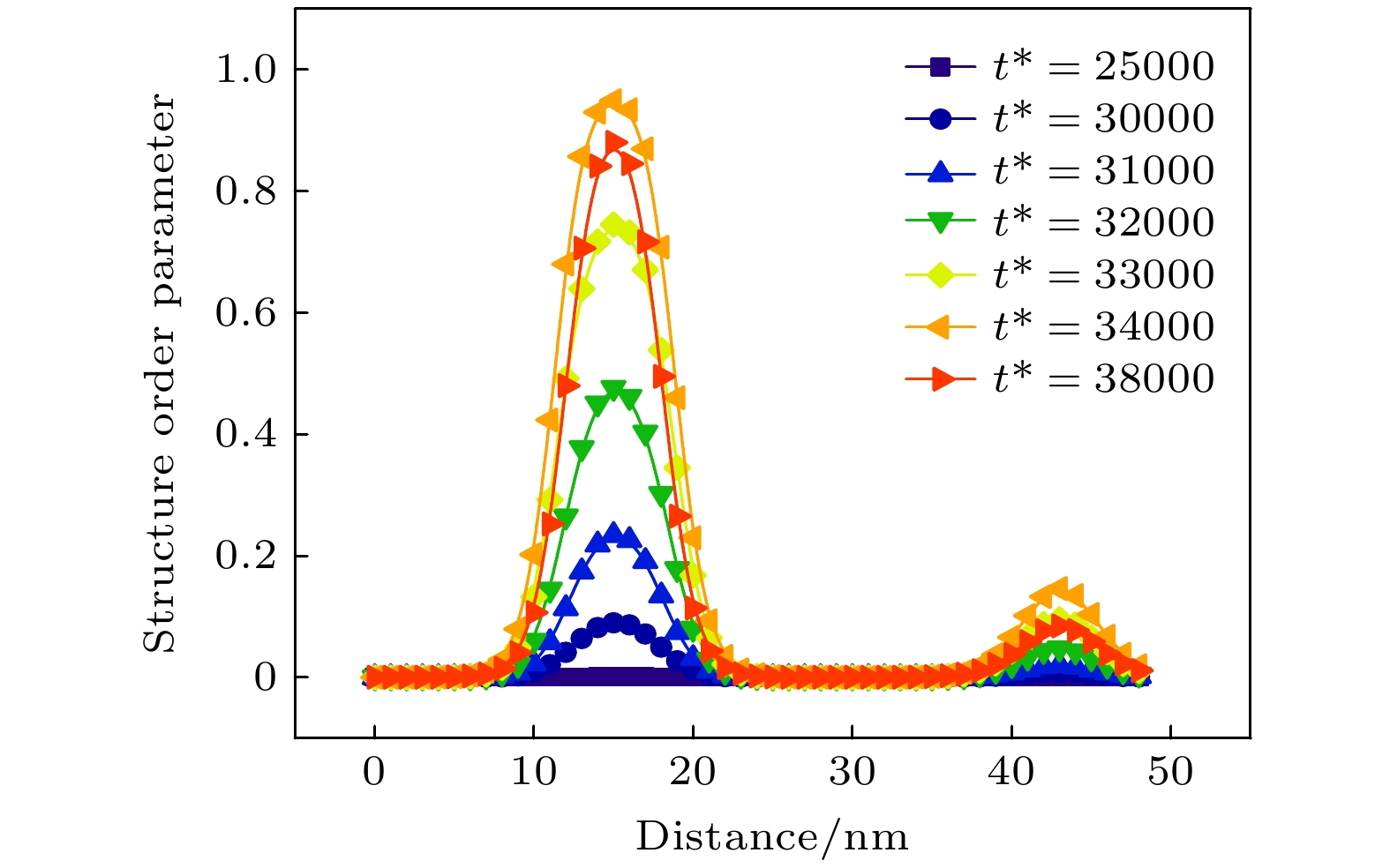
-
基于Ginzburg-Landau理论采用连续相场法模拟了Fe-15%Cu-3%Mn-xAl(质量分数x = 1%, 3%, 5%)合金在873 K等温时效时纳米富Cu析出相沉淀机制及Al含量对富Cu相析出的阻碍效应. 通过计算成分场变量和结构序参数, 研究了富Cu析出相的形貌、颗粒密度、平均颗粒半径、生长和粗化动力学. 研究结果表明: 在时效早期阶段, 纳米富Cu相通过失稳分解机制析出, 由于原子扩散速率存在差异, 从而形成以富Cu相为核心的核壳结构. 随着时效时间延长, 富Cu相析出物结构由体心立方转变为面心立方. 其中Al和Mn原子在富Cu核外偏析形成Al/Mn簇, 可以将其视为阻碍富Cu析出相形成的缓冲层; 在沉淀过程中, 随着Al含量的增大, Al/Mn金属间相促进了缓冲层的生长, 阻碍富Cu析出相的生长和粗化.Low carbon steel plays an important role in many applications due to its high strength. Its high strength comes from the strengthening effect of nano-Cu-rich phase precipitates. In order to effectively adjust the microstructure of Cu-rich phase precipitates and obtain Fe-Cu-based steel with the best properties by adding different alloying elements (Mn, Al), it is necessary to understand the precipitation process of Cu particles. In this paper, based on the Ginzburg-Landau theory, the previous phase field model is modified, and the continuous phase field method is used to simulate the precipitation mechanism of nanometer Cu-rich precipitates and the inhibiting of the effect of Al content on Cu-rich precipitates of Fe-15%Cu-3%Mn-xAl (x = 1%, 3%, 5% mass fraction) alloy at 873 K isothermal aging. Combining with the free energy derived from thermodynamics database, the microstructure evolution corresponds to the real alloy system. By calculating the composition field variables and structural order parameters, the evolution of phase separation and precipitated phase morphology in aging process are simulated. Moreover, the influence law of morphology, quantity density, average particle radius, growth and coarsening of Cu-rich precipitated phase are discussed. The results show that in the early stage of aging process, the nano-Cu-rich phase precipitates through the spinodal decomposition mechanism, and is randomly distributed in the iron matrix. Furthermore, due to the difference in atomic diffusion rate, the core-shell structure with Cu-rich phase as a core is formed. With the aging time extending, the structure of Cu-rich phase precipitates changes from bcc to fcc. Because of the synergistic effect between Al and Cu, the diffusion of Cu is slowed down. Besides, with the Al and Mn atoms precipitating, Al/Mn clusters are segregated around the Cu-rich precipitates, forming the Al/Mn intermetallic core-shell structure, and gradually wrapping the Cu-rich phase uniformly. During the evolution of the precipitation stage, the Al/Mn clusters are isolated around the Cu-rich precipitation phase, forming a gradually uniform Al/Mn intermetallic phase core shell structure covering the Cu-rich phase, which is to hinder the buffer layer from forming in the precipitation stage of the reservoir. In addition, with the Al content increasing, the Al/Mn intermetallic phase promotes the growth of the buffer layer and hinders the Cu-rich precipitate phase from growing and coarsening.
-
Keywords:
- phase field method /
- Fe-Cu alloy /
- Cu-rich precipitation phase /
- coarsening kinetics
[1] Zhu J M, Zhang T L, Yang Y, Liu C T 2019 Acta Mater. 166 560
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Han G, Shang C J, Misra R D K, Xie Z J 2019 Physica B 569 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li B Y, Zhang L, Li C L, Li Q L, Chen J, Shu G G, Weng Y Q, Xu B, Hu S Y, Liu W 2018 J. Nucl. Mater. 507 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li B Y, Hu S Y, Li C L, Li Q L, Chen J, Shu G G, Jr C H, Weng Y Q, Xu B, Liu W 2017 Model. Simul. Mater. Sc. 25 6
[5] Lv G C, Zhang H, He X F, Yang W, Su Y J 2016 Aip Adv. 6 045004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jiao Z B, Luan J H, Miller M K, Chung Y W, Liu C T 2017 Mater. Today 20 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shu S P, Wells P B, Almirall N, Odette G R, Morgan D D 2018 Acta Mater. 157 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Odette G R, Liu C L, Wirth B D 1996 MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive 439 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wen Y R, Hirata A, Zhang Z W, Fujita T, Liu C T, Jiang J H, Chen M W 2013 Acta Mater. 61 2133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Miller M K, Wirth B D, Odette G R 2003 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 353 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Osamura K, Okuda H, Asano K, Furusaka M, Kishida K, Kurosawa F, Uemori R 1994 ISIJ Int. 34 346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 沈琴, 王晓姣, 赵安宇, 何益锋, 方旭磊, 马佳荣, 刘文庆 2016 金属学报 52 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen Q, Wang X J, Zhao A Y, He Y F, Fang X L, Ma J R, Liu W Q 2016 Acta Metall. Sin. 52 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shen Q, Xiong X, Li T, Chen H, Cheng Y M, Liu W Q 2018 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 723 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Vaynman S, Isheim D, Kolli R P, Bhat S P, Seidman D N, Fine M E 2008 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39 363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sun Y Y, Zhao Y H, Zhao B J, Yang W K, Li X L, Hou H 2019 J. Mater. Sci. 54 11263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 赵宝军, 赵宇宏, 孙远洋, 杨文奎, 侯华 2019 金属学报 55 593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B J, Zhao Y H, Sun Y Y, Yang W K, Hou H 2019 Acta Metall. Sin. 55 593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wen Z Q, Zhao Y H, Hou H, Wang B, Han P D 2017 Mater. Design 114 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Huang Z W, Zhao Y H, Hou H, Wang Z, Mu Y Q, Niu X F, Han P D 2011 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 12 2136
[19] 田晓林, 赵宇宏, 田晋忠, 侯华 2018 67 230201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian X L, Zhao Y H, Tian J Z, Hou H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 230201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen L Q 2002 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 32 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhao Y H, Tian X L, Zhao B J, Sun Y Y, Guo H J, Dong M Y, Liu H, Wang X J, Guo Z H, Umar A, Hou H 2018 Sci. Adv. Mater. 10 1793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hou H, Zhao Y H, Zhao Y H 2009 Mater. Sci. Eng. 499 204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kuang W W, Wang H F, Li X, Zhang J B, Zhou Q, Zhao Y H 2018 Acta Mater. 159 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhao Y H, Zhang B, Hou H, Chen W P, Wang M 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang J B, Wang H F, Kuang W W, Zhang Y C, Li S, Zhao Y H, Herlach D M 2018 Acta Mater. 148 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cahn J W 1961 Acta Metal. 9 795
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhao Y H, Wang S, Zhang B, Yuan Y, Guo Q W, Hou H 2019 J. Solid State Chem. 276 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Koyama T, Hashimoto K, Onodera H 2006 Mater. Trans. 47 2765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Koyama T, Onodera H 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Dinsdale A T 1991 Calphad 15 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Bergner D, Khaddour Y 1993 Defect Diffus Forum 6 95
-
图 1 时效温度873 K时Fe-15%Cu-3%Mn-1%Al合金沉淀相三维演化相场模拟 (a1)−(a4) t* = 17000; (b1)−(b4) t* = 18500; (c1)−(c4) t* = 20000; (d1)−(d4) t* = 22500
Fig. 1. Three-dimensional phase-field simulation of precipitation phase of Fe-15%Cu-3%Mn-1%Al alloy when aged at 873 K: (a1)−(a4) t* = 17000; (b1)−(b4) t* = 18500; (c1)−(c4) t* = 20000; (d1)−(d4) t* = 22500.
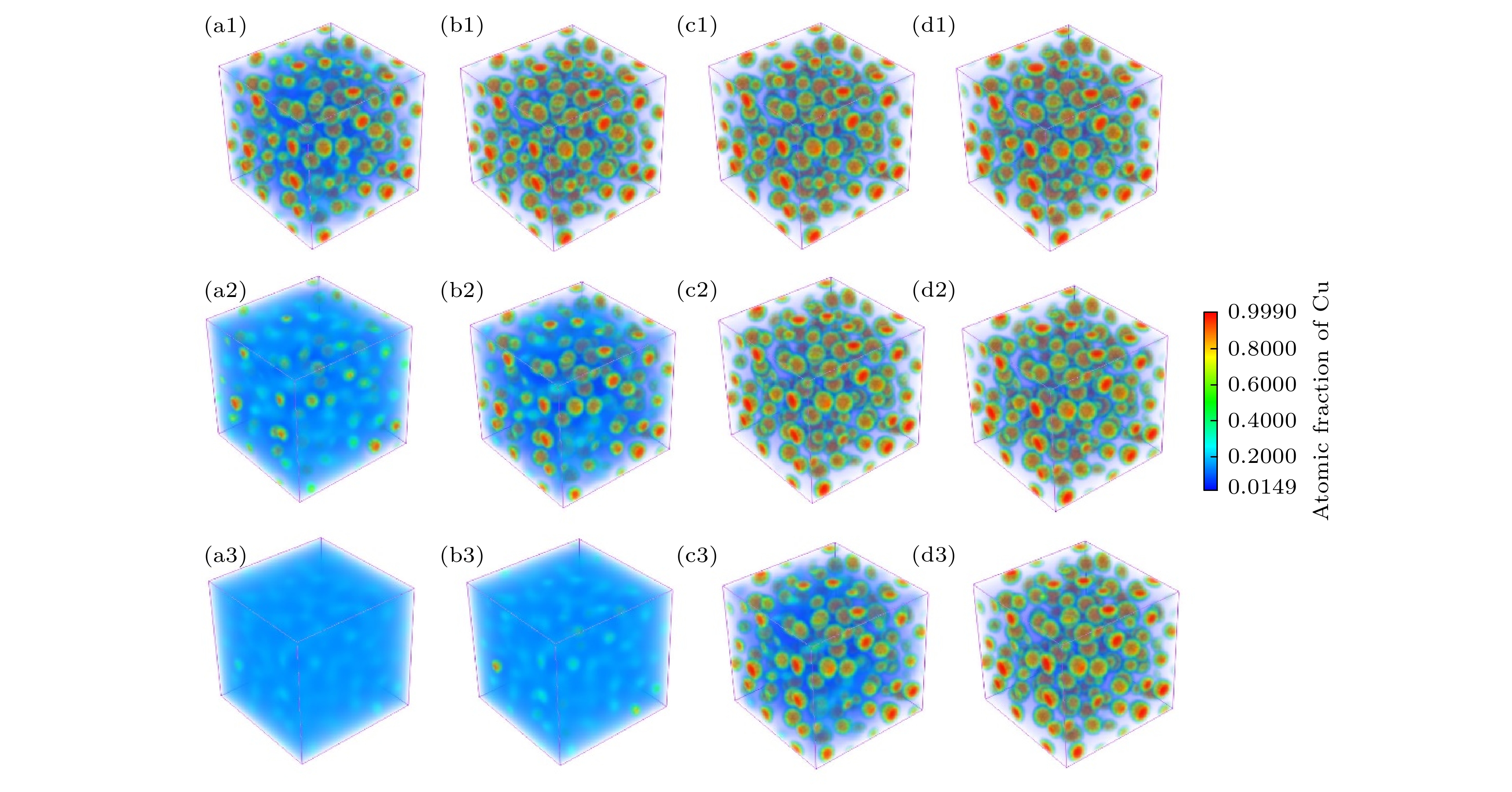
图 3 时效温度为873 K时Fe-15%Cu-3%Mn-xAl合金三维富Cu相演化相场模拟 (a1)−(d1) x = 1%; (a2)−(d2) x = 3%; (a3)−(d3) x = 5%; (a1)−(a3) t* = 21000; (b1)−(b3) t* = 22000; (c1)−(c3) t* = 25000
Fig. 3. Three dimensional evolution diagrams of Cu rich phase in quaternary alloy Fe-15%Cu-3%Mn-xAl alloy aged at 873 K: (a1)−(d1) x = 1%; (a2)−(d2) x = 3%; (a3)−(d3) x = 5%; (a1)−(a3) t* = 21000; (b1)−(b3) t* = 22000; (c1)−(c3) t* = 25000.
Parameter Value Unit $ {k}_{c}, {k}_{\eta } $ ${k}_{c}=5.0\times {10}^{-15}, $ $ {\mathrm{J} \cdot \mathrm{m}}^{2}/{\mathrm{mol}}^{} $ ${k}_{c}=1.0\times {10}^{-15} $ $ {V}_{m} $ $ 7.09\times {10}^{-6} $ $ {\mathrm{m}}^{3}/{\mathrm{mol}}^{} $ T $ 873 $ $ \mathrm{K} $ Y $ 214 $ $ \mathrm{GPa} $ $ {L}_{x}\times {L}_{y}\times {L}_{z} $ $ 64\times 64\times 64 $ $ \mathrm{n}{\mathrm{m}}^{3} $ W $ 5.0\times {10}^{3} $ $ \mathrm{J}/{\mathrm{mol}}^{} $ $ {D}_{i}^{0, \varphi }\left(\varphi =\alpha, \gamma \right) $ ${D}_{\mathrm{Cu} }^{0, \alpha }=4.7\times {10}^{-5},$
${D}_{\mathrm{Cu} }^{0, \gamma }=4.3\times {10}^{-5} $$ {\mathrm{m}}^{2}/{\mathrm{s}}^{} $ ${D}_{\mathrm{Mn} }^{0, \alpha }=1.49\times {10}^{-4}, $
${D}_{\mathrm{Mn} }^{0, \gamma }=1.78\times {10}^{-5} $${D}_{\mathrm{Al} }^{0, \alpha}$[31]$=5.35\times {10}^{-4}, $
$ {D}_{\mathrm{Al} }^{0, \gamma } $[31]$=2.20\times {10}^{-5} $$ {Q}_{i}^{0, \varphi }\left(\varphi =\alpha, \gamma \right) $ ${Q}_{\mathrm{Cu} }^{0, \alpha }=2.44\times {10}^{5}, $
${Q}_{\mathrm{Cu} }^{0, \gamma }=2.80\times {10}^{5} $$ \mathrm{J}/{\mathrm{mol}}^{} $ ${Q}_{\mathrm{Mn} }^{0, \alpha }=2.63\times {10}^{5},$
$ {Q}_{\mathrm{Mn} }^{0, \gamma }=2.64\times {10}^{5} $${Q}_{\mathrm{Al} }^{0, \alpha }$[31]$=2.71\times {10}^{5}, $
${Q}_{\mathrm{Al} }^{0, \gamma } $[31]$=2.67\times {10}^{5} $注: $ {k}_{c}, {k}_{\eta } $, 梯度能量系数; $ {V}_{m} $, 摩尔体积; T, 热力学温度; Y, 平均刚度系数; $ {L}_{x}, {L}_{y}, {L}_{z} $, 沿x, y, z轴的模拟区域宽度; W, 双势阱高度; $ {D}_{i}^{0, \varphi } $, 扩散系数; $ {Q}_{i}^{0, \varphi } $, 热扩散激活能. -
[1] Zhu J M, Zhang T L, Yang Y, Liu C T 2019 Acta Mater. 166 560
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Han G, Shang C J, Misra R D K, Xie Z J 2019 Physica B 569 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li B Y, Zhang L, Li C L, Li Q L, Chen J, Shu G G, Weng Y Q, Xu B, Hu S Y, Liu W 2018 J. Nucl. Mater. 507 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li B Y, Hu S Y, Li C L, Li Q L, Chen J, Shu G G, Jr C H, Weng Y Q, Xu B, Liu W 2017 Model. Simul. Mater. Sc. 25 6
[5] Lv G C, Zhang H, He X F, Yang W, Su Y J 2016 Aip Adv. 6 045004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jiao Z B, Luan J H, Miller M K, Chung Y W, Liu C T 2017 Mater. Today 20 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shu S P, Wells P B, Almirall N, Odette G R, Morgan D D 2018 Acta Mater. 157 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Odette G R, Liu C L, Wirth B D 1996 MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive 439 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wen Y R, Hirata A, Zhang Z W, Fujita T, Liu C T, Jiang J H, Chen M W 2013 Acta Mater. 61 2133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Miller M K, Wirth B D, Odette G R 2003 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 353 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Osamura K, Okuda H, Asano K, Furusaka M, Kishida K, Kurosawa F, Uemori R 1994 ISIJ Int. 34 346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 沈琴, 王晓姣, 赵安宇, 何益锋, 方旭磊, 马佳荣, 刘文庆 2016 金属学报 52 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen Q, Wang X J, Zhao A Y, He Y F, Fang X L, Ma J R, Liu W Q 2016 Acta Metall. Sin. 52 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shen Q, Xiong X, Li T, Chen H, Cheng Y M, Liu W Q 2018 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 723 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Vaynman S, Isheim D, Kolli R P, Bhat S P, Seidman D N, Fine M E 2008 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39 363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sun Y Y, Zhao Y H, Zhao B J, Yang W K, Li X L, Hou H 2019 J. Mater. Sci. 54 11263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 赵宝军, 赵宇宏, 孙远洋, 杨文奎, 侯华 2019 金属学报 55 593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B J, Zhao Y H, Sun Y Y, Yang W K, Hou H 2019 Acta Metall. Sin. 55 593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wen Z Q, Zhao Y H, Hou H, Wang B, Han P D 2017 Mater. Design 114 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Huang Z W, Zhao Y H, Hou H, Wang Z, Mu Y Q, Niu X F, Han P D 2011 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 12 2136
[19] 田晓林, 赵宇宏, 田晋忠, 侯华 2018 67 230201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian X L, Zhao Y H, Tian J Z, Hou H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 230201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen L Q 2002 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 32 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhao Y H, Tian X L, Zhao B J, Sun Y Y, Guo H J, Dong M Y, Liu H, Wang X J, Guo Z H, Umar A, Hou H 2018 Sci. Adv. Mater. 10 1793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hou H, Zhao Y H, Zhao Y H 2009 Mater. Sci. Eng. 499 204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kuang W W, Wang H F, Li X, Zhang J B, Zhou Q, Zhao Y H 2018 Acta Mater. 159 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhao Y H, Zhang B, Hou H, Chen W P, Wang M 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang J B, Wang H F, Kuang W W, Zhang Y C, Li S, Zhao Y H, Herlach D M 2018 Acta Mater. 148 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cahn J W 1961 Acta Metal. 9 795
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhao Y H, Wang S, Zhang B, Yuan Y, Guo Q W, Hou H 2019 J. Solid State Chem. 276 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Koyama T, Hashimoto K, Onodera H 2006 Mater. Trans. 47 2765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Koyama T, Onodera H 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Dinsdale A T 1991 Calphad 15 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Bergner D, Khaddour Y 1993 Defect Diffus Forum 6 95
计量
- 文章访问数: 10904
- PDF下载量: 189
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: