-
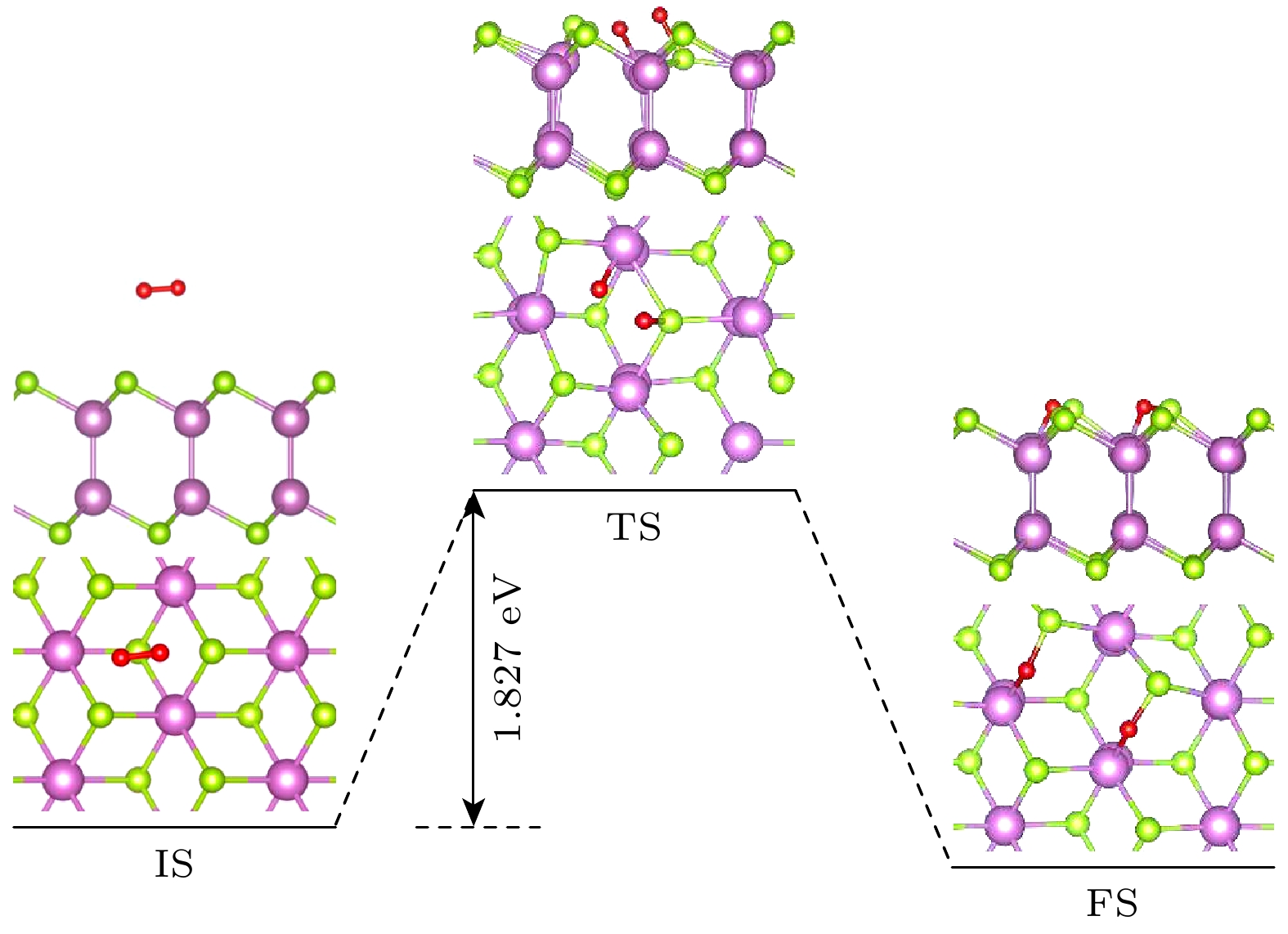
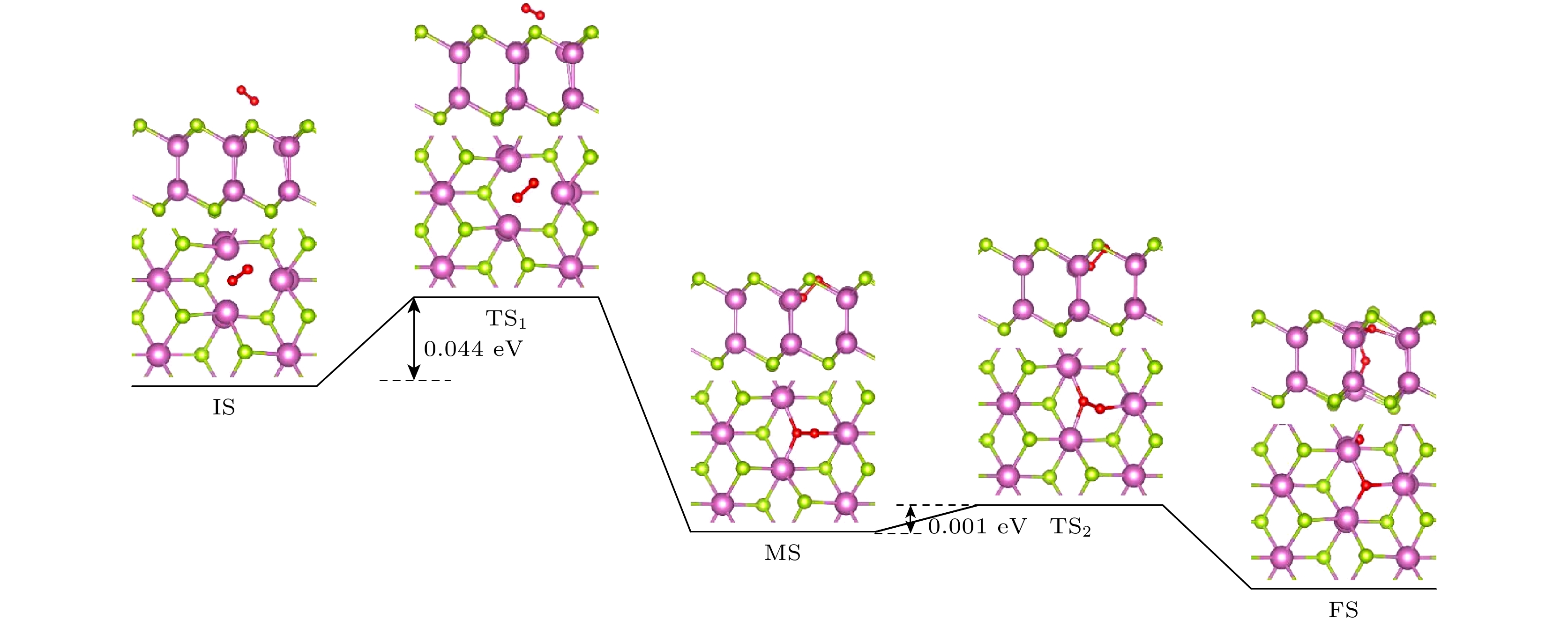
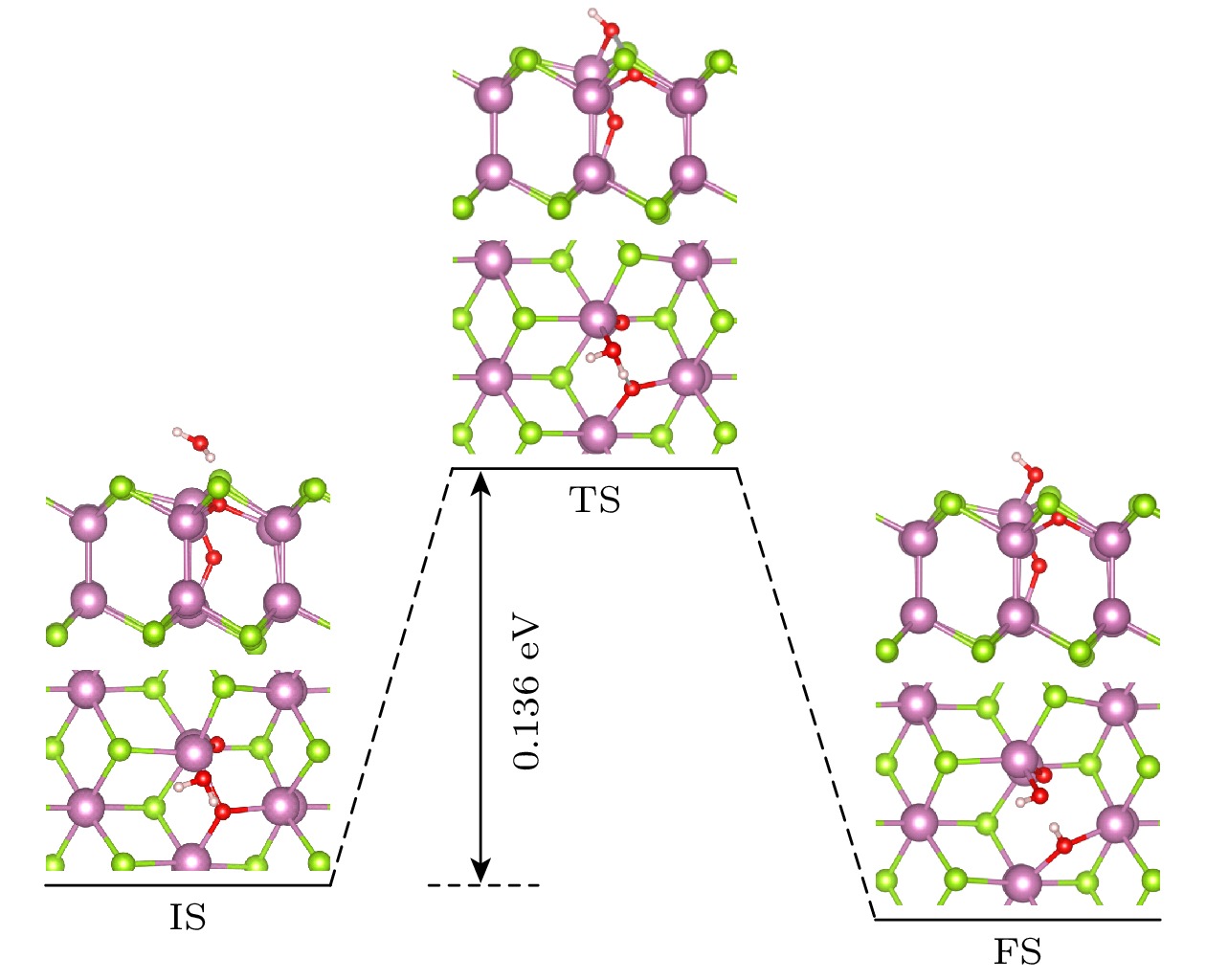
二维InSe半导体材料由于其优异的电学性能以及适中可调的带隙等优点, 引起了研究者的关注. 材料中的空位缺陷不仅影响材料的光电学特性, 还影响材料的环境稳定性. 相比于InSe材料中的其他相, δ-InSe具有更优异的材料性能, 然而关于对该材料环境稳定性影响的研究未见报道. 本文基于密度泛函理论, 系统研究了O2环境下二维δ-InSe材料的稳定性问题. 结果表明: 1)在O2环境下, 完美δ-InSe表面具有良好的惰性和稳定性, O2分子在其表面从物理吸附到解离吸附需要克服1.827 eV的势垒; 2) Se空位(VSe)的存在则会促进δ-InSe的氧化反应, 被氧化的过程仅需克服0.044 eV的势垒, 说明VSe的存在使δ-InSe在O2环境下的稳定性显著下降, 此外被O2分子氧化的δ-InSe单层有利于H2O分子的解离吸附; 3)含有In空位(VIn)的δ-InSe被氧化的速率较慢, O2分子在VIn表面的物理吸附的吸附能和电荷转移与完美表面基本一致, 被氧化的过程需克服1.234 eV的势垒. 这一研究结果将为更好地理解单空位缺陷对δ-InSe单层的氧化行为提供理论指导, 同时为高可靠二维δ-InSe器件的实验制备提供参考.The two-dimensional (2D) semiconductor material of InSe has received much attention due to its excellent electrical properties and moderate adjustable bandgap. The vacancy defects in the material affect not only the optical and electrical properties, but also the environmental stability. Compared with other phases in InSe materials, δ-InSe has superior material properties, however, the effect of environment on this material stabilityhas not been reported. In this work, we systematically investigate the stability of 2D δ-InSe material under oxygen environment based on density functional theory. The results are shown below. Firstly, in an oxygen environment, the perfect δ-InSe surface exhibits good inertness and stability, for O2 molecules need to overcome an exceptionally high energy barrier of 1.827 eV from physical adsorption to chemical adsorption on its surface. Secondly, the presence of Se vacancies (VSe) promotes the oxidation reaction of δ-InSe, which only requires overcoming a low energy barrier of 0.044 eV. This suggests that the stability of δ-InSe in an oxygen environment is significantly reduced because of the presence of VSe. The O2 molecules oxidized δ-InSe monolayer is beneficial to the dissociation and adsorption of H2O molecules. Finally, the oxidation rate of δ-InSe with In vacancies (VIn) is slower, with the adsorption energy and charge transfer involved in the physical adsorption of O2 molecules on the VIn surface being similar to those on a perfect surface. The oxidation process needs to overcome a higher energy barrier of 1.234 eV. The findings of this study will provide theoretical guidance for better understanding the oxidation behavior of single vacancy defects in monolayer δ-InSe, and reference for experimental preparation of high-reliability 2D δ-InSe devices.
-
Keywords:
- δ-InSe /
- O2 /
- single vacancy defect /
- stability
[1] Hu Y X, Feng W, Dai M J, Yang H H, Chen X S, Liu G B, Zhang S C, Hu P A 2018 Semicond. Sci. Technol. 33 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sucharitakul S, Goble N J, Kumar U R, Sankar R, Bogorad Z A, Chou F C, Chen Y T, Gao X P 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Han G, Chen Z G, Drennan J, Zou J 2014 Small 10 2747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Boukhvalov D W, Gürbulak B, Duman S, Wang L, Politano A, Caputi L S, Chiarello G, Cupolillo A 2017 Nanomaterials 7 372
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hao Q, Yi H, Su H, Wei B, Wang Z, Lao Z, Chai Y, Wang Z, Jin C, Dai J 2019 Nano Lett. 19 2634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sun Y, Li Y, Li T, Biswas K, Patanè A, Zhang L 2020 Adv. Funct. Mater. 30 2001920
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei X, Dong C, Xu A, Li X 2019 Appl. Surf. Sci. 475 487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kistanov A A, Cai Y, Zhou K, Dmitriev S V, Zhang Y W 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi L, Zhou Q, Zhao Y, Ouyang Y, Ling C, Li Q, Wang J 2017 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8 4368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xiao K, Carvalho A, Neto A C 2017 Phys. Rev. B 96 054112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 苗瑞霞, 谢妙春, 程开, 李田甜, 杨小峰, 王业飞, 张德栋 2023 72 123101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Miao R X, Xie M C, Cheng K, Li T T, Yang X F, Wang Y F, Zhang D D 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 123101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Gao J, Li B, Tan J, Chow P, Lu T M, Koratkar N 2016 ACS Nano 10 2628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kc S, Longo R C, Wallace R M, Cho K 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 135301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Guo Y, Zhou S, Bai Y, Zhao J 2017 J. Chem. Phys. 147 104709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tamalampudi S R, Lu Y Y, U R K, Sankar R, Liao C D, Cheng C H, Chou F C, Chen Y T 2014 Nano Lett. 14 2800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hohenberg P, Kohn W 1964 Tech. Phys. 136 B864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kohn W, Sham L J 1965 Tech. Phys. 140 A1133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kresse G, Joubert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wei X, Dong C, Xu A, Li X, MacDonald D D 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 2238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu X, Vargas M, Nayak S, Lotrich V, Scoles G 2001 J. Chem. Phys. 115 8748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘子媛, 潘金波, 张余洋, 杜世萱 2021 70 027301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z Y, Pan J B, Zhang Y Y, Du S X 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 027301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Mortensen J J, Hansen L B, Jacobsen K W 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 035109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Moellmann J, Grimme S 2014 J. Phys. Chem. C 118 7615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mills G, Jónsson H, Schenter G K 1995 Surf. Sci. 324 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kistanov A A, Cai Y, Kripalani D R, Zhou K, Dmitriev S V, Zhang Y W 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 4308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 孙建平, 缪应蒙, 曹相春 2013 62 036301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J P, Liao Y M, Cao X C 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 036301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ma D, Ju W, Tang Y, Chen Y 2017 Appl. Surf. Sci. 426 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ma D, Li T, He C, Lu Z, Lu Z, Yang Z, Wang Y 2017 arXiv: 1705.05140 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci
-
图 1 完美δ-InSe单层的晶体结构、能带结构和态密度图 (a) 完美δ-InSe单层超胞结构(俯视图和侧视图), 绿色代表Se原子, 紫色代表In原子; (b) 完美δ-InSe单层的能带结构, 蓝色实线箭头代表带隙(Eg), 绿色虚线代表费米能级(Ef); (c), (d) 完美δ-InSe单层的TDOS和PDOS
Fig. 1. Crystal structure, band structure, and density of states diagram of perfect δ-InSe monolayer: (a) Supercell structure of perfect δ-InSe monolayer (top view and side view), where green represents Se atoms and purple represents In atoms; (b) band structure of perfect δ-InSe monolaye, where the blue solid arrow represents the band gap (Eg) and the green dashed line represents the Fermi level (Ef); (c), (d) TDOS and PDOS of perfect δ-InSe monolayer.
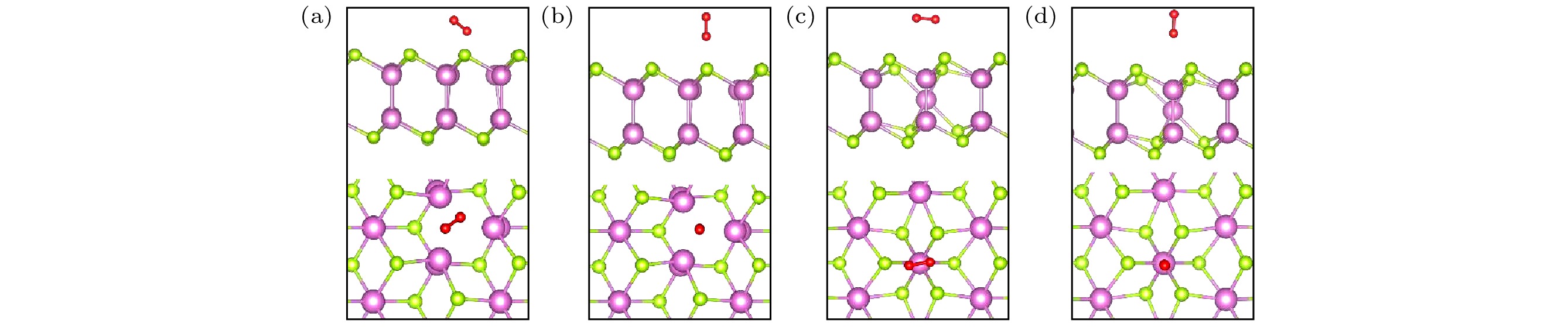
图 2 O2分子在完美δ-InSe单层表面的不同吸附位点(侧视图和俯视图), 红色代表O原子 (a), (e) TIn; (b), (f) TSe2; (c), (g) TB; (d), (h) TSe1
Fig. 2. Different adsorption sites of O2 molecules on the perfect δ-InSe monolayer surface (side view and top view), with red representing O atoms: (a), (e) TIn; (b), (f) TSe2; (c), (g) TB; (d), (h) TSe1.
图 4 δ-InSe-VSe的晶体结构、能带结构和态密度图 (a) δ-InSe-VSe晶体结构(俯视图和侧视图); (b) δ-InSe-VSe的能带结构, 蓝色实线箭头代表带隙(Eg), 绿色虚线代表费米能级(Ef); (c), (d) δ-InSe-VSe单层的TDOS和PDOS
Fig. 4. Crystal structure, band structure, and density of states diagram of δ-InSe-VSe: (a) Crystal structure diagrams of δ-InSe-VSe (top view and side view); (b) band structure of δ-InSe-VSe, where the blue solid arrow represents the band gap (Eg) and the green dashed line represents the Fermi level (Ef); (c), (d) TDOS and PDOS of δ-InSe-VSe.
图 5 δ-InSe-VIn的晶体结构、能带结构和态密度图 (a) δ-InSe-VIn晶体结构(俯视图和侧视图); (b) δ-InSe-VIn的能带结构; (c), (d) δ-InSe-VIn单层的TDOS和PDOS
Fig. 5. Crystal structure, band structure, and density of states diagram of δ-InSe-VIn: (a) Crystal structure diagrams of δ-InSe-VIn (top view and side view); (b) band structure of δ-InSe-VIn; (c), (d) TDOS and PDOS of δ-InSe-VIn.
图 7 O2分子吸附在δ-InSe单层的差分电荷密度, 黄色部分表示电荷积累区域, 蓝色部分表示电荷损耗区域(等值面设为1.5×10–4 e/Bohr3) (a) O2分子在完美δ-InSe的差分电荷密度; (b) O2分子在δ-InSe-VSe的差分电荷密度; (c) O2分子在δ-InSe-VIn的差分电荷密度
Fig. 7. Differential charge density of O2 adsorbed on δ-InSe monolayer, where yellow regions indicate charge accumulation and blue regions indicate charge depletion (the equivalent surface is set to 1.5×10–4 e/Bohr3) : (a) Differential charge density of O2 adsorbed on perfect δ-InSe; (b) differential charge density of O2 adsorbed on δ-InSe-VSe; (c) differential charge density of O2 adsorbed on δ-InSe-VIn.
表 1 O2分子在完美δ-InSe单层表面吸附的吸附能($ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}} $)和吸附距离($ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}} $)
Table 1. Adsorption energy ($ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}} $) and adsorption distance ($ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}} $) of O2 molecules on perfect δ-InSe monolayer surface.
δ-InSe TIn site TSe2 site TB site TSe1 site $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ O2∥δ-InSe 3.19 –0.078 3.30 –0.076 3.59 –0.064 3.65 –0.049 O2⊥δ-InSe 3.46 –0.070 3.82 –0.060 4.17 –0.047 4.19 –0.036 表 2 O2分子在δ-InSe-VSe和δ-InSe-VIn表面的吸附能($ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}} $)和吸附距离($ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}} $)
Table 2. Adsorption energy ($ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}} $) and adsorption distance ($ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}} $) of O2 molecules on δ-InSe-VSe and δ-InSe-VIn surfaces, respectively.
TVSe-1 site TVSe-2 site TVIn-1 site TVIn-2 site $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ $ {h}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{e}}}/{\mathrm{\AA }} $ $ {E}_{{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{d}}}/{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{V}} $ 1.83 –0.152 2.65 –0.097 2.63 –0.093 2.97 –0.077 -
[1] Hu Y X, Feng W, Dai M J, Yang H H, Chen X S, Liu G B, Zhang S C, Hu P A 2018 Semicond. Sci. Technol. 33 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sucharitakul S, Goble N J, Kumar U R, Sankar R, Bogorad Z A, Chou F C, Chen Y T, Gao X P 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Han G, Chen Z G, Drennan J, Zou J 2014 Small 10 2747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Boukhvalov D W, Gürbulak B, Duman S, Wang L, Politano A, Caputi L S, Chiarello G, Cupolillo A 2017 Nanomaterials 7 372
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hao Q, Yi H, Su H, Wei B, Wang Z, Lao Z, Chai Y, Wang Z, Jin C, Dai J 2019 Nano Lett. 19 2634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sun Y, Li Y, Li T, Biswas K, Patanè A, Zhang L 2020 Adv. Funct. Mater. 30 2001920
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei X, Dong C, Xu A, Li X 2019 Appl. Surf. Sci. 475 487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kistanov A A, Cai Y, Zhou K, Dmitriev S V, Zhang Y W 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi L, Zhou Q, Zhao Y, Ouyang Y, Ling C, Li Q, Wang J 2017 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8 4368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xiao K, Carvalho A, Neto A C 2017 Phys. Rev. B 96 054112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 苗瑞霞, 谢妙春, 程开, 李田甜, 杨小峰, 王业飞, 张德栋 2023 72 123101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Miao R X, Xie M C, Cheng K, Li T T, Yang X F, Wang Y F, Zhang D D 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 123101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Gao J, Li B, Tan J, Chow P, Lu T M, Koratkar N 2016 ACS Nano 10 2628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kc S, Longo R C, Wallace R M, Cho K 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 135301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Guo Y, Zhou S, Bai Y, Zhao J 2017 J. Chem. Phys. 147 104709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tamalampudi S R, Lu Y Y, U R K, Sankar R, Liao C D, Cheng C H, Chou F C, Chen Y T 2014 Nano Lett. 14 2800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hohenberg P, Kohn W 1964 Tech. Phys. 136 B864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kohn W, Sham L J 1965 Tech. Phys. 140 A1133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kresse G, Joubert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wei X, Dong C, Xu A, Li X, MacDonald D D 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 2238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu X, Vargas M, Nayak S, Lotrich V, Scoles G 2001 J. Chem. Phys. 115 8748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘子媛, 潘金波, 张余洋, 杜世萱 2021 70 027301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z Y, Pan J B, Zhang Y Y, Du S X 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 027301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Mortensen J J, Hansen L B, Jacobsen K W 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 035109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Moellmann J, Grimme S 2014 J. Phys. Chem. C 118 7615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Mills G, Jónsson H, Schenter G K 1995 Surf. Sci. 324 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kistanov A A, Cai Y, Kripalani D R, Zhou K, Dmitriev S V, Zhang Y W 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 4308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 孙建平, 缪应蒙, 曹相春 2013 62 036301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J P, Liao Y M, Cao X C 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 036301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ma D, Ju W, Tang Y, Chen Y 2017 Appl. Surf. Sci. 426 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ma D, Li T, He C, Lu Z, Lu Z, Yang Z, Wang Y 2017 arXiv: 1705.05140 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci
计量
- 文章访问数: 3766
- PDF下载量: 49
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: