-
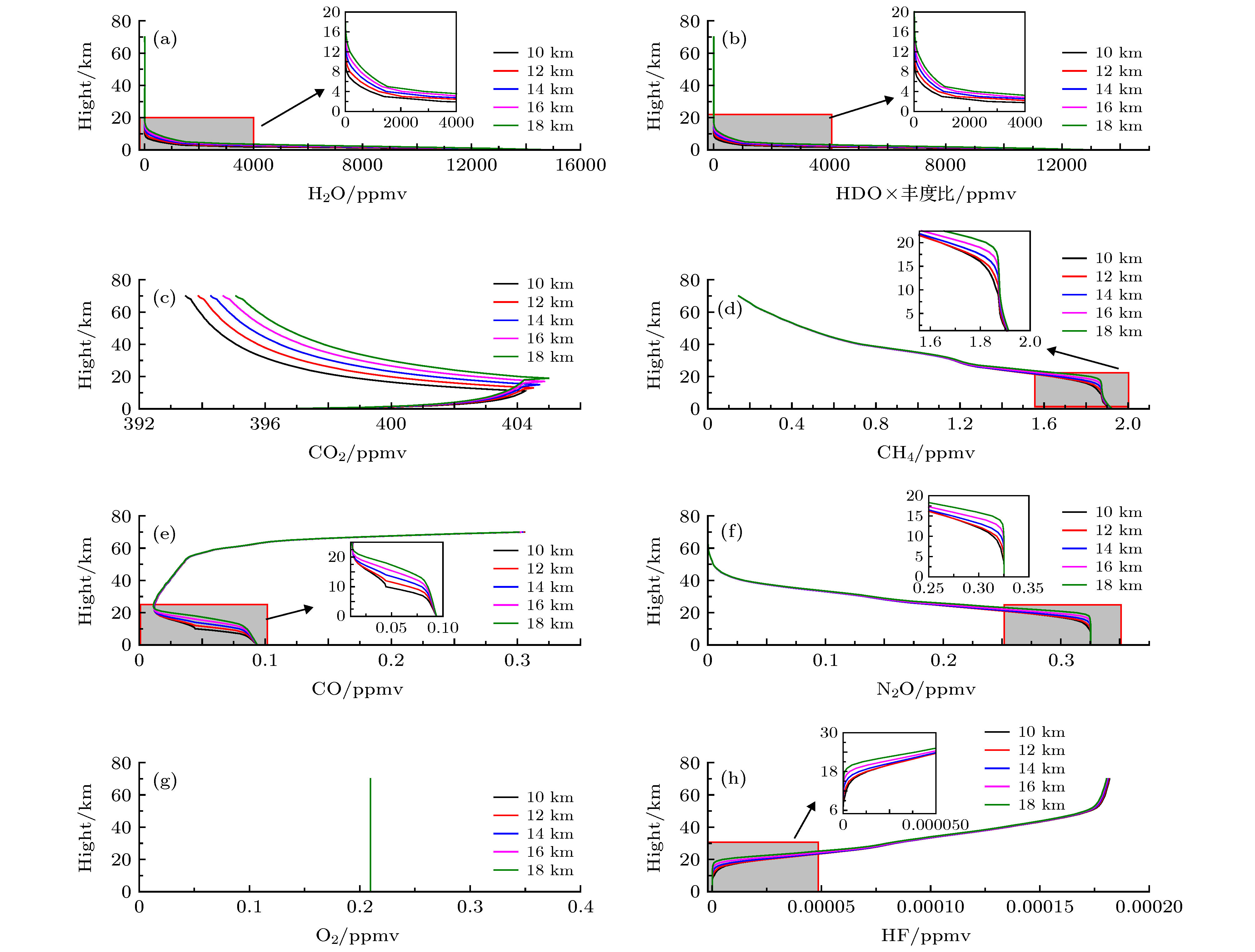
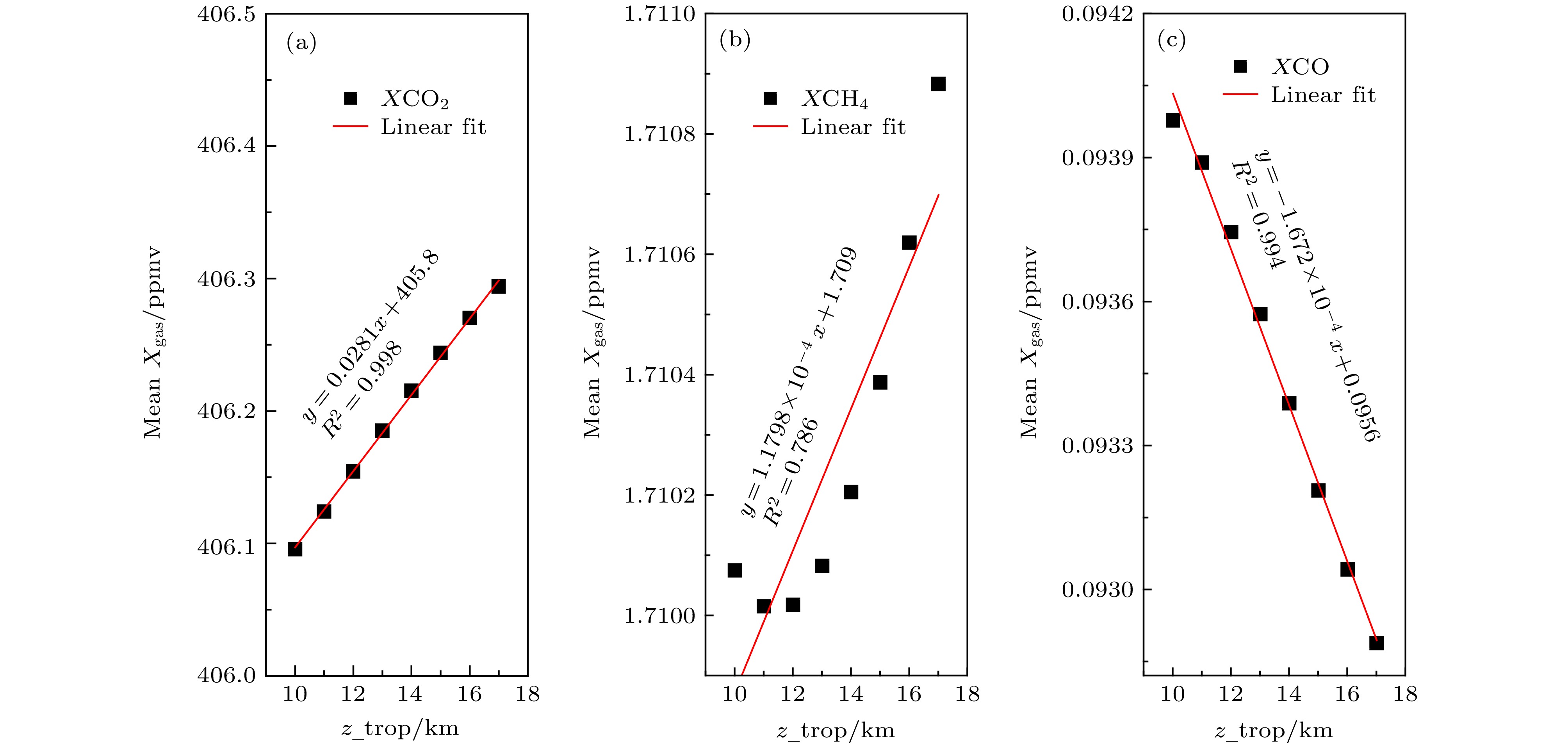
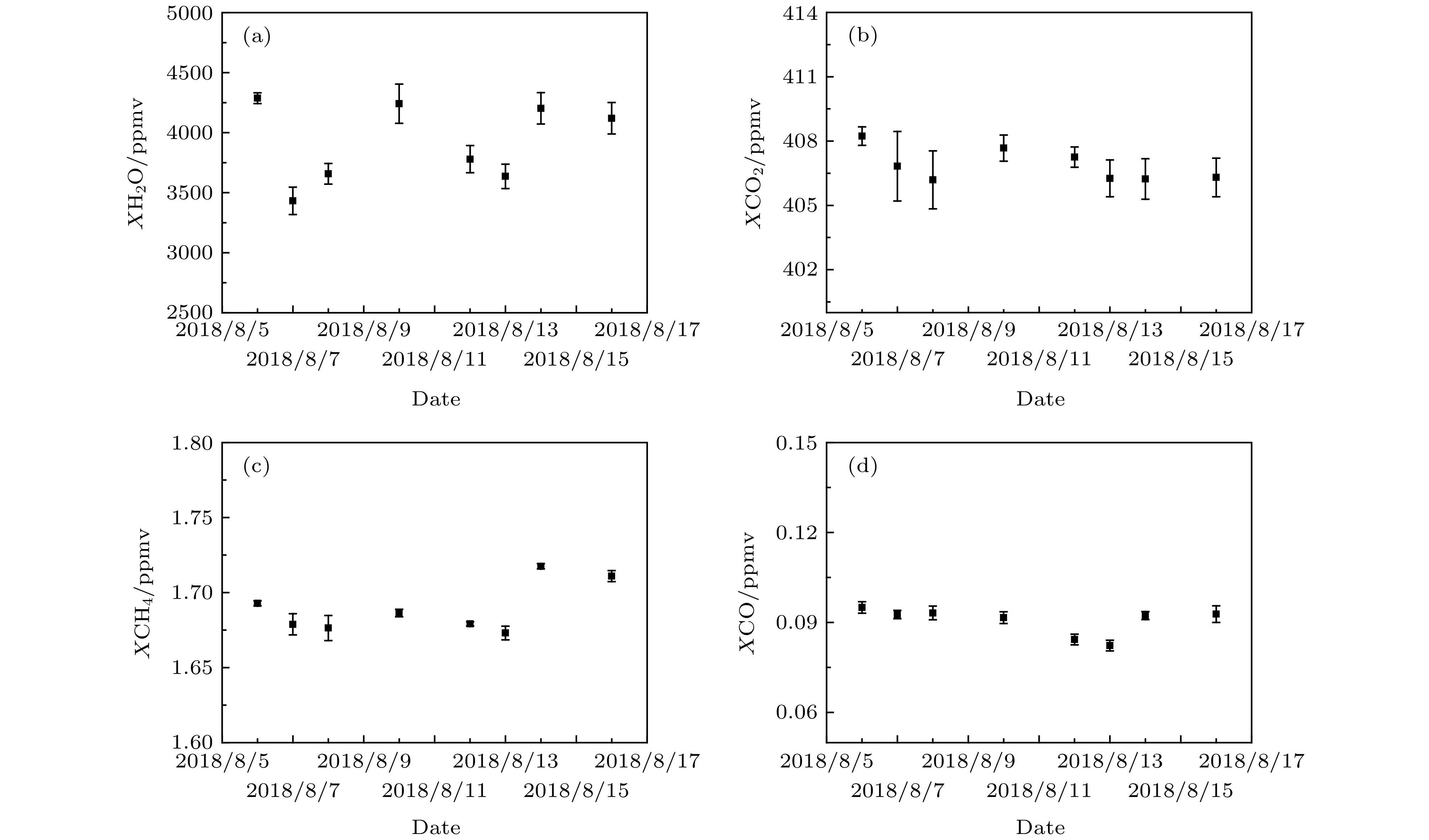
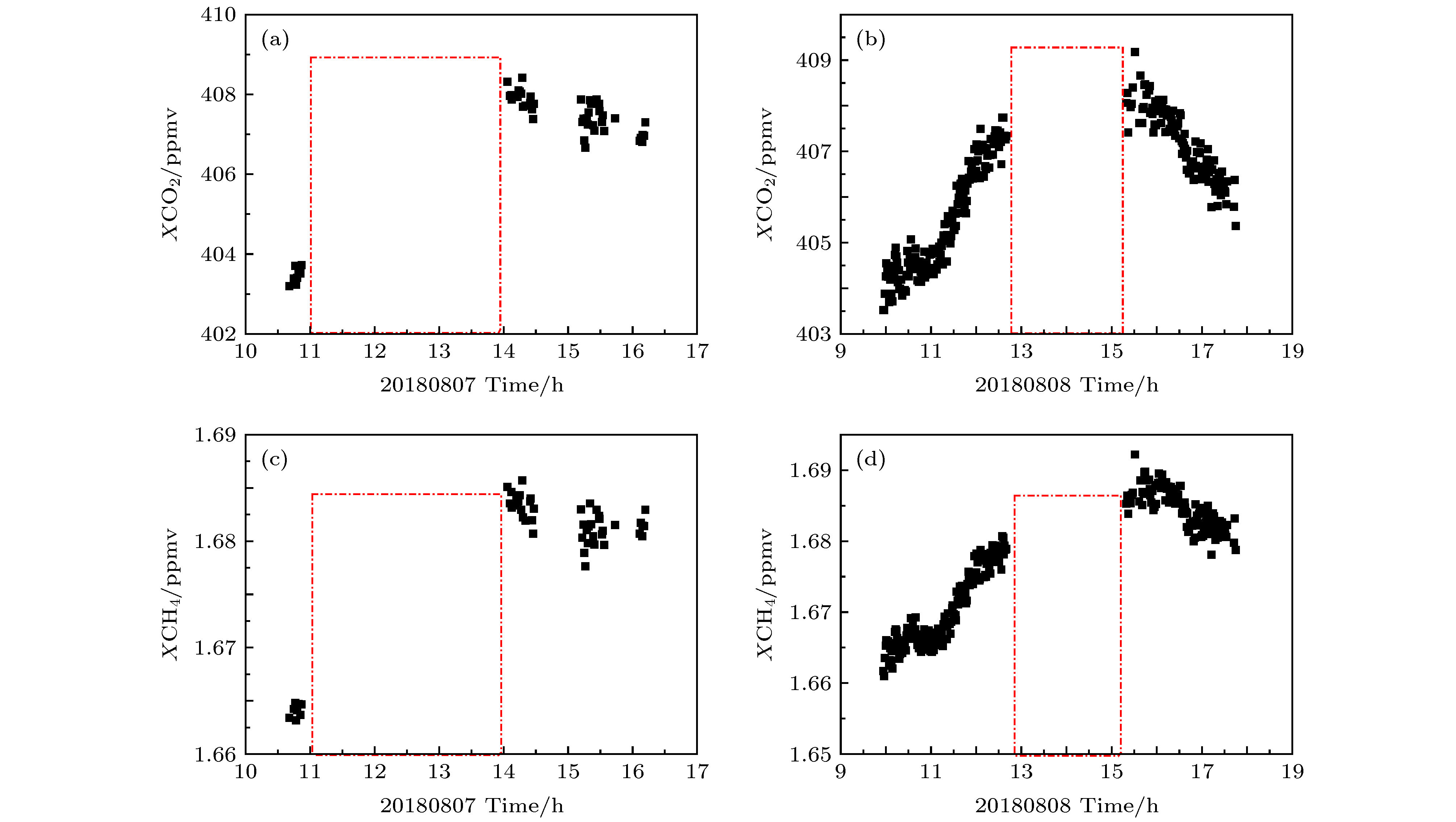
对流层顶作为对流层和平流层之间的过渡层, 对大气痕量气体浓度反演有非常重要的影响. 理论分析对流层顶高对大气分子含量垂直分布的影响, 并结合2018年8月(6—16日)拉萨观测数据, 定量分析对流层顶高的变化对气体柱-平均摩尔分数Xgas反演的影响. 结果表明: 对流层顶高的变化改变气体分子的垂直分布, XCO2, XCH4与对流层顶高度变化呈正相关, 相关系数分别为0.998和0.780; XCO与对流层顶高度变化呈负相关, 相关系数为0.994; 而XH2O与对流层顶高度变化的相关性非常小. 对流层顶高变化3 km, XCO2, XCH4及XCO误差范围在8.640%, 0.035%及0.049%以内. 观测期间, XH2O, XCO2, XCH4及XCO日平均值分别在3432—4287, 406.1~408.2, 1.673—1.720及0.082—0.095 ppmv之间变化. 观测数据显示, 该地区CO2, CH4气体柱-平均摩尔分数日变化趋势相似, XCO2与XCH4的相关系数大部分高于0.5. 观测结果可为我国研究高原温带地区温室气体浓度的时空分布及其变化规律提供参考和第一手的直接观测数据.The tropopause, as a transition layer between the troposphere and the stratosphere, has a significant influence on the inversion of trace gas concentration. Theoretical analysis of the influence of tropopause on the vertical distribution of atmospheric molecular content, combined with Lhasa observation data, is presented, and the quantitative analysis of the influence of tropopause on the inversion of column-averaged dry air mole fractions (DMFs) is given as well. The comparison results show that the tropopause height has a great influence on the inversion results. First, its height variation has a little effect on XH2O, but it has a great influence on XCO2, XCH4 and XCO. The XCO2 and XCH4 have positive correlation with tropopause height variation, but for XCO, negative correlation with the tropopause height variation is observed. The correlation coefficient of XCO2, XCH4 and XCO are 0.998, 0.78 and 0.994, respectively. When the tropopause height is varied by 3 km, XCO2, XCH4 and XCO are varied by 8.64%、0.0354% and 0.0488%, respectively. The column-averaged dry air mole water vapor, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and methane in Lhasa are observed based on ground-based Fourier transform infrared spectrometer EM27/SUN. The time series of XH2O, XCO2, XCH4 and XCO in a period from August 6 to August 16, 2018 in Lhasa were obtained. The main achievements are as follows. In the observation period, the daily average value of XH2O, XCO2, XCH4 and XCO vary between 3432 and 4287 ppmv, 406.1 and 408.2 ppmv, 1.673 and 1.720 ppmv, and 0.082 and 0.095 ppmv, respectively. The average value of XH2O, XCO2, XCH4 and XCO are 3919.70, 406.887, 1.689, and 0.091 ppmv, res[ectively. Comparison between XCO2 and XCH4 time series shows that XCO2 and XCH4 time series have similar daily trends, the correlation coefficient between XCO2 and XCH4 time serires is higher than 0.5. In particular, the correlation coefficient reached about 0.86 on August 7, 8, 13, 2018. High correlation coefficient indicates that CO2 and CH4 molecules come from the same source. Compared with the WACCM simulation values, the XCO2 and XCH4 of the ground-based observations are small. The observation results can provide reference and first-hand direct observation data for the study of the temporal and spatial distribution of greenhouse gases in the temperate zone of the plateau in China.
-
Keywords:
- Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy /
- greenhouse gases /
- column-averaged dry air mole fractions /
- tropopause
[1] 王鑫, 吕达仁 2007 自然科学进展 17 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Lu D R 2007 Prog. Nat. Sci. 17 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 洪健昌, 郭建平, 杜军, 王鹏祥 2016 气象学报 74 827
Hong J C, Guo J P, Du J, Wang P X 2016 Acta Meteorol. Sin. 74 827
[3] 周顺武, 杨双艳, 张人禾, 马振峰 2010 大气科学学报 33 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou S W, Yang S Y, Zhang R H, Ma Z F 2010 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 33 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 田红瑛, 田文寿, 雒佳丽, 张杰, 杨琴, 黄倩 2014 高原气象 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian H Y, Tian W S, Luo J L, Zhang J, Yang Q, Huang Q 2014 Plateau Meteorol. 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王敏仲, 魏文寿, 何清, 杨莲梅, 程玉景 2012 高原气象 31 1203
Wang M Z, Wei W S, He Q, Yang L M, Cheng Y J 2012 Plateau Meteorol. 31 1203
[6] 杨双艳, 周顺武, 张人禾, 吴萍, 李慧, 马振峰 2012 大气科学学报 35 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang S Y, Zhou S W, Zhang R H, Wu P, Li H, Ma Z F 2012 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 35 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 周秀骥, 李维亮, 陈隆勋, 刘煜 2004 气象学报 62 513
Zhou X J, Li W L, Chen L X, Liu Y 2004 Acta Meteorol. Sin. 62 513
[8] 薛志航, 邓创, 孙一 2018 成都信息工程大学学报 33 464
Xue Z H, Deng C, Sun Y 2018 J. Chengdu Univ. Inf. Technol. 33 464
[9] Guo D, Su Y C, Shi C H, Xu J J, Powell A M 2015 J. Atmos Sol. Terr. Phys. 130 127
[10] Wunch D, Toon G C, Wennberg P O 2010 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 8 2
[11] Hase F, Hannigan J W, Coffey M T, Goldman A, Hopfner M, Jones N B, Rinsland C P, Wood S W 2004 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 87 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 单昌功, 王薇, 刘诚, 徐兴伟, 孙友文, 田园, 刘文清 2017 66 220204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shan C G, Wang W, Liu C, Xu X W, Sun Y W, Tian Y, Liu W Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 220204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 田园, 孙友文, 谢品华, 刘诚, 刘文清, 刘建国, 李昂, 胡仁志, 王薇, 曾议 2015 64 070704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian Y, Sun Y W, Xie P H, Liu C, Liu W Q, Liu J G, Li A, Hu R Z, Wang W, Zeng Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 070704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 单昌功, 刘诚, 王薇, 孙友文, 刘文清, 田园, 杨维 2017 光谱学与光谱分析 37 1997
Shan C G, Liu C, Wang W, Sun Y W, Liu W Q, Tian Y, Yang W 2017 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 37 1997
[15] Kiel M, Hase F, Blumenstock T, Kirner O 2016 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 9 2223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hase F, Frey M, Blumenstock T, Groß J, Kiel M, Mengistu Tsidu G, Schäfer K, Sha M K, Orphal J 2015 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 8 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wunch D, Toon G C, Wennberg P Q, et al. 2010 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 3 1351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Frey M, Hase F, Blumenstock T, Gross J, Kiel M, Tsidu G M, Schafer K, Sha M K, Orphal J 2015 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 8 3047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hase F, Drouin B J, Roehl C M, et al. 2013 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 6 3527
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou Min Q, Langerock B, Wells K C, et al. 2019 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 12 1393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 反演波段
Table 1. Inversion band.
气体种类 反演波段 干扰分子 H2O 8353.4—8463.1 CH4 CO2 6173.0—6390.0 H2O, HDO, CH4 CH4 5897.0—6145.0 H2O CO 4208.7—4318.8 CH4, H2O, HDO O2 7765.0—8005.0 H2O, HF, CO2 -
[1] 王鑫, 吕达仁 2007 自然科学进展 17 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Lu D R 2007 Prog. Nat. Sci. 17 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 洪健昌, 郭建平, 杜军, 王鹏祥 2016 气象学报 74 827
Hong J C, Guo J P, Du J, Wang P X 2016 Acta Meteorol. Sin. 74 827
[3] 周顺武, 杨双艳, 张人禾, 马振峰 2010 大气科学学报 33 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou S W, Yang S Y, Zhang R H, Ma Z F 2010 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 33 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 田红瑛, 田文寿, 雒佳丽, 张杰, 杨琴, 黄倩 2014 高原气象 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian H Y, Tian W S, Luo J L, Zhang J, Yang Q, Huang Q 2014 Plateau Meteorol. 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王敏仲, 魏文寿, 何清, 杨莲梅, 程玉景 2012 高原气象 31 1203
Wang M Z, Wei W S, He Q, Yang L M, Cheng Y J 2012 Plateau Meteorol. 31 1203
[6] 杨双艳, 周顺武, 张人禾, 吴萍, 李慧, 马振峰 2012 大气科学学报 35 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang S Y, Zhou S W, Zhang R H, Wu P, Li H, Ma Z F 2012 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 35 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 周秀骥, 李维亮, 陈隆勋, 刘煜 2004 气象学报 62 513
Zhou X J, Li W L, Chen L X, Liu Y 2004 Acta Meteorol. Sin. 62 513
[8] 薛志航, 邓创, 孙一 2018 成都信息工程大学学报 33 464
Xue Z H, Deng C, Sun Y 2018 J. Chengdu Univ. Inf. Technol. 33 464
[9] Guo D, Su Y C, Shi C H, Xu J J, Powell A M 2015 J. Atmos Sol. Terr. Phys. 130 127
[10] Wunch D, Toon G C, Wennberg P O 2010 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 8 2
[11] Hase F, Hannigan J W, Coffey M T, Goldman A, Hopfner M, Jones N B, Rinsland C P, Wood S W 2004 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 87 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 单昌功, 王薇, 刘诚, 徐兴伟, 孙友文, 田园, 刘文清 2017 66 220204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shan C G, Wang W, Liu C, Xu X W, Sun Y W, Tian Y, Liu W Q 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 220204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 田园, 孙友文, 谢品华, 刘诚, 刘文清, 刘建国, 李昂, 胡仁志, 王薇, 曾议 2015 64 070704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian Y, Sun Y W, Xie P H, Liu C, Liu W Q, Liu J G, Li A, Hu R Z, Wang W, Zeng Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 070704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 单昌功, 刘诚, 王薇, 孙友文, 刘文清, 田园, 杨维 2017 光谱学与光谱分析 37 1997
Shan C G, Liu C, Wang W, Sun Y W, Liu W Q, Tian Y, Yang W 2017 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 37 1997
[15] Kiel M, Hase F, Blumenstock T, Kirner O 2016 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 9 2223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hase F, Frey M, Blumenstock T, Groß J, Kiel M, Mengistu Tsidu G, Schäfer K, Sha M K, Orphal J 2015 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 8 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wunch D, Toon G C, Wennberg P Q, et al. 2010 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 3 1351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Frey M, Hase F, Blumenstock T, Gross J, Kiel M, Tsidu G M, Schafer K, Sha M K, Orphal J 2015 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 8 3047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hase F, Drouin B J, Roehl C M, et al. 2013 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 6 3527
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou Min Q, Langerock B, Wells K C, et al. 2019 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 12 1393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8429
- PDF下载量: 78
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: