-
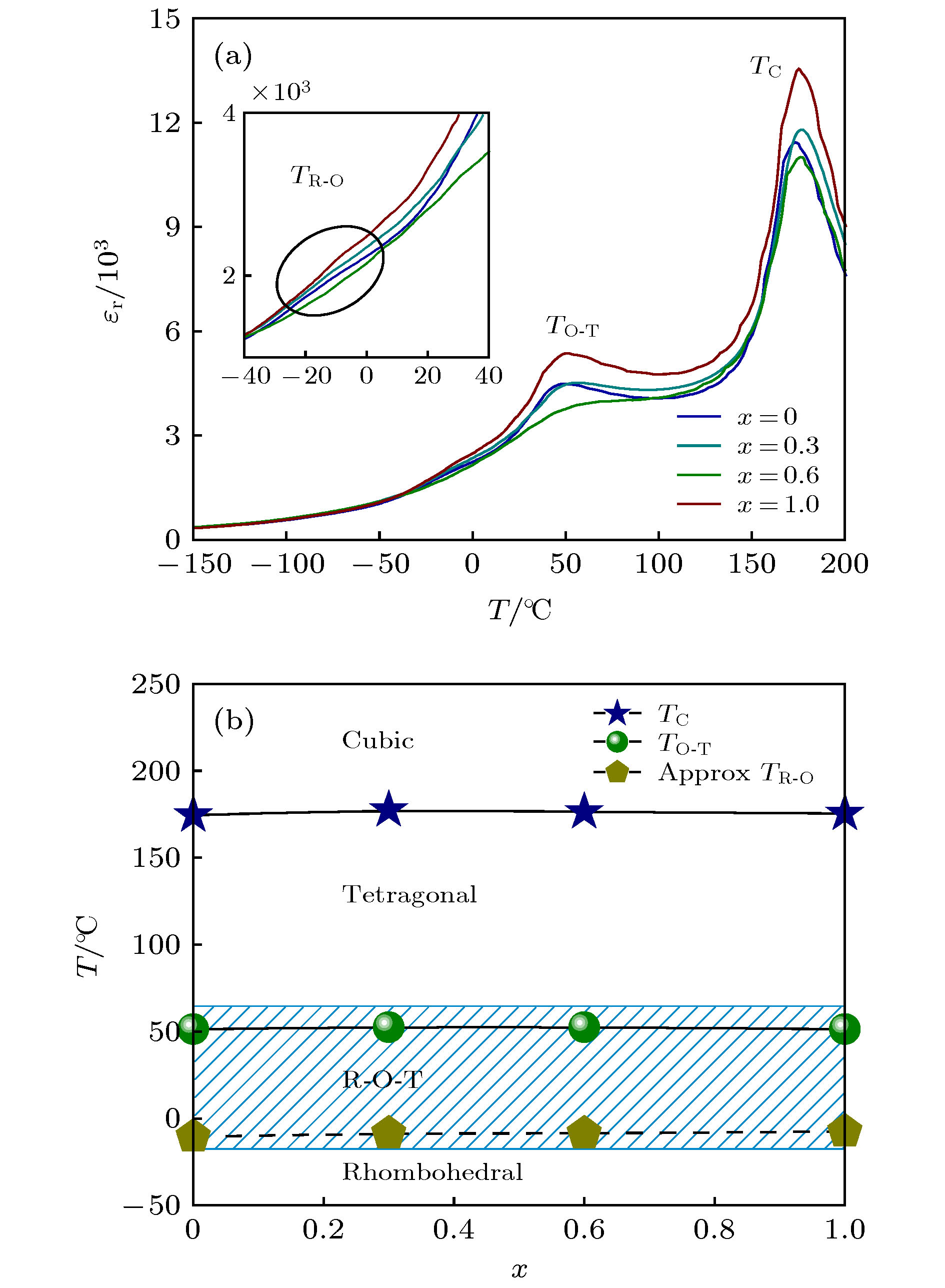
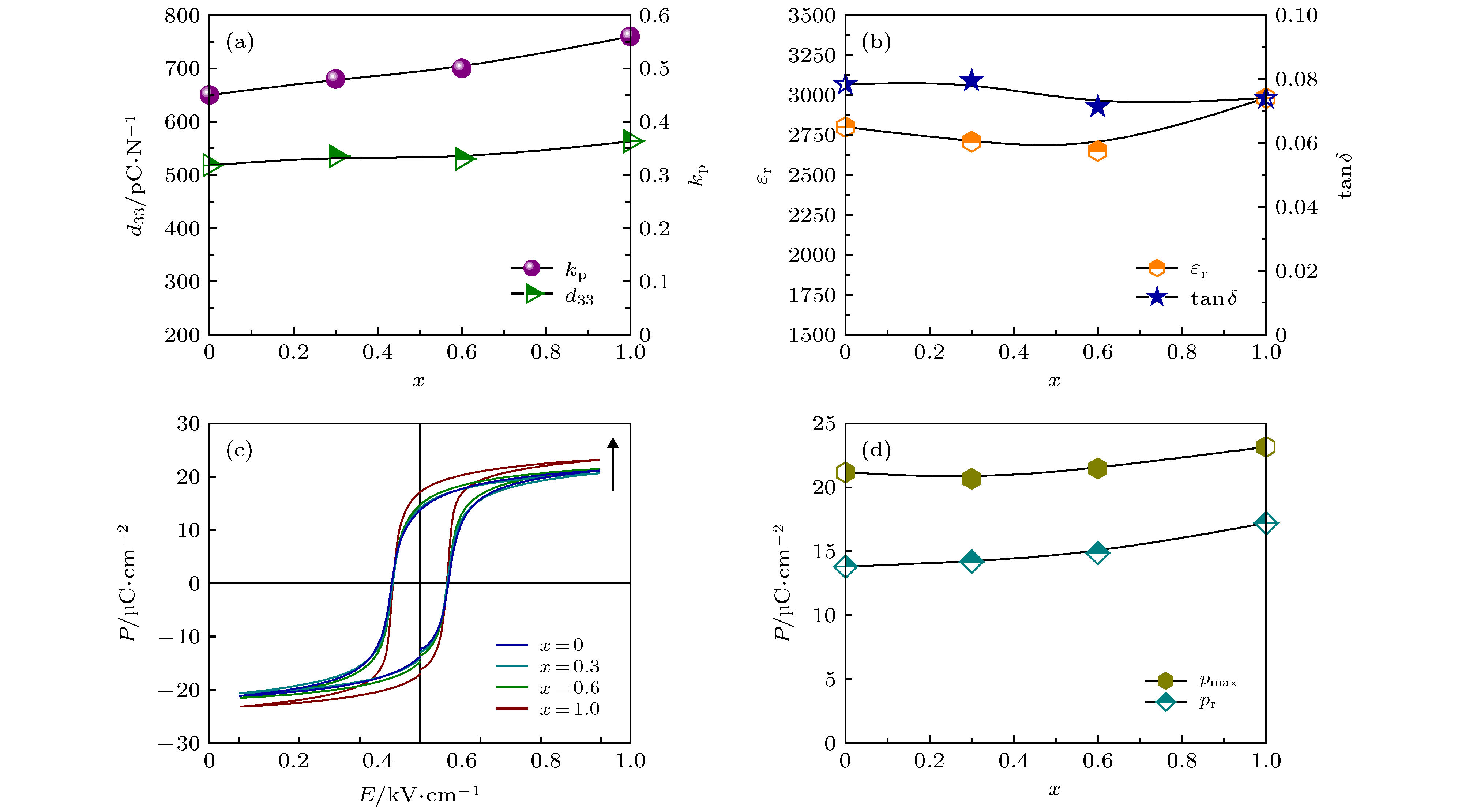
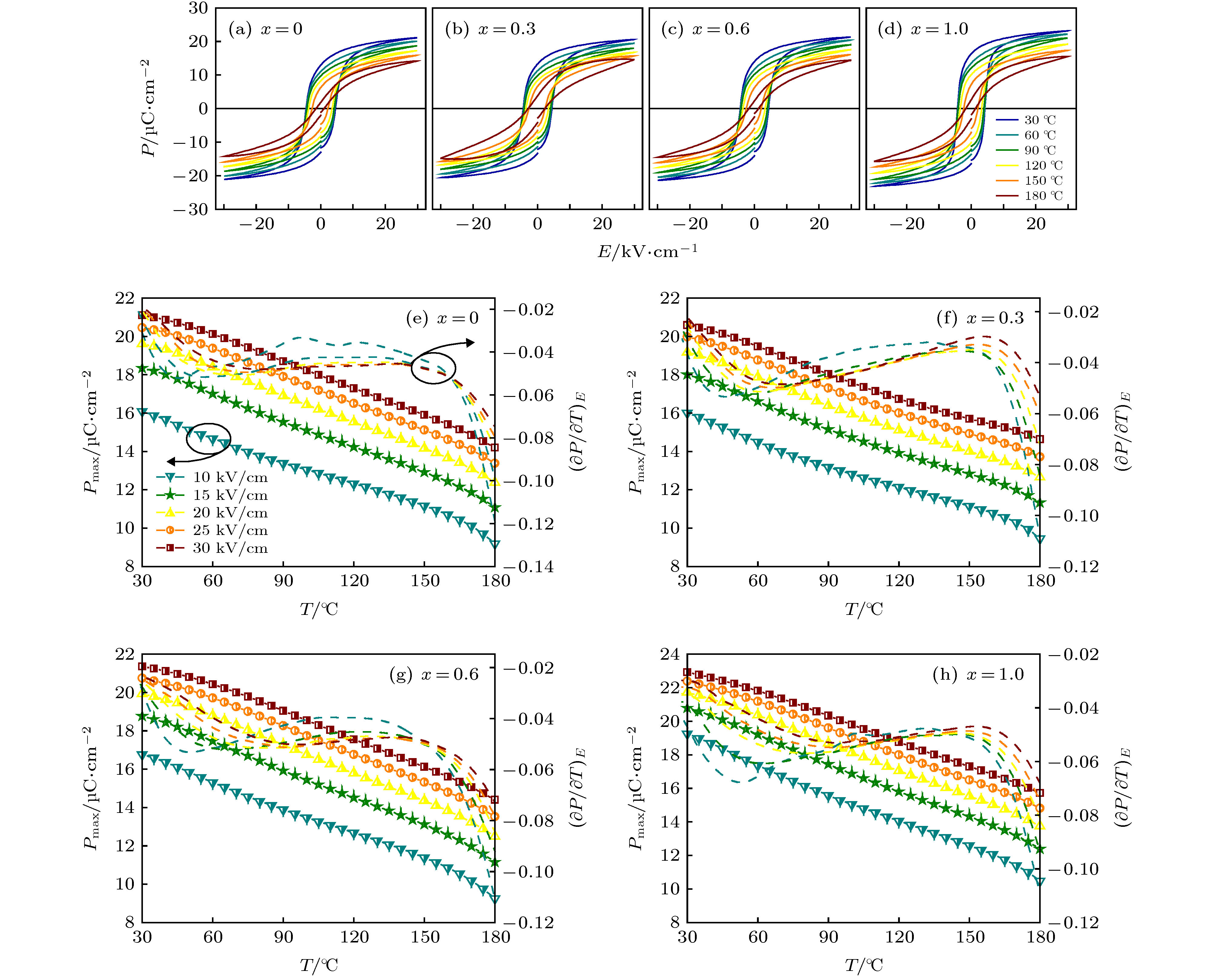
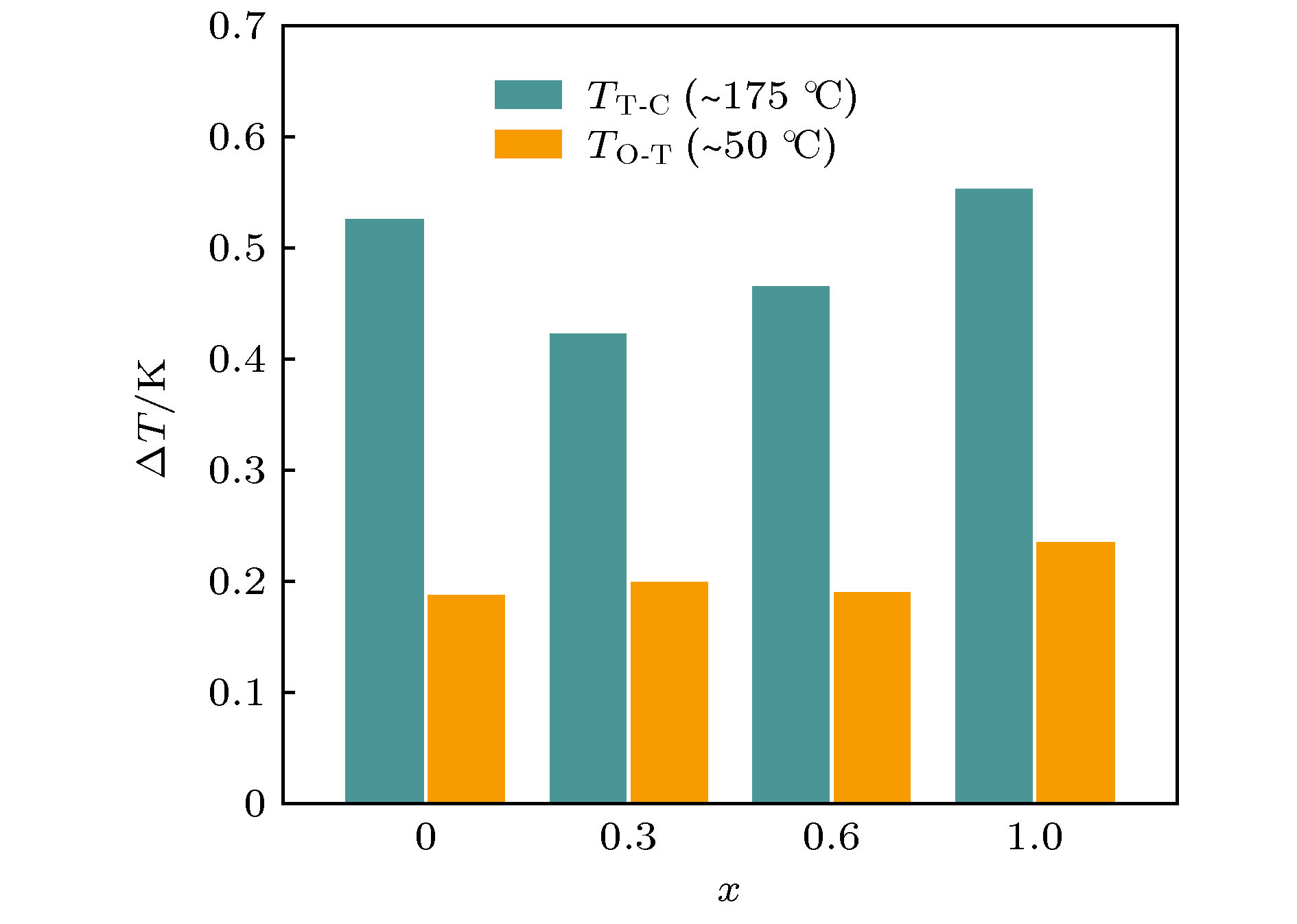
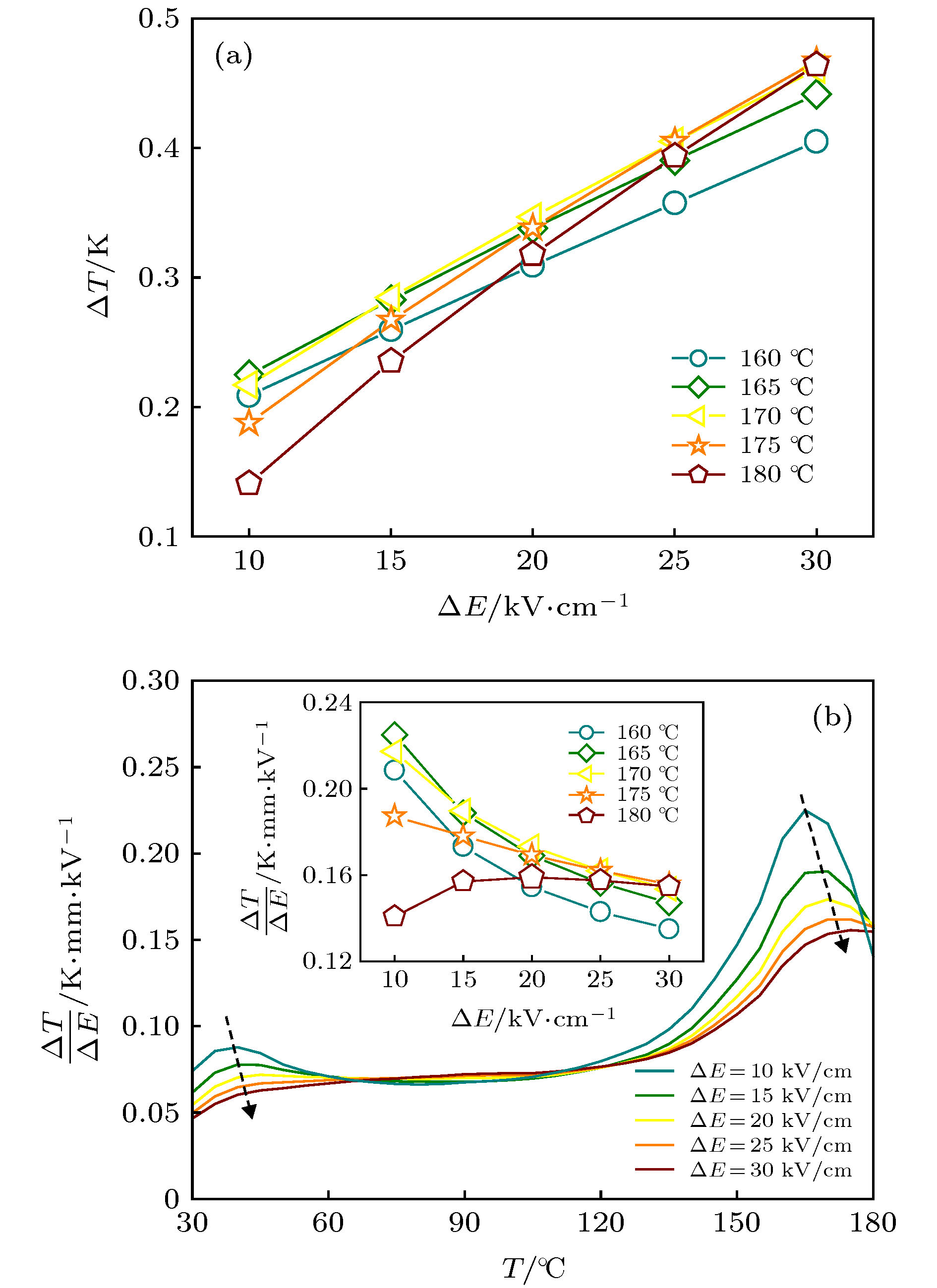
压电陶瓷作为一种能够实现机械能和电能相互转换的功能材料, 在民用和军事方面都有着广泛应用. 随着人们环保及健康意识的提高, 高性能兼具环境协调性的无铅压电陶瓷的研究成为了一项紧迫任务. 在众多无铅材料中, (K, Na)NbO3 (KNN)基陶瓷因其优异的综合性能而受到关注, 但是利用相界同时调控高压电和电卡性能的研究偏少. 本文采用传统固相方法制备了0.944K0.48Na0.52Nb0.95Sb0.05O3-0.04Bi0.5(Na0.82K0.18)0.5ZrO3-1.6%(AgxNa1–x)SbO3-0.4%Fe2O3 (x = 0—1.0)无铅压电陶瓷, 重点研究了AgSbO3/NaSbO3对陶瓷相结构、压电和电卡性能的影响. 研究结果表明: 陶瓷在研究组分范围内均为“三方-正交-四方”三相共存; 随着AgSbO3含量的增加, 该陶瓷的压电及铁电性能均有所波动(d33 = 518—563 pC/N, kp = 0.45—0.56, Pmax = 21—23 μC/cm2和Pr = 14—17 μC/cm2). 同时, 利用间接法表征了该陶瓷的电卡效应, 在居里温度附近得到了较高的电卡温变值(>0.6 K). 因此, 在KNN基陶瓷中通过相界构建能够同时实现高压电和良好的电卡性能.Piezoelectric ceramics, as a kind of functional material, can realize the mutual transformation between mechanical energy and electrical energy, and has been widely used in civil and military fields. With the improvement of people's awareness of environment protection and self-health care, the study of lead-free piezoelectric ceramics with excellent performance and environmental friendliness has become an urgent task. Among several kinds of lead-free piezoelectric materials, potassium sodium niobate [(K, Na)NbO3, KNN]-based ceramics has attracted much attention due to its good comprehensive properties, but there have been carried out few studies focusing on the utilization of phase boundary to regulate the properties of high piezoelectric and electrocaloric effect simultaneously. In this work, lead-free 0.944K0.48Na0.52Nb0.95Sb0.05O3 -0.04Bi0.5(Na0.82K0.18)0.5ZrO3-1.6%(AgxNa1–x)SbO3-0.4%Fe2O3 ceramics is prepared via the conventional solid-state method, and the effect of AS/NS ratio on phase structure, electrical properties, and electrocaloric effect are studied. The obtained results show that the ceramics has a multiphase coexistence with “rhombohedral-orthorhombic-tetragonal” (R-O-T) in all compositions. With the increase of AS content, the piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of the ceramics fluctuate (d33 = 518–563 pC/N, kp = 0.45–0.56; Pmax = 21–23 μC/cm2, Pr = 14–17 μC/cm2). In addition, the electrocaloric effect (ECE) for each of the samples is studied by the indirect method. Broadening temperature span (~90 K) of electrocaloric effect is obtained in the vicinity of O-T phase transition region, while a low ECE value is observed. A stronger ECE peak (ΔTmax > 0.6 K) can be observed when the measurement temperature reaches near the Curie temperature. Consequently, both large piezoelectric property and high electrocaloric performance can be realized in KNN-based ceramics by new phase boundary construction.
[1] 吴家刚 2019 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版) 42 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J G 2019 J. Sichuan Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 42 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Saito Y, Takao H, Tani T, Nonoyama T, Takatori K, Homma T, Nagaya T, Nakamura M 2004 Nature 432 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang X P, Wu J G, Xiao D Q, et al. 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 2905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu K, Li J, Lü X, Wu J G, Zhang X X, Xiao D Q, Zhu J G 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 8519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tao H, Wu H J, Liu Y, et al. 2019 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141 13987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yuan Y, Wu J G, Tao H, Lü X, Wang X J, Lou X J 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 084103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zheng T, Wu H J, Yuan Y, et al. 2017 Energy Environ Sci. 10 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li J F, Wang K, Zhu F Y, Cheng L Q, Yao F Z 2013 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96 3677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mischenko A S, Zhang Q, Scott J F, Whatmore R W, Mathur N D 2006 Science 311 1270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Saranya D, Chaudhuri A R, Parui J, Krupanidhi S B 2009 Bull. Mater. Sci. 32 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Peng B L, Fan H Q, Zhang Q 2013 Adv. Funct. Mater. 23 2987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bai Y, Zheng G P, Ding K, Qiao L J, Shi S Q, Guo D 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 094103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jiang X J, Luo L H, Wang B Y, Li W P, Chen H B 2014 Ceram. Int. 40 2627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kumar S, Singh S 2019 J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30 12924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Novak N, Pirc R, Kutnjak Z 2014 International Workshop on Relaxor Ferroelectrics St. Petersburg, Russia, July 1−6, 2013 p61
[16] Qian X S, Ye H J, Zhang Y T, Gu H M, Li X Y, Randall C A, Zhang Q M 2014 Adv. Funct. Mater. 24 1300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 白洋, 李建厅, 秦士强, 李俊杰, 苏小坡, 李中华, 殷若伟, 乔利杰, 王雨 2018 现代技术陶瓷 39 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai Y, Li J T, Qin S Q, Li J J, Su X P, Li Z H, Yin R W, Qiao L J, Wang Y 2018 Advanced Ceramics 39 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rozic B, Kosec M, Ursic H, Holc J, Malic B, Zhang Q M, Blinc R, Pirc R, Kutnjak Z 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 064118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Damjanovic D 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 62906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu J G 2018 Advances in Lead-free Piezoelectric Materials (Singapore: Springer Nature) pp412−417
[21] Setter N, Cross L E 1980 J. Mater. Sci. 15 2478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lü X, Wu J G, Zhu J G, Xiao D Q 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 20149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rubio-Marcos F, Banares M A, Romeroa J J, Fernandez J F 2011 J. Raman Spectrosc. 42 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Valant M 2012 Prog. Mater. Sci. 57 980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang X J, Wu J G, Dkhil B, Xu B X, Wang X P, Dong G H, Yang G, Lou X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 063904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zheng T, Wu J G 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 9242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 张沛霖, 钟维烈 1992 物理 20 600
Zhang P L, Zhong W L 1992 Physics 20 600
[28] 聂鑫 2018 博士学位论文 (上海: 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所)
Nie X 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[29] Rozic B, Koruza J, Kutnjak Z, Cordoyiannis G, Malic B, Kosec M 2013 Ferroelectrics 446 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang J L, Hao X H 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 6817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yu Y, Gao F, Weyland F, Du H L, Jin L, Hou L, Yang Z T, Novak N, Qu S B 2019 J. Mater. Chem. A 7 11665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Li J T, Bai Y, Qin S Q, Fu J, Zuo R Z, Qiao L J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 162902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Tao H, Yang J L, Lü X, Hao X H, Wu J G 2019 J. Am. Ceram Soc. 102 2578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
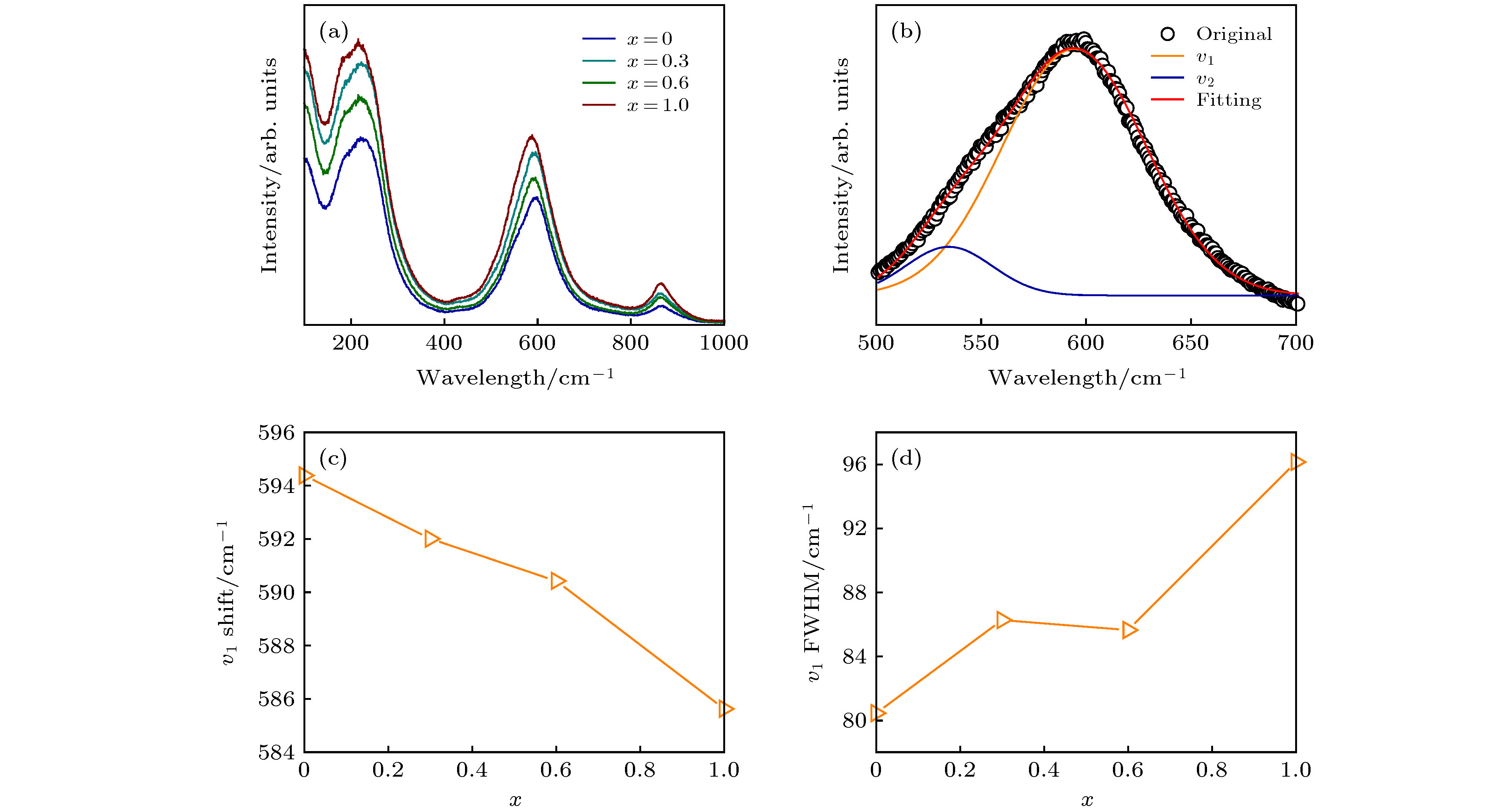
图 3 (a) KNNS-BNKZ-AxN1–xS-Fe陶瓷各组分的拉曼光谱; (b) x = 0组分的ν1和ν2特征峰拟合图; (c) ν1振动模式的拉曼位移; (d) ν1振动模式的半高宽随组分的变化
Fig. 3. (a) Raman spectra of KNNS-BNKZ-AxN1–xS-Fe; (b) Gaussian fitting of Raman spectra for x = 0; (c) Raman shift of v1 mode; (d) full width at half maximum (FWHM) as a function of composition at v1 mode.
-
[1] 吴家刚 2019 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版) 42 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J G 2019 J. Sichuan Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 42 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Saito Y, Takao H, Tani T, Nonoyama T, Takatori K, Homma T, Nagaya T, Nakamura M 2004 Nature 432 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang X P, Wu J G, Xiao D Q, et al. 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 2905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu K, Li J, Lü X, Wu J G, Zhang X X, Xiao D Q, Zhu J G 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 8519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tao H, Wu H J, Liu Y, et al. 2019 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141 13987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yuan Y, Wu J G, Tao H, Lü X, Wang X J, Lou X J 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 084103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zheng T, Wu H J, Yuan Y, et al. 2017 Energy Environ Sci. 10 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li J F, Wang K, Zhu F Y, Cheng L Q, Yao F Z 2013 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96 3677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mischenko A S, Zhang Q, Scott J F, Whatmore R W, Mathur N D 2006 Science 311 1270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Saranya D, Chaudhuri A R, Parui J, Krupanidhi S B 2009 Bull. Mater. Sci. 32 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Peng B L, Fan H Q, Zhang Q 2013 Adv. Funct. Mater. 23 2987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bai Y, Zheng G P, Ding K, Qiao L J, Shi S Q, Guo D 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 094103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jiang X J, Luo L H, Wang B Y, Li W P, Chen H B 2014 Ceram. Int. 40 2627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kumar S, Singh S 2019 J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30 12924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Novak N, Pirc R, Kutnjak Z 2014 International Workshop on Relaxor Ferroelectrics St. Petersburg, Russia, July 1−6, 2013 p61
[16] Qian X S, Ye H J, Zhang Y T, Gu H M, Li X Y, Randall C A, Zhang Q M 2014 Adv. Funct. Mater. 24 1300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 白洋, 李建厅, 秦士强, 李俊杰, 苏小坡, 李中华, 殷若伟, 乔利杰, 王雨 2018 现代技术陶瓷 39 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai Y, Li J T, Qin S Q, Li J J, Su X P, Li Z H, Yin R W, Qiao L J, Wang Y 2018 Advanced Ceramics 39 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rozic B, Kosec M, Ursic H, Holc J, Malic B, Zhang Q M, Blinc R, Pirc R, Kutnjak Z 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 064118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Damjanovic D 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 62906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu J G 2018 Advances in Lead-free Piezoelectric Materials (Singapore: Springer Nature) pp412−417
[21] Setter N, Cross L E 1980 J. Mater. Sci. 15 2478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lü X, Wu J G, Zhu J G, Xiao D Q 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 20149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rubio-Marcos F, Banares M A, Romeroa J J, Fernandez J F 2011 J. Raman Spectrosc. 42 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Valant M 2012 Prog. Mater. Sci. 57 980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang X J, Wu J G, Dkhil B, Xu B X, Wang X P, Dong G H, Yang G, Lou X J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 063904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zheng T, Wu J G 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 9242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 张沛霖, 钟维烈 1992 物理 20 600
Zhang P L, Zhong W L 1992 Physics 20 600
[28] 聂鑫 2018 博士学位论文 (上海: 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所)
Nie X 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[29] Rozic B, Koruza J, Kutnjak Z, Cordoyiannis G, Malic B, Kosec M 2013 Ferroelectrics 446 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang J L, Hao X H 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 6817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yu Y, Gao F, Weyland F, Du H L, Jin L, Hou L, Yang Z T, Novak N, Qu S B 2019 J. Mater. Chem. A 7 11665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Li J T, Bai Y, Qin S Q, Fu J, Zuo R Z, Qiao L J 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 162902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Tao H, Yang J L, Lü X, Hao X H, Wu J G 2019 J. Am. Ceram Soc. 102 2578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 14645
- PDF下载量: 638
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: