-
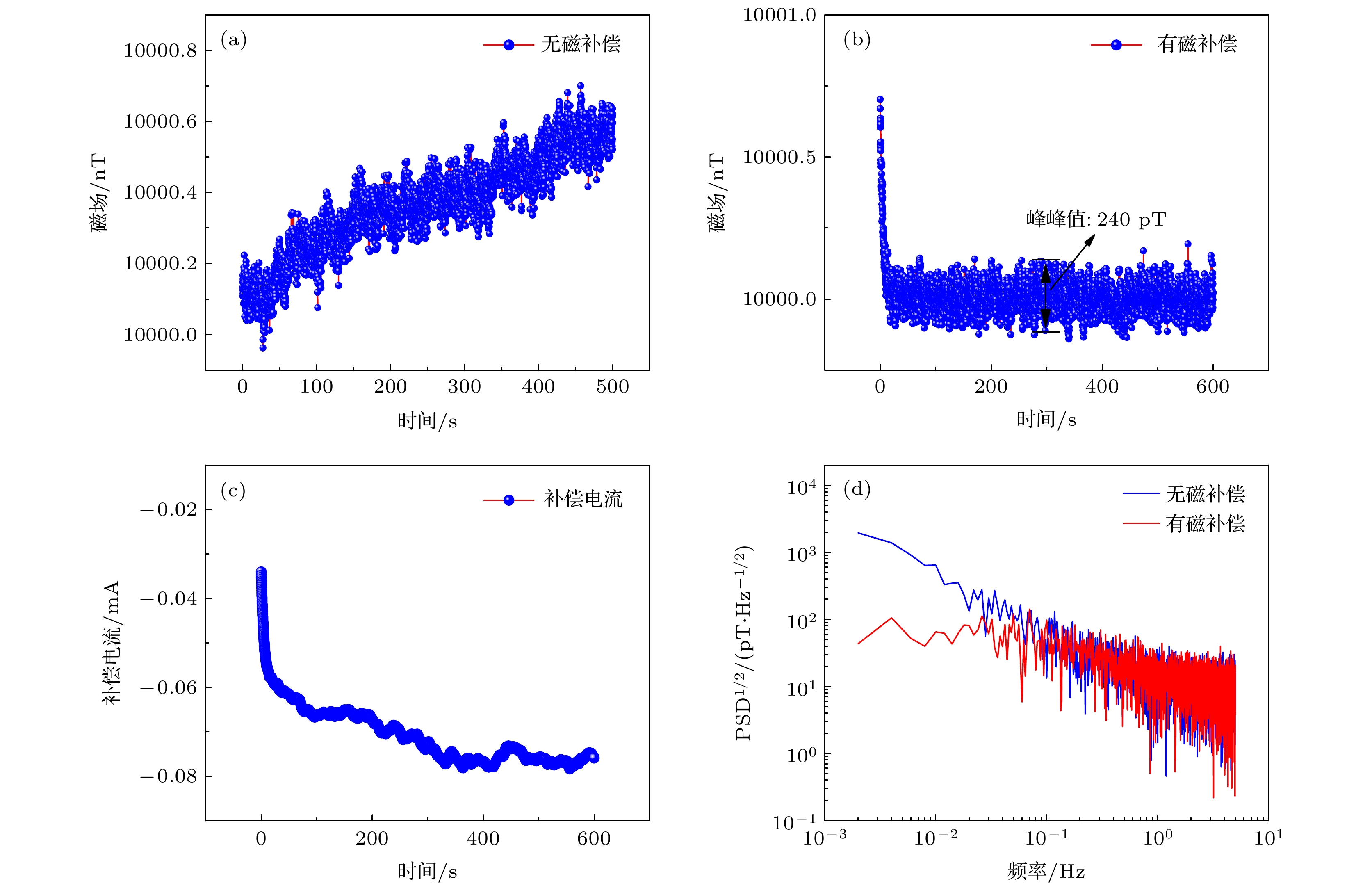
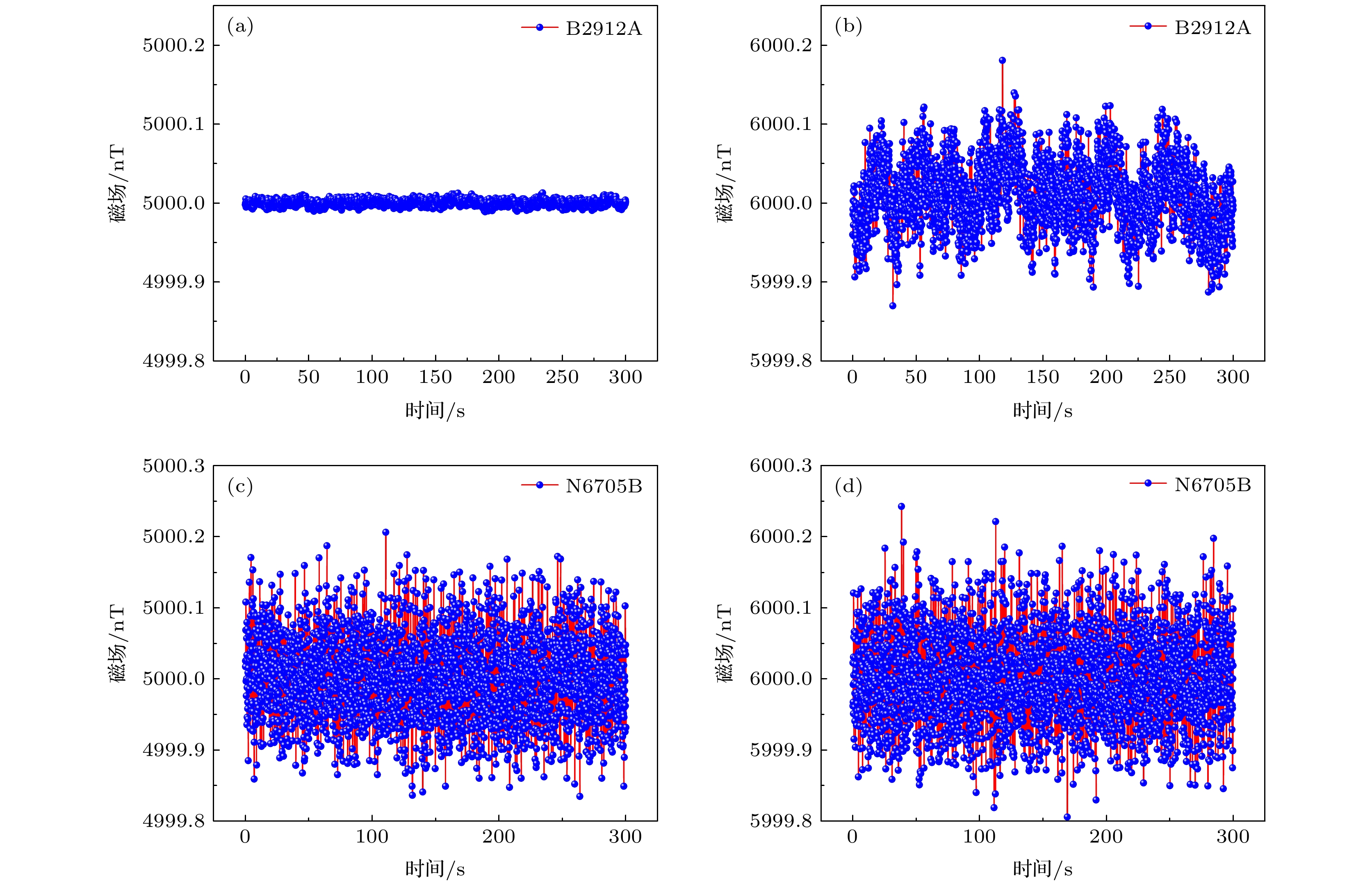
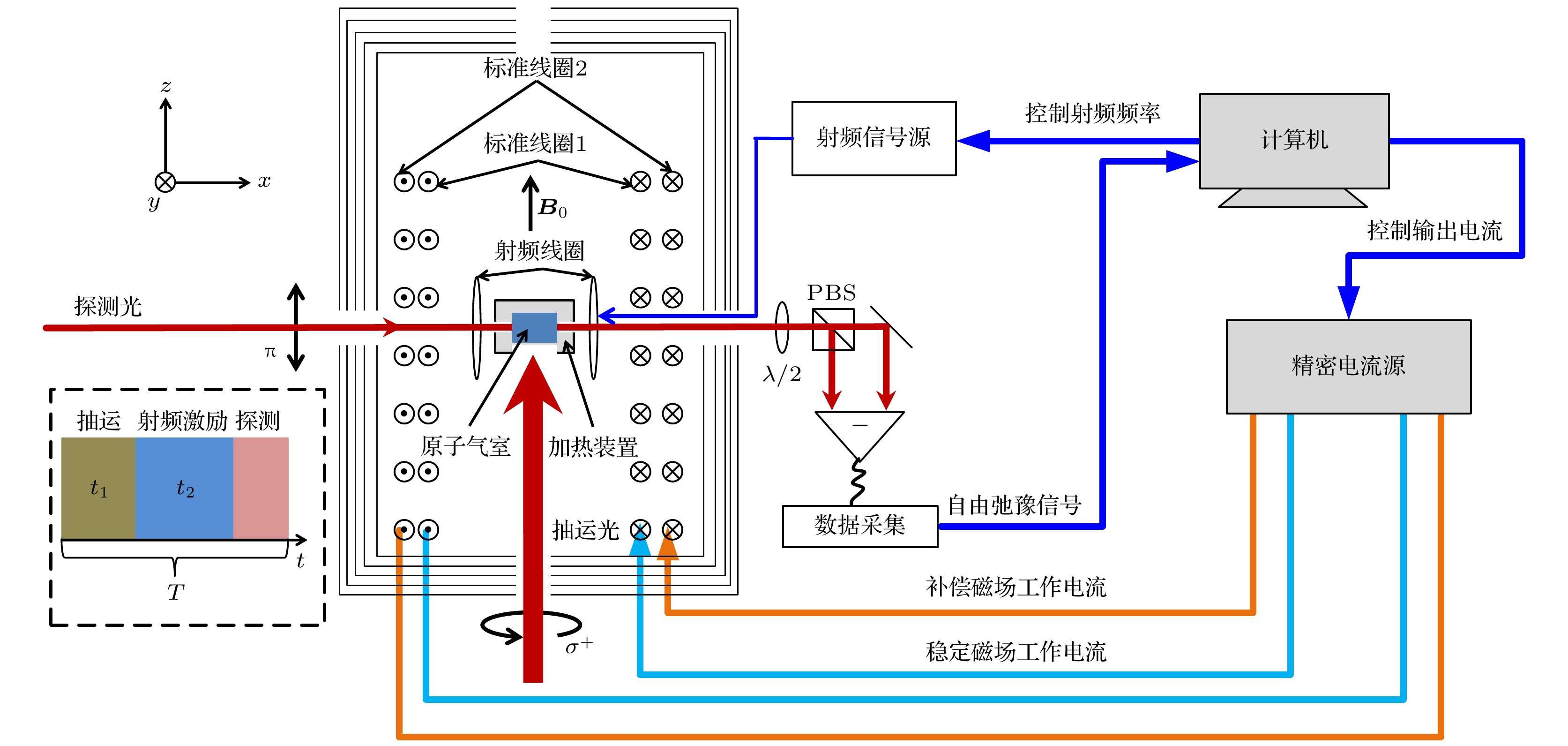
The stable and reproducible magnetic field generated by a precision current source and a coil is usually used to calibrate the sensitivity of an atomic magnetometer. The noise of the current source directly determines the noise of the magnetic field. Therefore a highly sensitive atomic magnetometer can be used to measure the noise of the current source. In this paper, a pump-probe atomic magnetometer is used to measure and estimate the noises of two current sources in a wide range. Firstly, in order to suppress the drift of magnetic field, which is caused by the drift of the current source or the gradual change of the magnetization of magnetic shielding materials, a method of implementing the magnetic compensation by using a precision source B2912A with small current is proposed and realized. The experimental results show that the magnetic compensation significantly suppresses the drift of magnetic field and reduces the amplitude of the power spectral density of magnetic field values to less than 0.1 Hz, but have little effect on the amplitude of the power spectral density of magnetic field values more than 0.1 Hz. Secondly, the relationship between the sensitivity of the pump-probe atomic magnetometer and the noises of two current sources in a wide range is respectively verified experimentally. When the magnetic field varies from 100 nT to 10000 nT, the sensitivity of the pump-probe atomic magnetometer increases stepwise from 0.2 pT/Hz1/2 to 15 pT/Hz1/2 by using a precision source B2912A to generate the magnetic field, while the magnetometer sensitivity is always about 20 pT/Hz1/2 by using a DC power analyzer N6705B to generate the magnetic field. When the magnetic field increases from 5000 nT to 6000 nT, the current resolution of B2912A changes from 100 nA to 1 μA, leading the peak to peak of the measured magnetic field to change from 23 pT to 230 pT. In the same transformation process of the magnetic field, the current resolution of N6705B is always about 2 μA, causing the peak to peak of the measured magnetic field to maintain at 300 pT. The experimental results show that the sensitivity of the pump-probe atomic magnetometer is limited by the noise of the magnetic field, thus the current noise can be estimated by the sensitivity of the pump-probe atomic magnetometer. When the magnetic field is set to 5000 nT, the current of B2912A or N6705B supplied to the coil is 94.8 mA, while the noise of B2912A or N6705B is 22.70 nA/Hz1/2 or 0.39 μA/Hz1/2, respectively. The value of the current noise is about 20% of the value of the current resolution, which will be given a more reasonable explanation by combining the data processing process and the calibration details of current source in the future. Our research is of great significance in calibrating the sensitivity of magnetic sensor, developing the high-precision current sources, and co-developing the magnetic induction metrology and current metrology. [1] Kornack T W, Ghosh R K, Romalis M V 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 230801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Meyer D, Larsen M 2014 Gyroscopy and Navigation 5 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shah V K, Wakai R T 2013 Phys. Med. Biol. 58 8153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Boto E, Holmes N, Legget J, et al. 2018 Nature 555 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Maus S, Sazonova T, Hemant K, Fairhead J D 2007 Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 8 1
[6] Cohen Y, Achache J 1990 J. Geophys. Res. 95 10783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Clem T R 1998 Nav. Eng. J. 110 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Savukov I M, Romalis M V 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 123001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vasilakis G, Brown J M, Kornack T W, Romal M V 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 261801
[10] Miao P X, Zheng W Q, Yang S Y, Wu B, Cheng B, Tu J H, Ke H L, Yang W, Wang J, Cui J Z, Lin Q 2019 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 36 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 杨宝, 缪培贤, 史彦超, 冯浩, 张金海, 崔敬忠, 刘志栋 2020 中国激光 47 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang B, Miao P X, Shi Y C, Feng H, Zhang J H, Cui J Z, Liu Z D 2020 Chin. J. Lasers 47 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘国宾, 孙献平, 顾思洪, 冯继文, 周欣 2012 物理 41 803
Liu G B, Sun X P, Gu S H, Feng J W, Zhou X 2012 Physics 41 803
[13] 顾源, 石荣晔, 王延辉 2014 63 110701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y, Shi R Y, Wang Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 110701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 李楠, 黄凯凯, 陆璇辉 2013 62 133201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li N, Huang K K, Lu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 133201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 缪培贤, 杨世宇, 王剑祥, 廉吉庆, 涂建辉, 杨炜, 崔敬忠 2017 66 160701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Miao P X, Yang S Y, Wang J X, Lian J Q, Tu J H, Yang W, Cui J Z 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 160701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 鄢建强, 崔敬忠, 缪培贤, 杨世宇, 王剑祥, 廉吉庆, 涂建辉 2018 真空与低温 24 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan J Q, Cui J Z, Miao P X, Yang S Y, Wang J X, Lian J Q, Tu J H 2018 Vacuum & Cryogenics 24 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 王晓峰, 韩晓东, 杨敬轩 2007 宇航计测技术 27 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X F, Han X D, Yang J X 2007 Journal of Astronautic Metrology and Measurement 27 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gan Q, Shang J T, Ji Y, Wu L 2017 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88 115009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li X, Shi Y, Xue H B, Ruan Y, Feng Y Y 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li G Z, Xin Q, Geng X X, Liang Z, Liang S Q, Huang G M, Li G X, Yang G Q 2020 Chin. Opt. Lett. 18 031202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shen L, Zhang R, Wu T, Peng X, Yu S, Chen J B, Guo H 2020 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 084701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 磁补偿设计对抽运-检测型原子磁力仪实测灵敏度的影响 (a) 无磁补偿时实测磁场值; (b) 有磁补偿时实测磁场值; (c) 磁补偿时精密电流源输出的补偿电流; (d) 图(a)和(b)中5 min稳定磁场值的功率谱密度
Fig. 3. The influence of the design of magnetic compensation on the sensitivity of pump-probe atomic magnetometer: (a) Magnetic field values without magnetic compensation; (b) magnetic field values with magnetic compensation; (c) compensation current in the process of the magnetic compensation; (d) the power spectral density of the magnetic field values in (a) and (b).
-
[1] Kornack T W, Ghosh R K, Romalis M V 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 230801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Meyer D, Larsen M 2014 Gyroscopy and Navigation 5 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shah V K, Wakai R T 2013 Phys. Med. Biol. 58 8153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Boto E, Holmes N, Legget J, et al. 2018 Nature 555 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Maus S, Sazonova T, Hemant K, Fairhead J D 2007 Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 8 1
[6] Cohen Y, Achache J 1990 J. Geophys. Res. 95 10783
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Clem T R 1998 Nav. Eng. J. 110 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Savukov I M, Romalis M V 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 123001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Vasilakis G, Brown J M, Kornack T W, Romal M V 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 261801
[10] Miao P X, Zheng W Q, Yang S Y, Wu B, Cheng B, Tu J H, Ke H L, Yang W, Wang J, Cui J Z, Lin Q 2019 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 36 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 杨宝, 缪培贤, 史彦超, 冯浩, 张金海, 崔敬忠, 刘志栋 2020 中国激光 47 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang B, Miao P X, Shi Y C, Feng H, Zhang J H, Cui J Z, Liu Z D 2020 Chin. J. Lasers 47 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘国宾, 孙献平, 顾思洪, 冯继文, 周欣 2012 物理 41 803
Liu G B, Sun X P, Gu S H, Feng J W, Zhou X 2012 Physics 41 803
[13] 顾源, 石荣晔, 王延辉 2014 63 110701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu Y, Shi R Y, Wang Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 110701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 李楠, 黄凯凯, 陆璇辉 2013 62 133201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li N, Huang K K, Lu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 133201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 缪培贤, 杨世宇, 王剑祥, 廉吉庆, 涂建辉, 杨炜, 崔敬忠 2017 66 160701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Miao P X, Yang S Y, Wang J X, Lian J Q, Tu J H, Yang W, Cui J Z 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 160701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 鄢建强, 崔敬忠, 缪培贤, 杨世宇, 王剑祥, 廉吉庆, 涂建辉 2018 真空与低温 24 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan J Q, Cui J Z, Miao P X, Yang S Y, Wang J X, Lian J Q, Tu J H 2018 Vacuum & Cryogenics 24 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 王晓峰, 韩晓东, 杨敬轩 2007 宇航计测技术 27 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X F, Han X D, Yang J X 2007 Journal of Astronautic Metrology and Measurement 27 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gan Q, Shang J T, Ji Y, Wu L 2017 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88 115009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li X, Shi Y, Xue H B, Ruan Y, Feng Y Y 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li G Z, Xin Q, Geng X X, Liang Z, Liang S Q, Huang G M, Li G X, Yang G Q 2020 Chin. Opt. Lett. 18 031202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shen L, Zhang R, Wu T, Peng X, Yu S, Chen J B, Guo H 2020 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 084701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6729
- PDF下载量: 102
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: