-
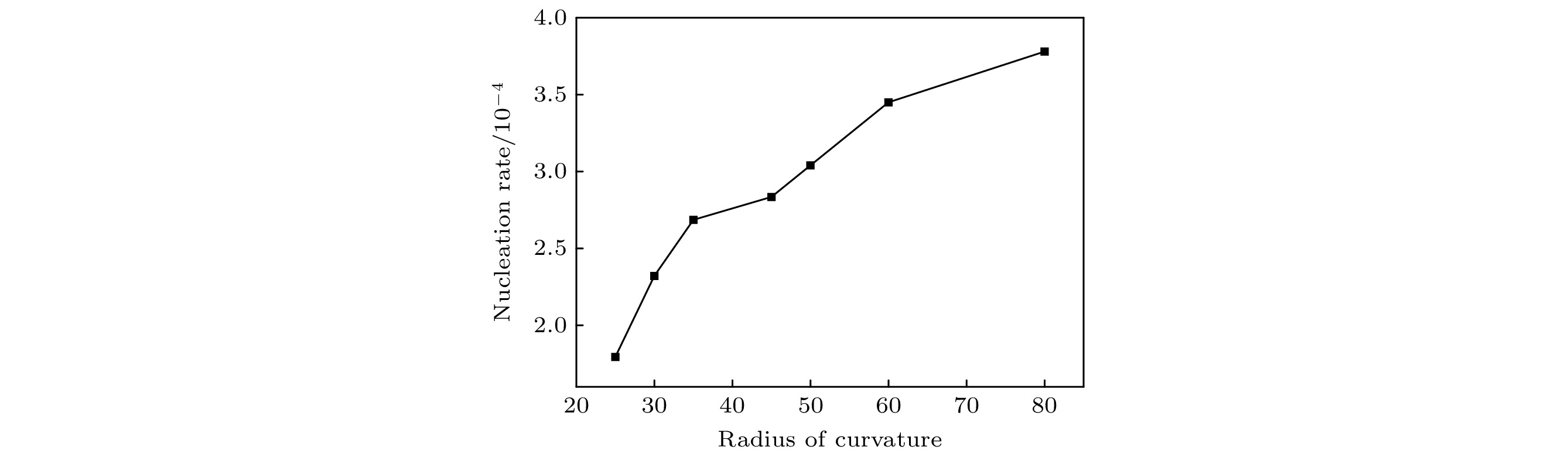
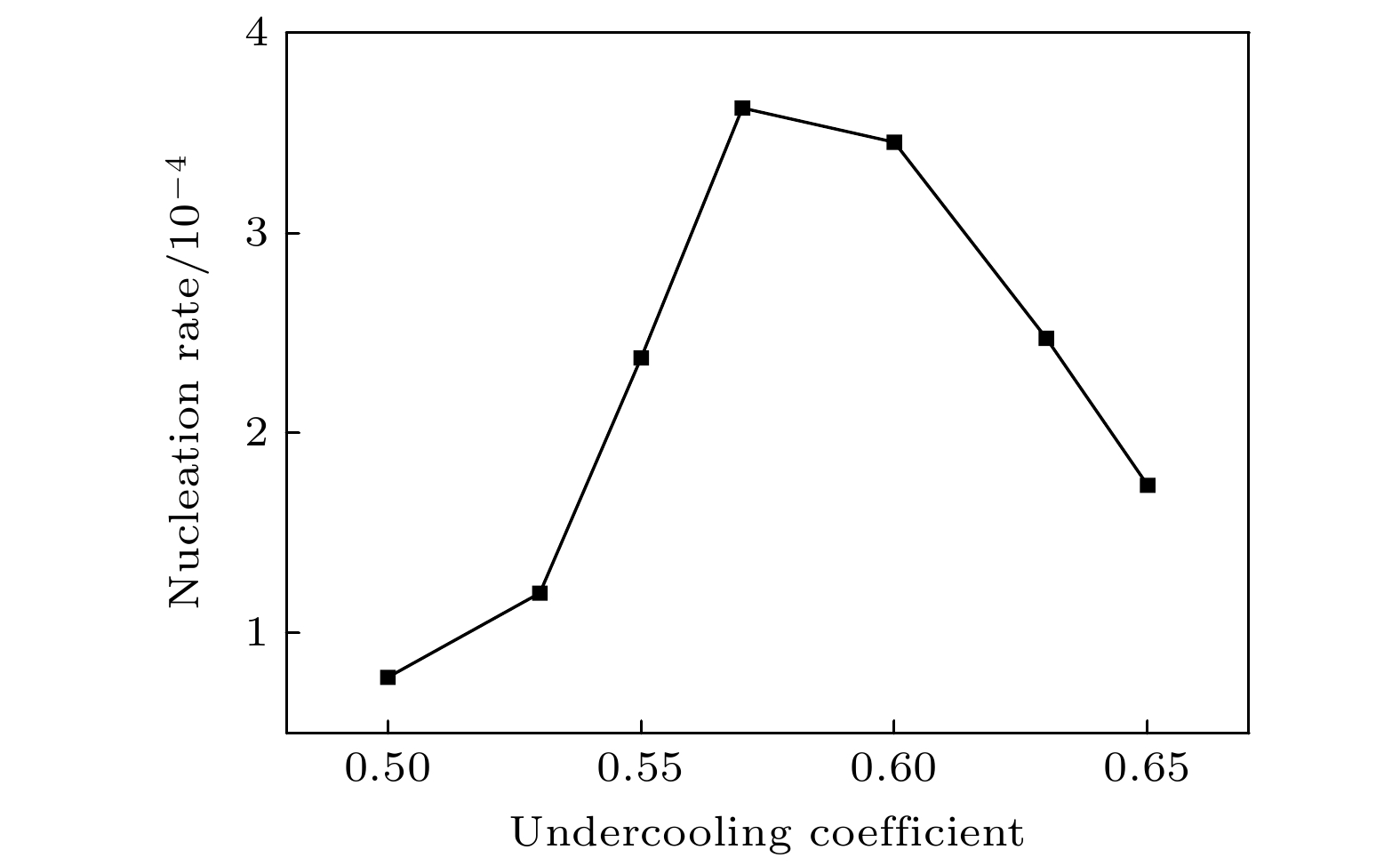
原位反应法制备金属基复合材料具有增强体与基体间无杂质、无污染、颗粒分布均匀等优点, 已成为制备金属基复合材料的一种重要方法, 揭示其动力学机制及规律具有重要的理论及工业价值. 然而, 原位反应过程具有反应时间短、随机发生、温度高等特点, 目前采用原位实验观测其反应过程仍存在较大困难. 本文采用相场法模拟金属熔体内的原位反应过程, 首先建立了能够描述双束金属熔体界面反应形核的相场模型, 并采用该模型模拟了不同参数下相界反应形核过程. 结果表明, 形核率随着曲率半径及噪声强度的增大而增大, 小曲率半径及强噪声条件下新相颗粒尺寸分布更加均匀, 形核率随着过冷度的增大而先增大后减小.The in-situ reaction is an important method of preparing metal matrix composites: it can produce more uniform distribution of the reinforcement particles and more excellent structure of the phase boundary between the particles and the matrix. Therefore, the kinetics of in-situ reaction process deserves to be further studied. However, as the in-situ reaction is a rapid random process under high-temperature condition, it is difficult to observe the reaction process of metal-matrix composite materials experimentally. In this work, we propose a new phase-field model to describe the in-situ reaction process, and investigate the nucleation kinetic processes of in-situ reaction under different physical conditions. We find that the nucleation rate increases with the augment of curvature radius and noise intensity, and the size distribution of the particles is more uniform under the conditions of a small curvature radius and strong noise. With the increase of the undercooling, the nucleation rate first increases and then decreases, which is consistent with the classical nucleation theory.
-
Keywords:
- phase-field model /
- in-situ reaction /
- nucleation /
- phase transformation
[1] 郭明星, 汪明朴, 申坤, 张真, 李树梅 2007 中国有色金属学报 09 1440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo M X, Wang M P, Shen K, Zhang Z, Li S M 2007 Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 09 1440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨滨, 王玉庆, 周本濂 1998 金属学报 01 100
Yang B, Wang Y Q, Zhou B L 1998 Acta. Metall. Sin. 01 100
[3] 张来启, 孙祖庆, 张跃, 杨王玥 1998 金属学报 11 1206
Zhang L Q, Sun Z Q, Zhang Y, Yang W Y 1998 Acta. Metall. Sin. 11 1206
[4] 孙靖 2015 硕士学位论文 (上海: 上海交通大学)
Sun J 2015 M. S. Thesis (Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University) (in Chinese)
[5] Qu L, Zhao N, Zhao H J, Huang M L, Ma H T 2014 Scr. Mater. 72 43
[6] Li H, Jiao L, Huang X P, Li F, Lu S B, Li Y L, Qiao Y P 2021 J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30 7295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jiang Y H, Li D, Liang S H, Zou J T, Liu F 2017 J. Mater. Sci. 52 2957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lan T, Jiang Y H, Zhang X J, Cao F, Liang S H 2021 Int. J. Miner., Metall. Mater. 28 1090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kavousi S, Novak B R, Hoyt J, Moldovan D 2020 Comput. Mater. Sci. 184 854
[10] 方辉, 薛桦, 汤倩玉, 张庆宇, 潘诗琰, 朱鸣芳 2019 68 048102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang H, Xue H, Tang Q Y, Zhang Q Y, Pan S Y, Zhu M F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 048102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 郭春文, 李俊杰, 马渊, 王锦程 2015 金属学报 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C W, Li J J, Ma Y, Wang J C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Z D, Cao Y T, Sun D K, Xing H, Wang J C, Ni Z H 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 028103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 魏雷, 林鑫, 王猛, 黄卫东 2015 64 018013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei L, Lin X, Wang M, Huang W D 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rolchigo M R, LeSar R 2019 Comput. Mater. Sci. 163 148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen L Q 2002 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 32 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Guo C, Wang J C, Li J J, Wang Z J, Huang Y H, Gu J W, Lin X 2018 Acta Mater. 145 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Deng Y Y, Guo C, Wang J C, Liu Q, Zhao Y P, Yang Q 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王锦程, 郭春文, 李俊杰, 王志军 2018 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J C, Guo C W, Li J J, Wang Z J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 郭灿, 王锦程, 王志军, 李俊杰, 郭耀麟, 唐赛 2015 64 028102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C, Wang J C, Wang Z J, Li J J, Guo Y L, Tang S 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 028102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Guo M X, Shen K, Wang M P 2009 Acta Mater. 57 4568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pan S Y, Zhu M F, Rettenmayr M 2017 Acta Mater. 132 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 柯常波, 周敏波, 张新平 2014 金属学报 50 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ke C B, Zhou M B, Zhang X P 2014 Metall. Sin. 50 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shi R P, Shen C, Dregia S A, Wang Y Z 2018 Scr. Mater. 146 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo M X, Shen K, Wang M P 2012 Mater. Chem. Phys. 131 589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Guo C, Wang J C, Wang Z J, Li J J, Guo Y L, Huang Y H 2016 Soft Matter 12 4666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 王巍, 付立铭 2008 金属学报 06 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W, Fu L M 2008 Metall. sin. 06 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a)—(c)原位反应形核过程, 红色区域为c = 1的液相, 蓝色区域为c = 0的液相, 黄色区域为c = 0.5的固相; (d) 沿图(a)中黑直线上的成分场随时间的演化曲线
Fig. 1. (a)–(c) Snapshots of the in-situ reactive process, the blue and red regions represent melt phases with c = 0 and c = 1, respectively. The yellow region is the new solid phase. (d) Temporal evolution of the concentration filed across the solid black line in panel (a).
图 2 不同曲率半径下的原位反应形核过程(左侧为bnds场(
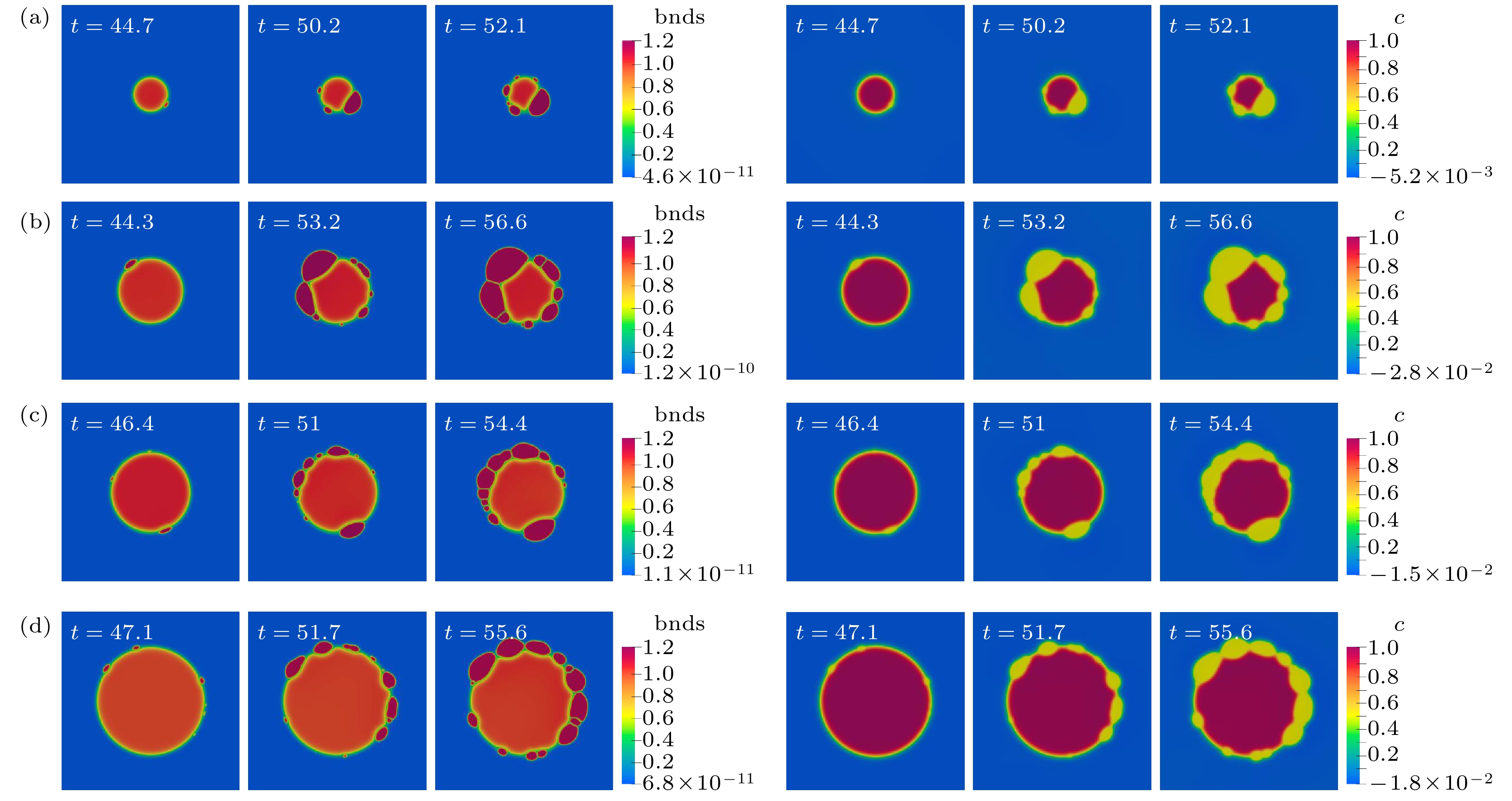
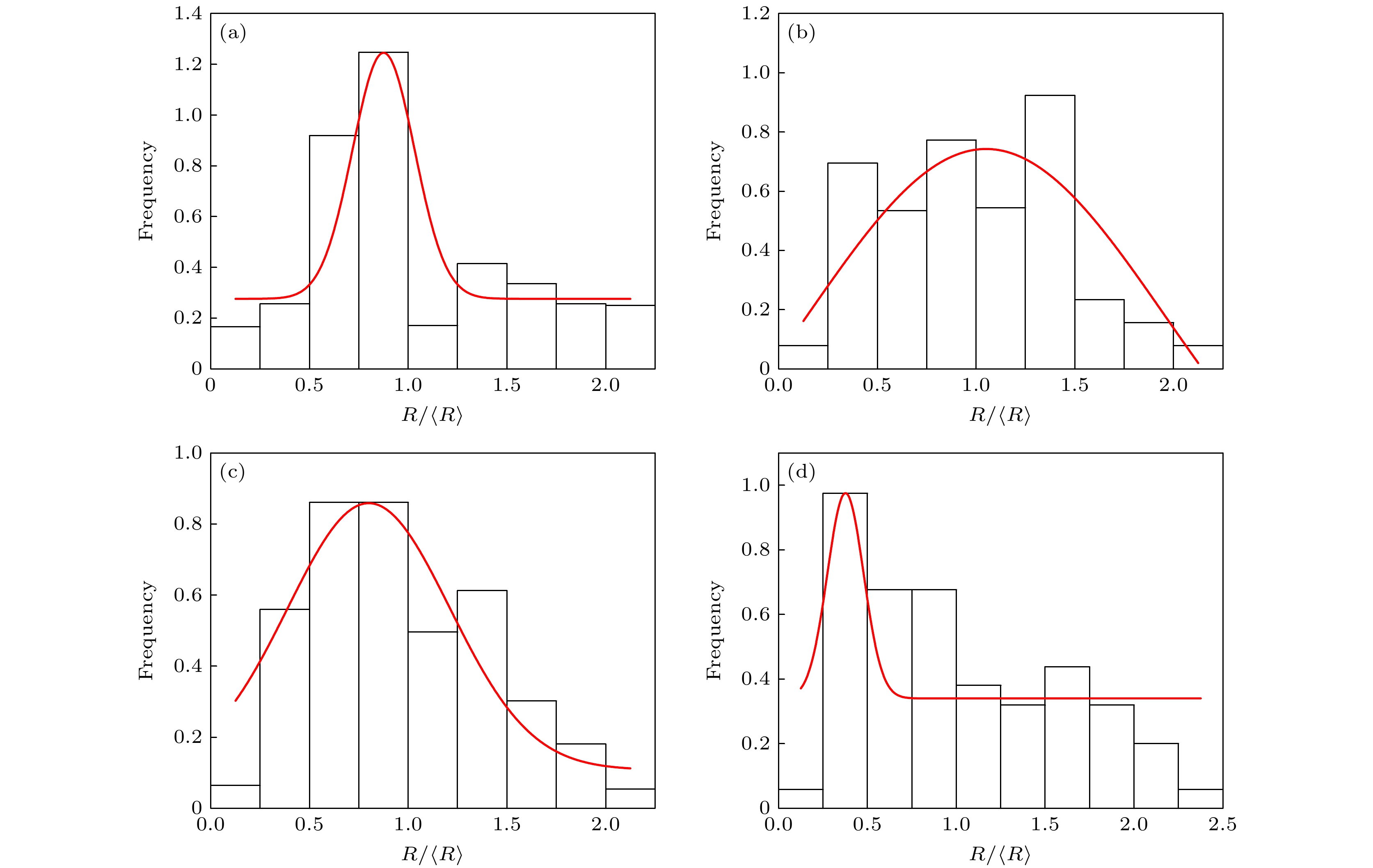
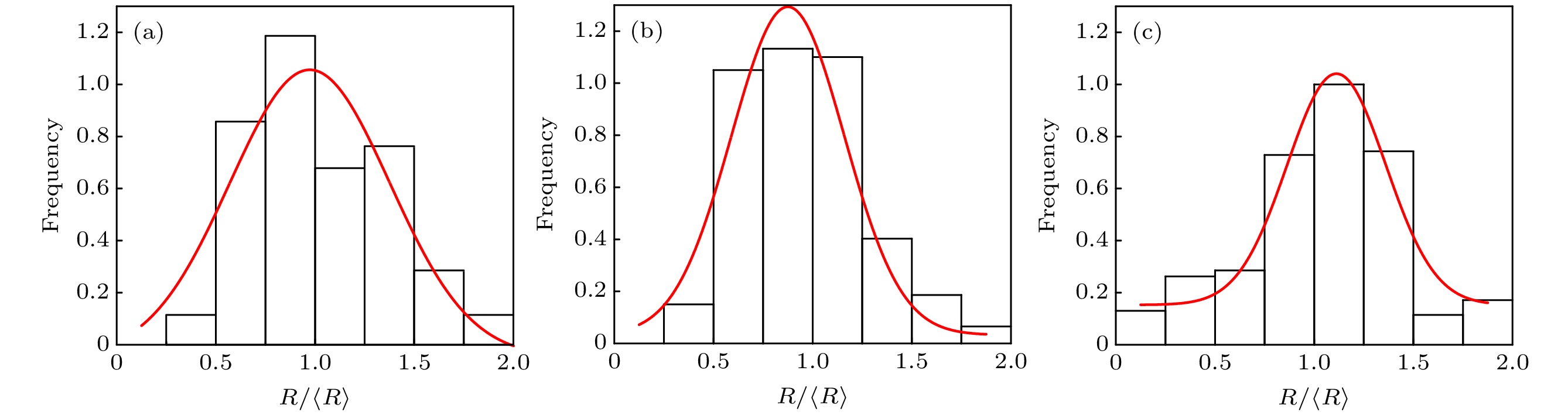
${\text{bnds}} = c + \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_i {{\eta _i}}$ ), 右侧为成分场) (a) ρ = 30; (b) ρ = 50; (c) ρ = 60; (d) ρ = 80Fig. 2. Snapshots of the in-situ reaction processes with different radius of curvatures: (a) ρ = 30; (b) ρ = 50; (c) ρ = 60; (d) ρ = 80. In each row, the left three figures show the temporal evolution of the bnds field, the right three figures show the temporal evolution of the concentration field.
-
[1] 郭明星, 汪明朴, 申坤, 张真, 李树梅 2007 中国有色金属学报 09 1440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo M X, Wang M P, Shen K, Zhang Z, Li S M 2007 Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 09 1440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨滨, 王玉庆, 周本濂 1998 金属学报 01 100
Yang B, Wang Y Q, Zhou B L 1998 Acta. Metall. Sin. 01 100
[3] 张来启, 孙祖庆, 张跃, 杨王玥 1998 金属学报 11 1206
Zhang L Q, Sun Z Q, Zhang Y, Yang W Y 1998 Acta. Metall. Sin. 11 1206
[4] 孙靖 2015 硕士学位论文 (上海: 上海交通大学)
Sun J 2015 M. S. Thesis (Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University) (in Chinese)
[5] Qu L, Zhao N, Zhao H J, Huang M L, Ma H T 2014 Scr. Mater. 72 43
[6] Li H, Jiao L, Huang X P, Li F, Lu S B, Li Y L, Qiao Y P 2021 J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30 7295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jiang Y H, Li D, Liang S H, Zou J T, Liu F 2017 J. Mater. Sci. 52 2957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lan T, Jiang Y H, Zhang X J, Cao F, Liang S H 2021 Int. J. Miner., Metall. Mater. 28 1090
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kavousi S, Novak B R, Hoyt J, Moldovan D 2020 Comput. Mater. Sci. 184 854
[10] 方辉, 薛桦, 汤倩玉, 张庆宇, 潘诗琰, 朱鸣芳 2019 68 048102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang H, Xue H, Tang Q Y, Zhang Q Y, Pan S Y, Zhu M F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 048102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 郭春文, 李俊杰, 马渊, 王锦程 2015 金属学报 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C W, Li J J, Ma Y, Wang J C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Z D, Cao Y T, Sun D K, Xing H, Wang J C, Ni Z H 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 028103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 魏雷, 林鑫, 王猛, 黄卫东 2015 64 018013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei L, Lin X, Wang M, Huang W D 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rolchigo M R, LeSar R 2019 Comput. Mater. Sci. 163 148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen L Q 2002 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 32 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Guo C, Wang J C, Li J J, Wang Z J, Huang Y H, Gu J W, Lin X 2018 Acta Mater. 145 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Deng Y Y, Guo C, Wang J C, Liu Q, Zhao Y P, Yang Q 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王锦程, 郭春文, 李俊杰, 王志军 2018 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J C, Guo C W, Li J J, Wang Z J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 郭灿, 王锦程, 王志军, 李俊杰, 郭耀麟, 唐赛 2015 64 028102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo C, Wang J C, Wang Z J, Li J J, Guo Y L, Tang S 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 028102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Guo M X, Shen K, Wang M P 2009 Acta Mater. 57 4568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pan S Y, Zhu M F, Rettenmayr M 2017 Acta Mater. 132 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 柯常波, 周敏波, 张新平 2014 金属学报 50 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ke C B, Zhou M B, Zhang X P 2014 Metall. Sin. 50 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shi R P, Shen C, Dregia S A, Wang Y Z 2018 Scr. Mater. 146 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Guo M X, Shen K, Wang M P 2012 Mater. Chem. Phys. 131 589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Guo C, Wang J C, Wang Z J, Li J J, Guo Y L, Huang Y H 2016 Soft Matter 12 4666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 王巍, 付立铭 2008 金属学报 06 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W, Fu L M 2008 Metall. sin. 06 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6367
- PDF下载量: 79
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: