-
随着我国水下探测、通信技术的发展, 传统的磁性测量模型已无法满足高精度、高效率建模的需要. 本文从舰船磁场积分模型出发, 综合分析模型离散化为磁偶极子阵列模型产生的复化中矩形, 以及Gauss-Legendre积分余项分析过程引起的离散误差、算法误差, 模型简化产生的拟合误差、模型误差等, 对模型适用性条件进行分析; 同时, 以建模精度和计算复杂度为目标构造多目标优化函数, 通过NSGA-II算法对多目标函数进行求解, 得到使精度、复杂度较为均衡的最优解集, 提出了不同精度、复杂度需求下的选择规则. 为了保证结果的有效性, 在舰船磁场混合模型的基础上利用数值实验对模型进行验证, 充分考虑模型拟合误差, 通过对磁性均匀、磁性不均匀潜艇的仿真分析得到模型达到适用范围时距离与磁偶极子数目的相关关系; 在保证模型适用的条件下, 基于NSGA-II算法的多目标优化过程所得结果运算效率、精度高, 具有很好的工程应用价值.With the development of underwater detection and communication technology, the traditional magnetic measurement model cannot meet the requirements for high precision and high efficiency modeling. In order to solve this problem, according to the integral model of ship magnetic field, we comprehensively analyze the discretization error caused by the composite middle rectangular and Gauss-Legendre integral remainders generated by discretizing the integral model into the magnetic dipole array model, the algorithm error, the fitting error caused by the model simplification, the model error, etc. and we also use these research results to analyze the model applicability conditions. Then based on the correlation between model error and parameters as well as accuracy and computational complexity, the multi-objective optimization problem is constructed. The NSGA-II algorithm is used to solve the multi-objective function, and the optimal solution set with balanced accuracy and complexity is obtained. The selection rules under the different requirements for accuracy and complexity are proposed. In order to ensure the effectiveness of the results, the model is simulated by using the actual submarine data on the basis of the hybrid model of ship magnetic field. The relationship between the distance to reach the applicable range of the model and the number of magnetic dipoles is obtained through the simulation analysis of the submarines with uniform and nonuniform magnetic field, and the simulation results are compared with the existing research results to ensure the effectiveness of the simulation results. At the same time, under the condition of ensuring the applicability of the model, the results obtained in the multi-objective optimization process based on NSGA-II algorithm are of high computational efficiency and accuracy. Therefore, this method has good engineering application value.
-
Keywords:
- magnetic dipole integral model /
- composite middle rectangular method remainder /
- multi-objective optimization /
- NSGA-II algorithm
[1] Jin H H, Guo J, Wang H B, Zhuang Z H, Qin J, Wang T L 2020 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 58 5944
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cameron D, Luca M, Ferruccio R 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 2346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jin H H, Zhuang Z H, Wang H B 2018 IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 15 1294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 张晓兵 2021 70 164101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Zhang X B 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 164101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Caruso M J, Smith C H, Bratland T, Schneider R 1998 Sensors 15 1
[6] Nelson J B, Richards T C https://cradpdf.drdc-rddc.gc.ca/ PDFS/unc80/p530746.pdf [2021-12-22]
[7] 张昌达 2006 工程地球 3 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C D 2006 Chin J. Eng. Geophys. 3 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 吴招才, 刘天佑 2008 地质科技情况报 27 107
Wu Z C, Liu T Y 2008 Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 27 107
[9] 胡祥超 2005 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 中国人民解放军国防科技大学)
Hu C X 2005 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[10] 黄玉 2011博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Huang Y 2011 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[11] Yoshii T 1982 US Patent 6 083 641
[12] 刘少丽, 杨向东, 吴聊, 陈恳 2011 机械设计与制造 6 1
Liu S L, Yang X D, Wu L, Chen K 2011 Mchnr. Dgn. Mfr. 6 1
[13] 金煌煌, 庄志洪, 付梦印, 郭健, 王宏波 2021 系统工程与电子技术 43 2066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin H H, Zhang Z H, Fu M Y, Guo J, Wang H B 2021 J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 43 2066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lutkenhoner B 1998 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 45 572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 吴旭东, 侯文生, 郑小林, 彭承琳 2008 仪器仪表学报 29 326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X D, Hou W S, Zheng X L, Peng C L 2008 Chin. J. Sci. Inst. 29 326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 牛龙飞, 李斌, 张静 2009 计算机仿真 26 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Niu L F, Lin B, Zhang J 2009 Comput. Sim. 26 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lucas C E, Richards T C 2015 A Novel Technique for Modelling Ship Magnetic Signatures Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, July 18, 2015 p1
[18] Nilsson M 2016 Modelling of Civilian Ships’ Ferromagnetic Signatures (Norwegian: FFI-rapport) pp13–19
[19] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 单珊 2017 水雷战与舰船防护 25 10
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Dan S 2017 Mine Warfare and Ship Self-Defence 25 10
[20] 樊明武, 颜威利 1988 电磁场积分方程法 (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第65页
Fan M W, Yan W L 1988 Magnetic Field Integral Equation (Beijing: Press of Machinery Industry) p65 (in Chinese)
[21] 盛剑霓 1991工程电磁场数值分析(西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第8页
Sheng J N 1991 Numerical Analysis of Engineering Electromagnetic Field (Xi’an: Press of Xi’an Jiaotong University) p8 (in Chinese)
[22] Maset S J 2021 Numer. Math. 29 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 周耀忠, 张国友 2004 舰船磁场分析计算(北京: 国防工业出版社) 第65—89页
Zhou Y Z, Zhang G Y 2004 Analysis and Calculation of Ship Magnetic Field (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp65–89 (in Chinese)
[24] 林春生, 向前, 龚沈光 2005 兵工学报 26 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin C S, Xiang Q, Gong S G 2005 Acta Armamentarii 26 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 林春生 1996 水雷与战舰防护 4 54
Lin C S 1996 Mine Warfare and Ship Self-Defence 4 54
[26] 裘益钟 1980 上海交通大学学报 18 53
Qiu Y Z 1980 J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 18 53
[27] John J H 2007 Modeling a Ship’s Ferromagnetic Signatures (USA: Morgan & Claypool) pp17–43
[28] Hua C C, Huang C, Zuo Y, Wang W Z, Yang J X 2020 6th Global Electromagnetic Compatibility Conference Xi’an, China, October 20–23, 2020 p1
[29] Shi L, Chen Y M 2017 International Conference on Information Science & Control Engineering Changsha, China, July 21–23, 2017 p55
[30] [31] 陶文华, 刘洪涛 2016 计算机工程 42 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tao W H, Liu H T 2016 Comput. Eng. 42 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 陈志旺, 陈林, 白锌, 杨七, 赵方亮 2015 控制与决策 30 865
Chen Z W, Chen L, Bai X, Yang Q, Zhao F L 2015 Contral. Decis. 30 865
[33] Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T 2002 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bandyopadhyay S, Bhattacharya R 2012 NSGA-II Based Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm for a Multi-objective Supply Chain Problem Nagapattinam, India, March 30–31, 2012 p126
-
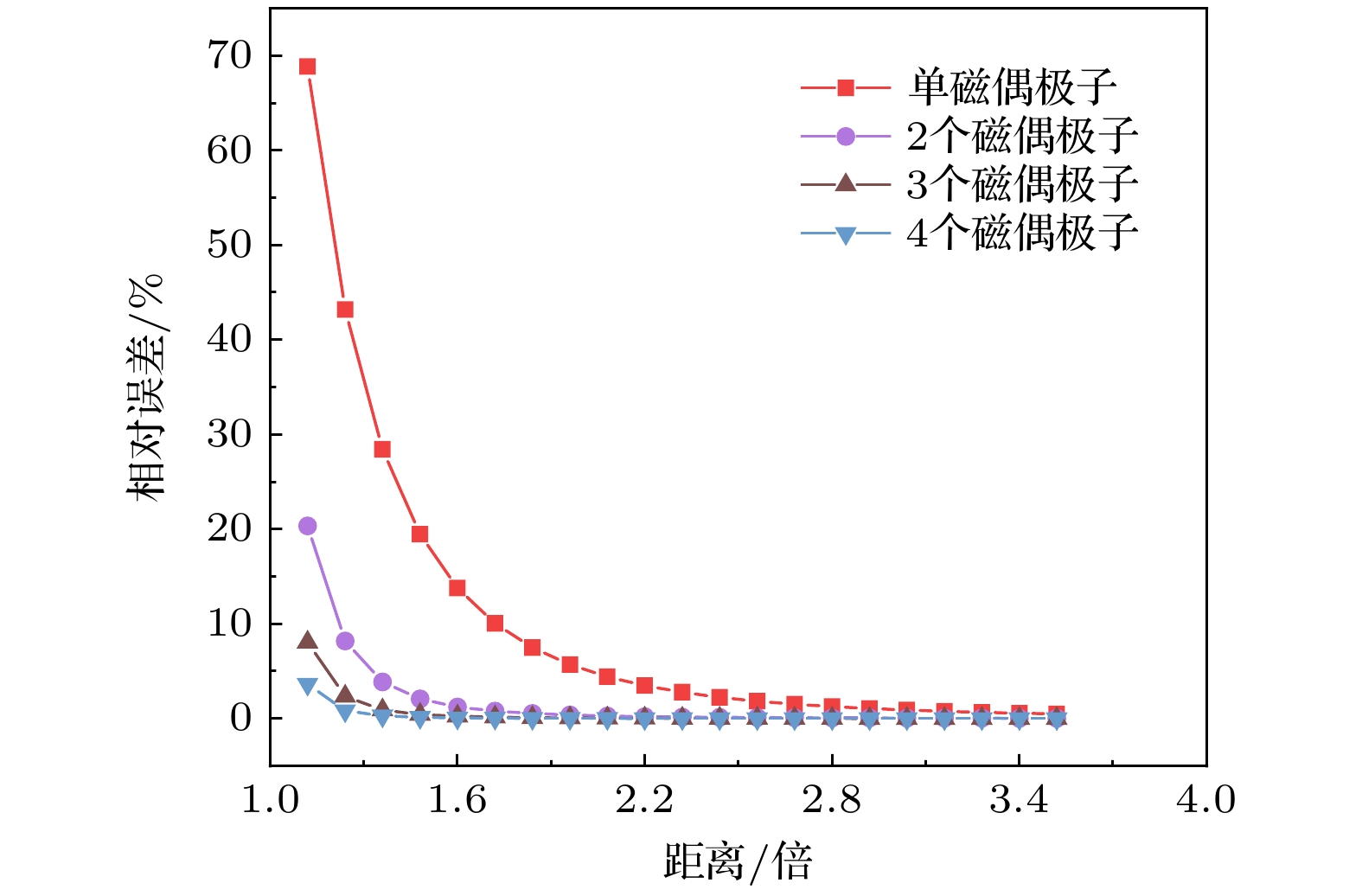
图 6 磁性均匀时模型相对误差变化趋势 (a)磁偶极子数目、距离对模型误差影响的三维柱状图; (b) 磁偶极子数目、距离对模型误差影响的等高线剖面图
Fig. 6. Trend of relative error of the model when the magnetic is uniform: (a) Three dimensional histogram of effects of number and distance of magnetic dipoles on model error; (b) contour of effects of number and distance of magnetic dipoles on model error.
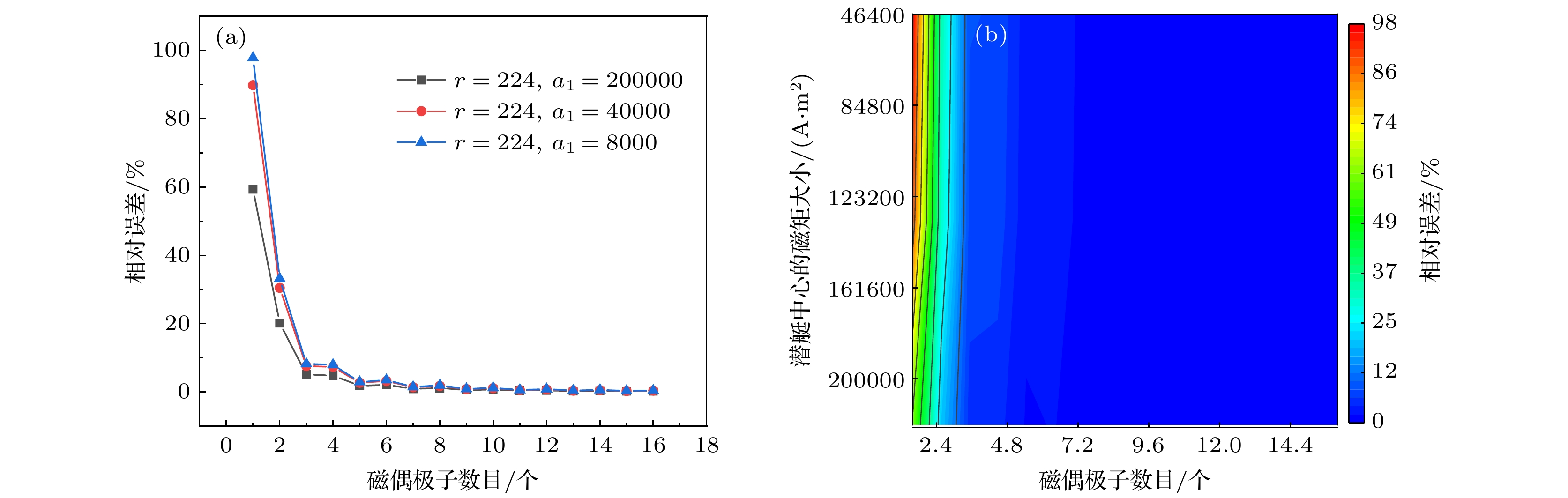
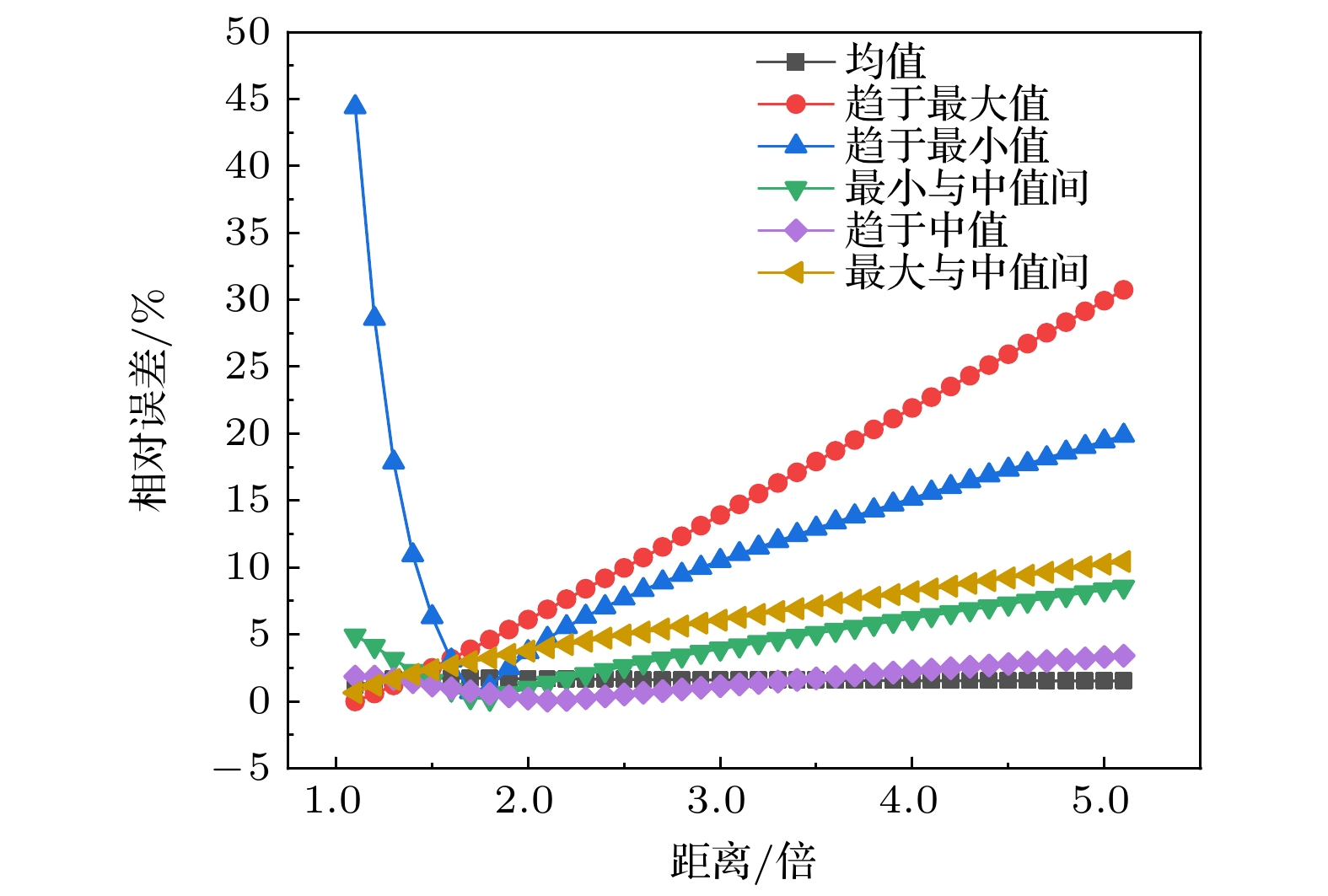
图 7 距离为224时模型相对误差随潜艇磁性差异的变化趋势 (a)潜艇磁性差异对模型相对误差影响的折线图; (b) 潜艇磁性差异对模型相对误差影响的等高线图
Fig. 7. Variation trend of model relative error with submarine magnetic difference when r = 224: (a) Line graph of the effect of submarine magnetic differences on the relative error of the model; (b) Contour plot of the effect of submarine magnetic differences on the relative error of the model
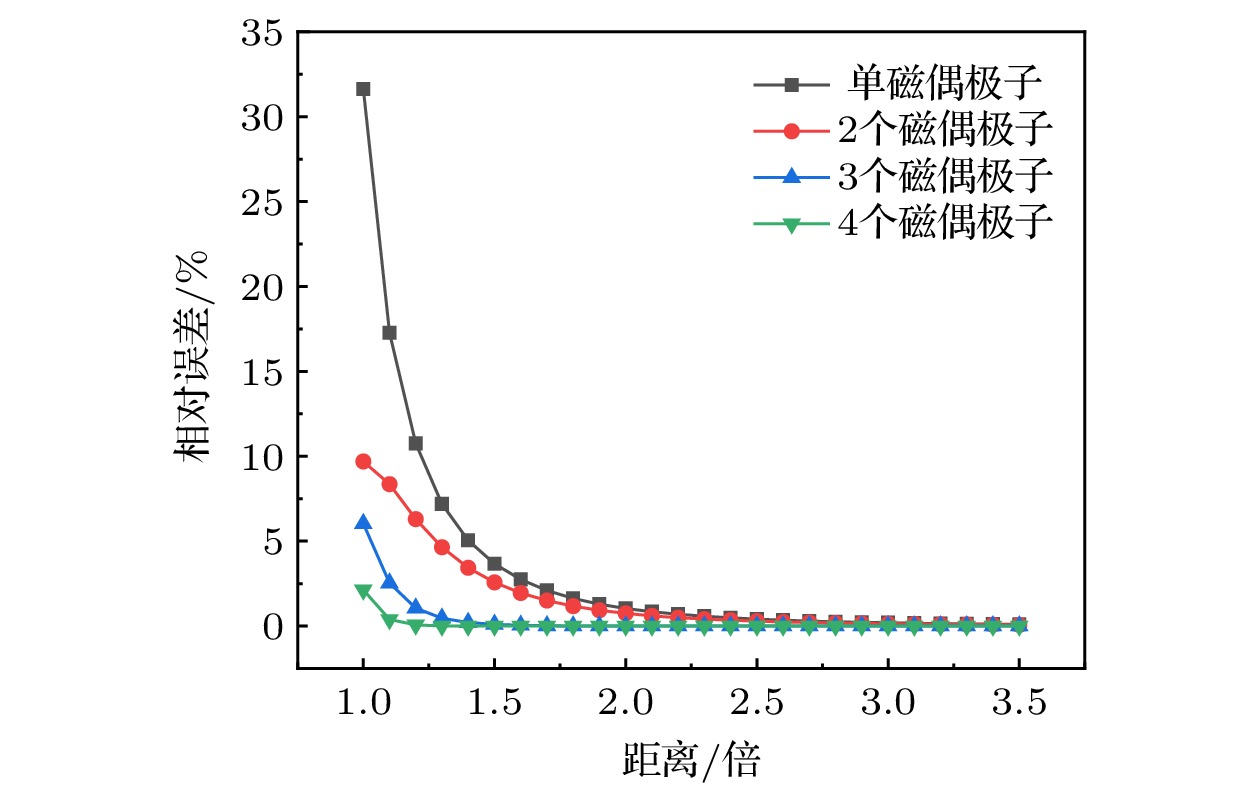
图 8 a1 = 40000时模型相对误差的变化趋势 (a)磁偶极子数目、距离对模型误差影响的三维柱状图; (b) 磁偶极子数目、距离对模型误差的影响等高线剖面图
Fig. 8. Tendency of the relative error of the model when a1 = 40000: (a) Three dimensional histogram of the effect of the number and distance of magnetic dipoles on the model error; (b) contour map of effects of the number and distance of magnetic dipoles on model errors.
表 1 磁性均匀情况下, 达到建模有效范围的磁偶极子数目及距离
Table 1. Number and distance of magnetic dipoles reaching the modeling effective range when the magnetic is uniform.
距离/m 倍数 磁偶极
子数目距离/m 倍数 磁偶极
子数目r = 84 1.050 3 r = 144 1.800 2 r = 94 1.175 3 r = 154 1.925 2 r = 104 1.300 2 r = 164 2.050 2 r = 114 1.425 2 r = 174 2.175 2 r = 124 1.550 2 r = 184 2.300 1 r = 134 1.675 2 r = 194 2.425 1 表 2 磁性不均匀情况下, 达到建模有效范围的磁偶极子数目及距离
Table 2. Number and distance of magnetic dipoles reaching modeling effective range when the magnetic is nonuniform.
距离/m 倍数 磁偶极
子数目距离/m 倍数 磁偶极
子数目r = 84 1.050 6 r = 164 2.050 5 r = 94 1.175 5 r = 174 2.175 5 r = 104 1.300 5 r = 184 2.300 5 r = 114 1.425 5 r = 194 2.425 5 r = 124 1.550 5 r = 204 2.550 5 r = 134 1.675 5 r = 214 2.675 5 r = 144 1.800 5 r = 224 2.800 5 r = 154 1.925 5 r = 234 2.925 5 表 3 平衡点附近磁偶极子数目及相对误差值
Table 3. Number of magnetic dipoles near equilibrium point and relative error.
距离 倍数 偶极子数目 相对误差 距离 倍数 偶极子数目 相对误差 r = 94 1.175 10 0.90% r = 184 2.300 6 0.39% r = 104 1.300 9 0.77% r = 194 2.425 6 0.32% r = 114 1.425 8 0.71% r = 204 2.550 6 0.32% r = 124 1.550 8 0.60% r = 214 2.675 6 0.30% r = 134 1.675 8 0.52% r = 224 2.800 6 0.27% r = 144 1.800 7 0.52% r = 234 2.925 5 0.30% r = 154 1.925 7 0.46% r = 300 3.750 5 0.18% r = 164 2.050 7 0.41% r = 400 5.000 5 0.11% r = 174 2.175 7 0.36% r = 500 6.250 5 0.085% -
[1] Jin H H, Guo J, Wang H B, Zhuang Z H, Qin J, Wang T L 2020 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 58 5944
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cameron D, Luca M, Ferruccio R 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 2346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jin H H, Zhuang Z H, Wang H B 2018 IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 15 1294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 张晓兵 2021 70 164101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Zhang X B 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 164101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Caruso M J, Smith C H, Bratland T, Schneider R 1998 Sensors 15 1
[6] Nelson J B, Richards T C https://cradpdf.drdc-rddc.gc.ca/ PDFS/unc80/p530746.pdf [2021-12-22]
[7] 张昌达 2006 工程地球 3 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C D 2006 Chin J. Eng. Geophys. 3 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 吴招才, 刘天佑 2008 地质科技情况报 27 107
Wu Z C, Liu T Y 2008 Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 27 107
[9] 胡祥超 2005 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 中国人民解放军国防科技大学)
Hu C X 2005 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[10] 黄玉 2011博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Huang Y 2011 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[11] Yoshii T 1982 US Patent 6 083 641
[12] 刘少丽, 杨向东, 吴聊, 陈恳 2011 机械设计与制造 6 1
Liu S L, Yang X D, Wu L, Chen K 2011 Mchnr. Dgn. Mfr. 6 1
[13] 金煌煌, 庄志洪, 付梦印, 郭健, 王宏波 2021 系统工程与电子技术 43 2066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin H H, Zhang Z H, Fu M Y, Guo J, Wang H B 2021 J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 43 2066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lutkenhoner B 1998 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 45 572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 吴旭东, 侯文生, 郑小林, 彭承琳 2008 仪器仪表学报 29 326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X D, Hou W S, Zheng X L, Peng C L 2008 Chin. J. Sci. Inst. 29 326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 牛龙飞, 李斌, 张静 2009 计算机仿真 26 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Niu L F, Lin B, Zhang J 2009 Comput. Sim. 26 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lucas C E, Richards T C 2015 A Novel Technique for Modelling Ship Magnetic Signatures Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, July 18, 2015 p1
[18] Nilsson M 2016 Modelling of Civilian Ships’ Ferromagnetic Signatures (Norwegian: FFI-rapport) pp13–19
[19] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 单珊 2017 水雷战与舰船防护 25 10
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Dan S 2017 Mine Warfare and Ship Self-Defence 25 10
[20] 樊明武, 颜威利 1988 电磁场积分方程法 (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第65页
Fan M W, Yan W L 1988 Magnetic Field Integral Equation (Beijing: Press of Machinery Industry) p65 (in Chinese)
[21] 盛剑霓 1991工程电磁场数值分析(西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第8页
Sheng J N 1991 Numerical Analysis of Engineering Electromagnetic Field (Xi’an: Press of Xi’an Jiaotong University) p8 (in Chinese)
[22] Maset S J 2021 Numer. Math. 29 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 周耀忠, 张国友 2004 舰船磁场分析计算(北京: 国防工业出版社) 第65—89页
Zhou Y Z, Zhang G Y 2004 Analysis and Calculation of Ship Magnetic Field (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp65–89 (in Chinese)
[24] 林春生, 向前, 龚沈光 2005 兵工学报 26 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin C S, Xiang Q, Gong S G 2005 Acta Armamentarii 26 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 林春生 1996 水雷与战舰防护 4 54
Lin C S 1996 Mine Warfare and Ship Self-Defence 4 54
[26] 裘益钟 1980 上海交通大学学报 18 53
Qiu Y Z 1980 J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 18 53
[27] John J H 2007 Modeling a Ship’s Ferromagnetic Signatures (USA: Morgan & Claypool) pp17–43
[28] Hua C C, Huang C, Zuo Y, Wang W Z, Yang J X 2020 6th Global Electromagnetic Compatibility Conference Xi’an, China, October 20–23, 2020 p1
[29] Shi L, Chen Y M 2017 International Conference on Information Science & Control Engineering Changsha, China, July 21–23, 2017 p55
[30] [31] 陶文华, 刘洪涛 2016 计算机工程 42 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tao W H, Liu H T 2016 Comput. Eng. 42 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 陈志旺, 陈林, 白锌, 杨七, 赵方亮 2015 控制与决策 30 865
Chen Z W, Chen L, Bai X, Yang Q, Zhao F L 2015 Contral. Decis. 30 865
[33] Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T 2002 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bandyopadhyay S, Bhattacharya R 2012 NSGA-II Based Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm for a Multi-objective Supply Chain Problem Nagapattinam, India, March 30–31, 2012 p126
计量
- 文章访问数: 9274
- PDF下载量: 154
- 被引次数: 0















 下载:
下载: