-
The experimental data of the global polarization of Λ hyperon, ϕ and K*0 vector mesons in high-energy heavy ion collision confirm the new phenomenon of global polarization of hot-dense QCD matter, which has attracted extensive attention from researchers and has become a new hot research direction in the frontier of high-energy nuclear physics. This paper reviews the recent global polarization measurements. We focus on the global polarization measurements of Λ hyperon and ϕ, K*0 mesons, carried out by the solenoidal tracker detector (STAR) collaboration group at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) at its Phase I of Beam Energy Scan program, and extend to the global polarization measurements containing multiple strange quark particles, such as Ξ, Ω and the local polarization studies of Λ along the beam direction. In the paper, we also briefly comment on the measurements at higher energy from the large hadron collider (LHC) and at very low energy in HADES experiment. In the end of the paper, the physical information given by these experimental results is also briefly discussed.
-
Keywords:
- heavy-ion collision /
- global polarization /
- hyperon polarization /
- vector meson spin alignment
[1] Liang Z T, Wang X N 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 102301; 96 039901(E)
[2] Liang Z T, Wang X N 2005 Phys. Lett. B 629 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration) 2007 Phys. Rev. C 76 024915; 95 039906(E)
[4] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration) 2008 Phys. Rev. C 77 061902(R)
[5] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2017 Nature 548 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2023 Nature 614 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2018 Phys. Rev. C 98 014910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration) 2020 Phys. Rev. C 101 044611; 105 029902
[9] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 162301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 L061901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yassine R, Arnold O, Becker M, et al. (HADES Collaboration). 2022 Phys. Lett. B 835 137506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Pang L G, Petersen H, Wang Q, Wang X N 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 192301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li H, Pang L G, Wang Q, Xia X L 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 054908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sun Y, Ko C M 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 024906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Karpenko I, Becattini F 2017 Eur. Phys. J. C 77 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vitiuk O, Bravina L, Zabrodin E, 2020 Phys. Lett. B 803 135298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo Y, Liao J, Wang E, Xing H, Zhang H 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 L041902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ivanov Y 2021 Phys. Rev. C 103 L031903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Deng X G, Huang X G, Ma Y G, Zhang S 2020 Phys. Rev. C 101 064908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wei D X, Deng W T, Huang X G 2019 Phys. Rev. C 99 014905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liang Z T, Song J, Upsal I Wang Q, Xu Z B 2021 Chin. Phys. C 45 014102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng X G, Huang X G, Ma Y G 2022 Phys. Lett. B 835 137560
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sheng X L, Oliva L, Wang Q 2020 Phys. Rev. D 101 096005; 105 099903(E)
[24] Sheng X L, Wang Q, Wang X N 2020 Phys. Rev. D 102 056013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sheng X L, Oliva L, Liang Z T, Wang Q, Wang X N arXiv: 2205.15689
[26] Sheng X L, Oliva L, Liang Z T, Wang Q, Wang X N arXiv: 2206.05868
[27] Gao J H, Ma G L, Pu S, Wang Q 2020 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 31 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lin, Z W, Zheng L 2021 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 32 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shao T H, Chen J H, Ko C M, Sun K J, Xu Z B 2020 Chin. Phys. C 44 114001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Peng H H, Zhang J J, Sheng X L, Wang Q 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett. 38 116701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Chen J H, Keane D, Ma Y G, Tang A H, Xu Z B 2018 Phys. Rept. 760 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang X N 2023 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 34 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 高建华, 黄旭光, 梁作堂, 王群, 王新年 2023 72 072501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J H, Huang X G, Liang Z T, Wang Q, Wang X N 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 072501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Workman R L et al. (Particle Data Group). 2022 PTEP 2022 083C01
[35] Poskanzer A M, Voloshin S A 1998 Phys. Rev. C 58 1671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Becattini F, Karpenko I 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 012302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 132301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration). 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 172005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Fu B C, Liu S, Pang L G, Song H C, Yin Y 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 142301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Tang A H, Tu B, Zhou C S 2018 Phys. Rev. C 98 044907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration). 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 012301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 盛欣力, 梁作堂, 王群 2023 72 072502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng X L, Liang Z T, Wang Q 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 072502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Shen D Y, Chen J H, Lin Z W 2021 Chin. Phys. C 45 054002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Li Z Y, Cha W M, Tang Z B 2022 Phys. Rev. C 106 064908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] 杨驰, 陈金辉, 马余刚, 徐庆华 2019 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 49 102008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang C, Chen J H, Ma Y G, Xu Q H 2019 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 49 102008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration) arXiv: 2204.10171
-
图 5 非对心重离子碰撞横平面中速度场和涡旋示意图[37]. z轴方向为束流方向, x-z平面为反应平面
Figure 5. A sketch illustrating the system created in a noncentral heavy-ion collision viewed in the transverse plane. Velocity field and expected vorticities are shown, the colliding beams are along the z axis and z-x plane defines the reaction plane.
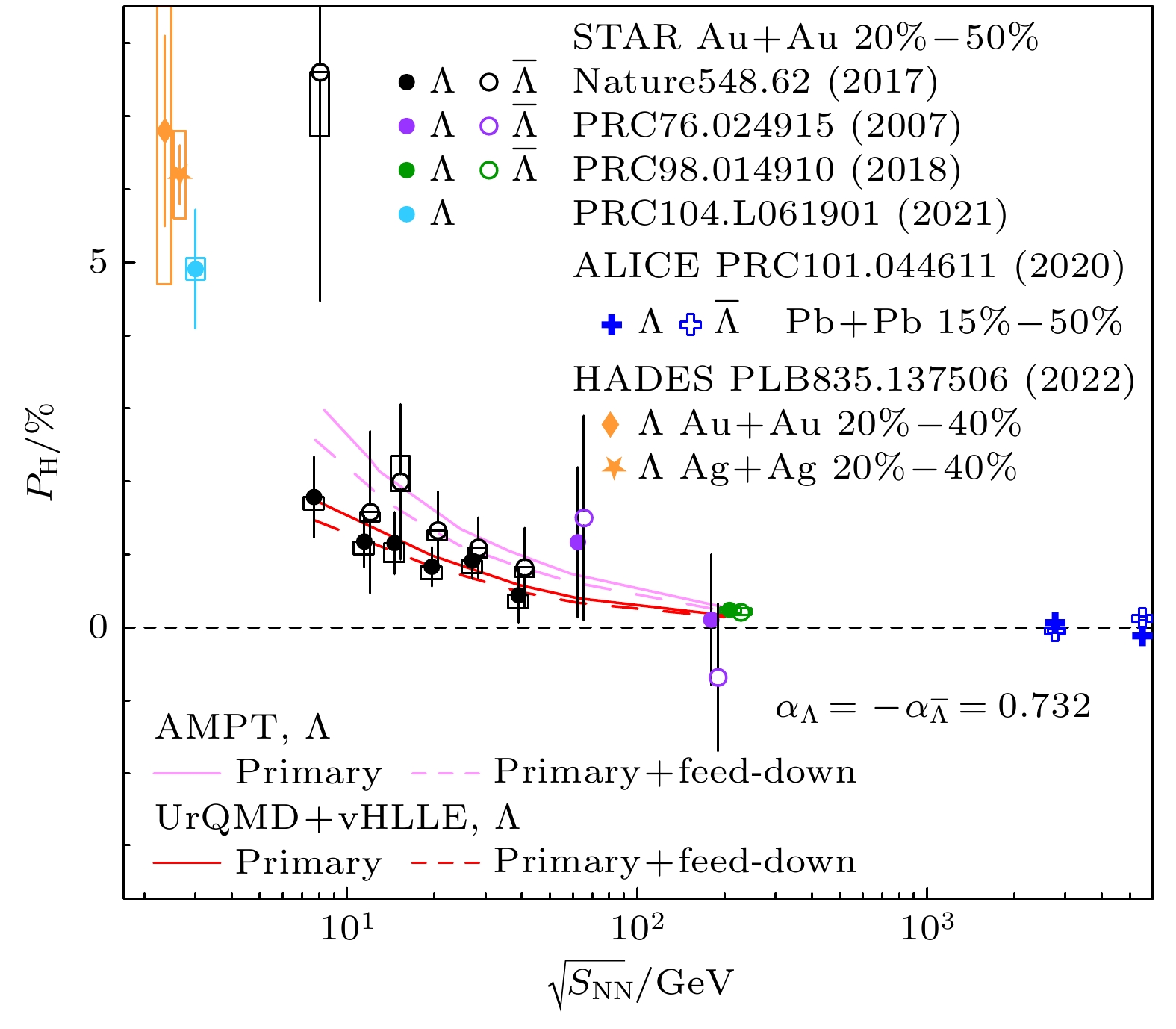
图 6 200 GeV金核-金核碰撞20%—60%中心度事例中Λ超子和其反粒子的
$ {\left\langle{{\rm{cos}}{\theta }_{{\rm{p}}}^{*}}\right\rangle}^{{\rm{s}}{\rm{u}}{\rm{b}}} $ 关于$\phi -{\varPsi }_{2}$ 的依赖[37]Figure 6.
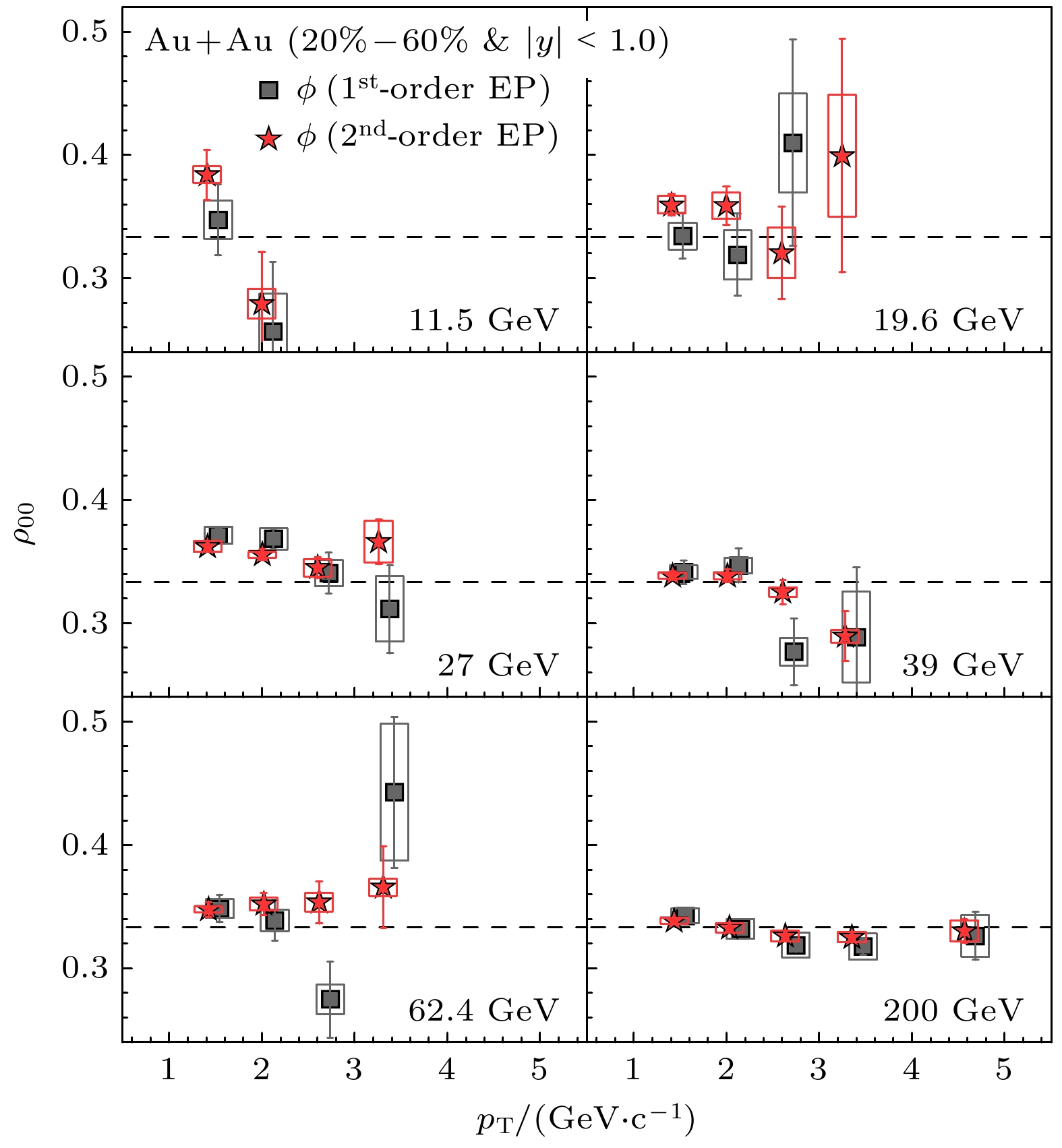
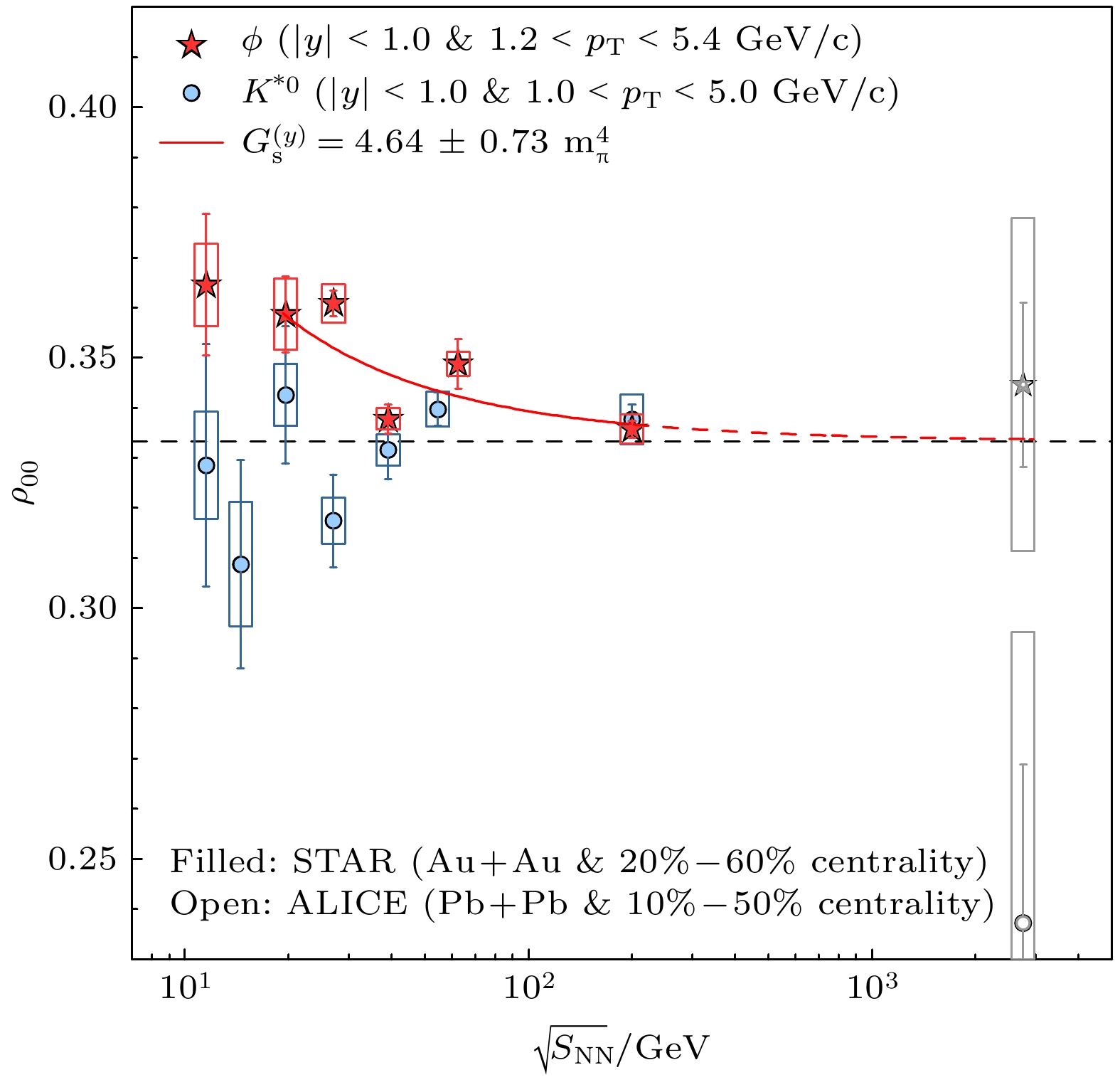
$ {\left\langle{{\rm{cos}}{\theta }_{{\rm{p}}}^{*}}\right\rangle}^{{\rm{s}}{\rm{u}}{\rm{b}}} $ of Lambda and anti-Lambda as a function of azimuthal angle$\phi$ relative to the second-order event plane$ {\varPsi }_{2} $ for 20%—60% centrality Au+Au collisions at 200 GeV[37].图 13 相对论重离子碰撞中ϕ和K*0整体极化测量结果[6]. 图中实心数据点来自STAR测量, 空心点是从ALICE实验中选出和STAR数据的动量区间, 中心度区间最接近的测量. 红色实心线是π介子场局域涨落理论对实验数据的拟合, 红色虚线则是该拟合外延到LHC能区[41]
Figure 13. Measurements of ϕ and K*0 global spin alignment in heavy-ion collisions[6]. Solid points are data from STAR measurement, open symbols indicate ALICE results with the pT bin nearest to the mean pT for the 1.0–5.0 GeV/c range assumed for each meson in the STAR analysis. The red solid line is the fitting of the local fluctuation theory of the π meson field to the experimental data, and the red dotted line is the extension of the fitting to the LHC energy region [41].
-
[1] Liang Z T, Wang X N 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 102301; 96 039901(E)
[2] Liang Z T, Wang X N 2005 Phys. Lett. B 629 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration) 2007 Phys. Rev. C 76 024915; 95 039906(E)
[4] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration) 2008 Phys. Rev. C 77 061902(R)
[5] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2017 Nature 548 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2023 Nature 614 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2018 Phys. Rev. C 98 014910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration) 2020 Phys. Rev. C 101 044611; 105 029902
[9] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 162301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 L061901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yassine R, Arnold O, Becker M, et al. (HADES Collaboration). 2022 Phys. Lett. B 835 137506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Pang L G, Petersen H, Wang Q, Wang X N 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 192301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li H, Pang L G, Wang Q, Xia X L 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 054908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sun Y, Ko C M 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 024906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Karpenko I, Becattini F 2017 Eur. Phys. J. C 77 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vitiuk O, Bravina L, Zabrodin E, 2020 Phys. Lett. B 803 135298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo Y, Liao J, Wang E, Xing H, Zhang H 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 L041902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ivanov Y 2021 Phys. Rev. C 103 L031903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Deng X G, Huang X G, Ma Y G, Zhang S 2020 Phys. Rev. C 101 064908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wei D X, Deng W T, Huang X G 2019 Phys. Rev. C 99 014905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liang Z T, Song J, Upsal I Wang Q, Xu Z B 2021 Chin. Phys. C 45 014102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Deng X G, Huang X G, Ma Y G 2022 Phys. Lett. B 835 137560
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sheng X L, Oliva L, Wang Q 2020 Phys. Rev. D 101 096005; 105 099903(E)
[24] Sheng X L, Wang Q, Wang X N 2020 Phys. Rev. D 102 056013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sheng X L, Oliva L, Liang Z T, Wang Q, Wang X N arXiv: 2205.15689
[26] Sheng X L, Oliva L, Liang Z T, Wang Q, Wang X N arXiv: 2206.05868
[27] Gao J H, Ma G L, Pu S, Wang Q 2020 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 31 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lin, Z W, Zheng L 2021 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 32 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shao T H, Chen J H, Ko C M, Sun K J, Xu Z B 2020 Chin. Phys. C 44 114001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Peng H H, Zhang J J, Sheng X L, Wang Q 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett. 38 116701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Chen J H, Keane D, Ma Y G, Tang A H, Xu Z B 2018 Phys. Rept. 760 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang X N 2023 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 34 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 高建华, 黄旭光, 梁作堂, 王群, 王新年 2023 72 072501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J H, Huang X G, Liang Z T, Wang Q, Wang X N 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 072501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Workman R L et al. (Particle Data Group). 2022 PTEP 2022 083C01
[35] Poskanzer A M, Voloshin S A 1998 Phys. Rev. C 58 1671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Becattini F, Karpenko I 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 012302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Abelev B I, Aggarwal M M, Ahammed Z, et al. (STAR Collaboration). 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 132301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration). 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 172005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Fu B C, Liu S, Pang L G, Song H C, Yin Y 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 142301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Tang A H, Tu B, Zhou C S 2018 Phys. Rev. C 98 044907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration). 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 012301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] 盛欣力, 梁作堂, 王群 2023 72 072502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng X L, Liang Z T, Wang Q 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 072502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Shen D Y, Chen J H, Lin Z W 2021 Chin. Phys. C 45 054002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Li Z Y, Cha W M, Tang Z B 2022 Phys. Rev. C 106 064908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] 杨驰, 陈金辉, 马余刚, 徐庆华 2019 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 49 102008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang C, Chen J H, Ma Y G, Xu Q H 2019 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 49 102008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Acharya S, AdamováD, Adhya S P, et al. (ALICE Collaboration) arXiv: 2204.10171
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10854
- PDF Downloads: 276
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: