-
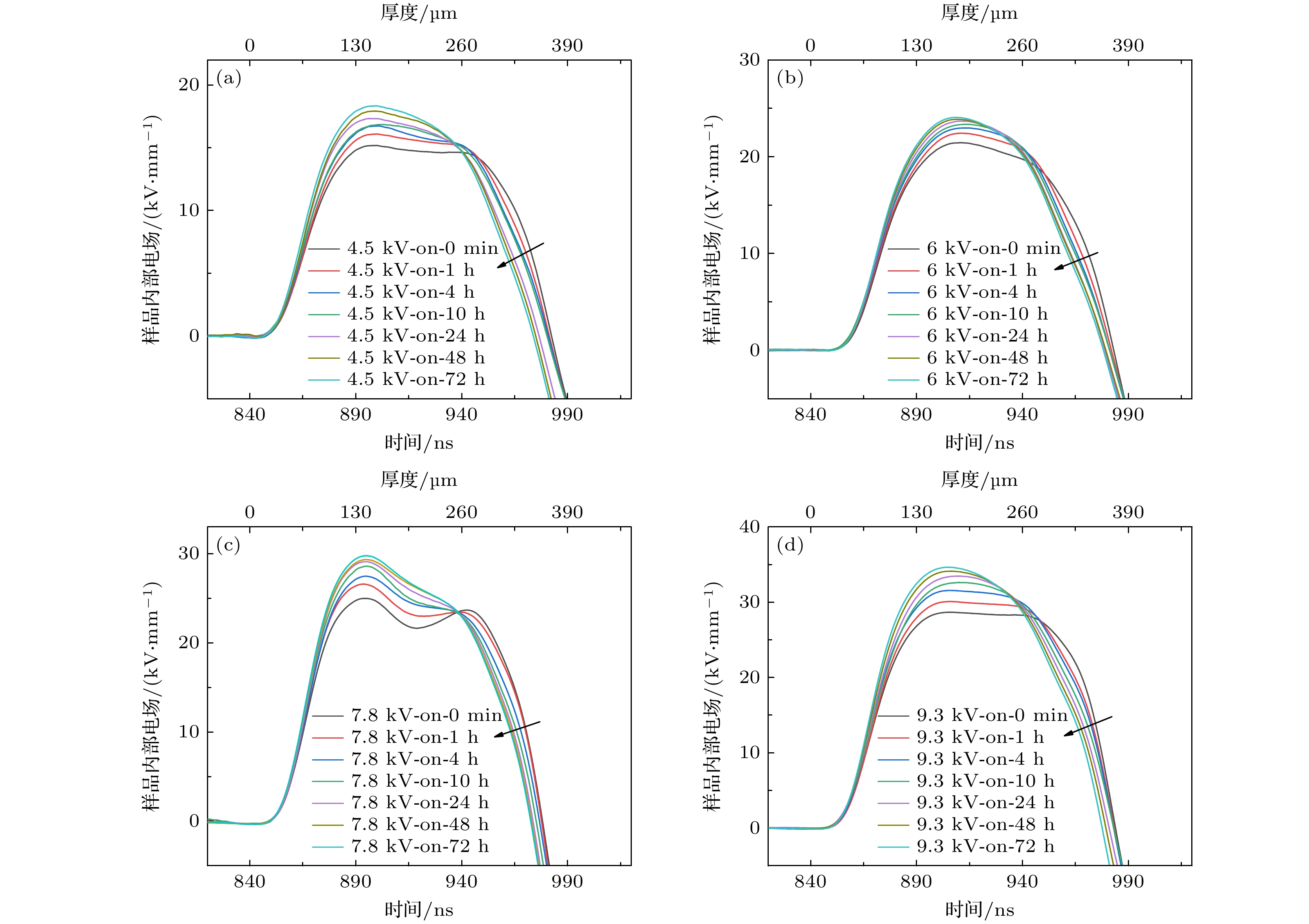
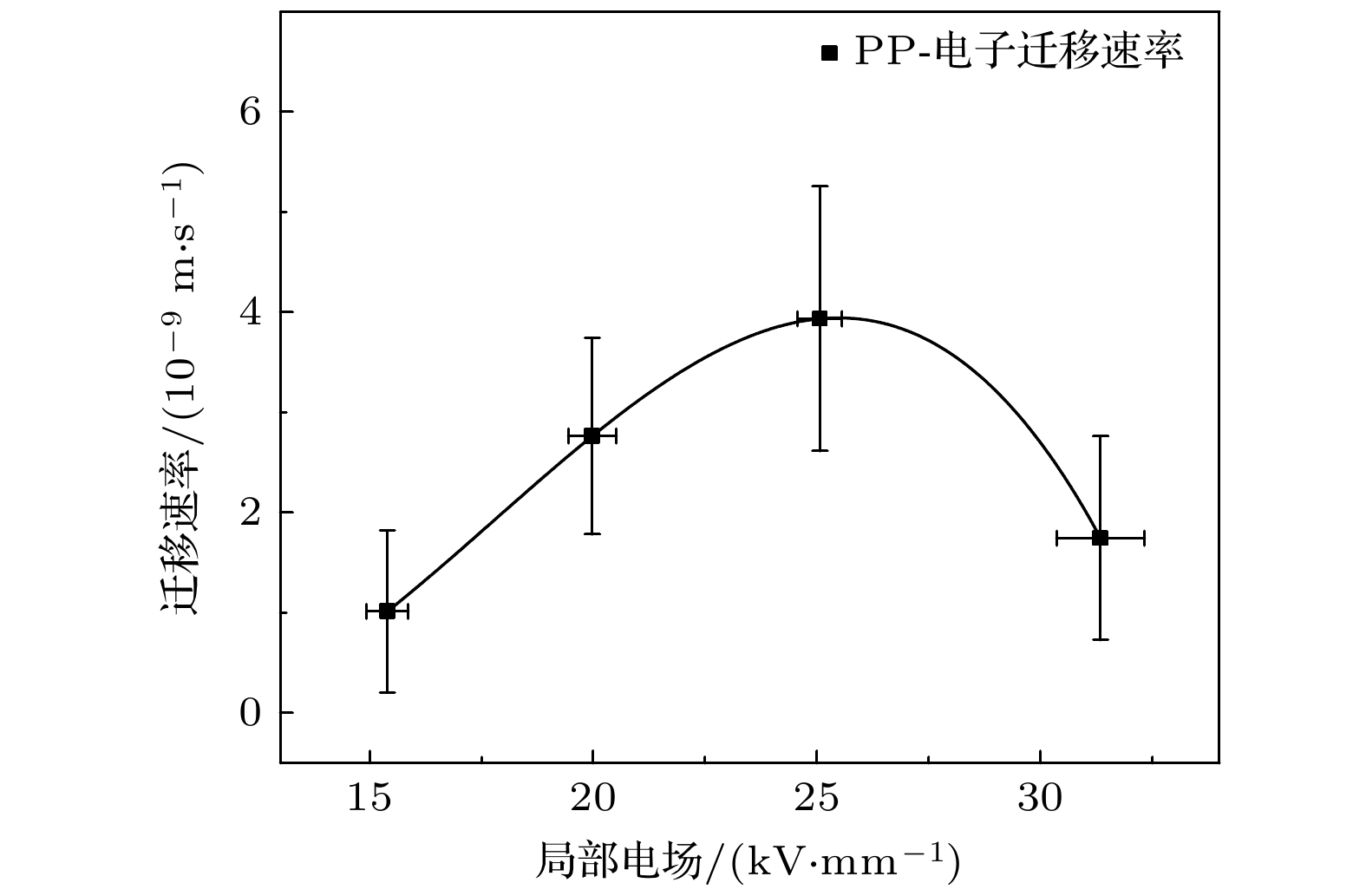
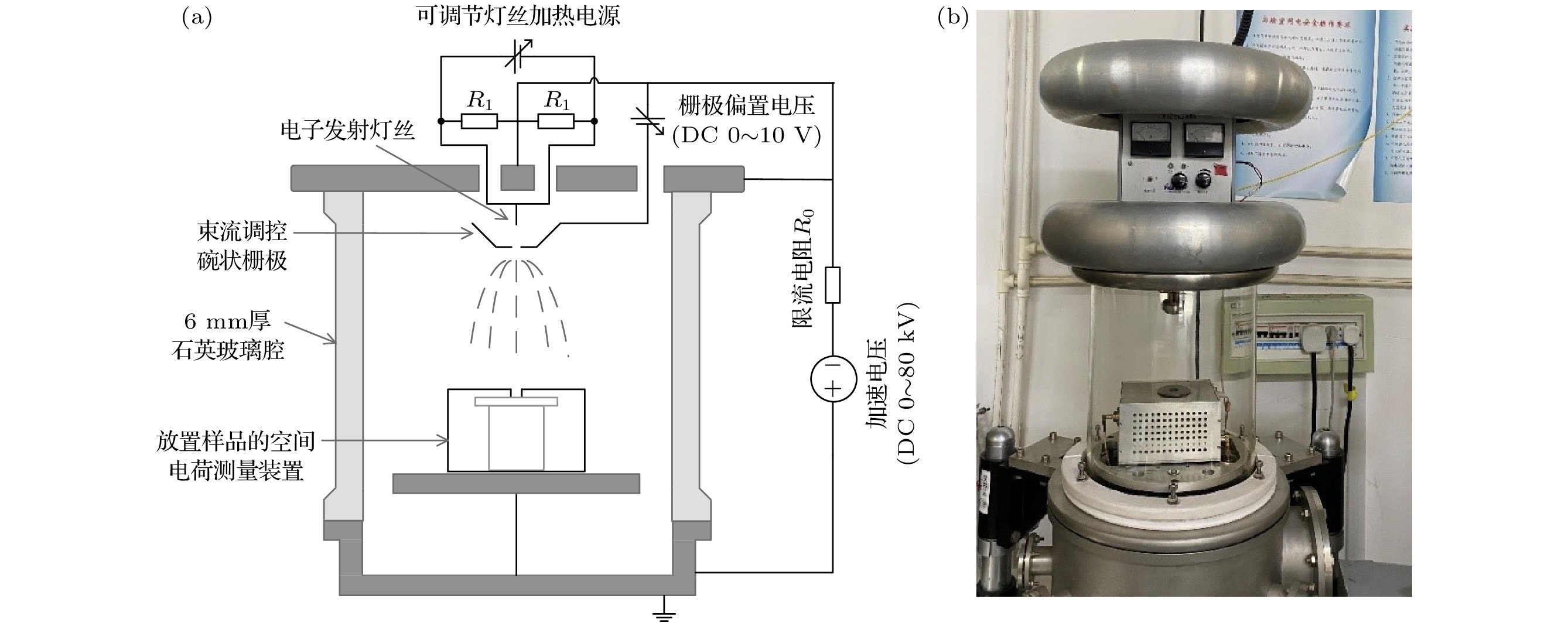
空间电荷包现象是一种特殊的空间电荷现象, 具体表现为空间电荷以包的形态沿着极化电场的方向进行迁移. 目前针对空间电荷包现象的研究还存在一些不足, 研究的对象通常集中在聚乙烯及其交联产物中的正极性空间电荷包. 本文提出了一套用于负极性空间电荷包特性研究的一体化实验系统, 可进行电子束辐照与压电压力波法空间电荷分布实时测量相结合的实验研究, 并简要介绍了该系统的结构与功能. 该系统适用于不同厚度范围的各类绝缘电介质样品在不同电场下的实验研究. 本文使用该实验系统初步研究了在不同外加电场(15, 20, 25, 30 kV/mm)下聚丙烯与聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯样品内负极性空间电荷包的迁移行为, 并从实验结果中提取了负极性载流子(电子)的迁移特性. 聚丙烯与聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯样品中电子的迁移速率均存在随着电场的增加而减小的负微分迁移率现象, 聚丙烯中该现象出现的阈值电场约为26.0 kV/mm, 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯中该现象出现的阈值电场约为19.5 kV/mm, 消失的截止电场约为27.5 kV/mm.The space charge packet is a special sort of space charge phenomenon that is characterized by the migration of aggregated space charge in the form of a packet in the sample. Currently, most of the experimental and simulation studies on the generation and migration of space charge packets focus on the space charge packets with positive polarity in polyethylene and their cross-linking products, while the characteristics of the space charge packets with negative polarity still need studying. This paper presents an integrated experimental system for studying space charge packet with negative polarity, which enables experimental studies combining electron beam irradiation technique and real-time space charge distribution measurement. The beam flux for electron beam irradiation is controlled by a metal grid with an optical fiber-electric relay, and the space charge distribution measurement is performed by the piezo- pressure wave propagation method. The system achieves a withstand voltage value of 17 kV and a measuring resolution of 25 ns for space charge distribution measurement and is suitable for experimental studies of various material samples with different thickness ranges under different electric fields. In this work, the migration behaviors of space charge packets with negative polarity in polypropylene (PP) and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) samples under different applied electric fields (15, 20, 25, 30 kV/mm) are studied by using the experimental system. The relationship between the migration properties of carriers with negative polarity (electrons) and the electric field can be extracted from the experimental results. The “negative differential mobility” phenomenon is found for both materials, i.e. the migration rate decreases with the increase of the electric field. The threshold electric field for the “negative differential mobility” phenomenon of electrons in PP sample is about 26.0 kV/mm while the threshold electric field for the “negative differential mobility” phenomenon of electrons in PMMA sample is 19.5 kV/mm, and the phenomenon disappears at an electric field of 27.5 kV/mm. The electric field where the "negative differential mobility" phenomenon of electrons appears and disappears in different materials can be extracted by using the experimental system proposed in this paper.
[1] 杜伯学, 韩晨磊, 李进, 李忠磊 2019 电工技术学报 34 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du B X, Han C L, Li J, Li Z L 2019 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 34 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 屠德民, 王霞, 吕泽鹏, 吴锴, 彭宗仁 2012 61 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tu D M, Wang X, Lü Z P, Wu K, Peng Z R 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang Y W, Lewiner J 1996 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 3 778
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hozumi N, Suzuki H 1994 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1 1068
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Matsui K, Tanaka Y, Takada T, Fukao T, Fukunaga K, Maeno T, Alison J M 2005 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 12 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 夏俊峰, 张冶文, 郑飞虎, 雷清泉 2009 58 8529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xia J F, Zhang Y W, Zheng F H, Lei Q Q 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zheng F H, Zhang Y W, Gong B, Zhu J W, Wu C S 2005 Sci. China Ser. E: Technol. Sci. 48 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kon H, Suzuoki Y, Mizutani T, Ieda M, Yoshifuji N 1996 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 3 380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hozumi N, Takeda T, Suzuki H, Okamoto T 1998 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 5 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fabiani D, Montanari G, Dissado L, Laurent C, Teyssedre G 2009 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 16 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhao J, Chen G, Lewin P L 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 112 034116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 夏俊峰, 张冶文, 郑飞虎, 雷清泉 2010 59 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xia J F, Zhang Y W, Zheng F H, Lei Q Q 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xia J F, Zhang Y W, Zheng F H, An Z L, Lei Q Q 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 张冶文, 赵晖, 郭世忠, 郑飞虎, 安振连 2016 电工技术学报 31 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y W, Zhao H, Guo Sh Z, Zheng F H, An Z L 2016 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 31 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 金维芳 1997 电介质物理学 (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第116页
Jin W F 1997 Dielectric Physics (Beijing: China Machine Press) p116
[16] 郑飞虎, 张冶文, 吴长顺, 李吉晓, 夏钟福 2003 52 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng F H, Zhang Y W, Wu C S, Li J X, Xia Z F 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Weber K H 1963 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 25 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ieda M 1984 IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. EI-19 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 夏钟福 2001 驻极体 (北京: 科学出版社) 第199—206页
Xia Z F 2001 Electret (Beijing: China Science Press) pp199–206
[20] Jones J P, Llewellyn J P, Lewis T J 2005 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 12 951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen G, Zhao J 2011 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44 212001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 杜伯学, 韩晨磊, 李进, 李忠磊 2019 电工技术学报 34 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du B X, Han C L, Li J, Li Z L 2019 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 34 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 屠德民, 王霞, 吕泽鹏, 吴锴, 彭宗仁 2012 61 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tu D M, Wang X, Lü Z P, Wu K, Peng Z R 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 017104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang Y W, Lewiner J 1996 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 3 778
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hozumi N, Suzuki H 1994 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1 1068
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Matsui K, Tanaka Y, Takada T, Fukao T, Fukunaga K, Maeno T, Alison J M 2005 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 12 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 夏俊峰, 张冶文, 郑飞虎, 雷清泉 2009 58 8529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xia J F, Zhang Y W, Zheng F H, Lei Q Q 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zheng F H, Zhang Y W, Gong B, Zhu J W, Wu C S 2005 Sci. China Ser. E: Technol. Sci. 48 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kon H, Suzuoki Y, Mizutani T, Ieda M, Yoshifuji N 1996 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 3 380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hozumi N, Takeda T, Suzuki H, Okamoto T 1998 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 5 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fabiani D, Montanari G, Dissado L, Laurent C, Teyssedre G 2009 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 16 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhao J, Chen G, Lewin P L 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 112 034116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 夏俊峰, 张冶文, 郑飞虎, 雷清泉 2010 59 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xia J F, Zhang Y W, Zheng F H, Lei Q Q 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xia J F, Zhang Y W, Zheng F H, An Z L, Lei Q Q 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 张冶文, 赵晖, 郭世忠, 郑飞虎, 安振连 2016 电工技术学报 31 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y W, Zhao H, Guo Sh Z, Zheng F H, An Z L 2016 Trans. Chin. Electrotech. Soc. 31 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 金维芳 1997 电介质物理学 (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第116页
Jin W F 1997 Dielectric Physics (Beijing: China Machine Press) p116
[16] 郑飞虎, 张冶文, 吴长顺, 李吉晓, 夏钟福 2003 52 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng F H, Zhang Y W, Wu C S, Li J X, Xia Z F 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Weber K H 1963 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 25 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ieda M 1984 IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. EI-19 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 夏钟福 2001 驻极体 (北京: 科学出版社) 第199—206页
Xia Z F 2001 Electret (Beijing: China Science Press) pp199–206
[20] Jones J P, Llewellyn J P, Lewis T J 2005 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 12 951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen G, Zhao J 2011 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44 212001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3508
- PDF下载量: 103
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: