. Fluorescence experiments further elucidate the mechanism by which nanoparticle surfactants inhibit the release of trapped droplets in pore-throat by inducing interfacial viscoelasticity. Nanoparticles react with polymers at the interface to form the viscoelastic film. This film-induced interfacial viscoelasticity hinders droplet deformation and increases the viscous resistance between droplets and wall, thereby impeding the release of trapped droplets in pore-throat.
-
Keywords:
- pore throat /
- droplet release /
- trapped droplet /
- nanoparticle surfactants
[1] Jia N H, Lv W F, Liu Q J, Wang D G, Liu F Z, Hu Z 2024 Int. J. Energy Res. 2024 3505763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Singh K, Jung M, Brinkmann M, Seemann R 2019 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 51 429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu Z X, Liang Y, Wang Q, Guo Y J, Gao M, Wang Z B, Liu W L 2020 J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 193 107449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Habib S, Yunus R, Zakaria R, Biak D, Jan B, Amir Z 2024 Fuel 363 130957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mir H, Siavashi M 2022 Energy 239 122149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tan Y S, Li Q, Xu L, Ghaffar A, Zhou X, Li P C 2022 Fuel 328 125256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu J B, Zhong L G, Hao T C, Liu Y G, Zhang S J 2022 J. Mol. Liq. 349 118207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhu X F, Chen L, Wang S, Feng Q H, Tao W Q 2022 Phys. Fluids 34 043320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Scanziani A, Lin Q, Alhosani A, Blunt M, Bijeljic B 2020 P. Roy. Soc. A 476 2240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pak T, Butler I, Geiger S, Van D, Sorbie K 2015 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 112 1947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Davis R, Alexander Z 2009 J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 334 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Moragues T, Arguijo D, Beneyton T, Modavi C, Simutis K, Abate A, Baret J, Demello A, Densmore D, Griffiths A 2023 Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 3 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen Z, Kheiri S, Young E, Kumacheva E 2022 Langmuir 38 6233-6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Elvira K, Gielen F, Tsai S, Nightingale A 2022 Lab Chip 22 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 邓梓龙, 李鹏宇, 张璇, 刘向东 2021 70 074701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng Z L, Li P Y, Zhang X, Liu X D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 074701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Anna S 2016 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 48 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Teh S, Lin R, Hung L, Lee A 2008 Lab Chip 8 198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xu K, Zhu P, Huh C, Balhoff M 2015 Langmuir 31 13673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2019 J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 554 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2020 Chem. Eng. Sci. 220 115649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张旋, 张天赐, 葛际江, 蒋平, 张贵才 2020 69 026801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang T C, Ge J J, Jiang P, Zhang G C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 026801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wen B R, Sun C, Bai B F 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 22796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 温伯尧, 杨海中, 姚秀田, 骆政园, 白博峰 2022 科学通报 67 3088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen B R, Yang H Z, Yao X T, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull 67 3088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tang X C, Li Y Q, Liu Z Y, Zhang N 2023 Pet. Sci. 20 2282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cui M, Emrick T, Russell T 2013 Science 342 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Toor A, Helms B, Russell T 2017 Nano Lett. 17 3119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Toor A, Lamb S, Helms B, Russell T 2018 ACS Nano 12 2365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chai Y, Lukito A, Jiang Y, Ashby P, Russell T 2017 Nano Lett. 17 6453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Huang C, Chai Y, Jiang Y, Forth J, Ashby P, Arras M, Hong K, Smith G, Yin P, Russell T 2018 Nano Lett. 18 2525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qi J, Yu Z, Liao G, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 112008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 齐杰, 彭佳庆, 杨圣贤, 骆政园, 白博峰 2022 科学通报 67 795804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi J, Peng J Q, Yang S X, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull. 67 795804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
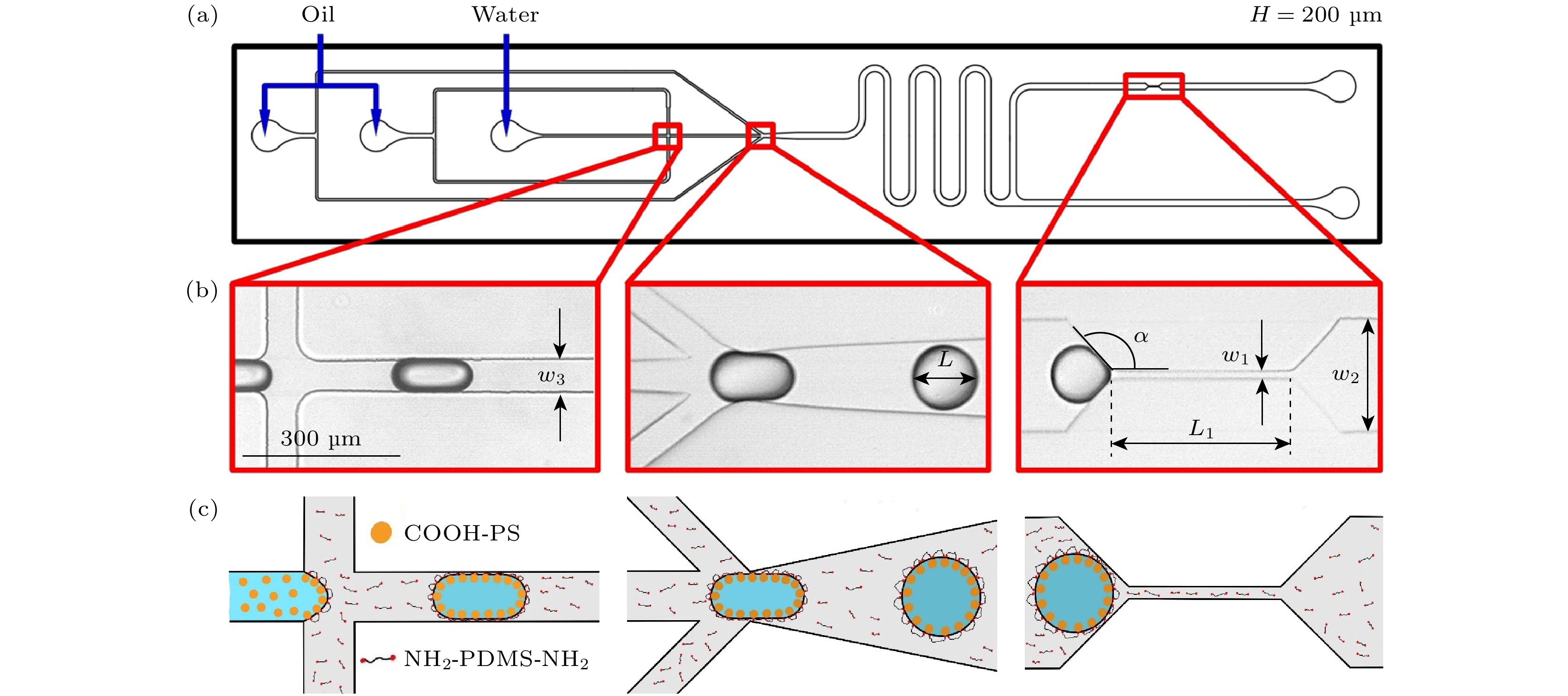
图 1 微流控芯片结构及纳米颗粒表面活性剂分布示意图 (a)微孔喉芯片结构; (b) 液滴生成、加速和堵塞束缚实验示意图; (c) 纳米颗粒与表面活性剂油水界面反应组装示意图
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the structure of the microfluidic chip and the distribution of nanoparticle surfactants: (a) Structure of the micro-pore throat chip; (b) schematic diagram of the experiments of droplet generation, acceleration and trapping confinement; (c) schematic diagram of the assembly of nanoparticle surfactants at the oil-water interface.
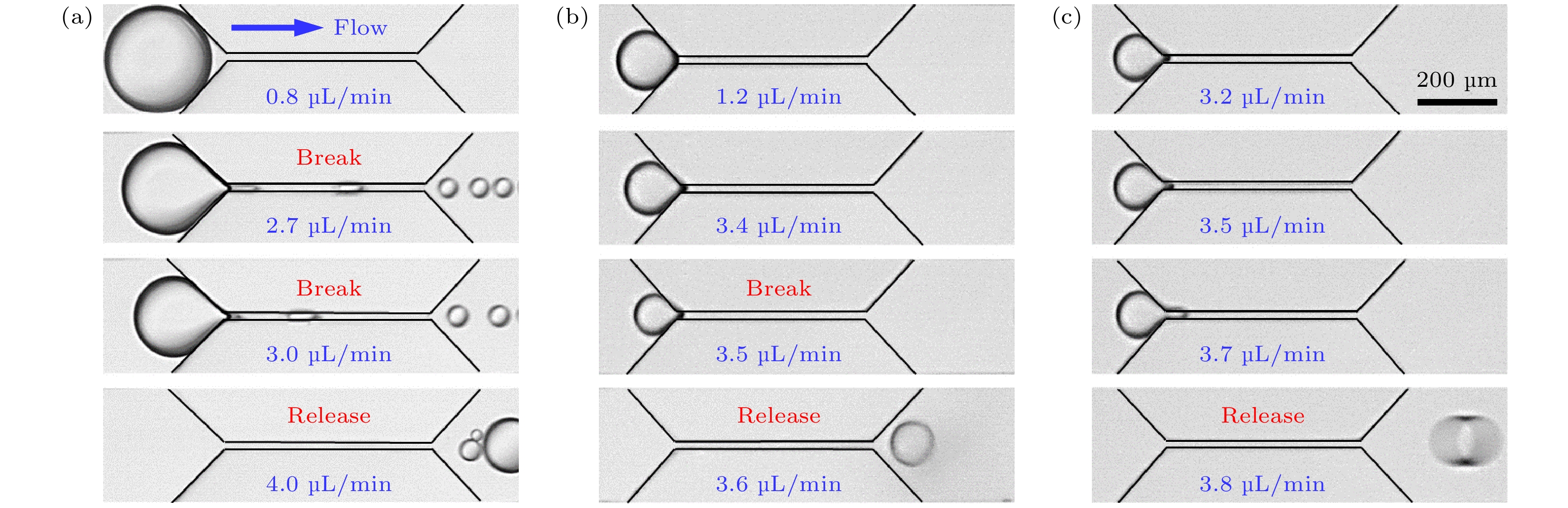
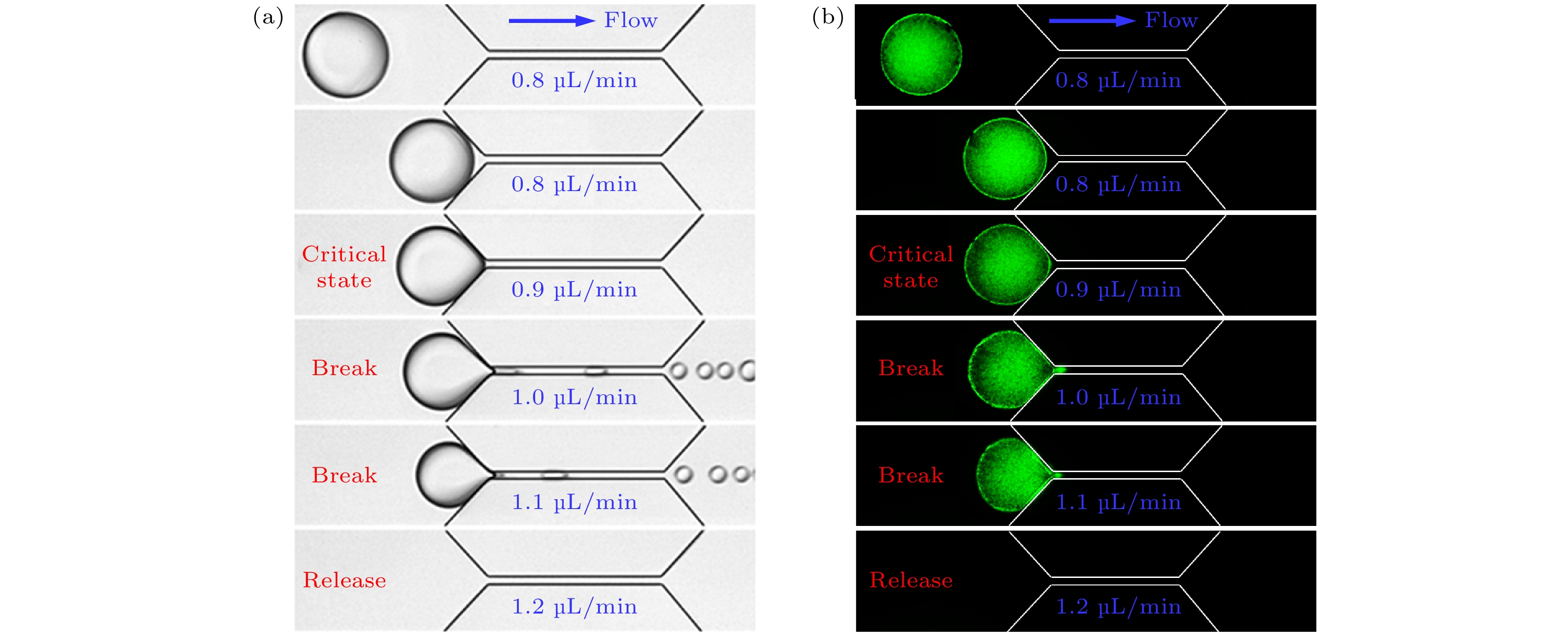
图 2 微孔喉中单个束缚液滴的典型释放过程 (a)束缚液滴尺寸 L/w1 = 8的释放过程; (b) 束缚液滴尺寸L/w1 = 5的释放过程; (c) 束缚液滴尺寸L/w1 = 3.5的释放过程
Fig. 2. Typical release processes of single trapped droplets in the micro-pore throat: (a) Release process of the trapped droplet with a size of L/w1 = 8; (b) release process of the trapped droplet with a size of L/w1 = 5; (c) release process of the trapped droplet with a size of L/w1 = 3.5.
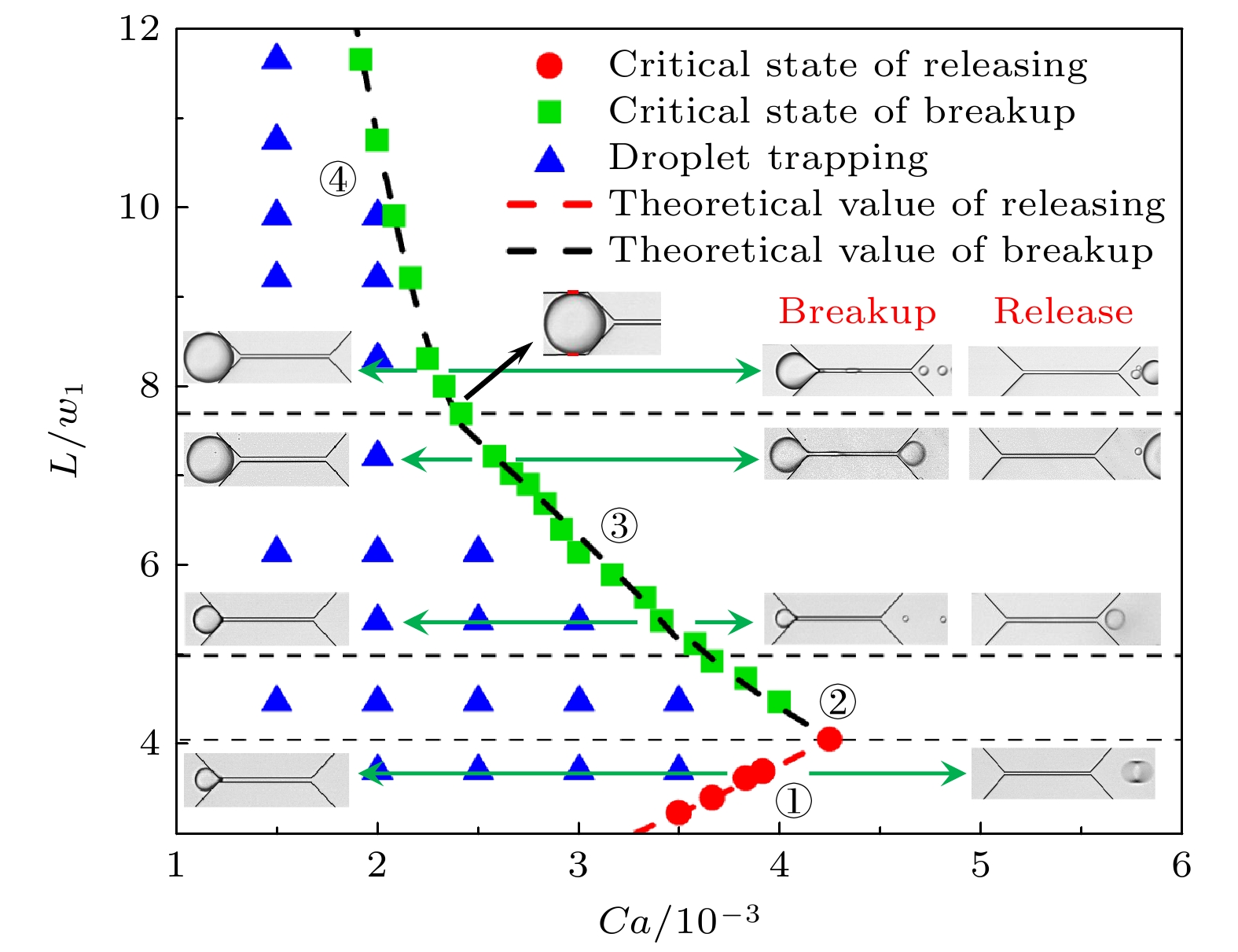
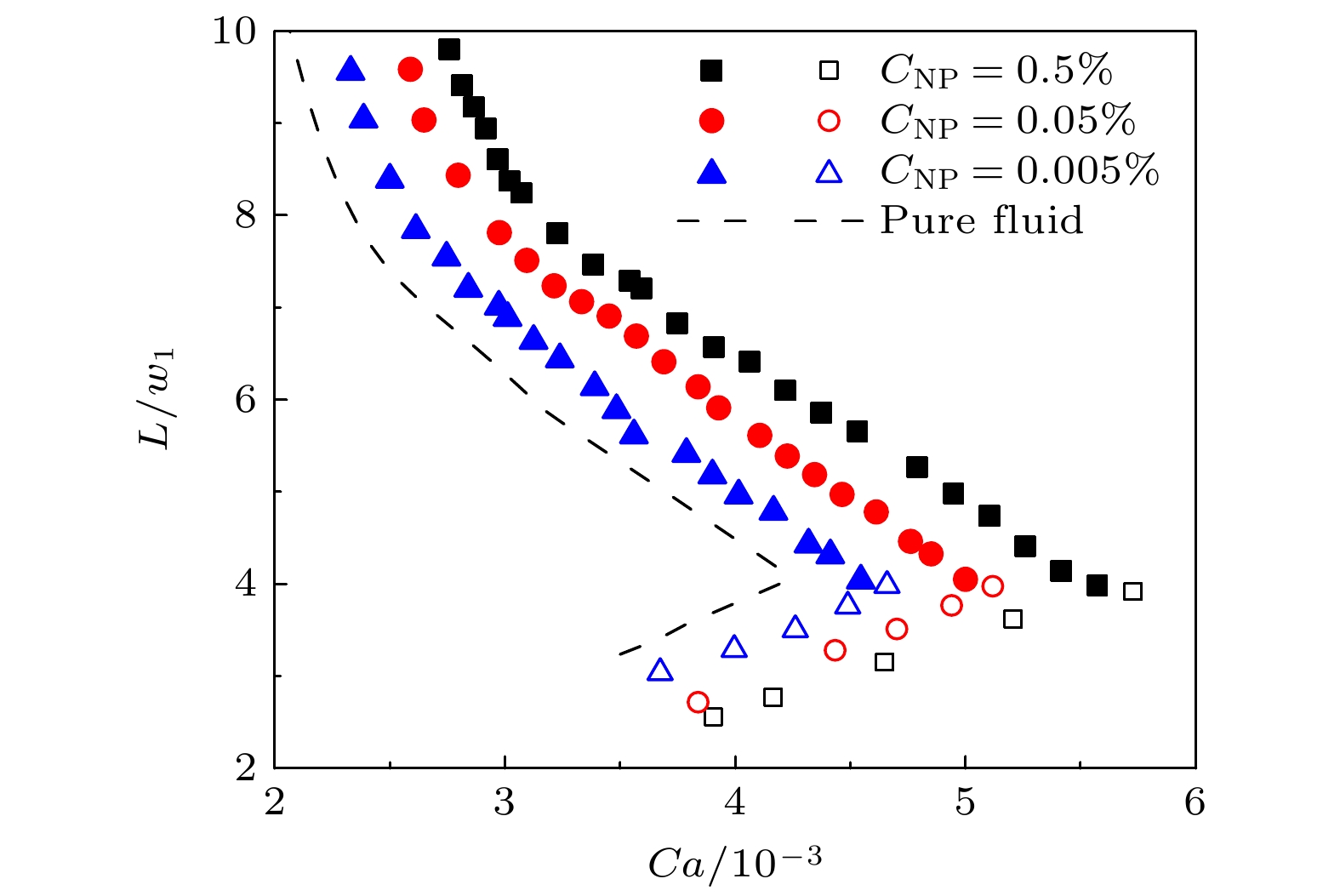
图 3 干净油水界面下单个液滴的束缚、破碎释放和直接释放相图, 图中的水平虚线从上至下分别为L/w1 = 7.7 (受限液滴额外受到孔隙壁面的摩擦阻滞作用), L/w1 = 5 (由于通道高度有限, 液滴被微通道挤压成饼状液滴), L/w1 = 4.1 (液滴破碎释放与直接释放的尺寸界限), 序号①, ②, ③, ④分别对应(3)式、(6)式、(8)式、(10)式的曲线形式
Fig. 3. Phase diagram of trapping, breakup and direct release of a single droplet with clean oil-water interface. In this diagram, the horizontal dashed lines from top to bottom represent the following scenarios: L/w1 = 7.7 (restricted droplets additionally experience frictional resistance from the wall), L/w1 = 5 (Owing to the limited channel height, droplets are squeezed into pancake droplets by the microchannel), and L/w1 = 4.1 (this value marks the size threshold between droplet breakup and direct release). The serial numbers ①, ②, ③, and ④ correspond to the curve forms of Eqs. (3), (6), (8), and (10), respectively.
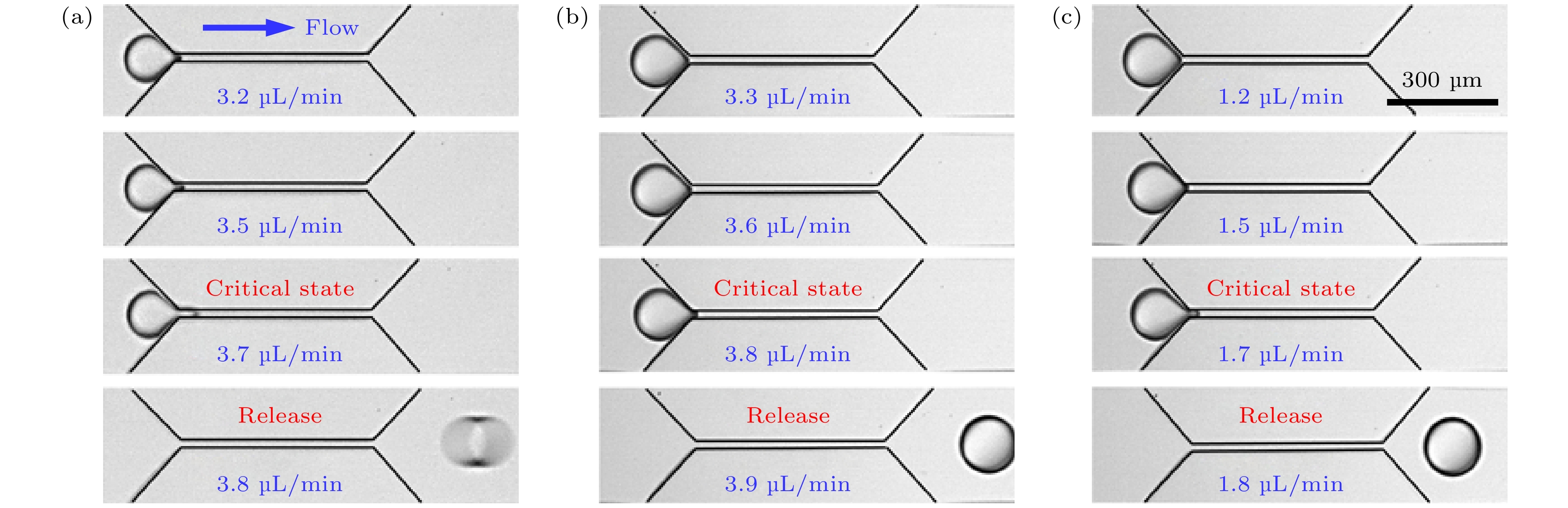
图 4 不同试剂作用下微孔喉中单个束缚液滴(相同大小L/w1 = 3.5)的临界释放状态 (a)纯水纯油组; (b)仅添加纳米颗粒组; (c)纳米颗粒表面活性剂组
Fig. 4. Critical release state of a single trapped droplet with the same size (L/w1 = 3.5) in the micro-pore throat under different reagents: (a) Pure liquid group; (b) only nanoparticles group; (c) nanoparticles surfactant group.
图 7 纳米颗粒表面活性剂作用下液滴破碎的荧光示意图 (a)纳米颗粒表面活性剂作用下的液滴破碎过程; (b)液滴破碎过程中的纳米颗粒荧光示意图
Fig. 7. Fluorescence diagram of droplet breakup under the action of nanoparticle surfactant: (a) Droplet breaking process under the action of nanoparticle surfactant; (b) fluorescence diagram of nanoparticles during droplet breakup.
表 1 不同流体系统的界面张力
Table 1. Interfacial tension for three different fluid systems.
试剂组别 质量百分比/% γ/(mN·m–1) COOH-PS NH2-PDMS-NH2 纯水纯油 0 0 25.2±0.6 仅添加纳米颗粒 0.5 0 24.7±0.4 纳米颗粒表活剂 0.001 1 12.0±0.7 0.005 1 10.3±0.7 0.05 1 6.4±0.8 -
[1] Jia N H, Lv W F, Liu Q J, Wang D G, Liu F Z, Hu Z 2024 Int. J. Energy Res. 2024 3505763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Singh K, Jung M, Brinkmann M, Seemann R 2019 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 51 429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu Z X, Liang Y, Wang Q, Guo Y J, Gao M, Wang Z B, Liu W L 2020 J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 193 107449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Habib S, Yunus R, Zakaria R, Biak D, Jan B, Amir Z 2024 Fuel 363 130957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mir H, Siavashi M 2022 Energy 239 122149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tan Y S, Li Q, Xu L, Ghaffar A, Zhou X, Li P C 2022 Fuel 328 125256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu J B, Zhong L G, Hao T C, Liu Y G, Zhang S J 2022 J. Mol. Liq. 349 118207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhu X F, Chen L, Wang S, Feng Q H, Tao W Q 2022 Phys. Fluids 34 043320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Scanziani A, Lin Q, Alhosani A, Blunt M, Bijeljic B 2020 P. Roy. Soc. A 476 2240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pak T, Butler I, Geiger S, Van D, Sorbie K 2015 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 112 1947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Davis R, Alexander Z 2009 J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 334 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Moragues T, Arguijo D, Beneyton T, Modavi C, Simutis K, Abate A, Baret J, Demello A, Densmore D, Griffiths A 2023 Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 3 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen Z, Kheiri S, Young E, Kumacheva E 2022 Langmuir 38 6233-6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Elvira K, Gielen F, Tsai S, Nightingale A 2022 Lab Chip 22 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 邓梓龙, 李鹏宇, 张璇, 刘向东 2021 70 074701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng Z L, Li P Y, Zhang X, Liu X D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 074701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Anna S 2016 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 48 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Teh S, Lin R, Hung L, Lee A 2008 Lab Chip 8 198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xu K, Zhu P, Huh C, Balhoff M 2015 Langmuir 31 13673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2019 J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 554 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2020 Chem. Eng. Sci. 220 115649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张旋, 张天赐, 葛际江, 蒋平, 张贵才 2020 69 026801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang T C, Ge J J, Jiang P, Zhang G C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 026801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wen B R, Sun C, Bai B F 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 22796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 温伯尧, 杨海中, 姚秀田, 骆政园, 白博峰 2022 科学通报 67 3088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen B R, Yang H Z, Yao X T, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull 67 3088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tang X C, Li Y Q, Liu Z Y, Zhang N 2023 Pet. Sci. 20 2282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cui M, Emrick T, Russell T 2013 Science 342 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Toor A, Helms B, Russell T 2017 Nano Lett. 17 3119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Toor A, Lamb S, Helms B, Russell T 2018 ACS Nano 12 2365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chai Y, Lukito A, Jiang Y, Ashby P, Russell T 2017 Nano Lett. 17 6453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Huang C, Chai Y, Jiang Y, Forth J, Ashby P, Arras M, Hong K, Smith G, Yin P, Russell T 2018 Nano Lett. 18 2525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qi J, Yu Z, Liao G, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 112008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 齐杰, 彭佳庆, 杨圣贤, 骆政园, 白博峰 2022 科学通报 67 795804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi J, Peng J Q, Yang S X, Luo Z Y, Bai B F 2022 Chin. Sci. Bull. 67 795804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3238
- PDF下载量: 88
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: