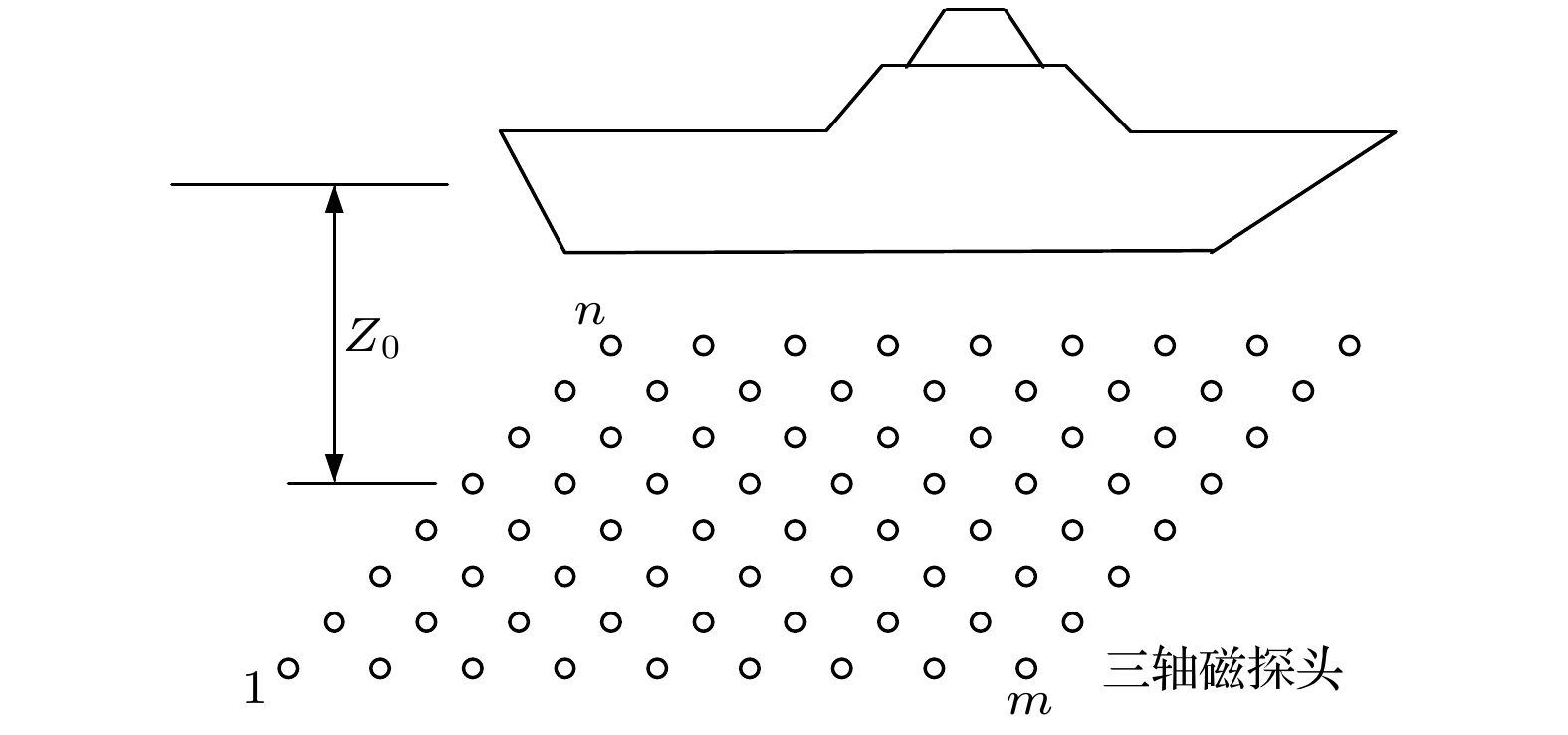
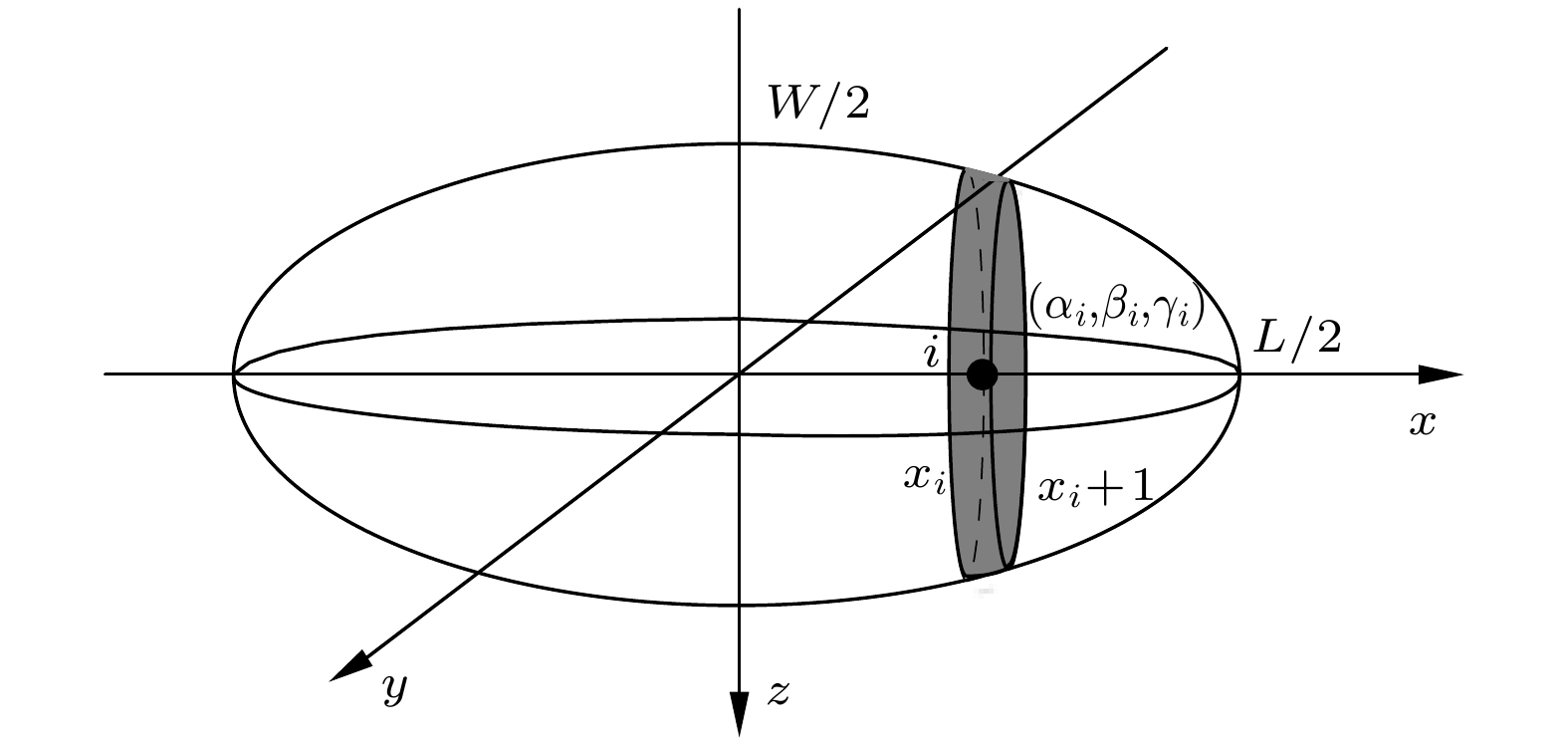
-
针对舰船磁场混合模型建模中存在的建模精度不高和稳定性差的问题, 提出一种高精度稳定模型建立方法, 结合混合模型中磁偶极子参数与舰船结构的相关性, 以建模精度和模型稳定性为目标构造了多目标函数, 通过对多目标函数优化获得合理的磁偶极子参数, 间接地将建模求解问题转化为多目标函数优化问题.利用多目标粒子群优化算法进行求解, 得到了建模问题求解结果的可选集, 以建模精度为基准设计了从可选集中选取最佳结果的选择规则. 三种类型的舰船船模实测数据建模结果表明: 本文方法所建模型相对误差小于3%, 换算误差小于6%, 能够有效对舰船磁场进行建模; 当存在测量数据误差时, 本文方法建模求解结果稳定, 验证了文本方法建模具有较好的稳定性. 海上的某型舰船实测数据建模结果表明, 本文方法建模具有较高的建模精度和换算精度, 能够有效地在相关的工程中应用.
-
关键词:
- 舰船磁场建模 /
- 多目标函数 /
- 多目标粒子群优化算法 /
- 选择规则
Ship magnetic field modeling is not only beneficial to understanding the characteristics of ship magnetic field, but also can predict the space distribution of ship magnetic field, which has an important application in ship protection and underwater weapons. Aiming at the problems of low modeling accuracy and poor stability in establishing the ship magnetic field hybrid model, a method of establishing a high precision stablity model is proposed in this paper. A hybrid model of magnetic field of a ship is established by using a uniformly magnetized rotating ellipsoid and a magnetic dipole array. Since the number and positions of magnetic dipoles in the hybrid model have an important effect on the modeling accuracy and stability, the fitting error function representing the modeling accuracy and the coefficient matrix condition number function representing the stability of the model are constructed by taking the magnetic dipole parameters as unknown variables. The multi-objective function is constructed by combining the fitting error function with the coefficient matrix conditional number function, which indirectly transforms the modeling problem into a multi-objective optimization problem. The multi-objective function is solved by using the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm, and an optional set of modeling solution results is obtained. In order to select the best results from the optional set, the corresponding selection rules are designed based on the modeling accuracy. The proposed method is validated by the measured data of three kinds of ship models, the modeling results show that the relative error of the model is less than 3%, and the conversion error is less than 6%, which verifies that the proposed method can effectively model the ship magnetic field. Though the measurement data error exists, the modeling solution results from the proposed method have the best stability, which verifies that the modeling method proposed in this work has good stability. Compared with the two existing modeling methods, the proposed method has very good modeling accuracy and stability. Finally, the actual data of a ship on the sea are used for modeling, and the modeling results further verify that the proposed method has high modeling accuracy and conversion accuracy, and can be effectively applied to the relevant projects.-
Keywords:
- ship magnetic field modeling /
- multi-objective function /
- multi-objective particle swarm optimizatialgorithm /
- selection rule
[1] 林春生, 龚沈光 2007 舰船物理场 (第2版) 第51页
Lin C S, Gong S G 2007 Ship Physical Field (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: Ordnance Industry Press) p51 (in Chinese)
[2] 林春生 1996 水雷战与舰船防护 3 54
Lin C S 1996 Mine Warfare & Ship Self-Defence 3 54
[3] Ginzburg B, Frumkis L, Kaplan B Z 2002 Sens. Actuators, A 102 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wahlström N, Gustafsson F 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 姚振宁, 刘大明, 刘胜道 2014 22 227502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao Z N, Liu D M, Liu S D 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 227502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张宏欣, 周穗华, 张伽伟 2017 自动化学报 43 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H X, Zhou S H, Zhang J W 2017 Acta Autom. Sin. 43 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 张宏欣 2019 电子学报 47 2457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Zhang H X 2019 Acta Electron. Sin. 47 2457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sui Y, Leslie K, Clark D 2017 IEEE Magn. Lett. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张晓峻, 康曦元, 樊黎明 2019 地球 62 1921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X J, Kang X Y, Fan L M 2019 Acta Geophys. Sin. 62 1921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 费春娇, 张群英, 吴佩霖 2018 电子与信息学报 11 2779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fei C J, Zhang Q Y, Wu P L 2018 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 11 2779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 陈路昭, 冯永强, 郭瑞杰 2020 电子与信息学报 42 573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen L Z, Feng Y Q, Guo R J 2020 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 42 573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 高俊杰, 刘大明, 姚琼 2006 兵工学报 27 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J J, Liu D M, Yao Q 2006 Acta Armamentarii 27 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 郭成豹, 肖昌汉, 刘大明 2008 07 4182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C B, Xiao H C, Liu D M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 07 4182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 闫辉, 肖昌汉, 周国华 2008 兵工学报 07 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan H, Xiao H C, Zhou G H 2008 Acta Armamentarii 07 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 王德强, 余强 2014 舰船科学技术 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D Q, Yu Q 2014 Ship Sci. Technol. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Holmes J J 2006 Synth. Lect. Comput. Electromagnet. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Holmes J J 2007 Synth. Lect. Comput. Electromagnet. 2 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杨明明, 刘大明, 刘胜道, 连丽婷 2010 兵工学报 9 1216
Yang M M, Liu D M, Liu S D, Lian L T 2010 Acta Armamentarii 9 1216
[19] 王金根, 龚沈光, 刘胜道 2001 海军工程大学学报 3 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J G, Gong S G, Liu S D 2001 J. Naval Univ. Eng. 3 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 刘胜道, 刘大明, 肖昌汉 2008 武汉理工大学学报 (交通科学与工程版) 6 1017
Liu S D, Liu D M, Xiao H C 2008 J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.(Transp. Sci. Eng.) 6 1017
[21] 徐杰, 刘大明, 周国华 2009 舰船科学技术 01 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu J, Liu D M, Zhou G H 2009 Ship Sci. Technol. 01 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王桓, 周耀忠, 周国华 2007 海军工程大学学报 01 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Zhou Y Z, Zhou G H 2007 J. Naval Univ. Eng. 01 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张朝阳, 肖昌汉, 徐杰 2010 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版) 11 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C Y, Xiao H C, Xu J 2010 J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Edition) 11 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 吴志东, 周穗华, 郭虎生 2013 武汉理工大学学报 09 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z D, Zhou S H, Guo H S 2013 J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 09 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 单珊 2018 电子学报 46 1524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Shan S 2018 Acta Electron. Sin. 46 1524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 郭成豹, 殷琦琦 2019 68 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C B, Yin Q Q 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Alqadah H F, Valdivia N P, Williams E G 2016 Prog. Electromagnet. Res. B 65 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Vuillermet Y, Chadebec O, Coulomb J L, Rouve L L, Cauffet G, Bongiraud J P, Demilier L 2008 IEEE Trans. Magn. 44 1054
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Coello C A C 2006 IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 1 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Dorigo M, Gambardella L M 1997 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Bandyopadhyay S, Saha S, Maulik U, Deb K 2008 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 12 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Coello C A C, Pulido G T, Lechuga M S 2004 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 8 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 公茂果, 焦李成, 杨咚咚, 马文萍 2009 软件学报 20 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong M G, Jiao L C, Yang D D, Ma W P 2009 J. Software 20 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kennedy J 1995 Process of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks Perth Australia, November 27, 1995 4 1942
-
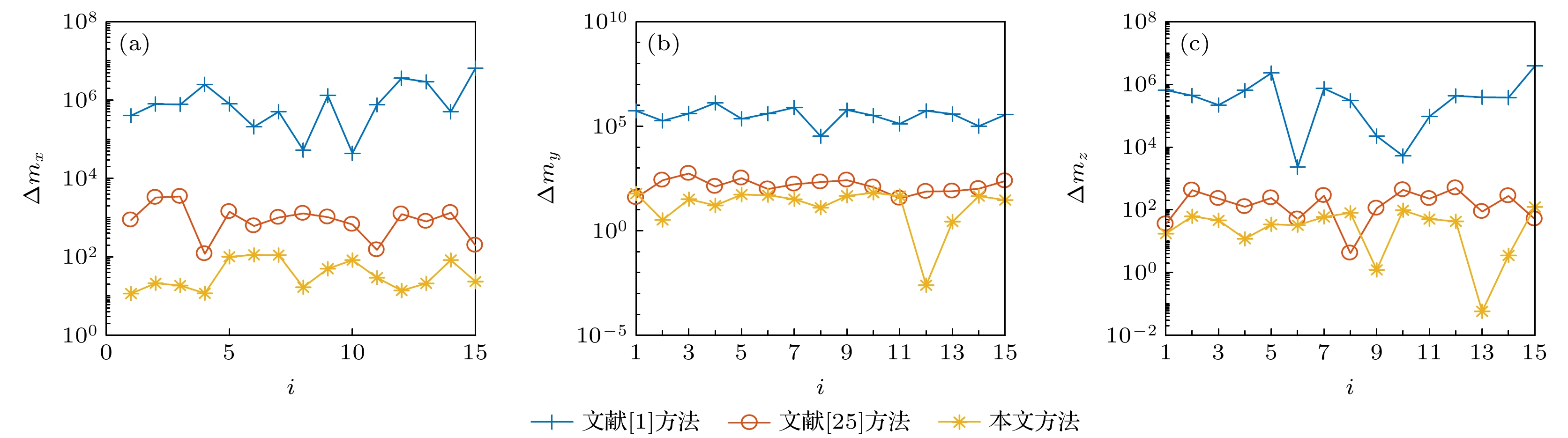
图 11 干扰下不同方法求解的小型舰船磁矩绝对误差 (a) x方向磁矩绝对误差
$\Delta {m_x}$ ; (b) y方向磁矩绝对误差$\Delta {m_y}$ ; (c) z方向磁矩绝对误差$\Delta {m_z}$ Fig. 11. Absolute errors of magnetic moment of small ships solved by different methods under disturbance: (a) Absolute errors of magnetic moment in x-direction; (b) absolute errors of magnetic moment in y-direction; (c) absolute errors of magnetic moment in z-direction.
图 12 干扰下不同方法求解的中型舰船磁矩绝对误差 (a) x方向磁矩绝对误差
$\Delta {m_x}$ ; (b) y方向磁矩绝对误差$\Delta {m_y}$ ; (c) z方向磁矩绝对误差$\Delta {m_z}$ Fig. 12. Absolute error of magnetic moment of medium ship solved by different methods under disturbance: (a) Absolute errors of magnetic moment in x-direction; (b) absolute errors of magnetic moment in y-direction; (c) absolute errors of magnetic moment in z-direction.
图 13 干扰下不同方法求解的大型舰船磁矩绝对误差 (a) x方向磁矩绝对误差
$ \Delta {m_x}$ ; (b) y方向磁矩绝对误差$ \Delta {m_y}$ ; (c) z方向磁矩绝对误差$ \Delta {m_z}$ Fig. 13. Absolute errors of magnetic moment of large ships solved by different methods under disturbance: (a) Absolute errors of magnetic moment in x-direction; (b) absolute errors of magnetic moment in y-direction; (c) absolute errors of magnetic moment in z-direction.
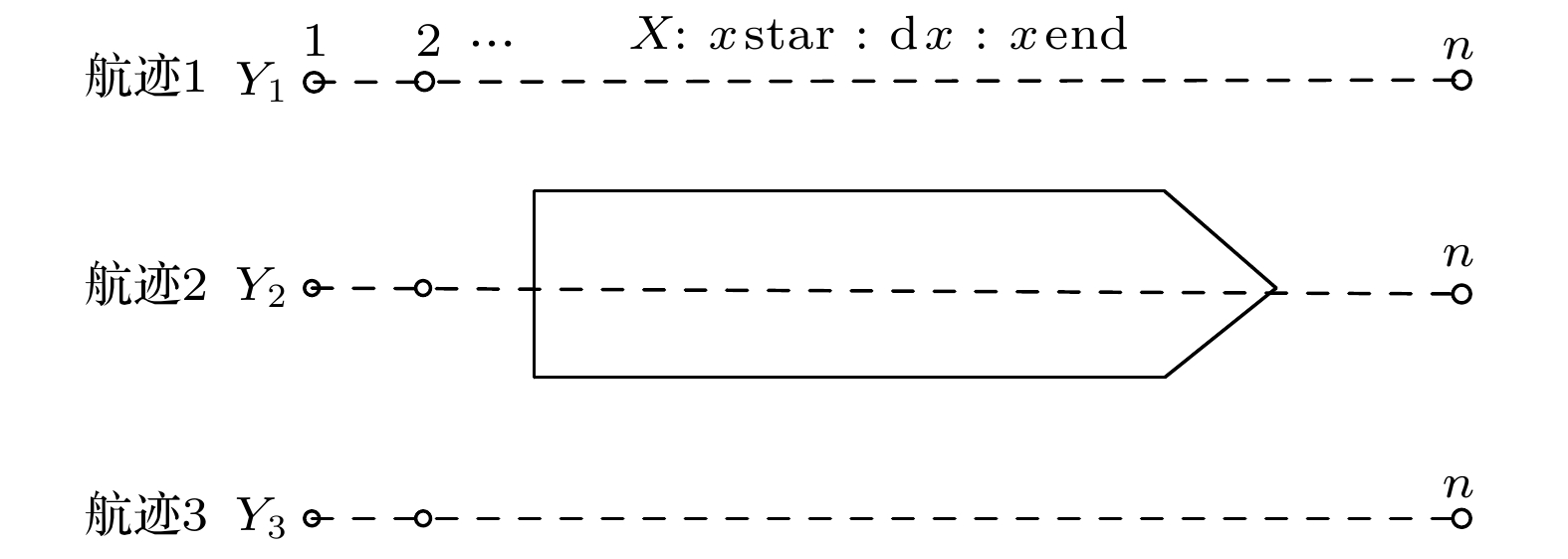
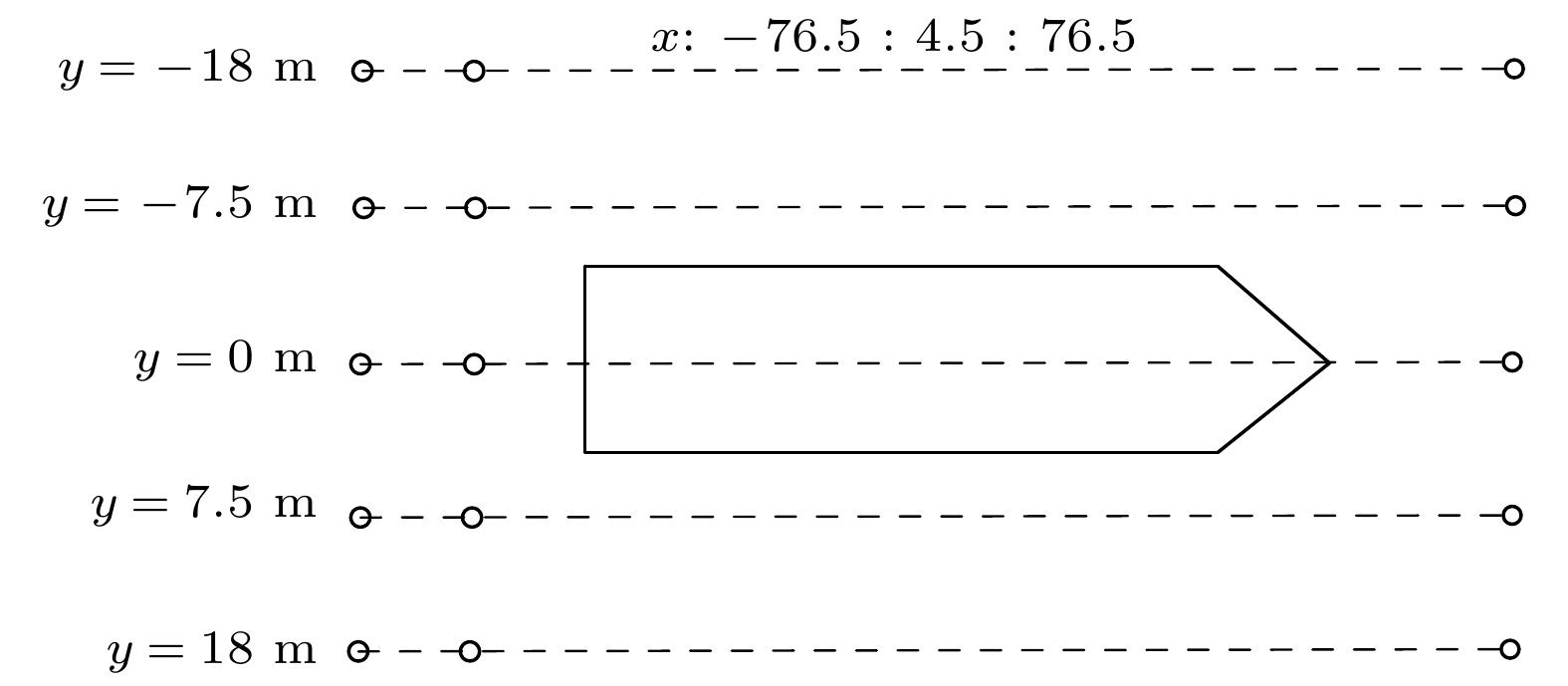
表 1 试验参数
Table 1. Test parameters.
目标 尺度参数/m 测量深度/m 航迹1/m 航迹2/m 航迹3/m L W ${Z_0}$ ${Z_1}$ 小型船模 57.2 8.6 8.6 17 X = –80:2:80,
Y = –4.2X = – 80:2:80,
Y = 0X = – 80:2:80,
Y = 4.2中型船模 76.5 8.5 12.75 20.5 X = –100:2.5:100,
Y =–15X = –100:2.5:100,
Y = 0X = –100:2.5:100,
Y = 15大型船模 153 17.3 17.2 28.8 X = –128:3.2:128,
Y = –8.64X = –128:3.2:128,
Y = 0X = –128:3.2:128,
Y = 8.64表 2 Z0深度平面上的三种舰船船模建模结果
Table 2. Modeling results of three kinds of ships on the Z0 depth plane.
目标 小型舰船 中型舰船 大型舰船 磁偶极子数 10 8 14 系数矩阵条件数 85.13 76.5 128.95 建模相对误差 0.0295 0.0290 0.0256 表 3 不同深度的建模相对误差和换算相对误差
Table 3. Modeling relative errors and converted relative errors of different depths.
目标 建模深度/m 换算深度/m 相对误差 小型舰船 8.6 8.6 0.0295 17 0.0402 17 8.6 0.0479 17 0.0256 中型舰船 12.75 12.75 0.0290 20.5 0.0323 20.5 12.75 0.0387 20.5 0.0201 大型舰船 17.2 17.2 0.0256 28.8 0.0301 28.8 17.2 0.0547 28.8 0.0152 表 4 不同方法的建模相对误差和换算相对误差
Table 4. Modeling relative error and conversion relative error of different methods.
目标 文献[1] 文献[25] 本文方法 小型舰船 磁偶极子数 10 10 10 系数矩阵条件数 1.28 × 103 34.65 85.13 建模相对误差 17 m 0.0464 0.1071 0.0295 8.6 m 0.0450 0.0458 0.0256 换算相对误差 8.6 m→17 m 0.0609 0.0913 0.0402 17 m→8.6 m 0.1208 0.1523 0.0497 中型舰船 磁偶极子数 8 8 8 系数矩阵条件数 709.8 28.02 76.5 建模相对误差 20.5 m 0.0568 0.0619 0.0290 12.75 m 0.0655 0.0872 0.0201 换算相对误差 12.75 m→20.5 m 0.077 0.1726 0.0323 20.5 m→12.75 m 0.129 0.1317 0.0387 大型舰船 磁偶极子数 14 14 14 系数矩阵条件数 2.36 × 103 78.29 128.95 建模相对误差 28.8 m 0.0991 0.1302 0.0256 17.2 m 0.0525 0.0602 0.0152 换算相对误差 17.2 m→28.8 m 0.0984 0.1033 0.0301 28.8 m→17.2 m 0.1769 0.1782 0.0547 表 5 干扰下不同方法的建模相对误差和换算误差
Table 5. Modeling relative errors and conversion errors of different methods under interference.
表 6 真实舰船测量数据建模结果
Table 6. Modeling results of real ship measurement data.
航向 建模相对误差 换算误差 东航向 0.0243 0.0543 西航向 0.0257 0.0621 南航向 0.0236 0.0325 北航向 0.0276 0.0421 -
[1] 林春生, 龚沈光 2007 舰船物理场 (第2版) 第51页
Lin C S, Gong S G 2007 Ship Physical Field (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: Ordnance Industry Press) p51 (in Chinese)
[2] 林春生 1996 水雷战与舰船防护 3 54
Lin C S 1996 Mine Warfare & Ship Self-Defence 3 54
[3] Ginzburg B, Frumkis L, Kaplan B Z 2002 Sens. Actuators, A 102 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wahlström N, Gustafsson F 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 姚振宁, 刘大明, 刘胜道 2014 22 227502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao Z N, Liu D M, Liu S D 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 227502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张宏欣, 周穗华, 张伽伟 2017 自动化学报 43 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H X, Zhou S H, Zhang J W 2017 Acta Autom. Sin. 43 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 张宏欣 2019 电子学报 47 2457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Zhang H X 2019 Acta Electron. Sin. 47 2457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sui Y, Leslie K, Clark D 2017 IEEE Magn. Lett. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张晓峻, 康曦元, 樊黎明 2019 地球 62 1921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X J, Kang X Y, Fan L M 2019 Acta Geophys. Sin. 62 1921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 费春娇, 张群英, 吴佩霖 2018 电子与信息学报 11 2779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fei C J, Zhang Q Y, Wu P L 2018 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 11 2779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 陈路昭, 冯永强, 郭瑞杰 2020 电子与信息学报 42 573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen L Z, Feng Y Q, Guo R J 2020 J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 42 573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 高俊杰, 刘大明, 姚琼 2006 兵工学报 27 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J J, Liu D M, Yao Q 2006 Acta Armamentarii 27 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 郭成豹, 肖昌汉, 刘大明 2008 07 4182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C B, Xiao H C, Liu D M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 07 4182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 闫辉, 肖昌汉, 周国华 2008 兵工学报 07 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan H, Xiao H C, Zhou G H 2008 Acta Armamentarii 07 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 王德强, 余强 2014 舰船科学技术 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D Q, Yu Q 2014 Ship Sci. Technol. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Holmes J J 2006 Synth. Lect. Comput. Electromagnet. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Holmes J J 2007 Synth. Lect. Comput. Electromagnet. 2 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杨明明, 刘大明, 刘胜道, 连丽婷 2010 兵工学报 9 1216
Yang M M, Liu D M, Liu S D, Lian L T 2010 Acta Armamentarii 9 1216
[19] 王金根, 龚沈光, 刘胜道 2001 海军工程大学学报 3 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J G, Gong S G, Liu S D 2001 J. Naval Univ. Eng. 3 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 刘胜道, 刘大明, 肖昌汉 2008 武汉理工大学学报 (交通科学与工程版) 6 1017
Liu S D, Liu D M, Xiao H C 2008 J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.(Transp. Sci. Eng.) 6 1017
[21] 徐杰, 刘大明, 周国华 2009 舰船科学技术 01 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu J, Liu D M, Zhou G H 2009 Ship Sci. Technol. 01 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王桓, 周耀忠, 周国华 2007 海军工程大学学报 01 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Zhou Y Z, Zhou G H 2007 J. Naval Univ. Eng. 01 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 张朝阳, 肖昌汉, 徐杰 2010 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版) 11 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C Y, Xiao H C, Xu J 2010 J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Edition) 11 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 吴志东, 周穗华, 郭虎生 2013 武汉理工大学学报 09 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z D, Zhou S H, Guo H S 2013 J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 09 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 戴忠华, 周穗华, 单珊 2018 电子学报 46 1524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z H, Zhou S H, Shan S 2018 Acta Electron. Sin. 46 1524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 郭成豹, 殷琦琦 2019 68 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C B, Yin Q Q 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Alqadah H F, Valdivia N P, Williams E G 2016 Prog. Electromagnet. Res. B 65 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Vuillermet Y, Chadebec O, Coulomb J L, Rouve L L, Cauffet G, Bongiraud J P, Demilier L 2008 IEEE Trans. Magn. 44 1054
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Coello C A C 2006 IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 1 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Dorigo M, Gambardella L M 1997 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Bandyopadhyay S, Saha S, Maulik U, Deb K 2008 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 12 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Coello C A C, Pulido G T, Lechuga M S 2004 IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 8 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 公茂果, 焦李成, 杨咚咚, 马文萍 2009 软件学报 20 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong M G, Jiao L C, Yang D D, Ma W P 2009 J. Software 20 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kennedy J 1995 Process of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks Perth Australia, November 27, 1995 4 1942
计量
- 文章访问数: 8635
- PDF下载量: 121
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: