-
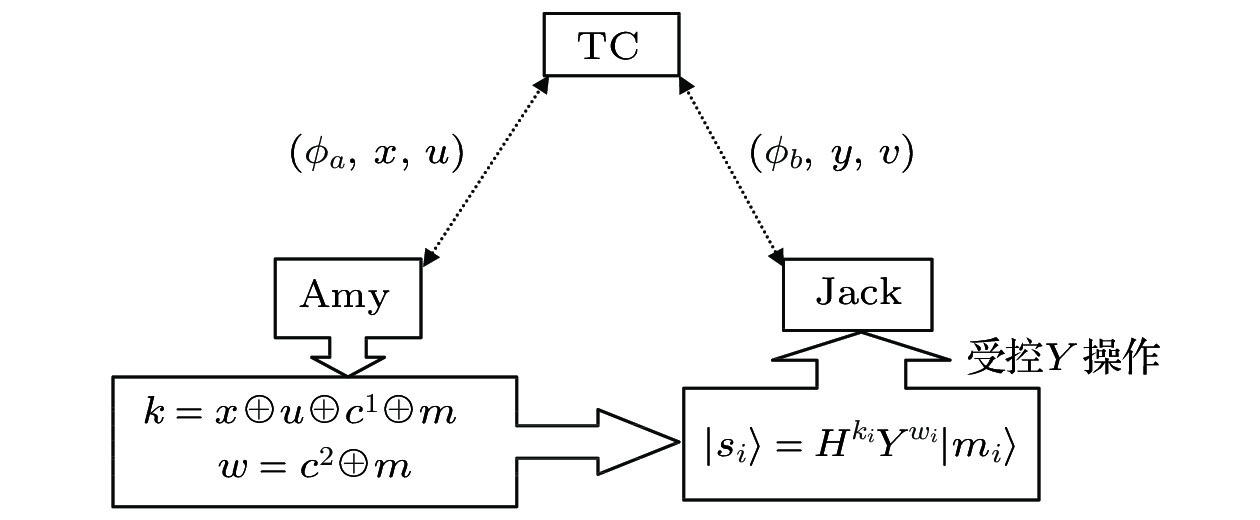
多数传统的指定验证者签名方案无法抵抗量子计算机的攻击. 本文给出一种具有强安全性的指定验证者量子签名方案. 在方案中, 参与方利用量子密钥分配协议和量子直接通信协议共享密钥. 密钥生成中心制备Bell态序列并将其分配给签名者和指定验证者. 签名者利用其密钥和受控量子态对消息进行签名. 同时, 指定的验证者可以利用对称的签名步骤对量子签名进行仿真. 而验证者仿真的量子签名与签名者产生的量子签名完全一样. 这使得量子签名具有不可传递的属性. 本文所给出的签名方案可以抵抗伪造攻击, 截获重放攻击和木马攻击. 并且, 其理论上的信息安全属性可以得到证明. 同时, 密钥生成中心无需完全可信. 方案无需使用量子单向函数. 当产生量子签名时, 签名者无需制备纠缠态序列. 当验证签名时, 验证者无需执行量子态比较算法. 方案的量子比特效率达到100%. 因此, 与类似方案相比, 本文所给的方案具有较好的安全性和效率.Most of the classical designated verifier signature schemes are insecure against quantum adversary. In this paper, a quantum signature scheme for the designated verifier is proposed. In our scheme, during the initialization phase, the partners share secret keys by performing the quantum key distribution protocol. On the other hand, by performing the quantum direct communication protocol, the key generator center shares secret keys with the signer and the designated verifier, respectively. The key generator center generates a particle sequence of Bell state and distributes the particles between the signer and the designated verifier. During the signature generation phase, the signer encrypts the particle sequence by the secret keys and Hardmard operators. After that, the signer performs the controlled unitary operations on the encrypted particle sequence so as to generate the quantum signature. The designated verifier can simulate the quantum signature by performing the same symmetric signing steps as that performed by the original signer. Hence, the quantum signature signed by the true signer is the same as the one simulated by the receiver, which makes our scheme possess the designated properties. During the signature verification phase, the designated verifier performs the controlled unitary operations on the quantum signature and obtains the quantum ciphertexts. After that, the designated verifier decrypts the quantum ciphertexts by the symmetric secret keys and Hardmard operators so that the quantum signature can be verified. Our signature is secure against forgery attack, inter-resending attacks and Trojan horse attack. Because the trace distance between the density operators of different quantum signatures is zero, the information-theoretical security of our quantum signature scheme can be proved. The unconditionally secure quantum key distribution protocol and the one-time pad encryption algorithm can guarantee the security of the secret keys shared by the partners. What is more, the security assumption about the key generation center is weak. That is, it is not necessary to assume that the key generation center should be fully trusted. On the other hand, in our scheme, the quantum one-way function is not used. To generate a quantum signature, the signer need not prepare for entangled particle sequence. To verify a quantum signature, the verifier need not apply any state comparison to the received particles. The qubit efficiency is 100%. Therefore, our scheme has the advantages in the security and efficiency over the other quantum signature schemes for the designated verifier.
-
Keywords:
- quantum signature /
- security /
- Bell state /
- non-transferability
[1] Diffie W, Hellmann M 1976 IEEE IT 22 644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Saeednia S, Kremer S, Markowitch O 2003 Information Security and Cryptology-ICISC Seoul, Korea, November 27–28, 2003 p40
[3] Ray I, Narasimhamurthi N 2001 Proceedings of the 3rd international workshop on advanced issues of E-commerce and web-based information systems San Juan, CA, USA, June 21–22, 2001 p188
[4] Schoenmakers B 1999 Advances in CRYPTO’99 Santa Barbara, California, USA, August 15–19, 1999 p148
[5] Huang X, Mu Y, Susilo W, Wu W 2007 Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Pairing-Based Cryptography, Pairing 2007 Tokyo, Japan, July 2–4, 2007 p367
[6] Wang B, Song Z 2009 Inf. Sci. 179 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jakobsson M, Sako K, Impagliazzo R 1996 Advances in Cryptology-Eurocrypt 1996 Santa Barbara, California, USA, August 18–22, 1996 p142
[8] Kang B, Boyd C, Dawson E 2009 J. Syst. Software 82 270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lee J, Chang J, Lee D 2010 Comput. Electr. Eng. 36 948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hafizul I S, Biswas G P 2015 Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40 1069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rastegari P, Susilo W, Dakhilalian M 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 18 619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shor P W 1997 SIAM J. Comput. 26 1484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gottesman D, Chuang I 2001 arxiv: quant-ph/0105032 v2
[14] Zeng G H, Keitel C H 2002 Phys. Rev. A. 65 042312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang Y G, Lei H, Liu Z C, Zhou Y H, Shi W M 2016 Quantum Inf. Process. 15 2487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang Y G, Zhou Z, Teng Y W, Wen Q Y 2010 Eur. Phys. J. D 61 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xin X, He Q, Wang Z, Yang Q, Li F 2019 Optik 189 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang M Q, Wang X, Zhan T 2018 Quantum Inf. Process. 17 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xin X, Wang Z, Yang Q 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 7346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang D H, Xu Y L, Xu G B 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ma H, Li F, Mao N, Guo Y 2017 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56 2551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang J L, Zhang J Z, Xie S C 2018 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57 1612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zeng G, Lee M, Guo Y, He G 2007 Int. J. Quantum Inf. 5 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo Y, Feng Y 2016 Int. J. Quantum Inf. 55 2290
[25] Shi W M, Zhou Y H, Yang Y G 2015 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54 3115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shi W M, Wang Y M, Zhou Y H, Yang Y G, Zhang J B 2018 Optik 164 753
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Menezes A J, Oorschot P V, Vanstone S A 1996 Handbook of Applied Cryptography (Boca Raton: CRC Press) p41
[28] Yang L, Yang B, Pan J 2012 SPIE Photonics Europe Belgium, April 16–19, 2012 p8440E1
[29] Yang L, Xiang C, Li B 2013 Chin. Commun. 10 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Xin X, Wang Z, Yang Q, Li F 2020 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59 918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Shannon C E 1949 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 28 656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Bennett C H, Brassard G 2014 Theor. Comput. Sci. 560 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Long G L, Liu X S 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 2302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hu Y G 2018 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57 2831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Yan L, Sun Y, Chang Y, Zhang S, Wan G, Sheng Z 2018 Quantum Inf. Process. 17 315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Deng F G, Long G L, Liu X S 2003 Phys. Rev. A 68 042317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Gottesman D, Lo H K, Lütkenhaus N, Preskill J 2004 Quantum Inf. Comput. 4 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Hwang W Y 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 057901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Lo H K, Ma X, Chen K 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 230504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Wang X B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 230503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Lu H, Fung C H F, Ma X, Cai Q 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 042344
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Fung C H F, Ma X, Chau H F, Cai Q 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 032308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Beaudry N J, Lucamarini M, Mancini S, Renner R 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 062302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Hwang T, Lee K C 2007 IET Inf. Secur. 1 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Shi W M, Zhou Y H, Yang U G 2015 International Journal of Theoretical Physics volume 54 3115
[46] 宋云 2019 电子学报 47 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Y 2019 Acta Electr. Sin. 47 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 安全与效率比较
Table 1. Comparisons of security and efficiency.
-
[1] Diffie W, Hellmann M 1976 IEEE IT 22 644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Saeednia S, Kremer S, Markowitch O 2003 Information Security and Cryptology-ICISC Seoul, Korea, November 27–28, 2003 p40
[3] Ray I, Narasimhamurthi N 2001 Proceedings of the 3rd international workshop on advanced issues of E-commerce and web-based information systems San Juan, CA, USA, June 21–22, 2001 p188
[4] Schoenmakers B 1999 Advances in CRYPTO’99 Santa Barbara, California, USA, August 15–19, 1999 p148
[5] Huang X, Mu Y, Susilo W, Wu W 2007 Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Pairing-Based Cryptography, Pairing 2007 Tokyo, Japan, July 2–4, 2007 p367
[6] Wang B, Song Z 2009 Inf. Sci. 179 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jakobsson M, Sako K, Impagliazzo R 1996 Advances in Cryptology-Eurocrypt 1996 Santa Barbara, California, USA, August 18–22, 1996 p142
[8] Kang B, Boyd C, Dawson E 2009 J. Syst. Software 82 270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lee J, Chang J, Lee D 2010 Comput. Electr. Eng. 36 948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hafizul I S, Biswas G P 2015 Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40 1069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rastegari P, Susilo W, Dakhilalian M 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 18 619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shor P W 1997 SIAM J. Comput. 26 1484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gottesman D, Chuang I 2001 arxiv: quant-ph/0105032 v2
[14] Zeng G H, Keitel C H 2002 Phys. Rev. A. 65 042312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang Y G, Lei H, Liu Z C, Zhou Y H, Shi W M 2016 Quantum Inf. Process. 15 2487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang Y G, Zhou Z, Teng Y W, Wen Q Y 2010 Eur. Phys. J. D 61 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xin X, He Q, Wang Z, Yang Q, Li F 2019 Optik 189 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang M Q, Wang X, Zhan T 2018 Quantum Inf. Process. 17 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xin X, Wang Z, Yang Q 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 7346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang D H, Xu Y L, Xu G B 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ma H, Li F, Mao N, Guo Y 2017 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56 2551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang J L, Zhang J Z, Xie S C 2018 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57 1612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zeng G, Lee M, Guo Y, He G 2007 Int. J. Quantum Inf. 5 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo Y, Feng Y 2016 Int. J. Quantum Inf. 55 2290
[25] Shi W M, Zhou Y H, Yang Y G 2015 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54 3115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shi W M, Wang Y M, Zhou Y H, Yang Y G, Zhang J B 2018 Optik 164 753
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Menezes A J, Oorschot P V, Vanstone S A 1996 Handbook of Applied Cryptography (Boca Raton: CRC Press) p41
[28] Yang L, Yang B, Pan J 2012 SPIE Photonics Europe Belgium, April 16–19, 2012 p8440E1
[29] Yang L, Xiang C, Li B 2013 Chin. Commun. 10 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Xin X, Wang Z, Yang Q, Li F 2020 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59 918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Shannon C E 1949 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 28 656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Bennett C H, Brassard G 2014 Theor. Comput. Sci. 560 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Long G L, Liu X S 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 2302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hu Y G 2018 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57 2831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Yan L, Sun Y, Chang Y, Zhang S, Wan G, Sheng Z 2018 Quantum Inf. Process. 17 315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Deng F G, Long G L, Liu X S 2003 Phys. Rev. A 68 042317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Gottesman D, Lo H K, Lütkenhaus N, Preskill J 2004 Quantum Inf. Comput. 4 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Hwang W Y 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 057901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Lo H K, Ma X, Chen K 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 230504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Wang X B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 230503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Lu H, Fung C H F, Ma X, Cai Q 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 042344
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Fung C H F, Ma X, Chau H F, Cai Q 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 032308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Beaudry N J, Lucamarini M, Mancini S, Renner R 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 062302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Hwang T, Lee K C 2007 IET Inf. Secur. 1 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Shi W M, Zhou Y H, Yang U G 2015 International Journal of Theoretical Physics volume 54 3115
[46] 宋云 2019 电子学报 47 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Y 2019 Acta Electr. Sin. 47 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8383
- PDF下载量: 90
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载:
