-
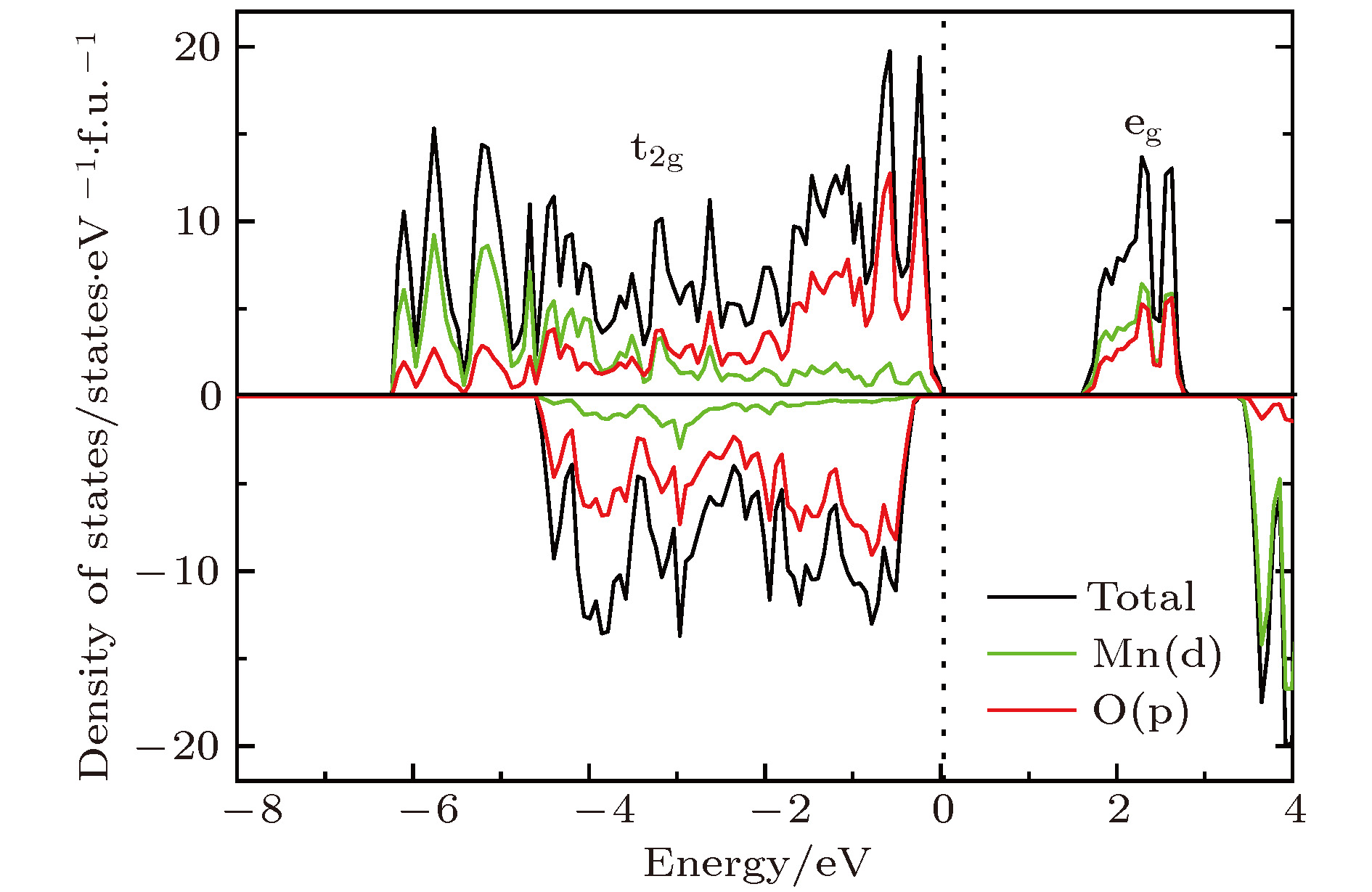
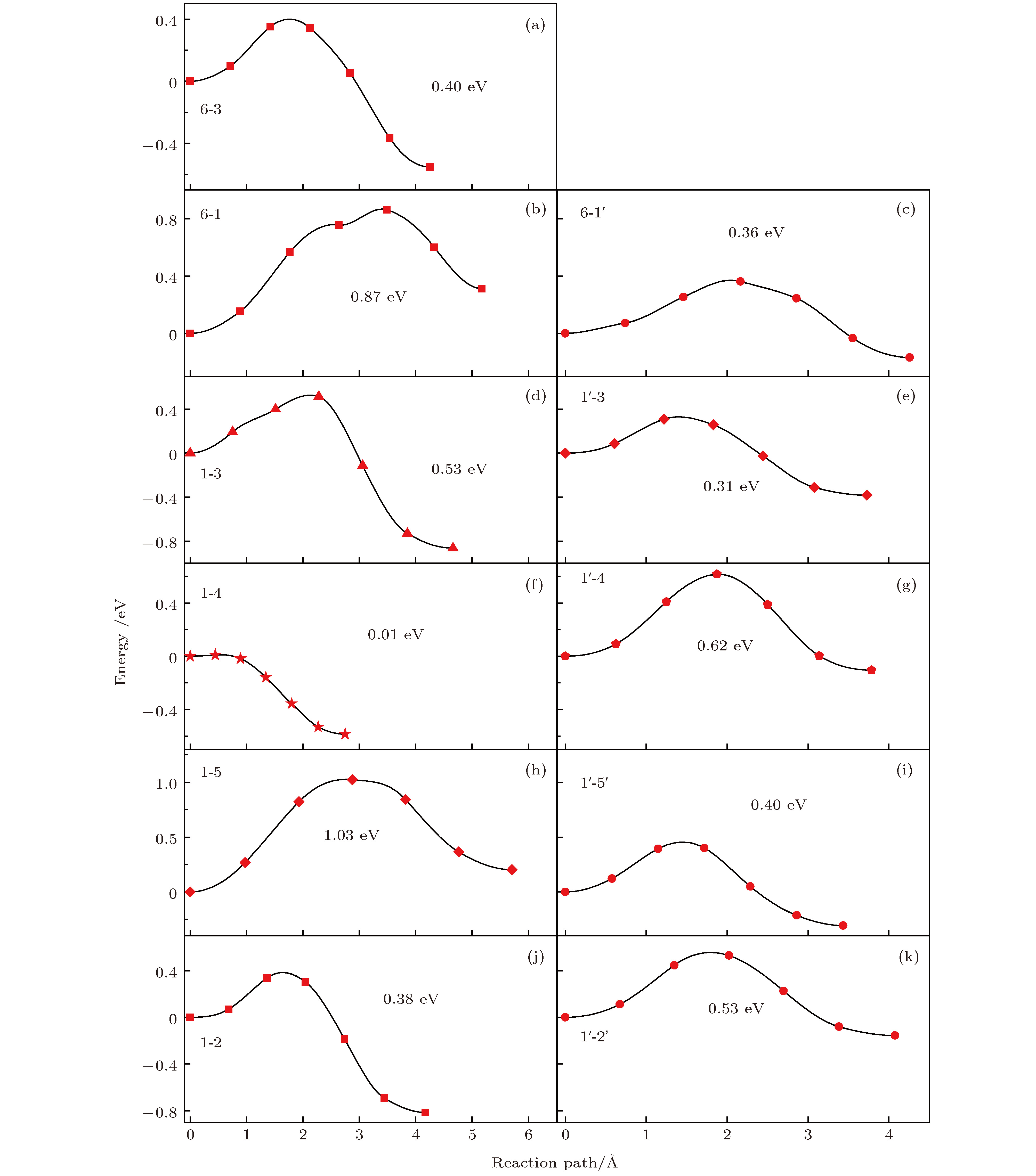
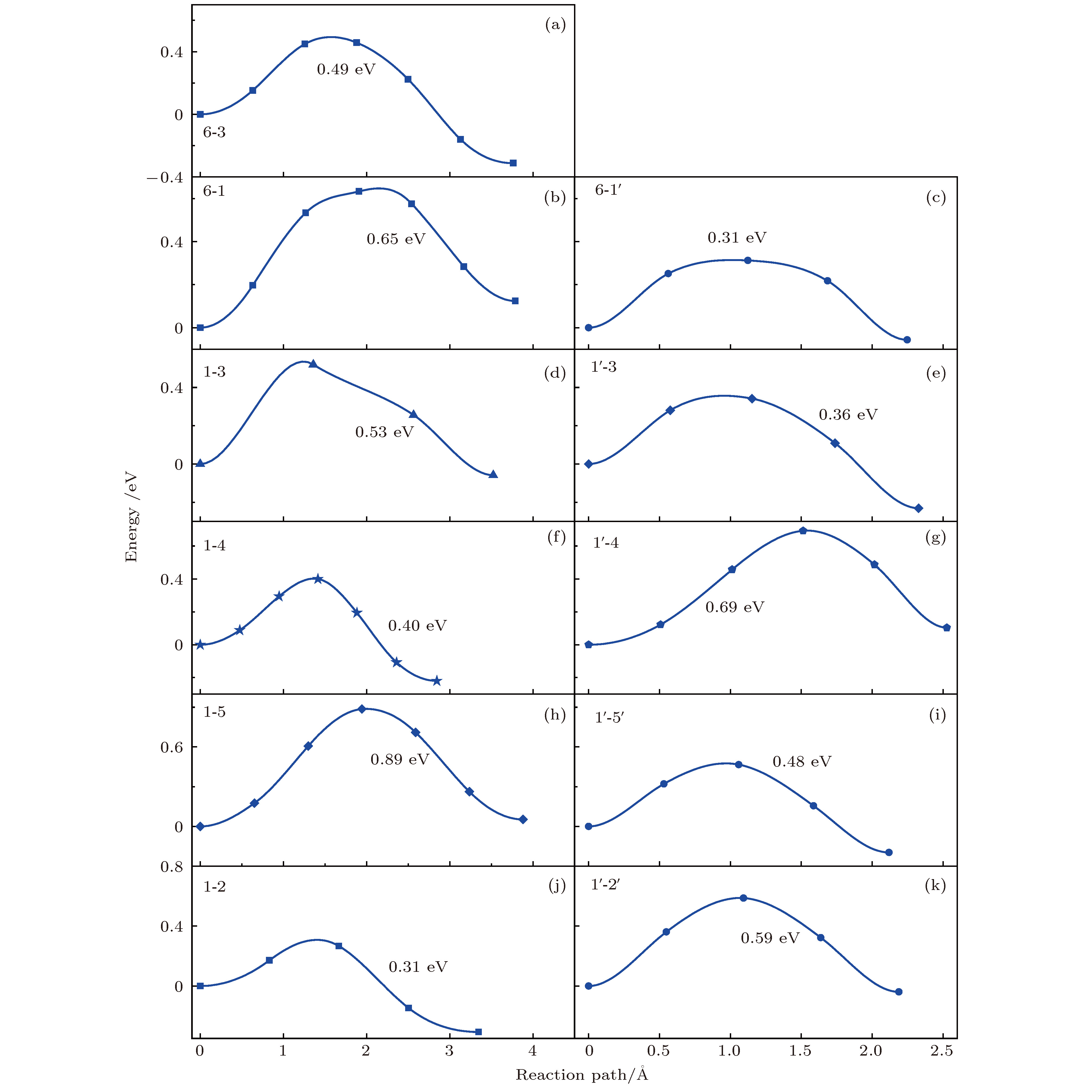
掺杂是锂离子电池电极材料优化改性的一种有效的方法. 稀土元素因其具有高的电子电荷、大的离子半径以及强的自极化能力, 成为掺杂改性的重要选择. 本文利用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理方法研究了稀土元素(La, Ce, Pr, Sm)掺杂的锂离子电池正极材料Li2MnO3的性质. 通过稀土元素的掺杂, Li2MnO3材料的晶格常数和晶胞体积都有不同程度的增大. 由于稀土原子的价态不同, 导致掺杂后的Li2MnO3的电子结构性质不同. La掺杂的Li2MnO3表现出金属性, 而Ce, Pr, Sm掺杂的结构为半导体性质, 但带隙与未掺杂情况下相比有所减小. Li2MnO3中的Li离子迁移在La和Ce掺杂后展示出复杂的能垒变化. 在远离稀土离子处, Li离子迁移势垒比未掺杂时减小, 但在靠近稀土离子处则表现为势垒变化的多样性. 当Li离子在离稀土离子最近的位置处进行迁移, 势垒有明显的增加, 这一结果与稀土离子周围的局域结构变化大密切相关.Although Li-ion batteries (LIBs) have had great success in portable electronic devices and electrical vehicles, the improvement of the performances has received intensive attention. Generally, doping is an effective method to modify the battery performance, such as cycling performance. Appropriate doping can effectively reduce the structural deformation of electrode materials during charging and discharging, thus improving the cycling performace of LIBs. Because of the large radius, large charge and strong self-polarization ability of rare earth ions, rare earth element is a promising candidate for doping modification. Motivated by this, we study the structural, electronic and ionic diffusion properties of rare-earth-doped cathode material Li2MnO3 by using first-principles calculations based on density functional theory as implemented in Vienna ab initio simulation package. After the doping of rare earth elements (La, Ce, Pr, Sm), the lattice constants and cell volumes increase with respect to the undoped one. The cell volume of La-doped Li2MnO3 has the biggest change, while the cell volume of Sm-doped one has the smallest change. Due to the different ionic valence states, the electronic structures of the doped Li2MnO3 are various. La-doped Li2MnO3 exhibits metallic characteristic, whereas Ce-, Pr-, and Sm-doped structures are semiconducting with smaller band gap than that of the undoped case. The Li diffusion energy barrier in Li2MnO3 shows complicated variation when the La and Ce are doped. At the sites far away from the rare earth ions, the Li diffusion barriers are lower than that of undoped one. The reason is that the diffusion channels, which are determined by the distance between neighboring O-layers, are enlarged due to the implantment of rare earth ions. However, the situations are various at the sites close to the rare earth ions. The Li diffusion barriers increase essentially when Li ions diffuse from the nearest sites to rare earth ions. Such a result is closely related to the huge changes of local structures around the rare earth ions. In addition, the effect of La doping on the Li diffusion barrier is more obvious than that of Ce doping, which is due to the local structure change around rare earth ions.
-
Keywords:
- frist-principle calculation /
- rare-earth doped /
- Li-ion battery /
- cathode materials
[1] Tarascon J M, Armand M 2001 Nature 414 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Liu H, Cao Q, Fu L J, Li C, Wu Y P, Wu H Q 2006 Electrochem. Commun. 8 1553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xiao P H, Deng Z Q, Manthiram A, Henkelman G 2012 J. Phys. Chem. C 116 23201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 候育花, 黄有林, 刘仲武, 曾德长 2015 64 037501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou Y H, Huang Y L, Liu Z W, Zeng D C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 037501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ghosh P, Mahanty S, Basu R N 2009 Electrochim. Acta 54 1654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 廖春发, 陈辉煌, 陈子平 2004 江西有色金属 18 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao C F, Chen H H, Chen Z P 2004 Jiangxi Nonferrous Metals 18 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei J P, Cao X Y, Pan G L, Ye M, Yan J 2003 J. Rare Earths 21 466
[8] Balaji S, Manichandran T, Mutharasu D 2012 Bull. Mater. Sci. 35 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Iqbal M J, Ahmad Z 2008 J. Power Sources 179 763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Khedr A M, Abou-Sekkina M M, El-Metwaly F G 2013 J. Electron. Mater. 42127 5
[11] Tang Z Y, Zhang N, Lu X H 2005 J. Rare Earths 23 120
[12] 叶兰, 张海朗 2012 稀有金属材料与工程 41 636
Ye L, Zhang H L 2012 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 41 636
[13] Luo S H, Tian Y, Li H, Shi K J, Tang Z L, Zhang Z T 2010 J. Rare Earths 28 439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 陈晗, 向楷雄, 龚文强, 刘建华 2011 稀有金属材料与工程 40 1936
Chen H, Xiang K X, Gong W Q, Liu J H 2011 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 40 1936
[15] Zhang Y J, Xia S B, Zhang Y N, Dong P, Yan Y X, Yang R M 2012 Chin. Sci. Bull. 57 4181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 杨书廷, 贾俊华, 郑立庆, 曹朝霞 2003 中国稀土学报 21 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang S T, Jia J H, Zheng L Q, Cao Z X 2003 J. Chin. Rare Earth Soc. 21 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun H B, Chen Y G, Xu C H, Zhu D, Huang L H 2012 J. Solid State Electrochem. 16 1247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tian Y W, Kang X X, Liu L Y 2008 J. Rare Earths 26 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ding Y H, Zhang P, Jiang Y, Gao D S 2007 Solid State Ionics 178 967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 赵世玺, 郭双桃, 邓玉峰, 熊凯, 徐亚辉, 南策文 2017 硅酸盐学报 45 495
Zhao S X, Guo S T, Deng Y F, Xiong K, Xu Y H, Nan C W 2017 J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 45 495
[21] He P, Yu H J, Li D, Zhou H S 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 3680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gao Y R, Ma J, Wang X F, Lu X, Bai Y, Wang Z X, Chen L Q 2014 J. Mater. Chem. A 2 4811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang Z Q, Wu M S, Xu B, Ouyang C Y 2016 J. Alloy Compd. 658 818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shi S, Gao J, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Wu Q, Ju W, Ouyang C, Xiao R 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 018212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 11169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Blöchl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Perdew J P, Chevary J A, Vosko S H, Jackson K A, Pederson M R, Singh D J, Fiolhais C 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 6671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Anisimov V I, Zaanen J, Andersen O K 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Koyama Y, Tanaka I, Nagao M, Kanno R 2009 J. Power Sources 189 798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhou F, Cococcioni M, Marianetti C A, Morgan D, Ceder G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 235121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ning F H, Xu B, Shi J, Wu M S, Hu Y Q, Ouyang C Y 2016 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 18428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Henkelman G, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9978
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Henkelman G, Uberuaga B P, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zheng L M, Wang H W, Luo M, Wang G Q, Wang Z Q, Ouyang C Y 2018 Solid State Ionics 320 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Strobel P, Lambert-Andron B 1988 J. Solid State Chem. 75 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Xiao R J, Li H, Chen L Q 2012 Chem. Mater. 24 4242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhu Y, Li J, Ji X, Li T, Jin M, Ou X, Shen X, Wang W, Huang F 2018 AIP Adv. 8 105014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 未掺杂与稀土掺杂的Li2MnO3的晶格常数、超胞体积与稀土元素的磁矩
Table 1. Lattice constants, volume of supercell, magnetic moment of rare-earth atom of Li2MnO3 without and with rare-earth doping
体系 稀土元素的磁矩/μB 2a/Å b/Å 2c/Å V/Å3 Li2MnO3(exp)[36] — 9.874 8.532 10.060 — Li2MnO3 — 10.030 8.670 10.191 835.566 La-Li2MnO3 0 10.244 8.828 10.317 877.527 Ce-Li2MnO3 0 10.157 8.769 10.266 861.058 Pr-Li2MnO3 1 10.151 8.765 10.263 859.917 Sm-Li2MnO3 0 10.136 8.755 10.248 856.630 表 2 未掺杂Li2MnO3中的Mn离子与最近邻O离子之间的键长和稀土掺杂结构中稀土离子与最近邻O离子之间的键长
Table 2. Distance between Mn and the nearest neighboring O in undoped Li2MnO3 and distance between rare-earth ion and the nearest neighboring O in rare-earth-doped Li2MnO3
Mn4+ La3+ Ce4+ Pr4+ Sm4+ dM—O (M = Mn, La, Ce, Pr, Sm)/Å 1.941 2.374 2.215 2.193 2.181 1.934 2.385 2.198 2.208 2.183 1.949 2.401 2.218 2.211 2.170 表 3 两种近邻结构中的Li离子迁移路径
Table 3. Diffusion paths of Li ions in two different structures with neighboring Li ions
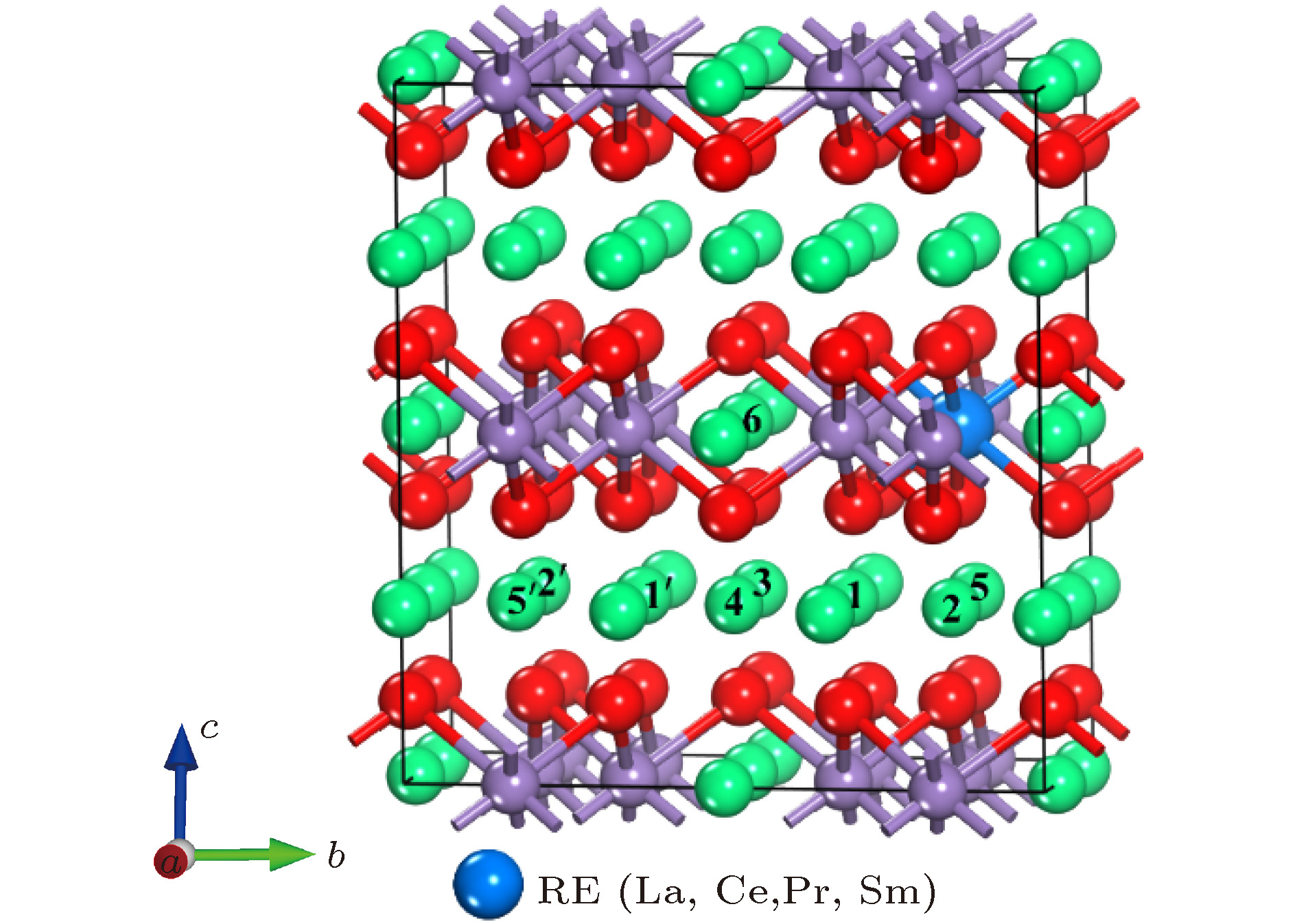
未掺杂 稀土掺杂 2b-2c 6-3 6-3 2b-4h 6-1 6-1 6-1' 4h-2c 1-3 1-3 1'-3 4h-2c 1-4 1'-4 4h-4h 1-5 1-5 1'-5' 4h-4h 1-2 1'-2' -
[1] Tarascon J M, Armand M 2001 Nature 414 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Liu H, Cao Q, Fu L J, Li C, Wu Y P, Wu H Q 2006 Electrochem. Commun. 8 1553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xiao P H, Deng Z Q, Manthiram A, Henkelman G 2012 J. Phys. Chem. C 116 23201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 候育花, 黄有林, 刘仲武, 曾德长 2015 64 037501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou Y H, Huang Y L, Liu Z W, Zeng D C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 037501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ghosh P, Mahanty S, Basu R N 2009 Electrochim. Acta 54 1654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 廖春发, 陈辉煌, 陈子平 2004 江西有色金属 18 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao C F, Chen H H, Chen Z P 2004 Jiangxi Nonferrous Metals 18 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei J P, Cao X Y, Pan G L, Ye M, Yan J 2003 J. Rare Earths 21 466
[8] Balaji S, Manichandran T, Mutharasu D 2012 Bull. Mater. Sci. 35 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Iqbal M J, Ahmad Z 2008 J. Power Sources 179 763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Khedr A M, Abou-Sekkina M M, El-Metwaly F G 2013 J. Electron. Mater. 42127 5
[11] Tang Z Y, Zhang N, Lu X H 2005 J. Rare Earths 23 120
[12] 叶兰, 张海朗 2012 稀有金属材料与工程 41 636
Ye L, Zhang H L 2012 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 41 636
[13] Luo S H, Tian Y, Li H, Shi K J, Tang Z L, Zhang Z T 2010 J. Rare Earths 28 439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 陈晗, 向楷雄, 龚文强, 刘建华 2011 稀有金属材料与工程 40 1936
Chen H, Xiang K X, Gong W Q, Liu J H 2011 Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 40 1936
[15] Zhang Y J, Xia S B, Zhang Y N, Dong P, Yan Y X, Yang R M 2012 Chin. Sci. Bull. 57 4181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 杨书廷, 贾俊华, 郑立庆, 曹朝霞 2003 中国稀土学报 21 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang S T, Jia J H, Zheng L Q, Cao Z X 2003 J. Chin. Rare Earth Soc. 21 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun H B, Chen Y G, Xu C H, Zhu D, Huang L H 2012 J. Solid State Electrochem. 16 1247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tian Y W, Kang X X, Liu L Y 2008 J. Rare Earths 26 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ding Y H, Zhang P, Jiang Y, Gao D S 2007 Solid State Ionics 178 967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 赵世玺, 郭双桃, 邓玉峰, 熊凯, 徐亚辉, 南策文 2017 硅酸盐学报 45 495
Zhao S X, Guo S T, Deng Y F, Xiong K, Xu Y H, Nan C W 2017 J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 45 495
[21] He P, Yu H J, Li D, Zhou H S 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 3680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gao Y R, Ma J, Wang X F, Lu X, Bai Y, Wang Z X, Chen L Q 2014 J. Mater. Chem. A 2 4811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang Z Q, Wu M S, Xu B, Ouyang C Y 2016 J. Alloy Compd. 658 818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shi S, Gao J, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Wu Q, Ju W, Ouyang C, Xiao R 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 018212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 11169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Blöchl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Perdew J P, Chevary J A, Vosko S H, Jackson K A, Pederson M R, Singh D J, Fiolhais C 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 6671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Anisimov V I, Zaanen J, Andersen O K 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Koyama Y, Tanaka I, Nagao M, Kanno R 2009 J. Power Sources 189 798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhou F, Cococcioni M, Marianetti C A, Morgan D, Ceder G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 235121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ning F H, Xu B, Shi J, Wu M S, Hu Y Q, Ouyang C Y 2016 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 18428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Henkelman G, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9978
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Henkelman G, Uberuaga B P, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zheng L M, Wang H W, Luo M, Wang G Q, Wang Z Q, Ouyang C Y 2018 Solid State Ionics 320 210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Strobel P, Lambert-Andron B 1988 J. Solid State Chem. 75 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Xiao R J, Li H, Chen L Q 2012 Chem. Mater. 24 4242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhu Y, Li J, Ji X, Li T, Jin M, Ou X, Shen X, Wang W, Huang F 2018 AIP Adv. 8 105014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 26351
- PDF下载量: 368
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: