-
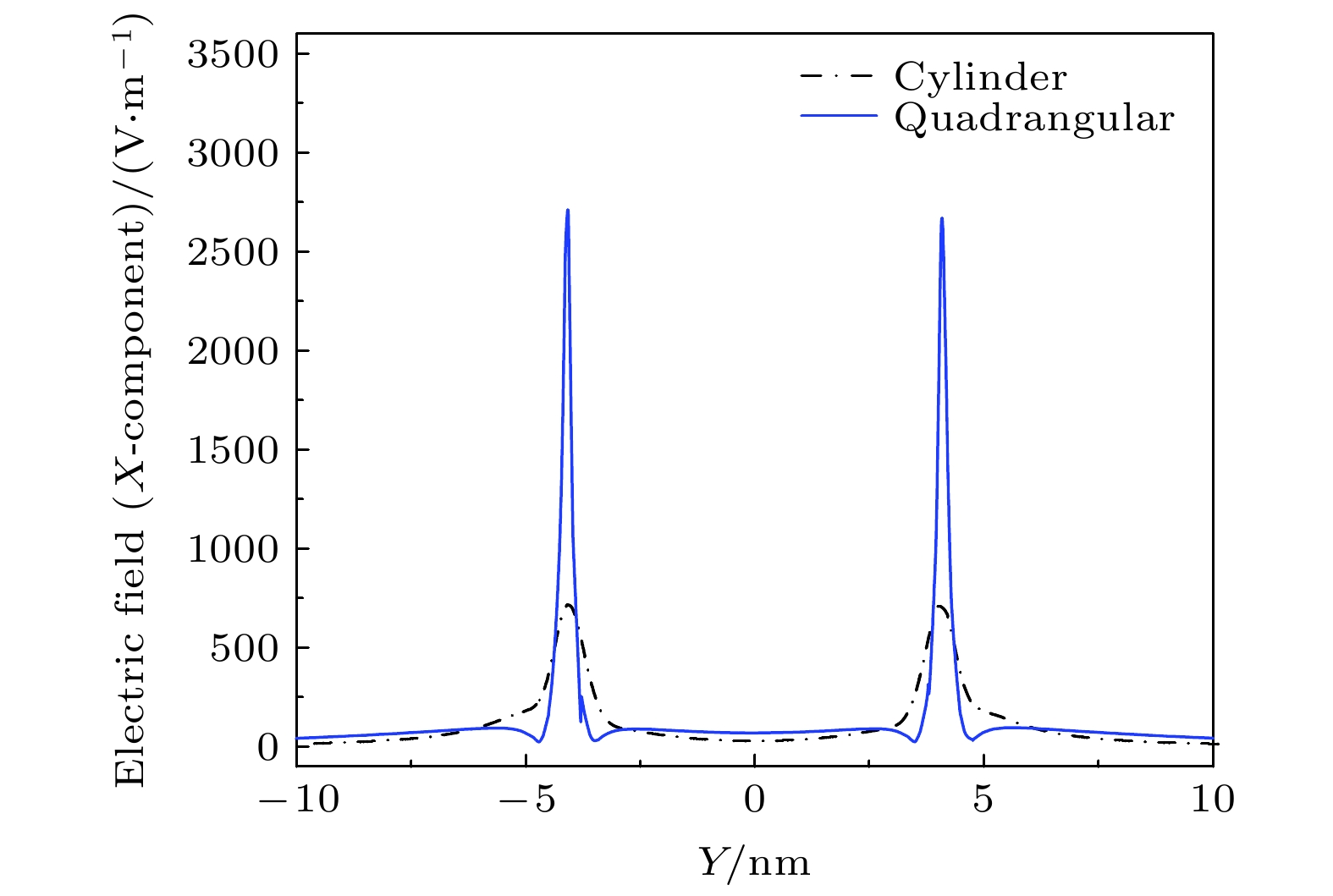
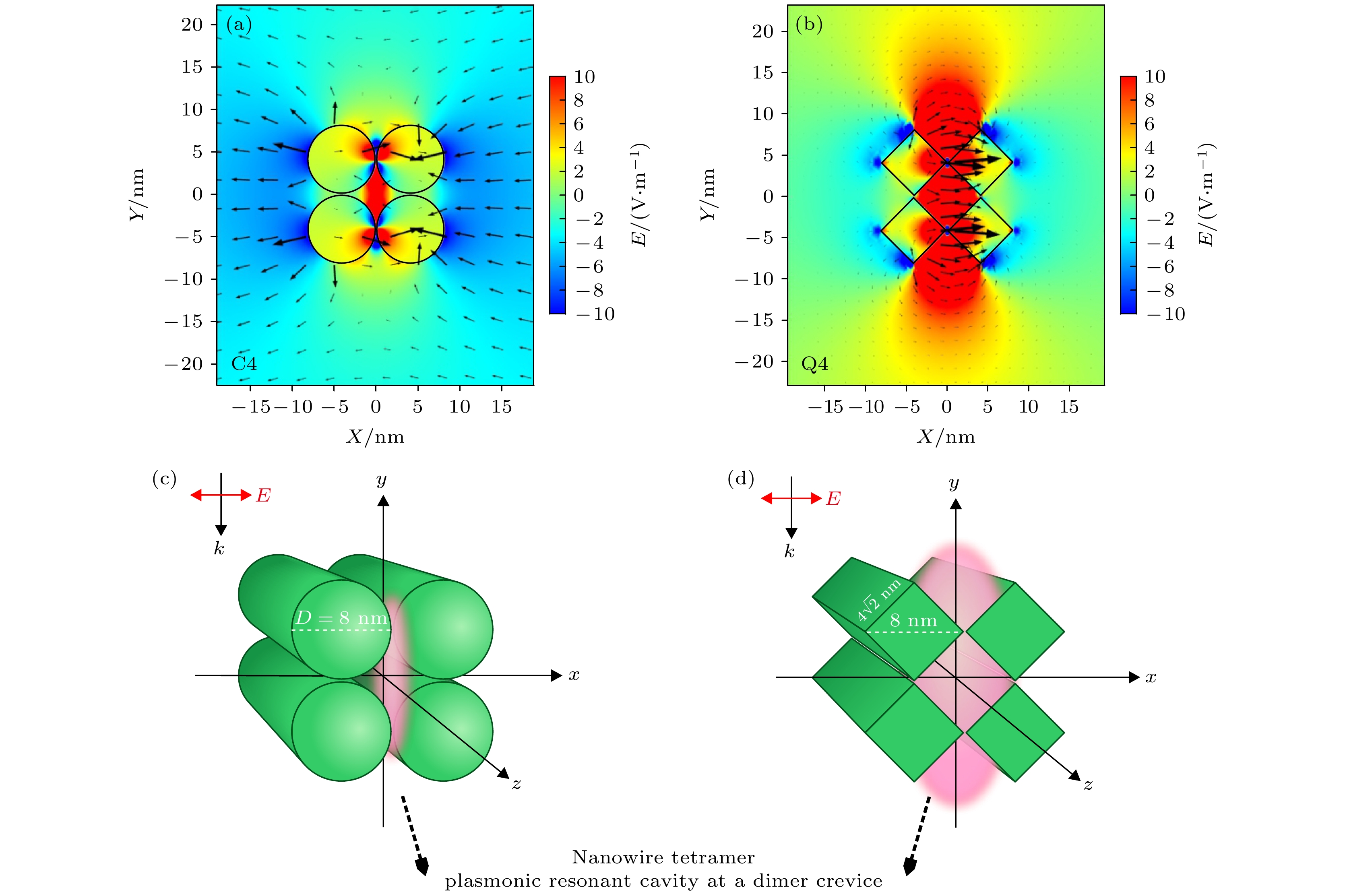
利用贵金属纳米线之间的相互作用可诱导局域表面等离子体共振效应, 从而增强纳米结构中电场的分布, 这在增强荧光特性和提升传感器的灵敏度等方面都有着非常重要的意义. 本文设计了几种基于贵金属Ag的四聚体纳米结构, 包括圆柱形和四棱柱形Ag四聚体结构, 并通过改变其排列方式与棱柱纳米线的旋转角度, 对其电场分布以及电场强度X分量对旋转角的依赖关系进行了理论模拟研究, 探讨了吸收谱共振峰位与模态体积变化关系的物理机制. 结果表明在Ag纳米线四聚体结构中, 圆柱形结构中的电场增强效果不明显, 棱柱形结构中的电场被大大增强, 棱柱形四聚体间隙内产生了明显的电偶极子共振模式, 极化的等离子体共振腔说明了形貌对于热点的产生起着决定性作用, 在改变四聚体纳米线的组合方式以及四棱柱的旋转角度后, 未旋转的非对称四聚体结构的局域表面等离激元共振特性最为理想, 高于对称四棱柱结构的共振强度. 因此, 我们的结果对于利用局域表面等离子共振效应增强电场强度提供了结构模型和理论参数.
-
关键词:
- Ag纳米线四聚体 /
- 电偶极子共振 /
- 等离子共振腔 /
- 局域表面等离子共振效应
The interaction between noble metal nanowires can induce the local surface plasmonic resonance effect, thereby enhancing the distribution of electric field in the nanostructures, which is of very important significance in improving the fluorescence characteristics and enhancing the sensitivity of sensors. In this study, we design several types of tetramers based on precious metals Ag nanostructures, including cylindrical and prismatic Ag tetramers, and by changing the arrangement and the rotation angle of prism nanowires, we simulate the rotation-angle dependent electric field distribution and electric field intensity of X component , and also discuss the physical mechanism of the relationship between the resonant peak position of absorption spectrum and the change of mode volume. The results show that in the Ag nanowires tetramer structure, the electric field in the cylindrical structure is not enhanced obviously, but the electric field in the prismatic structure is greatly enhanced, and an electric dipole resonance mode is produced in the gap between tetramers. The polarization of plasma resonant cavity revels that the morphology plays a decisive role in generating the hot spots, After changing both the combination mode of tetramer nanowires and the rotation angle of the four-prism, the local surface exciton resonance of the unrotated asymmetric tetramer structure is most ideal and has resonance intensity higher than the that of symmetrical four-prism structure. Therefore, our results provide a structural model and theoretical parameters for the enhancement of electric field intensity by local surface plasmon resonance effect.-
Keywords:
- Ag nanowire tetramer /
- electric dipole resonance /
- plasma resonance cavity /
- local surface plasmon resonance effect
[1] Bachelier G, Russier A I, Benichou E, Jonin C, Del F N, Valle'e F, Brevet P F 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 19740
[2] 洪昕, 杜丹丹, 裘祖荣, 张国雄 2007 56 7219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hong X, Du D D, Qiu Z R, Zhang G Q 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 7219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xia M, Zhang P, Qiao K, Bai Y, Xie Y H 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 527
[4] Cathcart N, Chen J I L, Kitaev V 2018 Langmuir 34 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bingham J M, Willets K A, Shah N C, Andrews D Q, Van Duyne R P 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C 113 16839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sherry L J, Chang S H, Schatz G C, Duyne R P V, Wiley B J, Xia Y N 2005 Nano Lett. 5 2034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 徐天宁, 李翔, 贾文旺, 隋成华, 吴惠桢 2015 64 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu T N, Li X, Jia W W, Sui C H, Wu H Z 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hou H, Chen L M, He H L, Chen L Z, Zhao Z L, Jin Y D 2015 J. Mater. Chem. B 3 5189
[9] Mahmud S, Satter S S, Singh A K, Rahman M M, Mollah M Y A, Hasan Susan M A B 2019 ACS Omega 4 18061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fernandez-Domınguez A I, Wiener A, García-Vidal F J, Maier S A, Pendry J B 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 106802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kessentini S, Barchiesi D, D’Andrea C, Toma A, Guillot N, Fabrizio E D, Fazio B, Maragó O M, Gucciardi P G, de la Chapelle M L 2014 J. Phys. Chem. C 118 3209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Khurgin J B, Tsai W Y, Tsai D P, Sun G 2017 ACS Photonics 4 2871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kanipe K N, Chidester P P F, Stucky G D, Meinhart C D, Moskovits M 2017 J. Phys. Chem. C 121 14269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Khoury C G, Norton S J, Vo-Dinh T 2009 ACS Nano 3 2776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tserkezis C, Wubs M, Mortensen N A 2018 ACS Photonics 5 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li G L, Chen H X, Ding J J 2020 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 35 2150203
[17] Deepak K S, Adrian A, Julien B, Gérard C D F, Kumar P G V, Alexandre B 2020 Phys. Rev. B 102 115414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Alexandre A, Dang Y L, Stefan A. M, Pendry J B 2011 ACS Nano 5 3293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bai F, Li M C, Fu P F, Li R K, Gu T S, Huang R, Chen Z, Jiang B, Li Y F 2015 APL Materials 3 056101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pinchuk A, Kreibig U 2003 New J. Phys. 5 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tamitake I, Yuko S Y, Yasutaka K, Jeyadevan B 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 115441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Park S M, Lee K S, Kim J H, Yeon G J, Shin H H, Park S, Kim Z H 2020 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11 9313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Beverly Z P, Dmitri D T, Akira K, Ludwig B 1998 J. Phys. Chem. B 102 752
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 6 不同结构Ag四聚体共振吸收谱 (a) 未旋转圆柱形四聚体与棱柱形四聚体; (b) 未旋转C3Q1, C2Q2-Ⅰ, C2Q2-Ⅱ, C1Q3四聚体; (c) C3Q1, C2Q2-Ⅰ, C2Q2-Ⅱ结构中棱柱纳米线旋转15°四聚体; (d) C1Q3-up, C1Q3-down, Q4结构中棱柱纳米线旋转15°四聚体
Fig. 6. Resonance absorption spectra of Ag tetramers with different structures: (a) Unrotated cylindrical tetramers and prismatic tetramers; (b) unrotated C3Q1, C2Q2-Ⅰ, C2Q2-Ⅱ, C1Q3tetramer; (c) prism nanowires rotated 15° in C3Q1, C2Q2-Ⅰ, C2Q2-Ⅱ structure; (d) prism nanowires rotated 15° in C1Q3-up, C1Q3-down, Q4 structure.
-
[1] Bachelier G, Russier A I, Benichou E, Jonin C, Del F N, Valle'e F, Brevet P F 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 19740
[2] 洪昕, 杜丹丹, 裘祖荣, 张国雄 2007 56 7219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hong X, Du D D, Qiu Z R, Zhang G Q 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 7219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xia M, Zhang P, Qiao K, Bai Y, Xie Y H 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 527
[4] Cathcart N, Chen J I L, Kitaev V 2018 Langmuir 34 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bingham J M, Willets K A, Shah N C, Andrews D Q, Van Duyne R P 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C 113 16839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sherry L J, Chang S H, Schatz G C, Duyne R P V, Wiley B J, Xia Y N 2005 Nano Lett. 5 2034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 徐天宁, 李翔, 贾文旺, 隋成华, 吴惠桢 2015 64 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu T N, Li X, Jia W W, Sui C H, Wu H Z 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 245201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hou H, Chen L M, He H L, Chen L Z, Zhao Z L, Jin Y D 2015 J. Mater. Chem. B 3 5189
[9] Mahmud S, Satter S S, Singh A K, Rahman M M, Mollah M Y A, Hasan Susan M A B 2019 ACS Omega 4 18061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fernandez-Domınguez A I, Wiener A, García-Vidal F J, Maier S A, Pendry J B 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 106802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kessentini S, Barchiesi D, D’Andrea C, Toma A, Guillot N, Fabrizio E D, Fazio B, Maragó O M, Gucciardi P G, de la Chapelle M L 2014 J. Phys. Chem. C 118 3209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Khurgin J B, Tsai W Y, Tsai D P, Sun G 2017 ACS Photonics 4 2871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kanipe K N, Chidester P P F, Stucky G D, Meinhart C D, Moskovits M 2017 J. Phys. Chem. C 121 14269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Khoury C G, Norton S J, Vo-Dinh T 2009 ACS Nano 3 2776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tserkezis C, Wubs M, Mortensen N A 2018 ACS Photonics 5 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li G L, Chen H X, Ding J J 2020 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 35 2150203
[17] Deepak K S, Adrian A, Julien B, Gérard C D F, Kumar P G V, Alexandre B 2020 Phys. Rev. B 102 115414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Alexandre A, Dang Y L, Stefan A. M, Pendry J B 2011 ACS Nano 5 3293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bai F, Li M C, Fu P F, Li R K, Gu T S, Huang R, Chen Z, Jiang B, Li Y F 2015 APL Materials 3 056101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pinchuk A, Kreibig U 2003 New J. Phys. 5 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tamitake I, Yuko S Y, Yasutaka K, Jeyadevan B 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 115441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Park S M, Lee K S, Kim J H, Yeon G J, Shin H H, Park S, Kim Z H 2020 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11 9313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Beverly Z P, Dmitri D T, Akira K, Ludwig B 1998 J. Phys. Chem. B 102 752
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8087
- PDF下载量: 100
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: