-
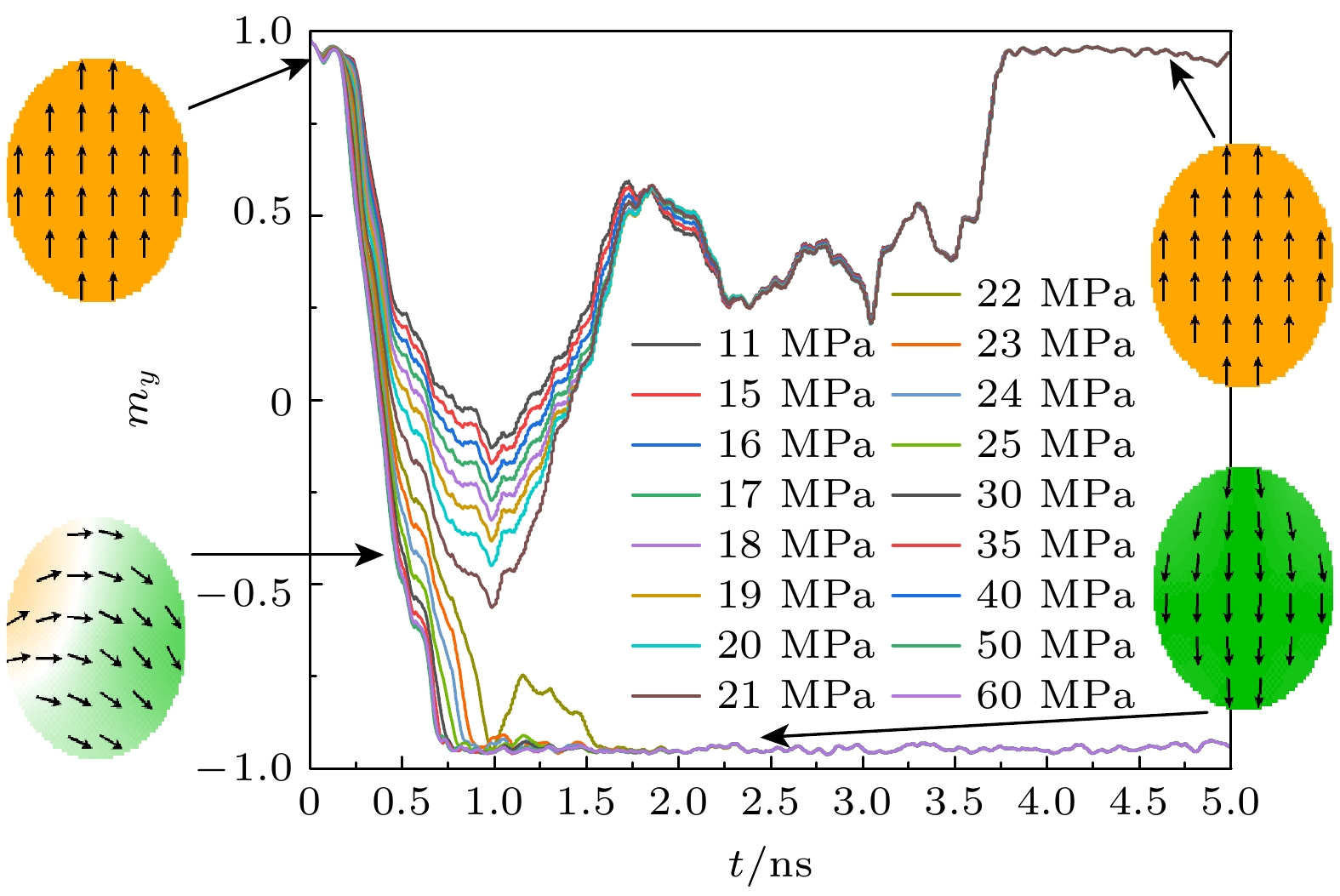
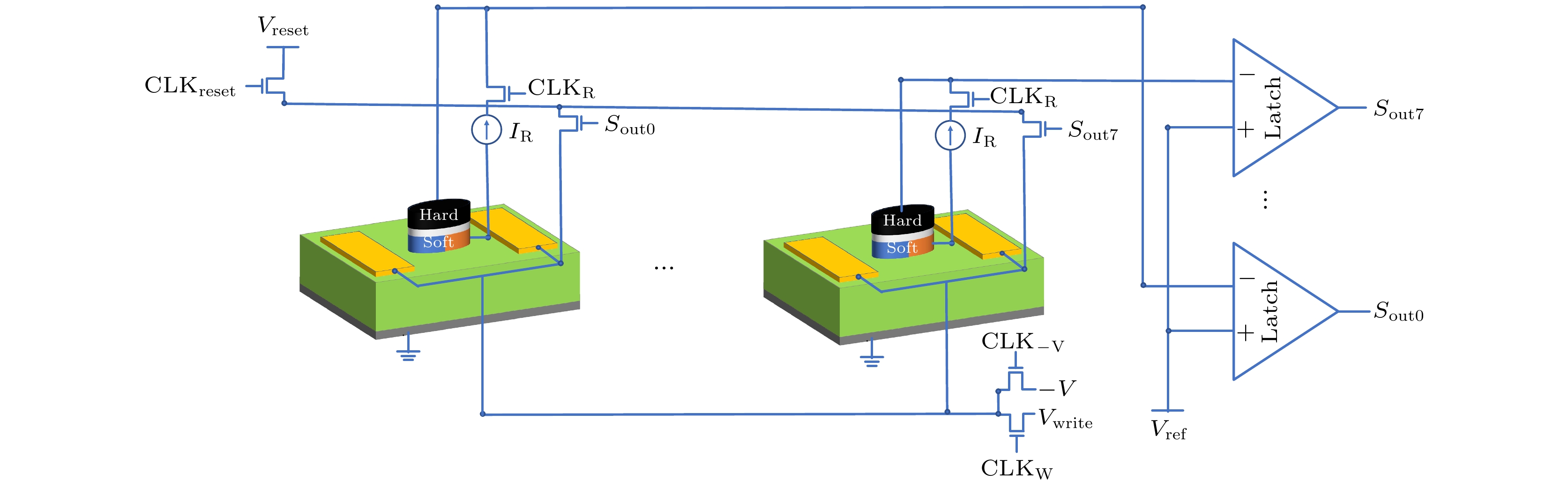
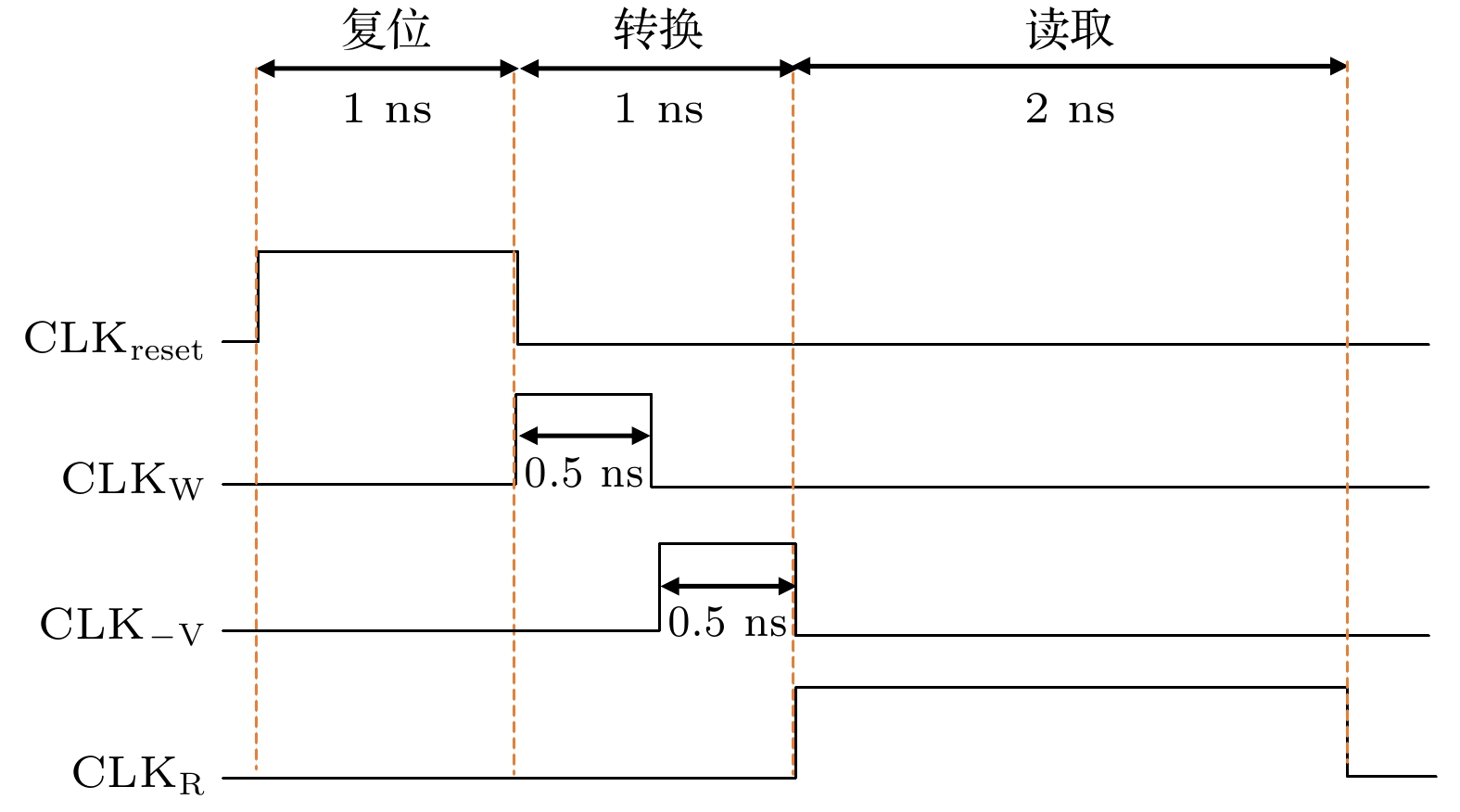
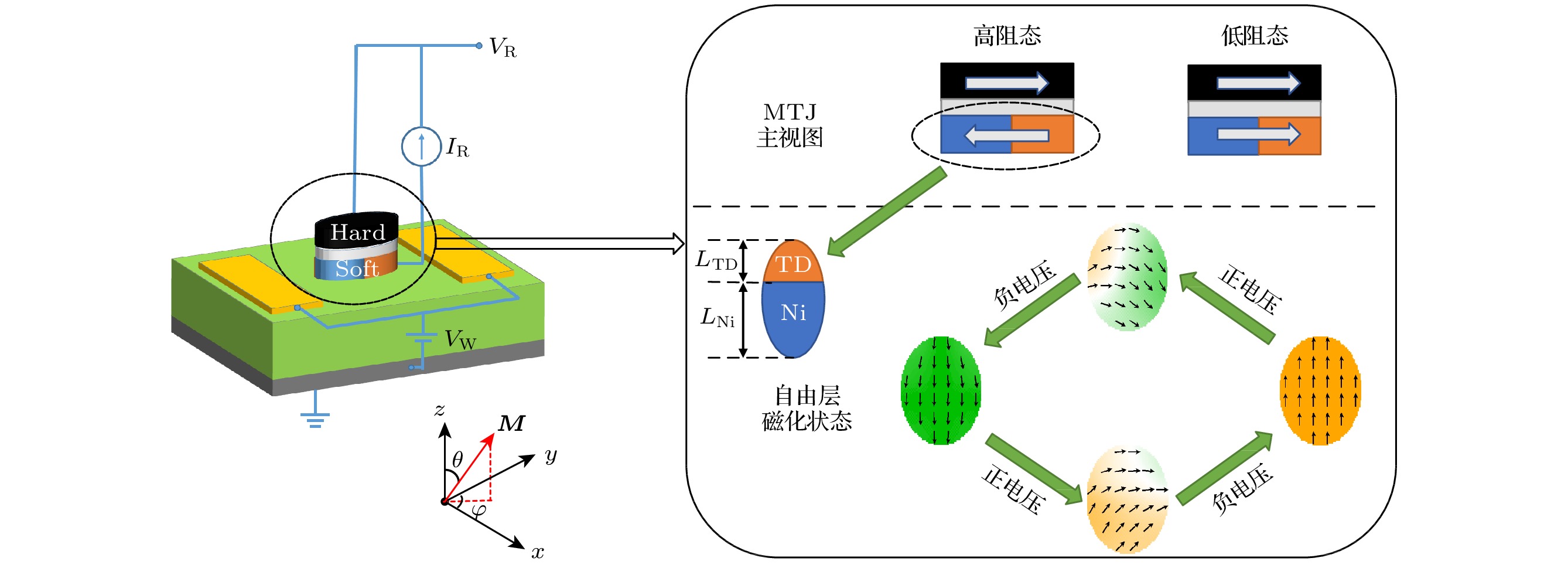
In recent years, the utilization of artificial intelligence and big data has led to the rise of compute-in-memory signal processing as the primary method for ADC design. Spintronic memory devices, which have non-volatile and low static power consumption characteristics, are particularly suitable for the design of low-power, high-bandwidth compute-in-memory ADCs. In this paper, a 3-bit magneto-elastic analog-to-digital converter (MEADC) is proposed, which comprises eight magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs), where the MTJ free layer is a bicomponent multiferroic nanomagnet. The bicomponent multiferroic nanomagnet can attain deterministic magnetization switching under zero-field condition by regulating the strain-mediated voltage. It has been discovered that there is a linear correlation between the thickness of the piezoelectric layer and the critical flip voltage in a bicomponent multiferroic nanomagnet of a given size and material. Using this principle, the thickness of the piezoelectric layer is adjusted to allow the MEADC to have eight different voltage switching thresholds. This can make the analog signal converted into a combination of different magnetization states of eight multiferroic MTJ. A latch comparator and an independent read circuit are designed to detect the MTJ’s resistance state output a digital signal. Monte Carlo simulations indicate that the MEADC can achieve a 100% success rate of writing at room temperature. Additionally, the read circuit and write circuit are separated from each other, thus the same reference voltage can be set for each MTJ and result in higher readability. Micromagnetic simulation and numerical analysis demonstrate that the MEADC can operate at a maximum frequency of 250 MHz, and the energy consumption of a single conversion is only 20 aJ. Compared with the magnetic analog-to-digital converter based on the Racetrack technology, the energy consumption is reduced by 1000 times, and the sampling rate is increased by 10 times. The MEADC proposed in this paper offers an essential technical support for the spintronics-based compute-in-memory integrated circuit architecture. -
Keywords:
- magnetoelastic analog-to-digital converters /
- magnetic tunnel junctions /
- spintronics /
- nanomagnets
[1] Murmann B 2015 IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 7 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang S, Huang K, Shen H 2020 IEEE T. Circuits I 67 1867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jiang Y F, Lü Y, Jamali M, Wang J P 2015 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 36 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Salehi S, DeMara R F 2018 Microelectron. J. 81 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu B, Wang Z H, Li Y X, Wang Y, Liu D J, Zhao W S, Hu X B S 2021 IEEE T. Circuits II 68 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xia Y S, Yang X K, Dou S Q, Cui H Q, Wei B, Liang B J, Yan X 2024 AIP Adv. 14 045239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Z 1991 IEEE T. Circuits Syst. 38 660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu J H, Yang X K, Cui H Q, Wei B, Li C, Chen Y, Zhang M, Li C, Dong D N 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 491 165607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Biswas A K, Ahmad H, Atulasimha J, Bandyopadhyay S 2017 Nano Lett. 17 3478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bandyopadhyay S, Atulasimha J, Barman A 2021 Appl. Phys. Rev. 8 041323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fidler J, Schrefl T 2000 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 33 R135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Salehi-Fashami M, D’Souza N 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 438 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen Y B, Wei B, Yang X K, Liu J H, Li J, Cui H Q, Li C, Song M X 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 514 167216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ghanatian H, Farkhani H, Rezaeiyan Y, Bohnert T, Ferreira R, Moradi F 2022 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69 1691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brown W F 1963 Phys. Rev 130 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zeng J W, Yi P Y, Chen B Y, Huang C L, Qi X L, Qiu S, Fang L 2021 Microelectron. J. 116 105235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fashami M S, Atulasimha J, Bandyopadhyay S J N 2012 Nanotechnology 23 105201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Peng R C, Hu J M, Momeni K, Wang J J, Chen L Q, Nan C W 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dou S Q, Yang X K, Yuan J H, Xia Y S, Bai X, Cui H Q, Wei B 2023 IEEE Magn. Lett. 14 4500305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 豆树清, 杨晓阔, 夏永顺, 袁佳卉, 崔焕卿, 危波, 白馨, 冯朝文 2023 72 157501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dou S Q, Yang X K, Xia Y S, Yuan J H, Cui H Q, Wei B, Bai X, Feng C W 2023 Acta Physica Sinica 72 157501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] He Z, Fan D 2016 Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design San Francisco, August 8–10, 2016 p314
[22] Park C J, Geddada H M, Karsilayan A I, Silva-Martinez J, Onabajo M 2013 Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) Beijing, May 19–23, 2013 p141
[23] Dong Q, Yang K Y, Fick L, Fick D, Blaauw D, Sylvester D 2017 IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 25 907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Qi X L, Yi P Y, Liu J H, Li C, Chen Y B, Qiu S, Xu N, Fang L 2021 IEEE Magn. Lett. 12 4503305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
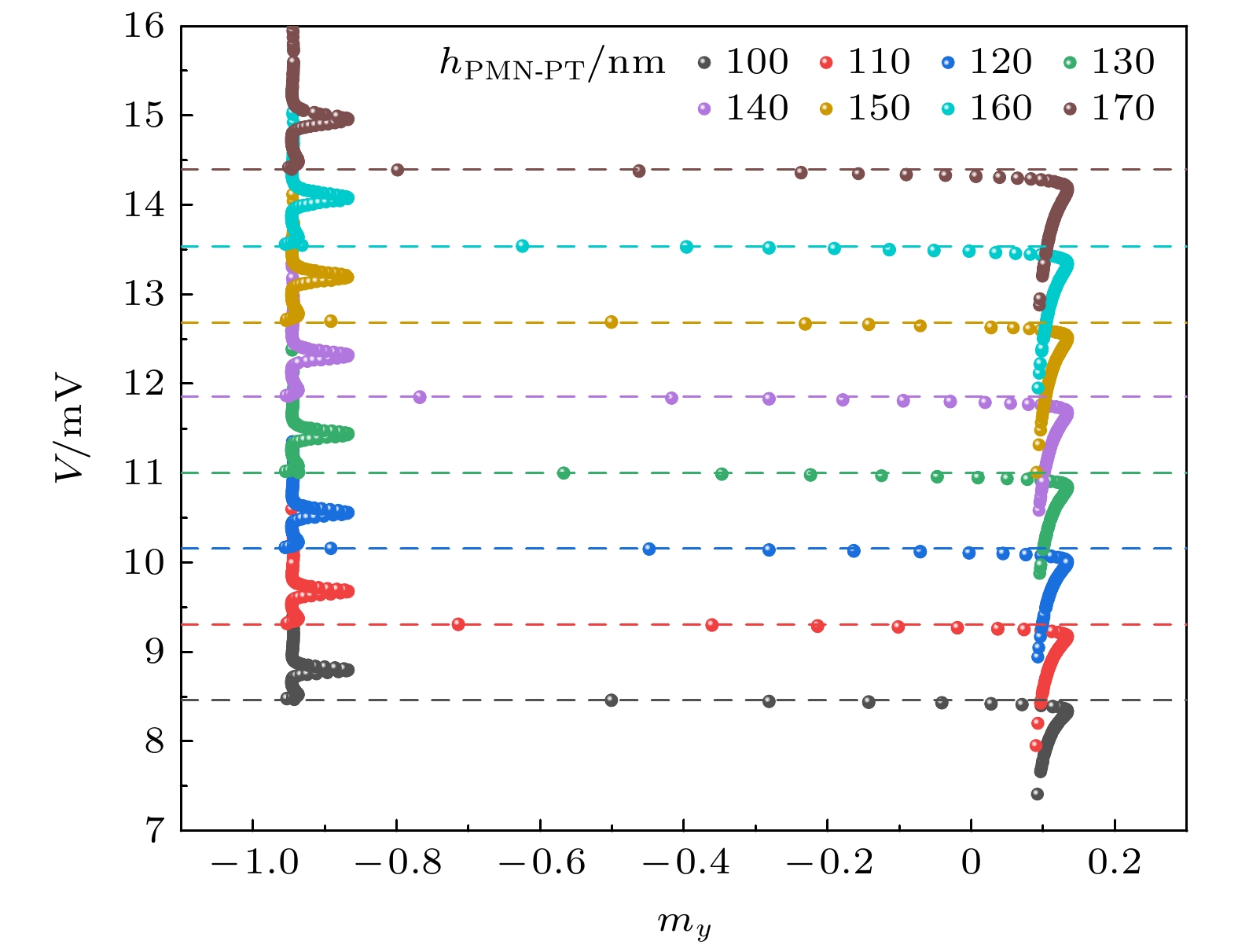
参数 Tb0.7Dy0.3Fe2 Ni 杨氏模量 Y/(1010 Pa) 8 21.4 磁致伸缩系数 λs/10–4 6.0 -0.2 吉尔伯特阻尼系数 α 0.100 0.045 回磁比 γ /(105 rad·s–1·T–1) 2.21 2.21 饱和磁化率 Ms/(105 A·m–1) 8.00 4.85 交换作用常数 A/(10–11 J·m–1) 0.90 1.05 表 2 MEADC输入输出
Table 2. MEADC input/output.
Vwrite/mV Sout7-0 Binary 0—8.53 00000000 000 8.53—9.38 00000001 001 9.38—10.24 00000011 010 10.24—11.09 00000111 011 11.09—11.95 00001111 100 11.95—12.80 00011111 101 12.80—13.66 00111111 110 13.66—14.51 01111111 111 14.51— 11111111 — 表 3 不同类型Flash ADC
Table 3. Different types of Flash ADCs.
-
[1] Murmann B 2015 IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 7 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhang S, Huang K, Shen H 2020 IEEE T. Circuits I 67 1867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jiang Y F, Lü Y, Jamali M, Wang J P 2015 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 36 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Salehi S, DeMara R F 2018 Microelectron. J. 81 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu B, Wang Z H, Li Y X, Wang Y, Liu D J, Zhao W S, Hu X B S 2021 IEEE T. Circuits II 68 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xia Y S, Yang X K, Dou S Q, Cui H Q, Wei B, Liang B J, Yan X 2024 AIP Adv. 14 045239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Z 1991 IEEE T. Circuits Syst. 38 660
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu J H, Yang X K, Cui H Q, Wei B, Li C, Chen Y, Zhang M, Li C, Dong D N 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 491 165607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Biswas A K, Ahmad H, Atulasimha J, Bandyopadhyay S 2017 Nano Lett. 17 3478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bandyopadhyay S, Atulasimha J, Barman A 2021 Appl. Phys. Rev. 8 041323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fidler J, Schrefl T 2000 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 33 R135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Salehi-Fashami M, D’Souza N 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 438 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen Y B, Wei B, Yang X K, Liu J H, Li J, Cui H Q, Li C, Song M X 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 514 167216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ghanatian H, Farkhani H, Rezaeiyan Y, Bohnert T, Ferreira R, Moradi F 2022 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69 1691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brown W F 1963 Phys. Rev 130 1677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zeng J W, Yi P Y, Chen B Y, Huang C L, Qi X L, Qiu S, Fang L 2021 Microelectron. J. 116 105235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fashami M S, Atulasimha J, Bandyopadhyay S J N 2012 Nanotechnology 23 105201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Peng R C, Hu J M, Momeni K, Wang J J, Chen L Q, Nan C W 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dou S Q, Yang X K, Yuan J H, Xia Y S, Bai X, Cui H Q, Wei B 2023 IEEE Magn. Lett. 14 4500305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 豆树清, 杨晓阔, 夏永顺, 袁佳卉, 崔焕卿, 危波, 白馨, 冯朝文 2023 72 157501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dou S Q, Yang X K, Xia Y S, Yuan J H, Cui H Q, Wei B, Bai X, Feng C W 2023 Acta Physica Sinica 72 157501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] He Z, Fan D 2016 Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design San Francisco, August 8–10, 2016 p314
[22] Park C J, Geddada H M, Karsilayan A I, Silva-Martinez J, Onabajo M 2013 Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) Beijing, May 19–23, 2013 p141
[23] Dong Q, Yang K Y, Fick L, Fick D, Blaauw D, Sylvester D 2017 IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 25 907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Qi X L, Yi P Y, Liu J H, Li C, Chen Y B, Qiu S, Xu N, Fang L 2021 IEEE Magn. Lett. 12 4503305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4820
- PDF Downloads: 83
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: