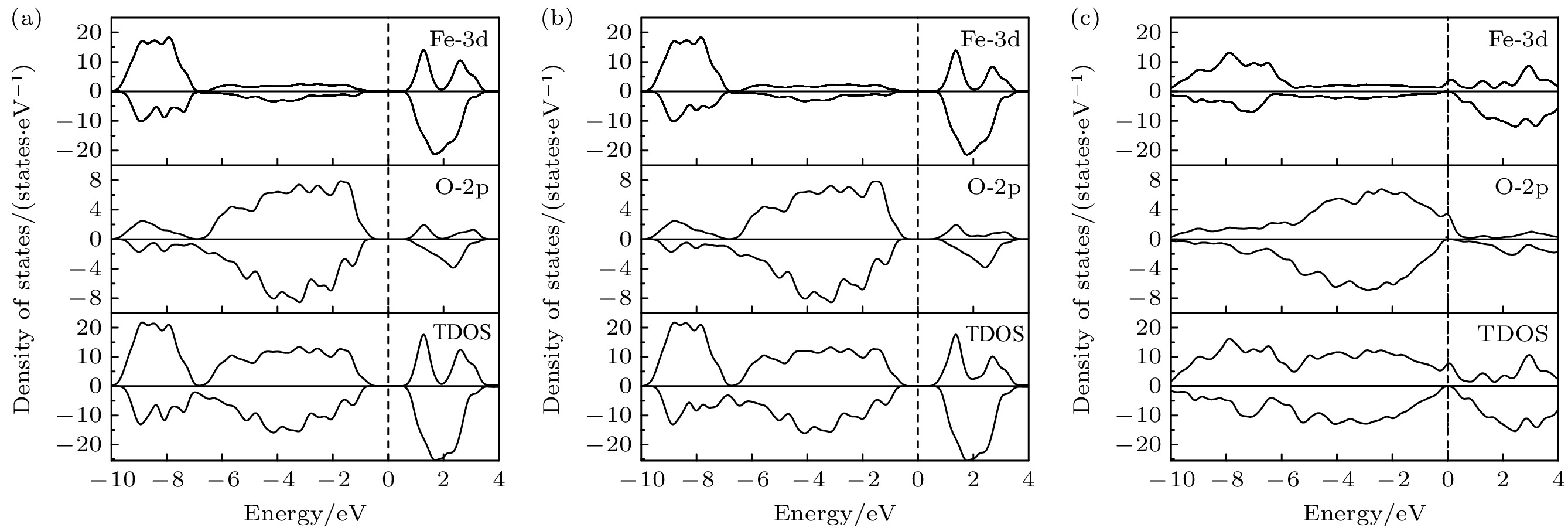
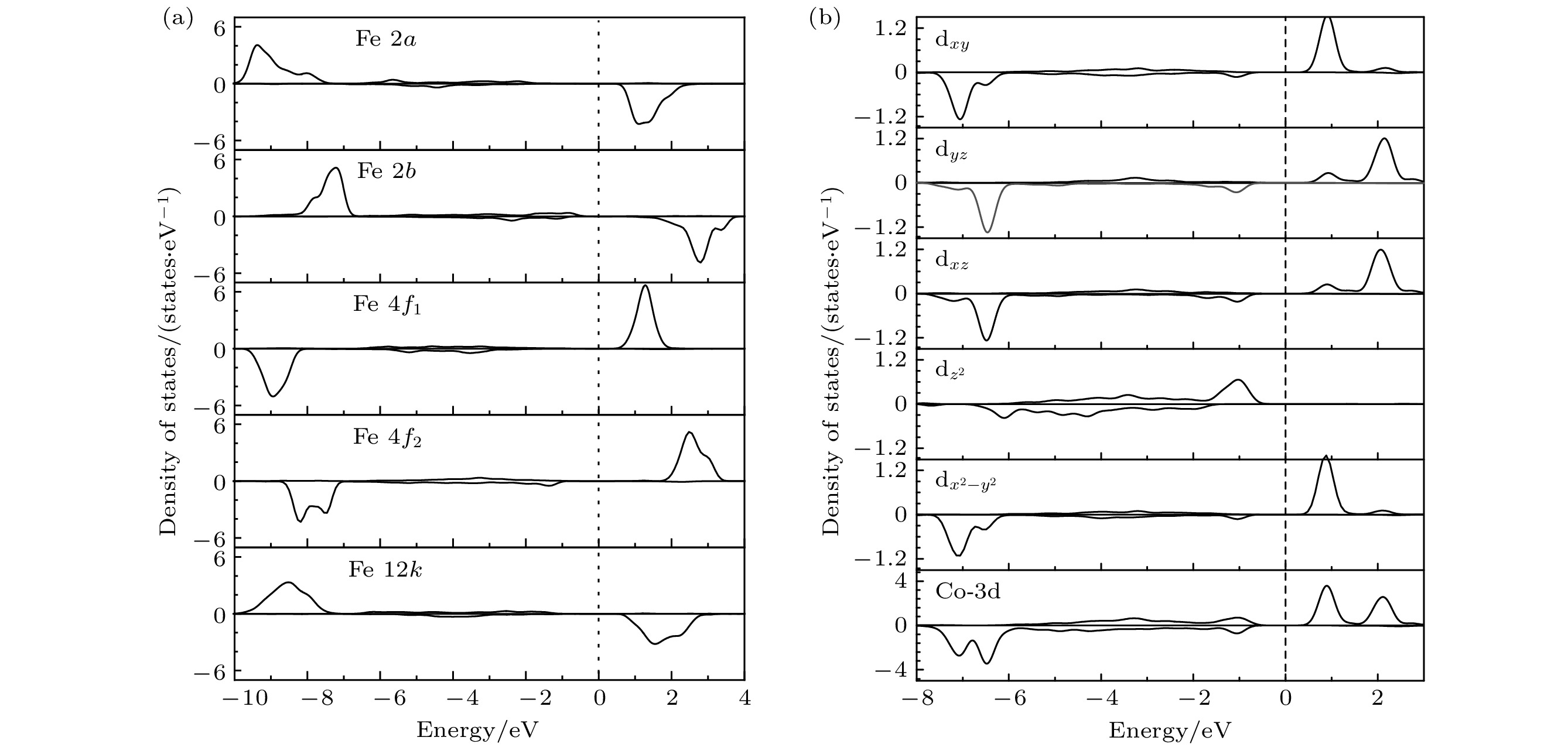
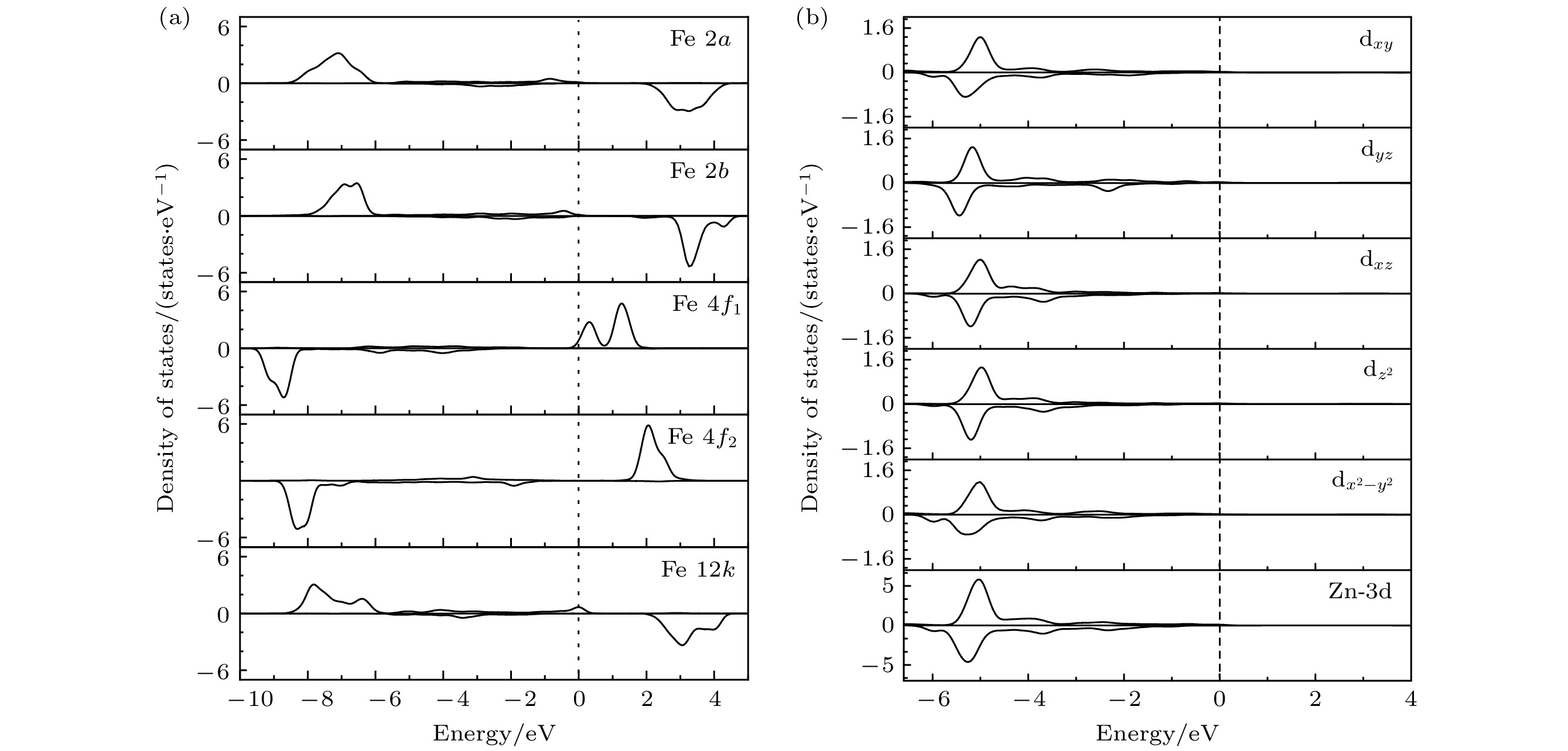
-
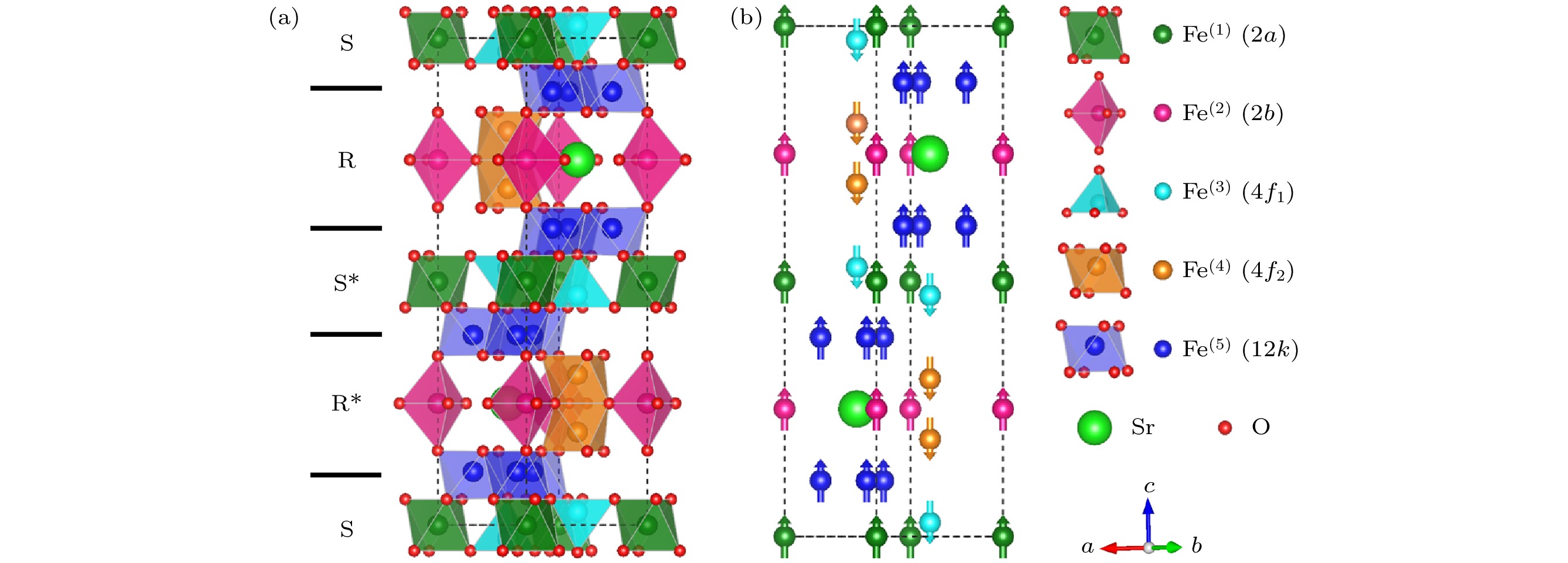
六角晶系磁铅石型(M型)锶铁氧体因其独特的磁性、介电性能和热稳定性, 在永磁材料领域备受关注. 但相比于稀土永磁Nd2Fe14B材料来说, M型锶铁氧体(SrFe12O19)永磁材料的综合磁性能较低, 这极大地限制了其使用范围. 本文基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算方法, 结合广义梯度近似(GGA+U ), 系统研究了Ca-Co(Zn)共掺杂对M型锶铁氧体的电子结构、力学性能、导电性和磁性能的影响. 计算结果表明, Ca-Co(Zn)共掺杂SrFe12O19铁氧体均具有良好的结构稳定性和力学性能. Ca-Zn共掺杂可以使体系导电性增强, 这是因为二价Zn离子取代了4f1晶位的三价Fe离子. 同时, Ca-Co(Zn)共掺杂使体系的总磁矩增大, 磁晶各向异性能下降, 但相比于Co和Zn单掺杂体系, 磁晶各向异性能有所改善. 这表明, Ca-Co(Zn)共掺杂能够有效地提高M型锶铁氧体的磁性能, 并具备节约成本和环保的优点.M-type strontium ferrite has attracted widespread attention in the field of permanent magnet materials due to its unique magnetic properties, dielectric performance, and thermal stability. However, compared with rare-earth permanent magnets such as Nd2Fe14B, strontium ferrite (SrFe12O19) permanent magnets possess relatively low comprehensive magnetic properties, which limits their application range. The effects of Ca-Co (Zn) doping on the electronic structure, mechanical properties, and magnetic properties of M-type strontium ferrite are systematically investigated by first-principles plane-wave pseudopotential method based on density functional theory (DFT), combined with the generalized gradient approximation (GGA + U ) in this work. The calculation results indicate that the Ca-Co (Zn) co-doped M-type strontium ferrite systems exhibit good structural stability and mechanical properties. In the Ca-Zn co-doped structures, the conductivity of the system is enhanced because of the substitution of divalent Zn ionsfortrivalent Fe ions at the 4f1 site. The Ca-Co (Zn) co-doping increases the total magnetic moment of the system, while the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy decreases. However, compared with the single Co doped system and single Zn doped system, the Co-Zn co-doped system has the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy improved, indicating that Ca-Co (Zn) co-doping can effectively enhance the magnetic properties of strontium ferrite. In this work, the mechanisms of the effects of Ca-Co and Ca-Zn co-doping on the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy of strontium ferrite are also analyzed. The results indicate that the decrease of magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy in the Ca-Co co-doped system is mainly due to the effects of dxy and ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2-y^2} $ orbital electrons of Co3+ ion and dxy and ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2-y^2} $ orbital electrons of Fe ions at the 2b site. In the Ca-Zn co-doped system, the reduction is mainly influenced by Fe-3d orbitals at the 4f1 site, while the dxy and ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2 - y^2} $ orbital electrons of the 2b site enhance the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy of the system. These results provide theoretical guidance for modifying M-type strontium ferritein future.
[1] Hu J W, Wu Y X, He J Y, Liu Z W 2023 Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. 156 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu Z M, Stenning G B G, Koval V, Wu J Y, Yang B, Leavesley A, Wylde R, Reece M J, Jia C L, Yan H X 2022 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14 46123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Vidal J V, Fonte T, Lopes L S, Bernardo R, Carneiro P, Pires D G, Dos Santos M S 2024 Appl. Energy 376 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shirk B T, Buessem W R 1969 J. Appl. Phys. 40 1294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gutfleisch O, Willard M A, Bruck E, Chen C H, Sankar S G, Liu J P 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pullar RC 2012 Prog. Mater Sci. 57 1191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Fernández C, Sangregorio C, Figuera J, Belec B, Makovec D, Quesada A 2021 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54 153001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Granados-Miralles C, Jenu P 2021 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54 303001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Palomino-Resendiz R L, Castañeda-Ovando A, Conde-Gallardo A, Palomino-Resendiz S I, Jaguey-Hernández Y, Tapia-Ignacio C 2025 Acta Mater. 39 102352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Díaz-Pardo R, Bierlich S, Töpfer J, Monjaras R V 2016 AIP Adv. 6 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Luo H, Rai B K, Mishra S R, Nguyen V V, Liu J P 2012 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324 2602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Huang F, Liu X, Niu X, Ma Y, Huang X, Lü F, Feng S, Zhang Z 2015 Mater. Technol. 30 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Anantharamaiah P N, Chandra N S, Shashanka H M, Kumar R, Sahoo B 2020 Adv. Powder Technol. 31 2385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ashiq M N, Iqbal M, Najam-Ul-Haq M, Gomez P, Qureshi A M 2012 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang W J, Bai Y, Han X, Wang L, Lu X F, Qiao L J 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 546 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhou Z P, Wang Z Y, Wang X T, Li Q, Jin M, Xu J Y 2015 J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 28 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nguyen H H, Tran N, Phan T L, Yang D S, Dang N T, Lee B W 2020 Ceram. Int. 46 19506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nguyen H H, Jeong W H, Phan T L, Lee B W, Yang D S, Tran N, Dang N T 2021 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 537 168195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu C X, Cao H L, Wang S Y, Wu N N, Qiu S, Lyu H L, Li J R 2017 New J. Chem. 41 6427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tuyen N L, Hue N T, Tho P T, Toan H N, Xuan C T A, Dang N V, Ho T A, Tuan N Q, Tran N 2024 J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices 9 100796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li X, Yang W G, Bao D X, Meng X D, Lou B Y, Yang W G, Bao D X, Meng X D, Lou B Y 2013 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Anbarasu V, Gazzali P MM, Karthik T, Manigandan A, Sivakumar K 2013 J. Mater. Sci. -Mater. Electron. 24 916
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Patel C D, Dhruv P N, Meena S S, Singh C, Kavita S, Ellouze M, Jotania R B 2020 Ceram. Int. 46 24816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Comput. Mater. Sci. 6 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kresse G, Joubert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Hou Y H, Chen X, Guo X L, Li W, Huang Y L, Tao X M 2021 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 538 168257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Fei Z, Cococcioni M, Marianetti C A, Morgan D, Ceder G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 235121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Anisimov V I, Zaanen J, Andersen O K 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Abdelouahed S, Alouani M 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 054406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 李荫远, 李国栋 1978 铁氧体物理学(第一版) (北京: 科学出版社) 第34—36页
Li Y Y, Li G D 1978 Ferrite Physics (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Science Press) pp34–36
[32] Fang C M, Kools F, Metselaar R, WithG D, Groot R A D 2003 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 15 6229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Nemrava S, Vinnik D A, Hu Z, Valldor M, Kuo C Y, Zherebtsov A D, Gudkova S A, Chen C T, Tjeng L H, Niewa R 2017 Inorg. Chem. 56 3861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bavarsiha F, Montazeri-Pour M, Rajabi M 2020 J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30 2386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang Z Y, Liu X, Wang X J, Wu Y P, Li R 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 525 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Lechevallier L, Breton J M L, Wang J F, Harris I R 2004 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16 5359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wagner T R 1998 J. Solid State Chem. 136 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Fang Q, Cheng H, Huang K, Wang J, Li R, Jiao Y 2005 J. Magn. Magn Mater. 294 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Banihashemi V, Ghazi M E, Izadifard M 2021 Physica B 605 412670
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Buerger M J 1961 Z. Kristallogr. 115 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Liu Y, Li R, Qing Y C 2024 Mater. Res. Bull. 172 112661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Zhu L, Zeng Y R, Wen J, Li L, Cheng T M 2018 Electrochim. Acta 292 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Hill R 1952 Proc. Phys. Soc. London, Sect. A 65 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] 高娟, 刘其军, 蒋城露, 樊代和, 张淼, 刘福生, 唐斌 2022 高压 36 051101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J, Liu Q J, Jang C L, Fan D H, Zhang M, Liu F S, Tang B 2022 Chin. J. High. Pressure Phys. 36 051101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Pugh S F 1954 Philos. Mag. 45 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Morita A, Frood D G 1978 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 11 2409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] 韩志全 2010 铁氧体及其磁性物理(北京: 航空工业出版社)第20页
Han Z Q 2010 Ferrite and its Magnetic Physics (Beijing: Aviation Industry Press) p20
[48] 蒋有为 2020 博士学位论文(成都: 电子科技大学)
Jang Y W 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[49] Steinbeck L, Richter M, Eschrig H 2001 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 226-230 1011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
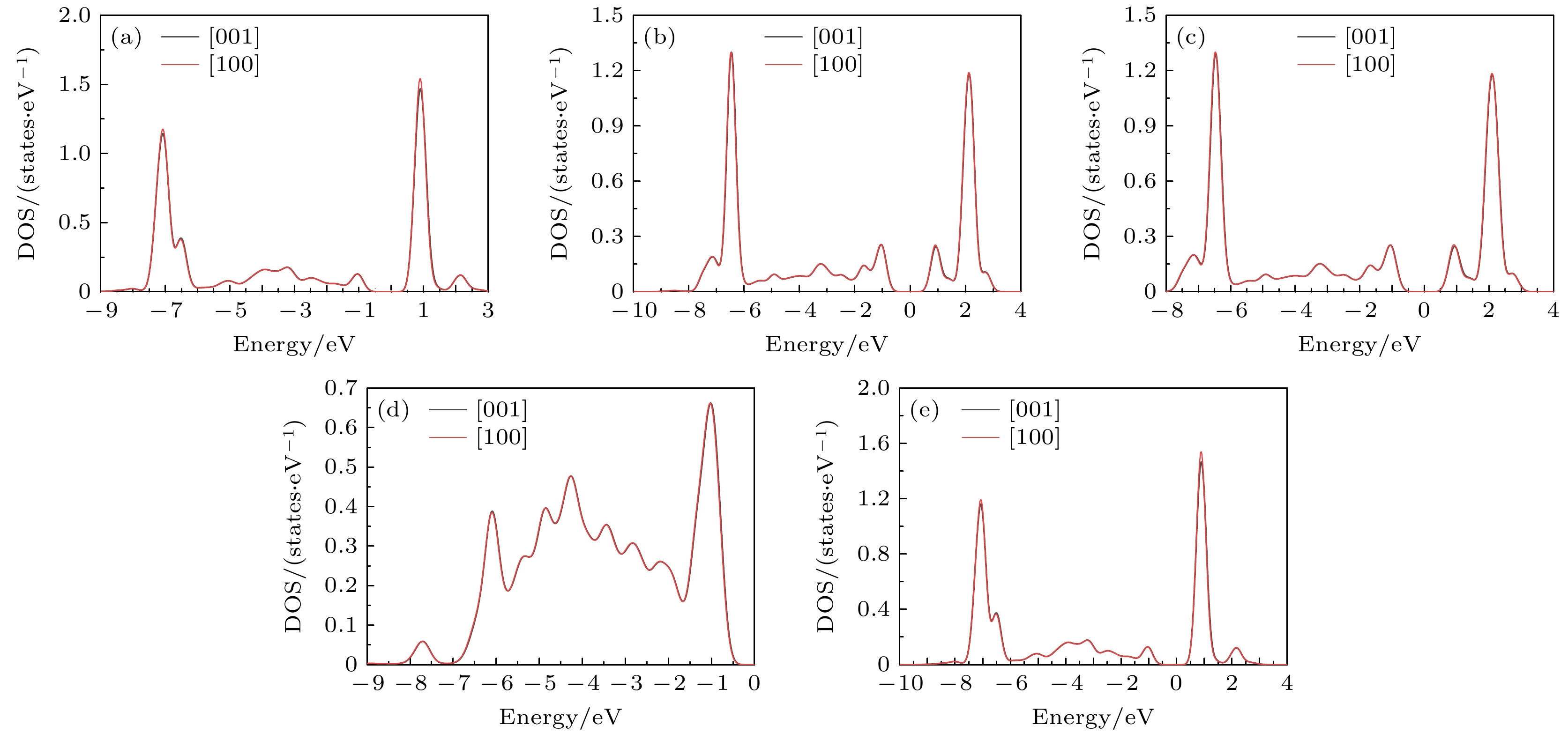
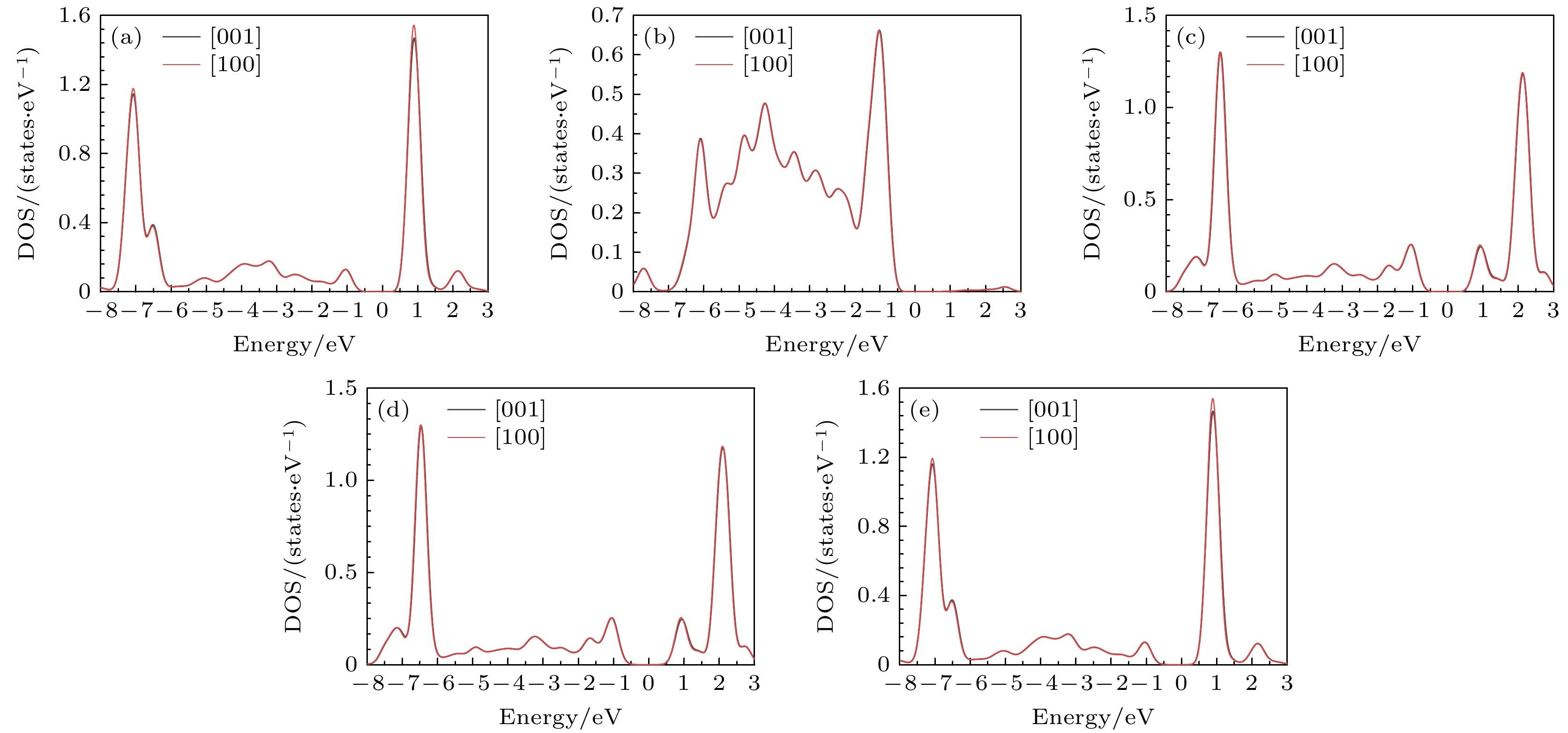
图 5 Ca-Co-Sr铁氧体Co离子分别沿[001]和[100]轴向磁化后的轨道态密度 (a) dxy; (b) $ {{\mathrm{d}}}_{z}^{2} $; (c) dyz; (d) dxz; (e) ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2-y^2} $
Fig. 5. Orbital density of states of Co ion in Ca-Co-Sr ferrite magnetized along the [001] and[100] axes: (a) dxy; (b) $ {{\mathrm{d}}}_{z}^{2} $; (c) dyz; (d) dxz; (e) ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2 -y^2} $.
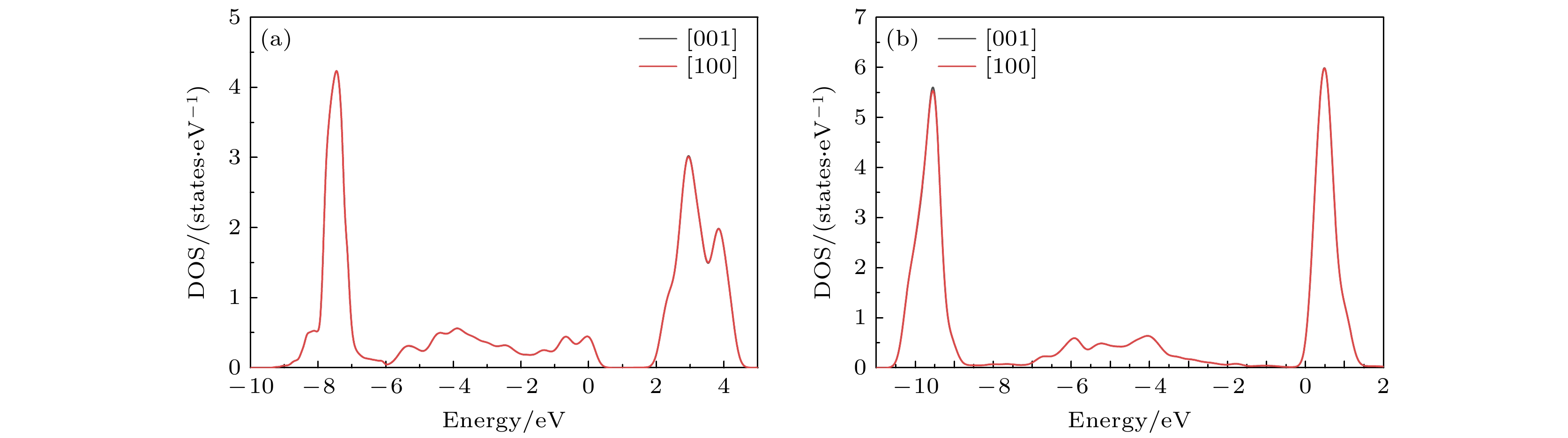
图 6 Ca-Co-Sr铁氧体2b晶位Fe离子分别沿[001]和[100]轴向磁化的轨道态密度 (a) dxy; (b) $ {{\mathrm{d}}}_{z}^{2} $; (c) dyz; (d) dxz; (e)${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2 - y^2}$
Fig. 6. Orbital density of states for Fe ions at the 2b site in Ca-Co-Sr ferrite magnetized along the [001] and [100] axes, respectively: (a) dxy; (b) $ {{\mathrm{d}}}_{z}^{2} $; (c) dyz; (d) dxz; (e) ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2- y^2} $.
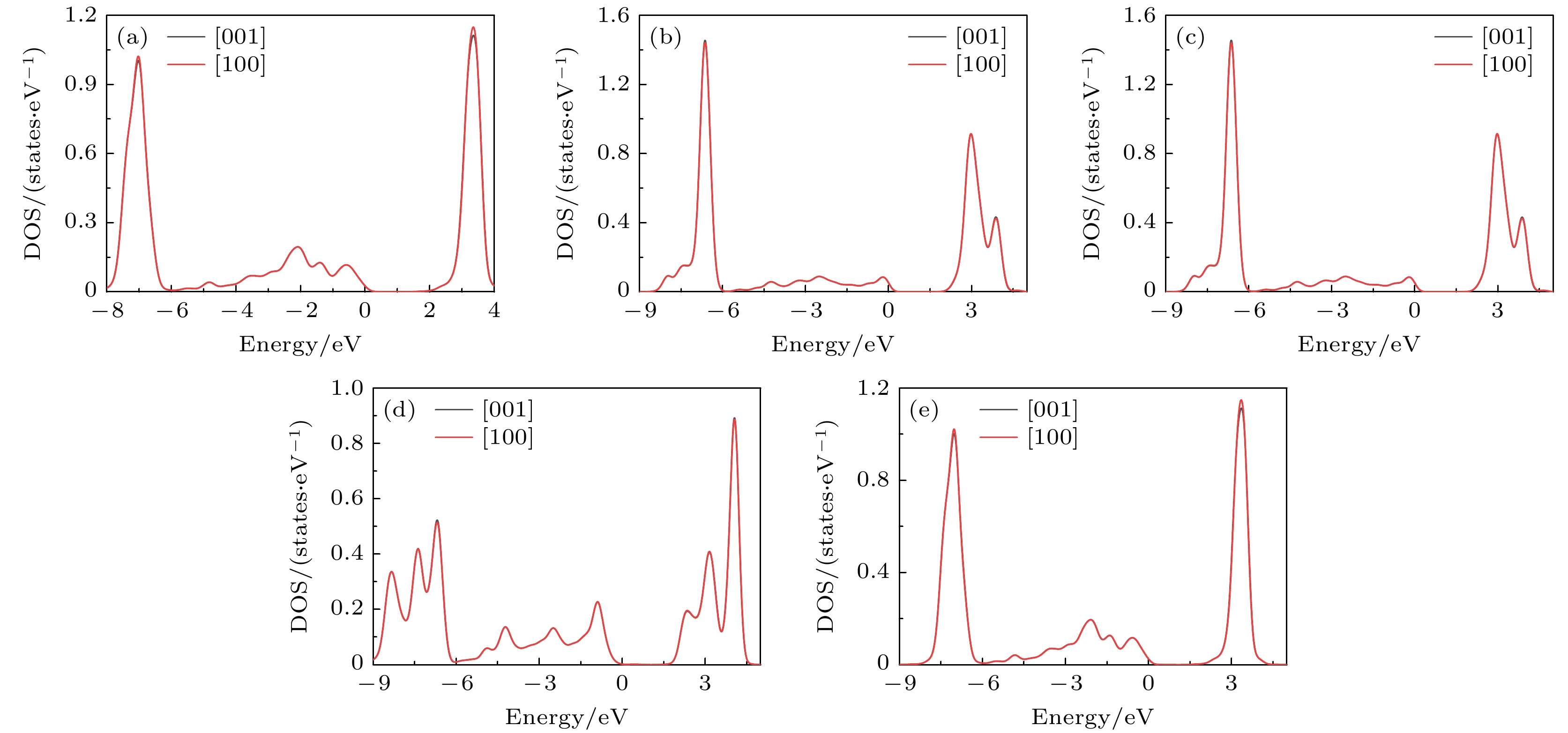
图 8 Ca-Zn-Sr铁氧体2b晶位处Fe离子分别沿[001]和[100]轴向磁化的轨道态密度 (a) dxy; (b) dxz; (c) dyz; (d) $ {{\mathrm{d}}}_{z}^{2} $; (e) ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2 - y^2} $
Fig. 8. Orbital density of states for Fe ions at the 2b site in Ca-Zn-Sr ferrite magnetized along the [001] and [100] axes: (a) dxy; (b) dxz; (c) dyz; (d) $ {{\mathrm{d}}}_{z}^{2} $; (e) ${\mathrm{d}}_{x^2 - y^2} $.
表 1 Sr铁氧体、Co、Zn单掺杂以及Ca-Co(Zn)共掺杂体系的晶格参数、c/a值
Table 1. Lattice parameters and c/a values for Sr ferrite, single doping with Co or Zn, and co-doping with Ca-Co(Zn).
体系 a/Å c/Å c/a Sr铁氧体 5.85 23.09 3.94 Co-Sr铁氧体 5.84 23.05 3.95 Zn-Sr铁氧体 5.80 22.94 3.96 Ca-Co-Sr铁氧体 5.85 23.10 3.95 Ca-Zn-Sr铁氧体 5.81 22.94 3.95 表 2 Sr铁氧体、Co、Zn单掺杂及Ca-Co(Zn)共掺杂体系的弹性常数和力学参数
Table 2. Elastic constants and mechanical parameters for Sr ferrite, single doping with Co or Zn, and co-doping with Ca-Co(Zn).
体系 C11 C12 C13 C33 C44 B/GPa G/GPa B/G ν E/GPa Sr铁氧体 311 158 116 280 70 186 77 2.43 0.32 202 Co-Sr铁氧体 287 163 110 259 36 167 66 2.51 0.32 176 Zn-Sr铁氧体 363 168 133 280 73 205 82 2.50 0.32 217 Ca-Co-Sr铁氧体 456 103 179 159 107 188 80 2.37 0.32 208 Ca-Zn-Sr铁氧体 347 163 128 258 76 199 83 2.40 0.32 218 表 3 Sr铁氧体及掺杂体系各离子及总磁晶各向异性能 (单位: meV)
Table 3. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy energies (unit: meV) of ionsand the total for Sr ferrite and doped systems.
晶位 Co(4f2) Zn(4f1) Fe(2a) Fe(2b) Fe(4f1) Fe(4f2) Fe(12k) Total $ {{E}}_{\text{Sr}}^{\text{MAC}} $ — — 0.007 0.872 –0.086 –0.042 0.466 0.830 $ {{E}}_{\text{Co-Sr}}^{\text{MAC}} $ –2.377 — 0.010 0.406 –0.069 –0.084 0.067 0.257 $ {{E}}_{\text{Zn-Sr}}^{\text{MAC}} $ — 0.000 0.189 0.381 –1.031 –0.035 0.058 0.308 $ {{E}}_{\text{Ca-Co-Sr}}^{\text{MAC}} $ –2.329 — 0.001 0.397 –0.046 –0.081 0.058 0.370 $ {{E}}_{\text{Ca-Zn-Sr}}^{\text{MAC}} $ — –0.015 0.040 0.225 –0.280 –0.017 0.037 0.490 表 4 Sr铁氧体中各晶位Fe离子沿c轴方向轨道磁矩值(单位: μB)
Table 4. Orbital magnetic moment (unit: μB) of Fe ions at different sites in Sr ferrite along the c-axis.
晶位 Fe(2a) Fe(2b) Fe(4f1) Fe(4f2) Fe(12k) Total p轨道 0.000 0.001 –0.002 –0.001 0.000 0.021 d轨道 0.001 0.015 –0.012 –0.010 0.011 0.113 总磁矩 0.001 0.016 –0.014 –0.011 0.011 0.135 表 5 Ca-Co-Sr铁氧体中各离子沿c轴方向的平均轨道磁矩值(单位: μB)
Table 5. Average orbital magnetic moment (unit: μB) of each ion in Ca-Co-Sr ferrite along the c-axis.
晶位 Co(4f2) Fe(2a) Fe(2b) Fe(4f1) Fe(4f2) Fe(12k) Total p轨道 –0.001 0.000 0.001 –0.002 –0.001 0.000 0.015 d轨道 –0.033 0.012 0.015 –0.012 –0.010 0.011 0.096 总磁矩 –0.033 0.012 0.016 –0.014 –0.011 0.011 0.111 表 6 Ca-Zn-Sr铁氧体各离子沿c轴方向的平均轨道磁矩(单位: μB)
Table 6. Average orbital magnetic moment (unit: μB) of each ion in Ca-Zn-Sr ferrite along the c-axis.
晶位 Zn(4f1) Fe(2a) Fe(2b) Fe(4f1) Fe(4f2) Fe(12k) Total p轨道 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.020 d轨道 0.000 0.011 0.015 –0.017 –0.012 0.011 0.099 总磁矩 –0.001 0.011 0.015 –0.017 –0.012 0.011 0.119 -
[1] Hu J W, Wu Y X, He J Y, Liu Z W 2023 Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. 156 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu Z M, Stenning G B G, Koval V, Wu J Y, Yang B, Leavesley A, Wylde R, Reece M J, Jia C L, Yan H X 2022 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14 46123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Vidal J V, Fonte T, Lopes L S, Bernardo R, Carneiro P, Pires D G, Dos Santos M S 2024 Appl. Energy 376 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shirk B T, Buessem W R 1969 J. Appl. Phys. 40 1294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gutfleisch O, Willard M A, Bruck E, Chen C H, Sankar S G, Liu J P 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pullar RC 2012 Prog. Mater Sci. 57 1191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Fernández C, Sangregorio C, Figuera J, Belec B, Makovec D, Quesada A 2021 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54 153001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Granados-Miralles C, Jenu P 2021 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54 303001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Palomino-Resendiz R L, Castañeda-Ovando A, Conde-Gallardo A, Palomino-Resendiz S I, Jaguey-Hernández Y, Tapia-Ignacio C 2025 Acta Mater. 39 102352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Díaz-Pardo R, Bierlich S, Töpfer J, Monjaras R V 2016 AIP Adv. 6 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Luo H, Rai B K, Mishra S R, Nguyen V V, Liu J P 2012 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324 2602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Huang F, Liu X, Niu X, Ma Y, Huang X, Lü F, Feng S, Zhang Z 2015 Mater. Technol. 30 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Anantharamaiah P N, Chandra N S, Shashanka H M, Kumar R, Sahoo B 2020 Adv. Powder Technol. 31 2385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ashiq M N, Iqbal M, Najam-Ul-Haq M, Gomez P, Qureshi A M 2012 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang W J, Bai Y, Han X, Wang L, Lu X F, Qiao L J 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 546 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhou Z P, Wang Z Y, Wang X T, Li Q, Jin M, Xu J Y 2015 J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 28 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nguyen H H, Tran N, Phan T L, Yang D S, Dang N T, Lee B W 2020 Ceram. Int. 46 19506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nguyen H H, Jeong W H, Phan T L, Lee B W, Yang D S, Tran N, Dang N T 2021 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 537 168195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu C X, Cao H L, Wang S Y, Wu N N, Qiu S, Lyu H L, Li J R 2017 New J. Chem. 41 6427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tuyen N L, Hue N T, Tho P T, Toan H N, Xuan C T A, Dang N V, Ho T A, Tuan N Q, Tran N 2024 J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices 9 100796
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li X, Yang W G, Bao D X, Meng X D, Lou B Y, Yang W G, Bao D X, Meng X D, Lou B Y 2013 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Anbarasu V, Gazzali P MM, Karthik T, Manigandan A, Sivakumar K 2013 J. Mater. Sci. -Mater. Electron. 24 916
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Patel C D, Dhruv P N, Meena S S, Singh C, Kavita S, Ellouze M, Jotania R B 2020 Ceram. Int. 46 24816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Comput. Mater. Sci. 6 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kresse G, Joubert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Hou Y H, Chen X, Guo X L, Li W, Huang Y L, Tao X M 2021 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 538 168257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Fei Z, Cococcioni M, Marianetti C A, Morgan D, Ceder G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 235121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Anisimov V I, Zaanen J, Andersen O K 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Abdelouahed S, Alouani M 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 054406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 李荫远, 李国栋 1978 铁氧体物理学(第一版) (北京: 科学出版社) 第34—36页
Li Y Y, Li G D 1978 Ferrite Physics (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Science Press) pp34–36
[32] Fang C M, Kools F, Metselaar R, WithG D, Groot R A D 2003 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 15 6229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Nemrava S, Vinnik D A, Hu Z, Valldor M, Kuo C Y, Zherebtsov A D, Gudkova S A, Chen C T, Tjeng L H, Niewa R 2017 Inorg. Chem. 56 3861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bavarsiha F, Montazeri-Pour M, Rajabi M 2020 J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30 2386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang Z Y, Liu X, Wang X J, Wu Y P, Li R 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 525 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Lechevallier L, Breton J M L, Wang J F, Harris I R 2004 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16 5359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wagner T R 1998 J. Solid State Chem. 136 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Fang Q, Cheng H, Huang K, Wang J, Li R, Jiao Y 2005 J. Magn. Magn Mater. 294 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Banihashemi V, Ghazi M E, Izadifard M 2021 Physica B 605 412670
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Buerger M J 1961 Z. Kristallogr. 115 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Liu Y, Li R, Qing Y C 2024 Mater. Res. Bull. 172 112661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Zhu L, Zeng Y R, Wen J, Li L, Cheng T M 2018 Electrochim. Acta 292 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Hill R 1952 Proc. Phys. Soc. London, Sect. A 65 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] 高娟, 刘其军, 蒋城露, 樊代和, 张淼, 刘福生, 唐斌 2022 高压 36 051101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J, Liu Q J, Jang C L, Fan D H, Zhang M, Liu F S, Tang B 2022 Chin. J. High. Pressure Phys. 36 051101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Pugh S F 1954 Philos. Mag. 45 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Morita A, Frood D G 1978 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 11 2409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] 韩志全 2010 铁氧体及其磁性物理(北京: 航空工业出版社)第20页
Han Z Q 2010 Ferrite and its Magnetic Physics (Beijing: Aviation Industry Press) p20
[48] 蒋有为 2020 博士学位论文(成都: 电子科技大学)
Jang Y W 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[49] Steinbeck L, Richter M, Eschrig H 2001 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 226-230 1011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2953
- PDF下载量: 100
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: