-
Dispersive media refer to a class of natural substances, including living organisms, composite materials, plasma and water, with diverse applications in areas such as biomedicine, microwave sensing, electromagnetic protection, and stealth technology. In the pursuit of investigating the electromagnetic properties of these media, time-domain numerical methods, including finite difference in time domain (FDTD), finite element method, and time domain boundary integral equation method, have been widely utilized. Time-domain numerical methods are preferred to their frequency-domain counterparts owing to their ability to handle nonlinear and wideband problems, as well as various material properties. The FDTD method, in particular, is a highly adaptable, robust, and easy-to-use numerical method that directly solves the Maxwell equations while also simulating the reflection, transmission, and scattering of electromagnetic waves in complex dispersion media. Nonetheless, the traditional FDTD method suffers low computational efficiency arising from the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy (CFL) stability condition. To solve the problem of low computational efficiency, a new method, the complying divergence implicit finite-difference time-domain (CDI-FDTD) method with a one-step leapfrog scheme, is introduced for lossy Debye dispersive media. The Maxwell equations in the frequency domain form a starting point, and the Fourier transform is utilized to transform the electromagnetic field components from the frequency domain to the time domain. To approximate the integral terms arising from the frequency-to-time domain transformation, a recursive integration (RI) method is employed. Subsequently, the time-domain Maxwell equations and auxiliary variables are discretized with a one-step leapfrog implicit scheme. The iterative formula of the RI-CDI-FDTD algorithm for lossy Debye dispersive media is then derived. The RI-CDI-FDTD method does not change the formulas of the traditional CDI-FDTD method while only requiring to add auxiliary variables for updating field components to the dispersive medium region. The numerical implementation is straightforward, and the electromagnetic modeling is flexible. Moreover, the unconditional stability of the RI-CDI-FDTD algorithm is proven by using the von Neumann method. Finally, some numerical examples are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method. In conclusion, our work contributes a crucial numerical simulation tool to accurately modeling complex dispersive media while providing a systemic stability analysis method for time-domain numerical methods.
-
Keywords:
- Debye dispersive medium /
- complying divergence implicit finite-difference time-domain method /
- recursive integration method /
- unconditionally stable
[1] Cheng X, Shao W, Wang K, Wang B Z 2019 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 18 1931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chakarothai J 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 6076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fang Y, Liu J F, Jiao Z H, Bai G H, Xi X L 2018 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tian H M, He S M, Wang M Y, Li G P, Yu M X, Zhang S T, Xu J 2021 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 20 2392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 陈碧云, 张业荣, 王磊, 王芳芳 2016 65 144101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B Y, Zhang Y R, Wang L, Wang F F 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 144101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈伟, 黄海, 杨利霞, 薄勇, 黄志祥 2023 72 060201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W, Huang H, Yang L X, Bo Y, Huang Z X 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 060201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 杨利霞, 刘超, 李清亮, 闫玉波 2022 71 064101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang L X, Liu C, Li Q L, Yan Y B 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 064101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 葛德彪, 闫玉波 2005 电磁波时域有限差分方法 (第三版) (西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社) 第259—294页
Ge D B, Yan Y B 2005 Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetic Waves (3rd Ed.) (Xi’an: Xidian University Press) pp259–294 (in Chinese)
[9] 陈娟, 王建国, 许宁 2016 弱条件稳定时域有限差分方法 (北京: 科学出版社) 第28—30页
Chen J, Wang J G, Xu N 2016 Weakly Conditionally Stable Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method (Beijing: Science Press) pp28–30 (in Chinese)
[10] Shemshadi A 2018 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gong Z, Yang S 2021 IEEE Trans. Magn. 57 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lasisi S O, Benson T M, Greenaway M T, Gradoni G, Cools K 2022 IEEE J. Multiscale Multiphys. Comput. Techn. 7 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pereda A, Vielva L A, Vegas A, Prieto A 2001 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 49 377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Park J, Jung K Y 2021 Opt. Express 29 21639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 牟春晖, 陈娟, 范凯航, 鲁艺 2022 71 184101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mou C H, Chen J, Fan K H, Lu Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 184101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Feng N, Zhang Y, Zhu J, Zeng Q, Wang G P 2021 IEEE Access 9 18550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu H, Zhao X, Wang X H, Yang S, Chen Z 2022 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 64 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu S, Zou B, Zhang L M, Ren S L 2020 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 19 816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fang M, Feng J, Xie G D, Lu Y C, Zhang X Q, Han J G, Huang Z X, Wu X L 2023 IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 33 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gan T H, Tan E L 2012 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60 5801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tan E L 2021 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 20 853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tan E L 2022 Axioms 11 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xie G D, Fang M, Huang Z X, Wu X L, Ren X G, Feng N X 2023 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 71 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kurnaz O, Aksoy S 2022 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 64 2149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kim Y J, Jung K Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 69 6600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang Y, Feng N, Zhu J, Xie G, Yang L, Huang Z 2022 Remote Sens. 14 2397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Giannopoulos A 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 2987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xie G D, Fang M, Huang Z X, Ren X G, Wu X L 2022 Comput. Phys. Commun. 280 108463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu S, Tan E L, Zou B, Zhang L M 2023 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 71 522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tekbas K, Costen F, Bérenger J P, Himeno R, Yokota H 2016 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
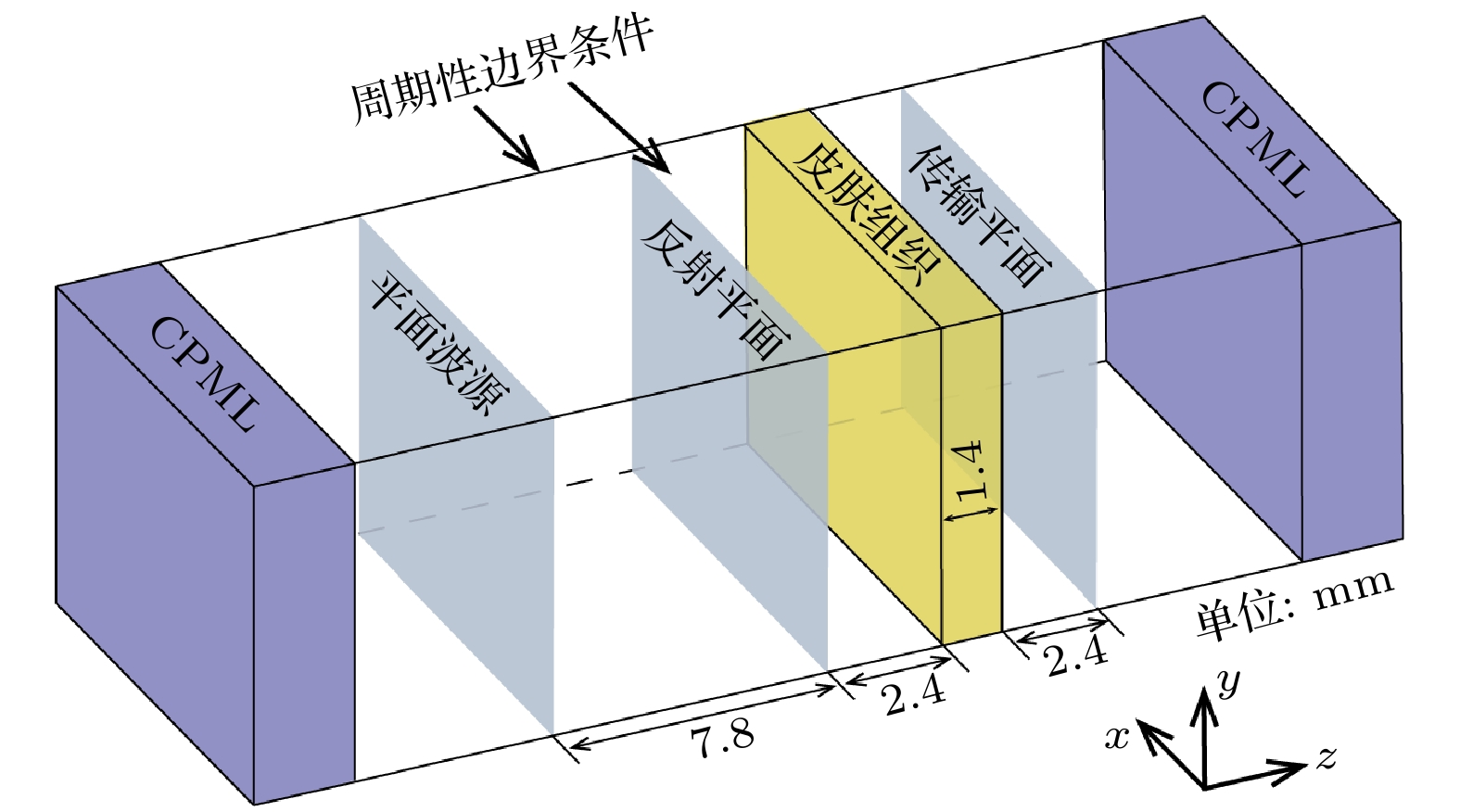
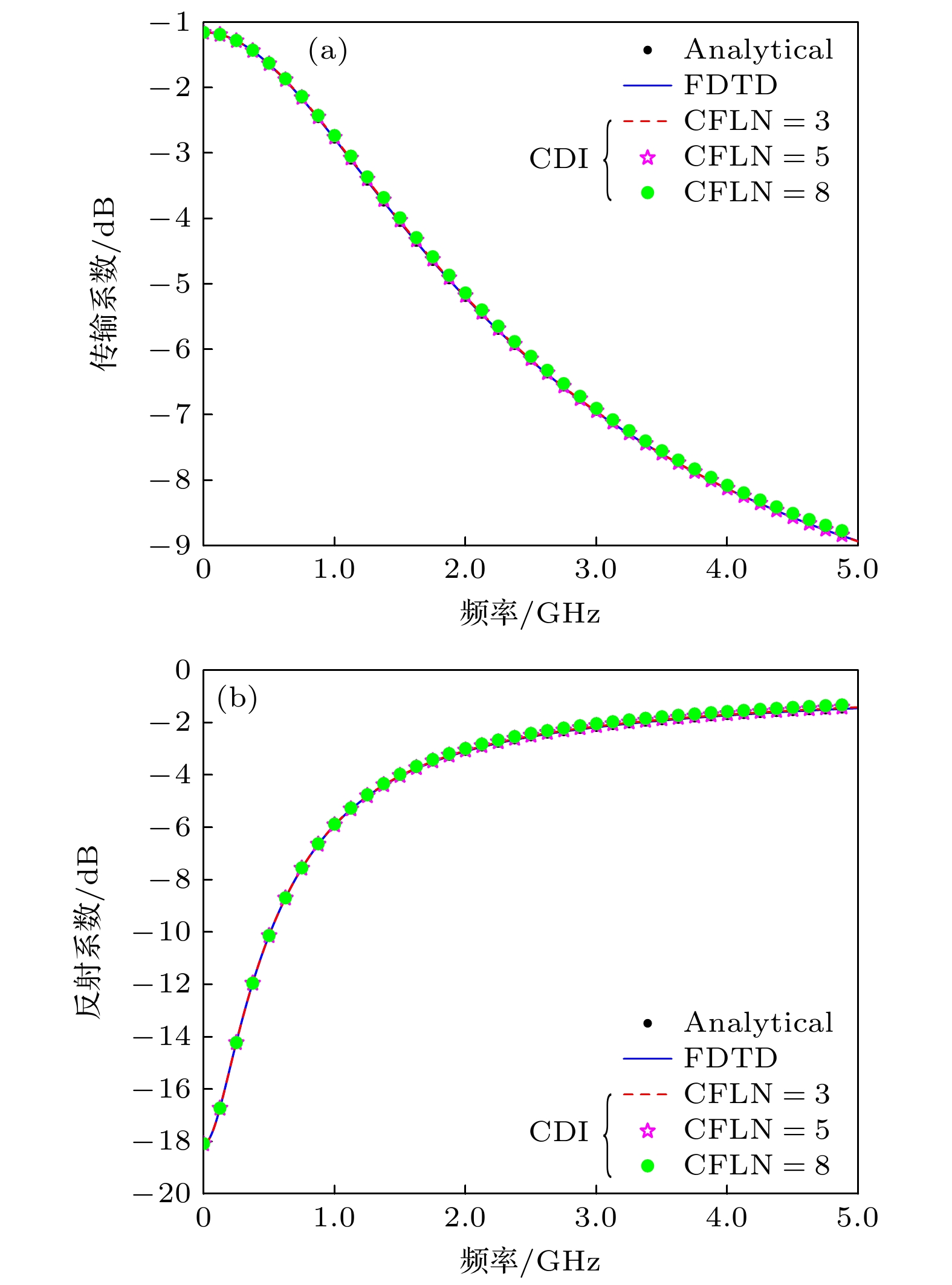
图 3 解析方法、传统FDTD方法(CFLN = 1)及RI-CDI-FDTD方法(CFLN = 3, 5, 8)计算所得色散介质板的传输和反射系数 (a) 传输系数; (b) 反射系数
Figure 3. Transmission and reflection coefficients of a dispersive medium slab calculated by using analytical method, traditional FDTD method (CFLN=1), and RI-CDI-FDTD method (CFLN = 3, 5, 8): (a) Transmission coefficient; (b) reflection coefficient.
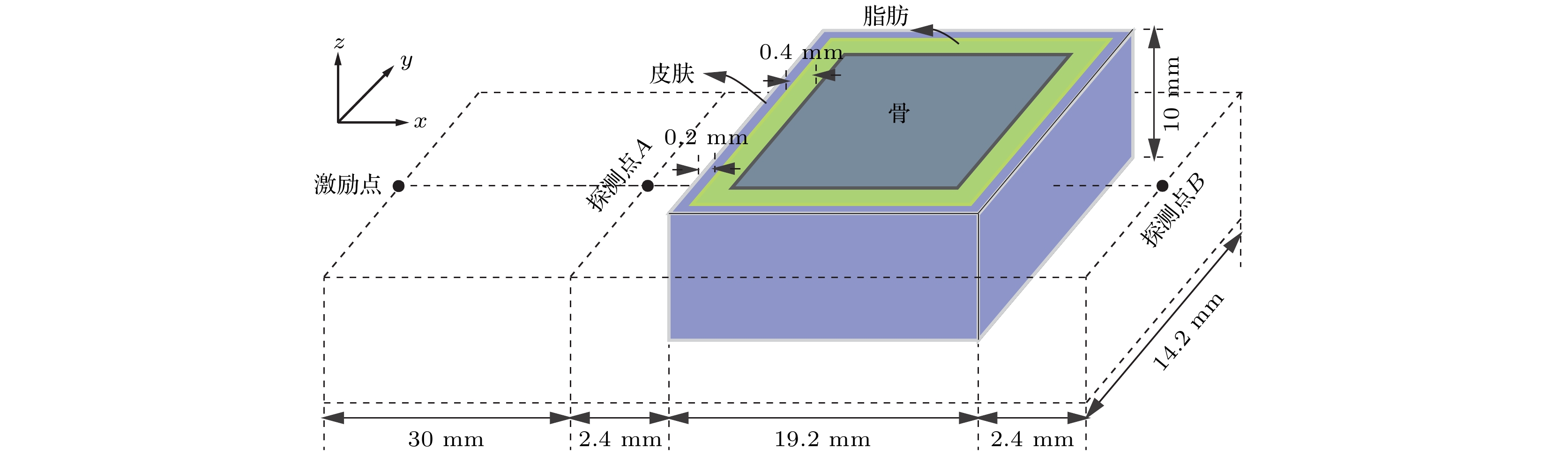
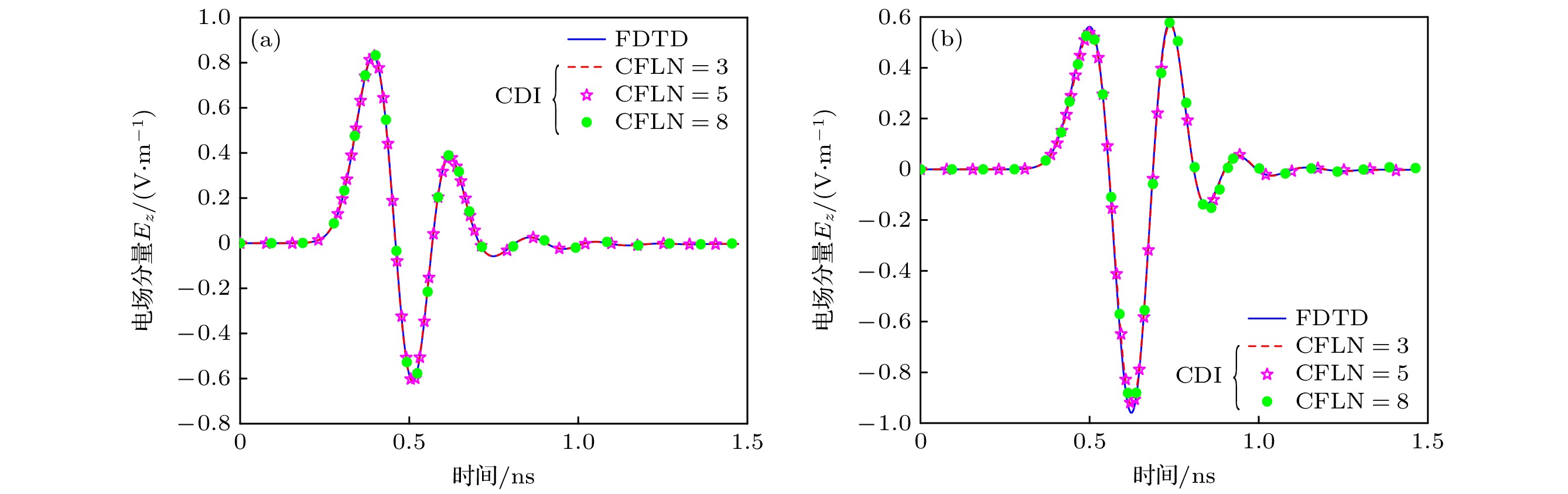
图 5 解析方法、传统FDTD方法(CFLN = 1)及RI-CDI-FDTD方法(CFLN = 3, 5, 8)计算所得探测的时域波形变化曲线 (a) A点; (b) B点
Figure 5. Time-domain waveform variation curves of detection points calculated by analytical method, traditional FDTD method (CFLN = 1), and RI-CDI-FDTD method (CFLN = 3, 5, 8): (a) The detection point A; (b) the detection point B.
表 1 不同生物组织的参数
Table 1. Parameters of different biological tissues.
生物组织 σ/(S·m–1) εs ε∞ τ/ps CPU time/s 皮肤 0.540 47.9 29.9 43.6 72.7038 脂肪 0.037 5.53 4.00 23.6 89.7149 骨头 0.104 14.2 7.36 34.1 29.9594 表 2 两种方法的仿真时间比较
Table 2. Comparison of simulation time between two methods.
方法 时间/s RI-FDTD 621.5737 RI-CDI-FDTD (CFLN = 3) 562.0881 RI-CDI-FDTD (CFLN = 5) 352.1662 RI-CDI-FDTD (CFLN = 8) 219.5618 -
[1] Cheng X, Shao W, Wang K, Wang B Z 2019 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 18 1931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chakarothai J 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 6076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fang Y, Liu J F, Jiao Z H, Bai G H, Xi X L 2018 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47 173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tian H M, He S M, Wang M Y, Li G P, Yu M X, Zhang S T, Xu J 2021 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 20 2392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 陈碧云, 张业荣, 王磊, 王芳芳 2016 65 144101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B Y, Zhang Y R, Wang L, Wang F F 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 144101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈伟, 黄海, 杨利霞, 薄勇, 黄志祥 2023 72 060201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W, Huang H, Yang L X, Bo Y, Huang Z X 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 060201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 杨利霞, 刘超, 李清亮, 闫玉波 2022 71 064101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang L X, Liu C, Li Q L, Yan Y B 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 064101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 葛德彪, 闫玉波 2005 电磁波时域有限差分方法 (第三版) (西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社) 第259—294页
Ge D B, Yan Y B 2005 Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetic Waves (3rd Ed.) (Xi’an: Xidian University Press) pp259–294 (in Chinese)
[9] 陈娟, 王建国, 许宁 2016 弱条件稳定时域有限差分方法 (北京: 科学出版社) 第28—30页
Chen J, Wang J G, Xu N 2016 Weakly Conditionally Stable Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method (Beijing: Science Press) pp28–30 (in Chinese)
[10] Shemshadi A 2018 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gong Z, Yang S 2021 IEEE Trans. Magn. 57 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lasisi S O, Benson T M, Greenaway M T, Gradoni G, Cools K 2022 IEEE J. Multiscale Multiphys. Comput. Techn. 7 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pereda A, Vielva L A, Vegas A, Prieto A 2001 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 49 377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Park J, Jung K Y 2021 Opt. Express 29 21639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 牟春晖, 陈娟, 范凯航, 鲁艺 2022 71 184101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mou C H, Chen J, Fan K H, Lu Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 184101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Feng N, Zhang Y, Zhu J, Zeng Q, Wang G P 2021 IEEE Access 9 18550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu H, Zhao X, Wang X H, Yang S, Chen Z 2022 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 64 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu S, Zou B, Zhang L M, Ren S L 2020 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 19 816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fang M, Feng J, Xie G D, Lu Y C, Zhang X Q, Han J G, Huang Z X, Wu X L 2023 IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 33 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gan T H, Tan E L 2012 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60 5801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tan E L 2021 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 20 853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tan E L 2022 Axioms 11 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xie G D, Fang M, Huang Z X, Wu X L, Ren X G, Feng N X 2023 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 71 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kurnaz O, Aksoy S 2022 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 64 2149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kim Y J, Jung K Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 69 6600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang Y, Feng N, Zhu J, Xie G, Yang L, Huang Z 2022 Remote Sens. 14 2397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Giannopoulos A 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 2987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xie G D, Fang M, Huang Z X, Ren X G, Wu X L 2022 Comput. Phys. Commun. 280 108463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu S, Tan E L, Zou B, Zhang L M 2023 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 71 522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Tekbas K, Costen F, Bérenger J P, Himeno R, Yokota H 2016 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3863
- PDF Downloads: 89
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: