-
扫描隧道显微镜(scanning tunneling microscope, STM)针尖与衬底形成的等离激元腔系统因其可以突破衍射极限将电磁场增强上百倍并局域在纳米甚至亚纳米尺度而备受关注. 扫描隧道显微镜针尖与衬底形成的等离激元腔系统可以作为研究超快尺度下超辐射现象的先进平台. 本文应用宏观量子电动力学与开放量子系统理论, 探讨了不同几何构形的亚甲基蓝分子团簇在特定扫描隧道显微镜纳米腔和皮米腔下的辐射动力学. 在扫描隧道显微镜纳米腔中, 允许在多种分子团簇构形和激发波长下实现超辐射. 而扫描隧道显微镜皮米腔对产生超辐射的分子团簇构形较为严格, 具有较高排列对称性的分子团簇更容易产生超辐射现象, 且对激发波长的变化更加敏感. 此外, 相对于扫描隧道显微镜皮米腔, 在扫描隧道显微镜纳米腔中观察到的超辐射强度较低, 持续时间较长. 这些结果表明, 合理设计腔结构及分子团簇的几何构形可以有效调控超辐射现象的发生和增强, 为未来在光学和纳米技术领域的实际应用提供了新思路和方法.The plasmon cavity system composed of a scanning tunneling microscope tip and a substrate has attracted much attention due to its ability to break through the diffraction limit, enhance the electromagnetic field by hundreds of times, and localize it on a nanometer or even sub-nanometer scale. This plasmon cavity system can serve as an advanced platform for studying superradiance phenomena on an ultrafast scale. Methylene blue molecules have many applications in the field of optics due to their significant light absorption and fluorescence emission characteristics. In this work, macroscopic quantum electrodynamics and open quantum system theory are used to explore the radiation dynamics of methylene blue molecular clusters with three different configurations: cyclic, two-dimensional planar, and one-dimensional chain, in specific scanning tunneling microscope nanocavity and picocavity. Taking the cyclic molecular clusters for example, the radiation effects of different external field excitations on the molecular clusters in the cavity are studied. The research results indicate that for the same molecular cluster configuration, the scanning tunneling microscope picocavity has a more significant superradiance intensity, while the scanning tunneling microscope nanocavity has a longer duration of superradiance. From the perspective of symmetry, the one-dimensional chain molecular clusters only have axial symmetry, while the two-dimensional planar and cyclic molecular clusters have both axial symmetry and central symmetry. The cyclic molecular clusters also have multiple rotational symmetries. Therefore, within the same scanning tunneling microscope cavity, the higher the symmetry of the arrangement of molecular clusters, the easier it is to generate significant superradiance pulses. In addition, because of its higher spatial resolution and stronger local field enhancement effect, the picocavity of scanning tunneling microscope is more sensitive to changes of external conditions such as excitation wavelength. These results indicate that the occurrence and enhancement of superradiance can be effectively controlled by reasonably designing the cavity structure and geometric configuration of molecular clusters, and the time scale of superradiance pulses can be extended to the picosecond order, which provides new ideas and methods for practical applications in the fields of optics and nanotechnology in the future.
-
Keywords:
- surface plasmon /
- scanning tunneling microscope cavity /
- geometric configuration of molecular clusters /
- superradiance
[1] Binnig G, Rohrer H, Gerber Ch, Weibel E 1982 Appl. Phys. Lett. 40 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Binnig G, Rohrer H, Gerber Ch, Weibel E 1982 Phys. Rev. Lett. 49 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Gimzewski J K, Joachim C 1999 Science 283 1683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu S W, Ogawa N, Nazin G V, Ho W 2008 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 5241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen C, Chu P, Bobisch C A, Mills D L, Ho W 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 217402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang Y, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Yu Y J, Kuang Y M, Zhang L, Meng Q S, Luo Y, Yang J L, Dong Z C, Hou J G 2016 Nature 531 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Schwarz F, Wang Y F, Hofer W A, Berndt R, Runge E, Kröger J 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 119 15716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Stroscio J A, Eigler D M 1991 Science 254 1319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Benz F, Schmidt M K, Dreismann A, Chikkaraddy R, Zhang Y, Demetriadou A, Carnegie C, Ohadi H, De Nijs B, Esteban R, Aizpurua J, Baumberg J J 2016 Science 354 726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shin H H, Yeon G J, Choi H K, Park S M, Lee K S, Kim Z H 2018 Nano. Lett. 18 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lee J, Tallarida N, Chen X, Liu P, Jensen L, Apkarian V A 2017 ACS Nano 11 11466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tallarida N, Lee J, Apkarian V A 2017 ACS Nano 11 11393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dicke R H 1954 Phys. Rev. 93 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Luo Y, Chen G, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yu Y J, Kong F F, Tian X J, Zhang Y, Shan C X, Luo Y, Yang J L, Sandoghdar V, Dong Z C, Hou J G 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 233901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chikkaraddy R, De Nijs B, Benz F, Barrow S J, Scherman O A, Rosta E, Demetriadou A, Fox P, Hess O, Baumberg J J 2016 Nature 535 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bergmann K, O’Konski C T 1963 J. Phys. Chem. 67 2169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Johnson P B, Christy R W 1972 Phys. Rev. B 6 4370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yang B, Chen G, Ghafoor A, Zhang Y F, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Yang J L, Sandoghdar V, Aizpurua J, Dong Z C, Hou J G 2020 Nat. Photonics 14 693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jaculbia R B, Imada H, Miwa K, Iwasa T, Takenaka M, Yang B, Kazuma E, Hayazawa N, Taketsugu T, Kim Y 2020 Nat. Nanotechnol. 15 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Scheel S, Buhmann S Y 2008 Acta Phys. Slovaca 58 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Rivera N, Kaminer I 2020 Nat. Rev. Phys. 2 538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Scully M O, Zubairy M S 1997 Quantum Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp460–486
[23] Steck D A http://steck.us/teaching [2020-9-24]
[24] Plankensteiner D, Hotter C, Ritsch H 2022 Quantum 6 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Asenjo-Garcia A, Moreno-Cardoner M, Albrecht A, Kimble H J, Chang D E 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 031024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gross M, Haroche S 1982 Phys. Rep. 93 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kasha M 1963 Radiat. Res. 20 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Spano F C, Silva C 2014 Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 65 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
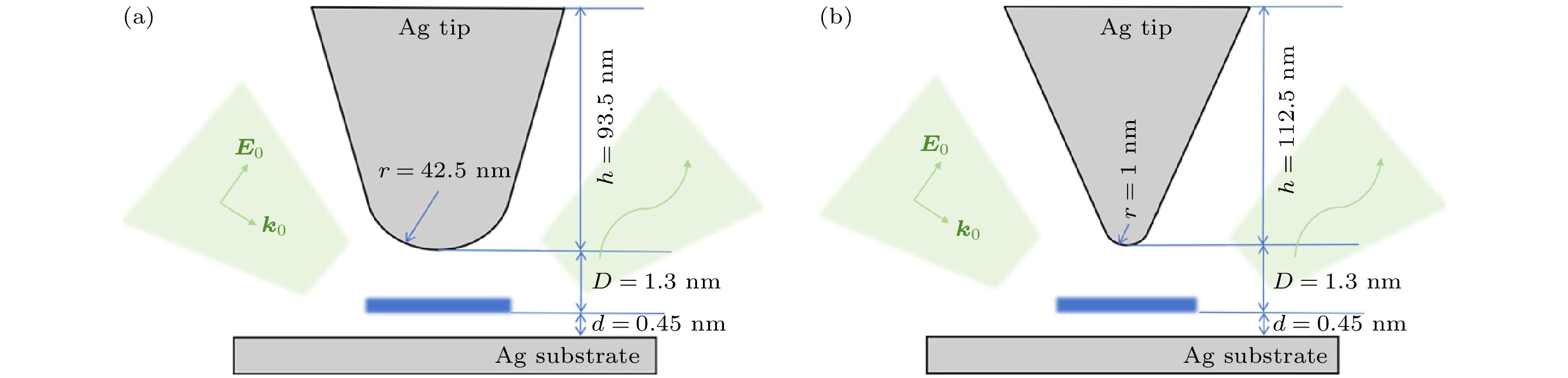
图 1 (a) 针尖尖端半径为42.5 nm, 高度为93.5 nm的银针尖与银衬底形成的STM纳米腔; (b) 针尖尖端半径为1 nm, 高度为112.5 nm的银针尖与银衬底形成的STM皮米腔, 其中腔中的蓝色区域表示不同构形的亚甲基蓝分子团簇
Fig. 1. (a) An STM nanocavity formed by a silver needle tip with a radius of 42.5 nm and a height of 93.5 nm with a silver substrate; (b) an STM picocavity formed by a silver needle tip with a radius of 1 nm and a height of 112.5 nm with a silver substrate, the blue areas in the cavity are clusters of methylene blue molecules of different configurations.
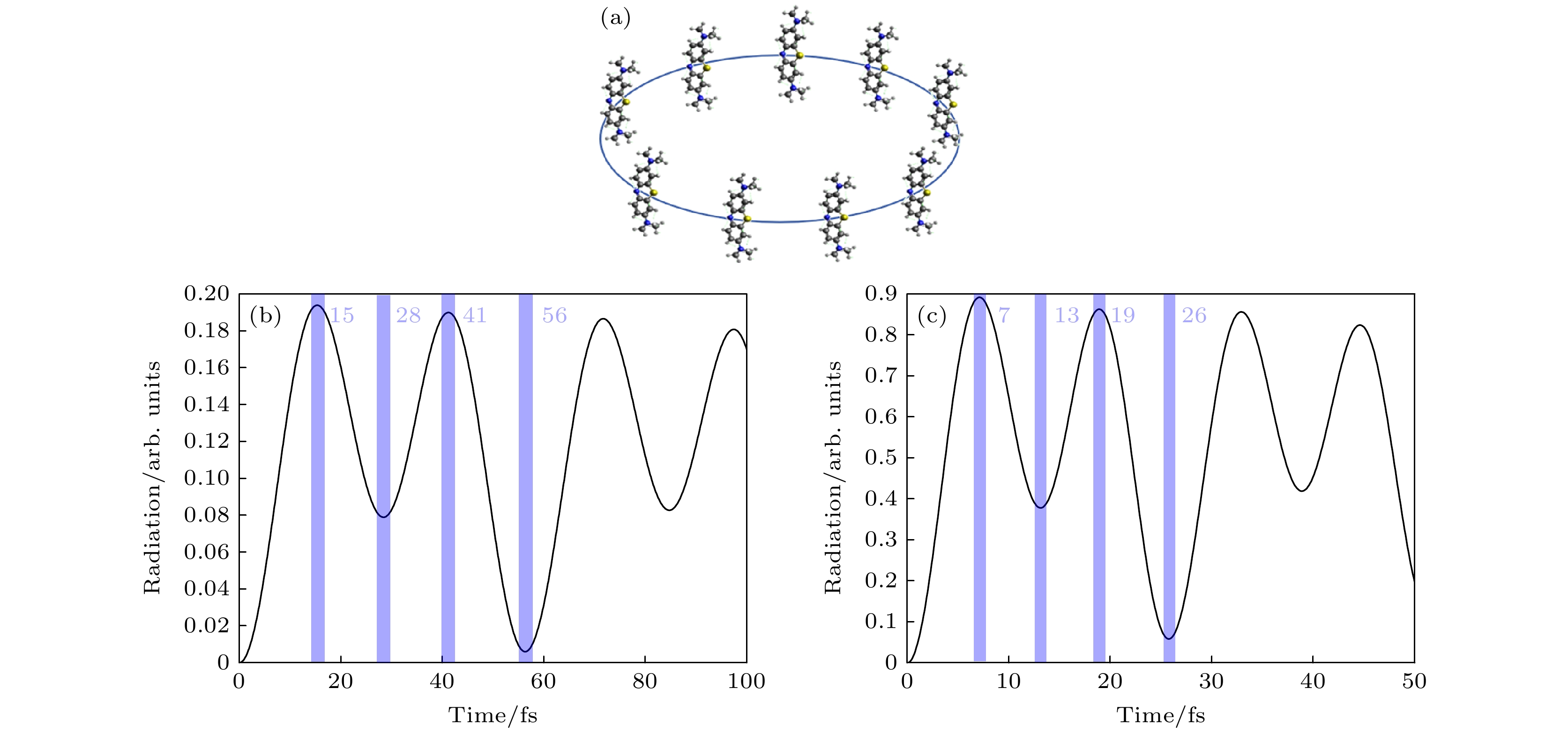
图 2 (a) 9个全同亚甲基蓝分子组成的半径为2 nm的环状分子团簇; (b) 连续激光激发下STM纳米腔中的远场辐射谱; (c) 连续激光激发下STM皮米腔中的远场辐射谱
Fig. 2. (a) A circular molecular cluster with a radius of 2 nm composed of 9 identical methylene blue molecules; (b) far-field radiation spectra in STM nanocavity by continuous laser excitation; (c) far-field radiation spectra in STM picocavity by continuous laser excitation.
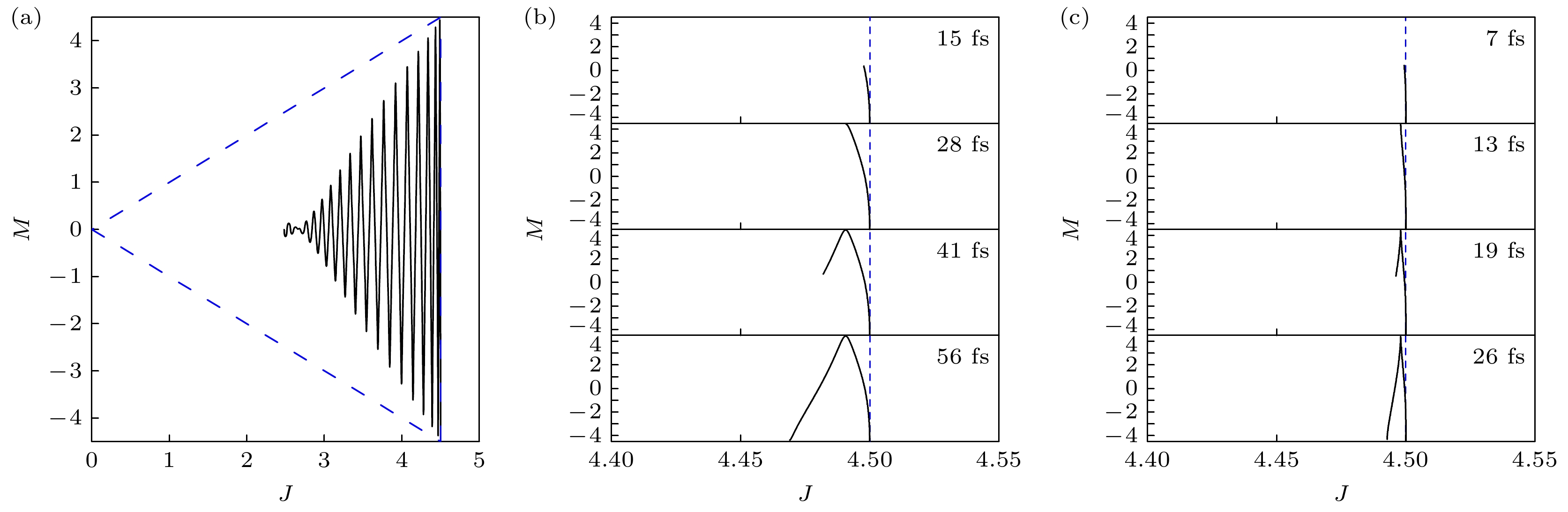
图 3 (a) 连续激光激发下Dicke态量子数平均值表示的STM纳米腔中的分子动力学; (b) 不同激发时长时, STM纳米腔中用Dicke态量子数的平均值表示的分子动力学; (c) 不同激发时长下, STM皮米腔中用Dicke态量子数的平均值表示的分子动力学, 其中蓝色虚线表示Dicke态边界
Fig. 3. (a) Molecular dynamics in STM nanocavity represented by the mean value of quantum numbers in Dicke states by continuous laser excitation; (b) molecular dynamics in STM nanocavity expressed by the average of the quantum numbers of the Dicke states at different excitation durations; (c) molecular dynamics in the STM picocavity expressed by the average of the quantum numbers of the Dicke states at different excitation durations, where the blue dotted line represents the Dicke state boundary.
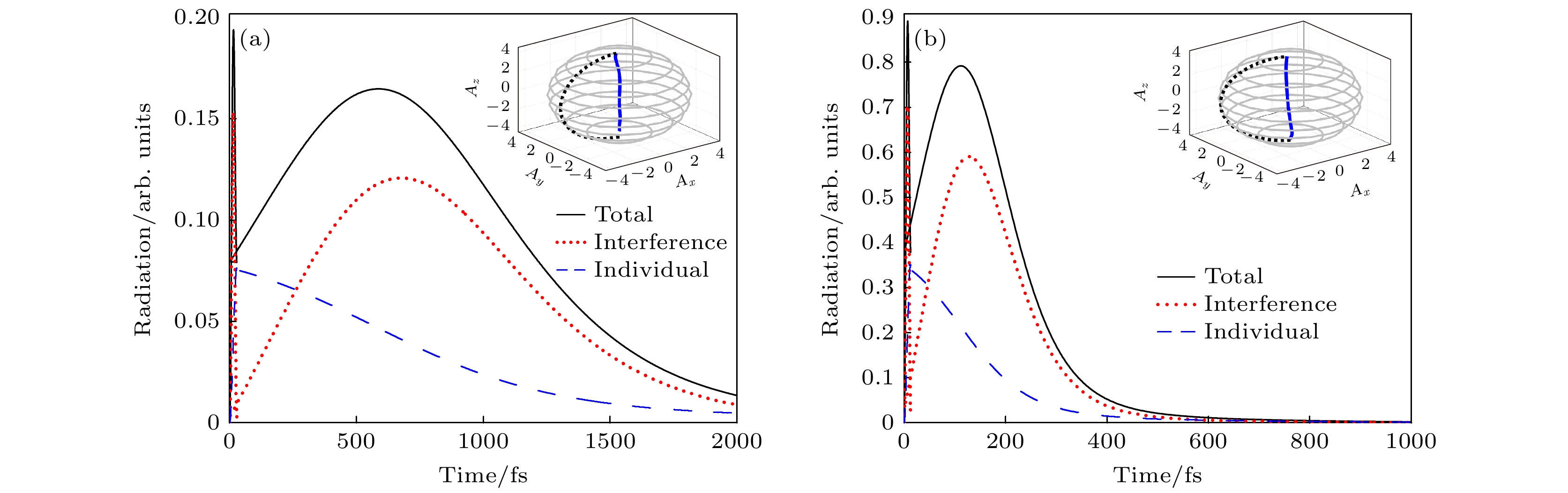
图 4 (a) 持续时间为28 fs的激光脉冲激励下, STM纳米腔中远场辐射谱; (b) 持续时间为13 fs的激光脉冲激励下, STM皮米腔中远场辐射谱; 插图分别对应STM纳米腔和皮米腔中用集体自旋矢量表示的分子动力学, 其中灰色线表示最外层球面
Fig. 4. (a) Far-field radiation spectra in STM nanocavity by laser pulse excitation with a duration of 28 fs; (b) far-field radiation spectra in STM picocavity by laser pulse excitation with a duration of 13 fs; the insets correspond to molecular dynamics represented by collective spin vectors in STM nanocavity and picocavity, respectively, where the gray line represents the outermost sphere.
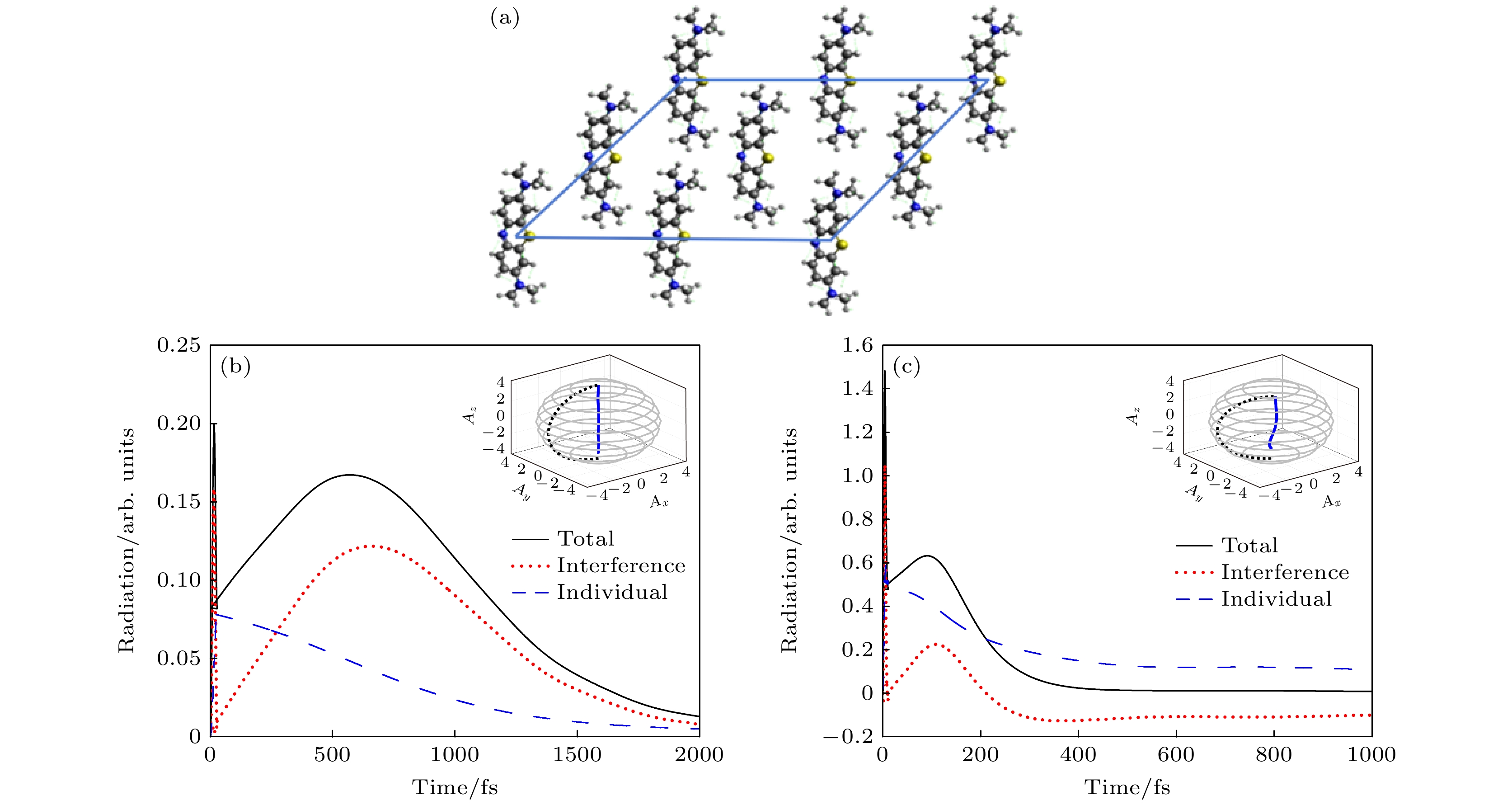
图 5 (a) 9个全同亚甲基蓝分子组成的二维平面构形分子团簇; (b) 持续时间为28 fs的激光脉冲激励下, STM纳米腔中远场辐射谱; (c) 持续时间为11 fs的激光脉冲激励下, STM皮米腔中远场辐射谱
Fig. 5. (a) A two-dimensional planar configuration molecular cluster composed of 9 identical methylene blue molecules; (b) far-field radiation spectra in STM nanocavity by laser pulse excitation with a duration of 28 fs; (c) far-field radiation spectra in STM picocavity by laser pulse excitation with a duration of 11 fs.
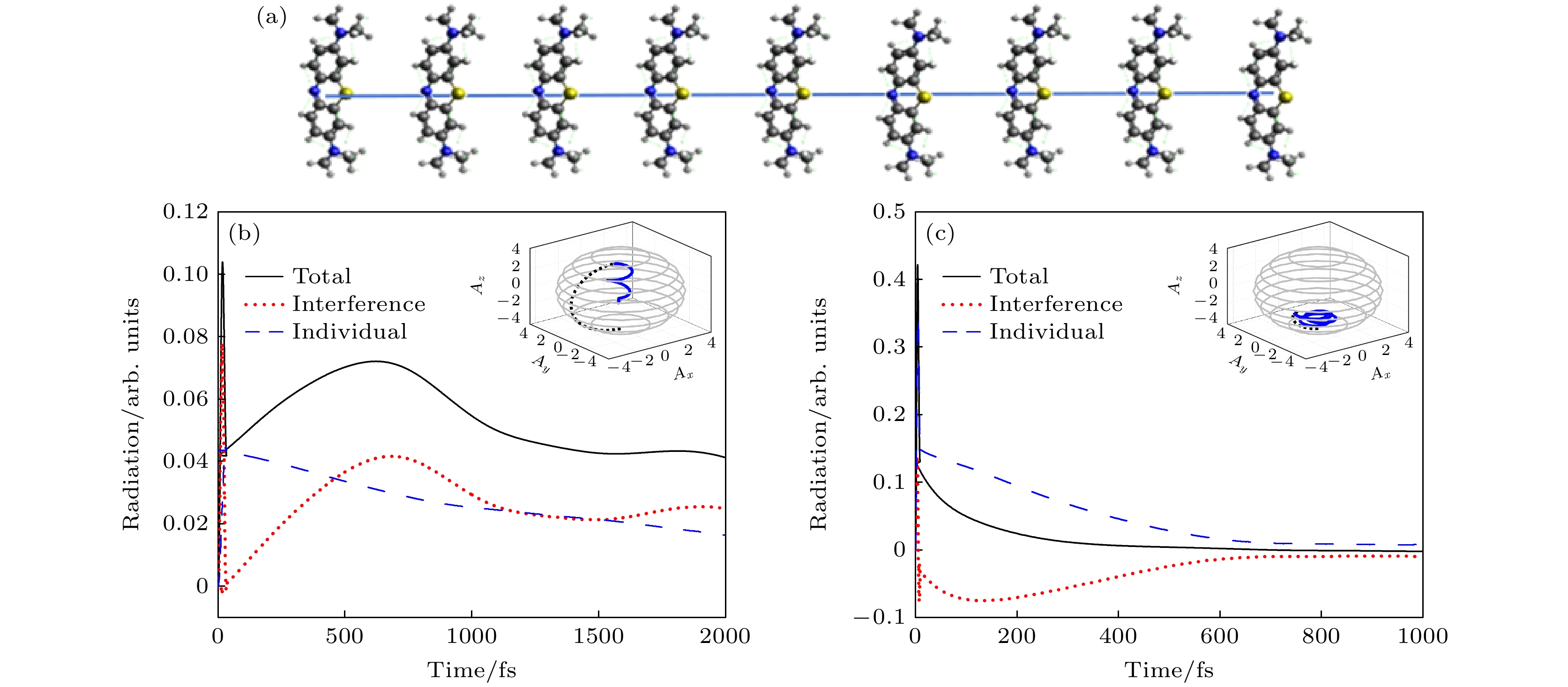
图 6 (a) 9个全同亚甲基蓝分子组成的一维链状分子团簇; (b) 持续时间为33 fs的激光脉冲激励下, STM纳米腔中远场辐射谱; (c) 持续时间为9 fs的激光脉冲激励下, STM皮米腔中远场辐射谱
Fig. 6. (a) A one-dimensional chain of molecular clusters composed of 9 identical methylene blue molecules; (b) far-field radiation spectra in STM nanocavity by laser pulse excitation with a duration of 33 fs; (c) far-field radiation spectra in STM picocavity by laser pulse excitation with a duration of 9 fs.
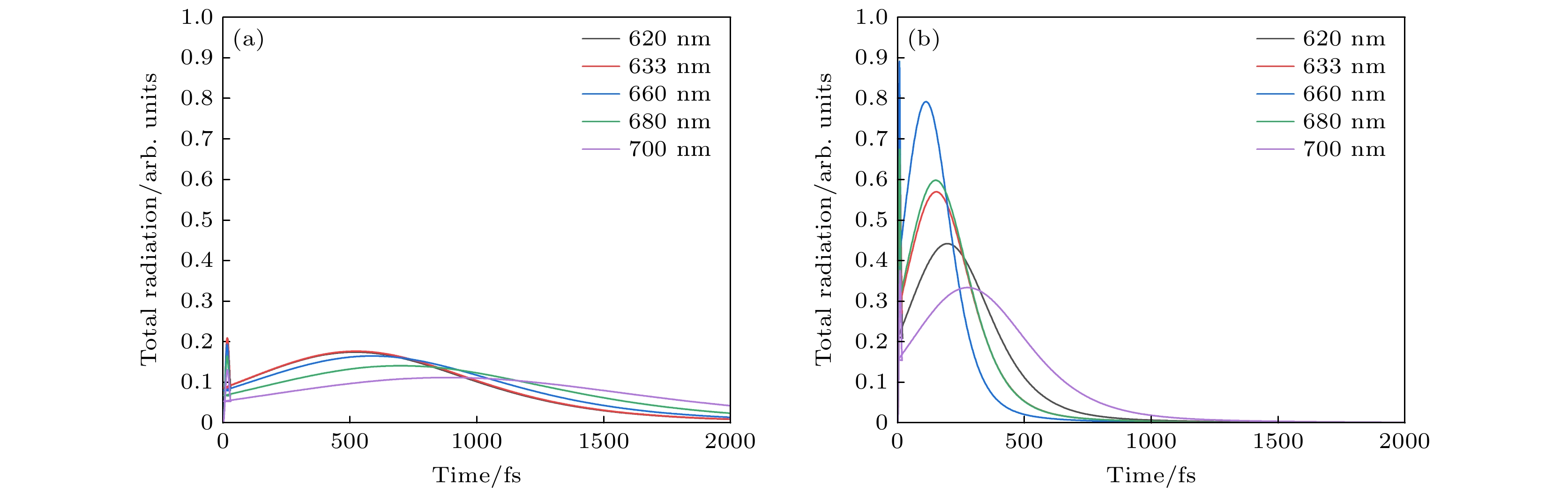
图 7 波长620—700 nm, 强度为Iext = 103 μW/μm2激光激发下 (a) STM纳米腔中环状分子团簇的远场辐射谱; (b) STM皮米腔中环状分子团簇的远场辐射谱
Fig. 7. By laser excitation with wavelengths from 620—700 nm and an intensity of Iext = 103 μW/μm2: (a) Far-field radiation spectra of clusters of cyclic molecules in STM nanocavity; (b) far-field radiation spectra of clusters of cyclic molecules in STM picocavity.
-
[1] Binnig G, Rohrer H, Gerber Ch, Weibel E 1982 Appl. Phys. Lett. 40 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Binnig G, Rohrer H, Gerber Ch, Weibel E 1982 Phys. Rev. Lett. 49 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Gimzewski J K, Joachim C 1999 Science 283 1683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu S W, Ogawa N, Nazin G V, Ho W 2008 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 5241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen C, Chu P, Bobisch C A, Mills D L, Ho W 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 217402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang Y, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Yu Y J, Kuang Y M, Zhang L, Meng Q S, Luo Y, Yang J L, Dong Z C, Hou J G 2016 Nature 531 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Schwarz F, Wang Y F, Hofer W A, Berndt R, Runge E, Kröger J 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 119 15716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Stroscio J A, Eigler D M 1991 Science 254 1319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Benz F, Schmidt M K, Dreismann A, Chikkaraddy R, Zhang Y, Demetriadou A, Carnegie C, Ohadi H, De Nijs B, Esteban R, Aizpurua J, Baumberg J J 2016 Science 354 726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shin H H, Yeon G J, Choi H K, Park S M, Lee K S, Kim Z H 2018 Nano. Lett. 18 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Lee J, Tallarida N, Chen X, Liu P, Jensen L, Apkarian V A 2017 ACS Nano 11 11466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tallarida N, Lee J, Apkarian V A 2017 ACS Nano 11 11393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dicke R H 1954 Phys. Rev. 93 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Luo Y, Chen G, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yu Y J, Kong F F, Tian X J, Zhang Y, Shan C X, Luo Y, Yang J L, Sandoghdar V, Dong Z C, Hou J G 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 233901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chikkaraddy R, De Nijs B, Benz F, Barrow S J, Scherman O A, Rosta E, Demetriadou A, Fox P, Hess O, Baumberg J J 2016 Nature 535 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bergmann K, O’Konski C T 1963 J. Phys. Chem. 67 2169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Johnson P B, Christy R W 1972 Phys. Rev. B 6 4370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yang B, Chen G, Ghafoor A, Zhang Y F, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Yang J L, Sandoghdar V, Aizpurua J, Dong Z C, Hou J G 2020 Nat. Photonics 14 693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jaculbia R B, Imada H, Miwa K, Iwasa T, Takenaka M, Yang B, Kazuma E, Hayazawa N, Taketsugu T, Kim Y 2020 Nat. Nanotechnol. 15 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Scheel S, Buhmann S Y 2008 Acta Phys. Slovaca 58 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Rivera N, Kaminer I 2020 Nat. Rev. Phys. 2 538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Scully M O, Zubairy M S 1997 Quantum Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp460–486
[23] Steck D A http://steck.us/teaching [2020-9-24]
[24] Plankensteiner D, Hotter C, Ritsch H 2022 Quantum 6 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Asenjo-Garcia A, Moreno-Cardoner M, Albrecht A, Kimble H J, Chang D E 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 031024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gross M, Haroche S 1982 Phys. Rep. 93 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kasha M 1963 Radiat. Res. 20 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Spano F C, Silva C 2014 Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 65 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2511
- PDF下载量: 40
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: