-
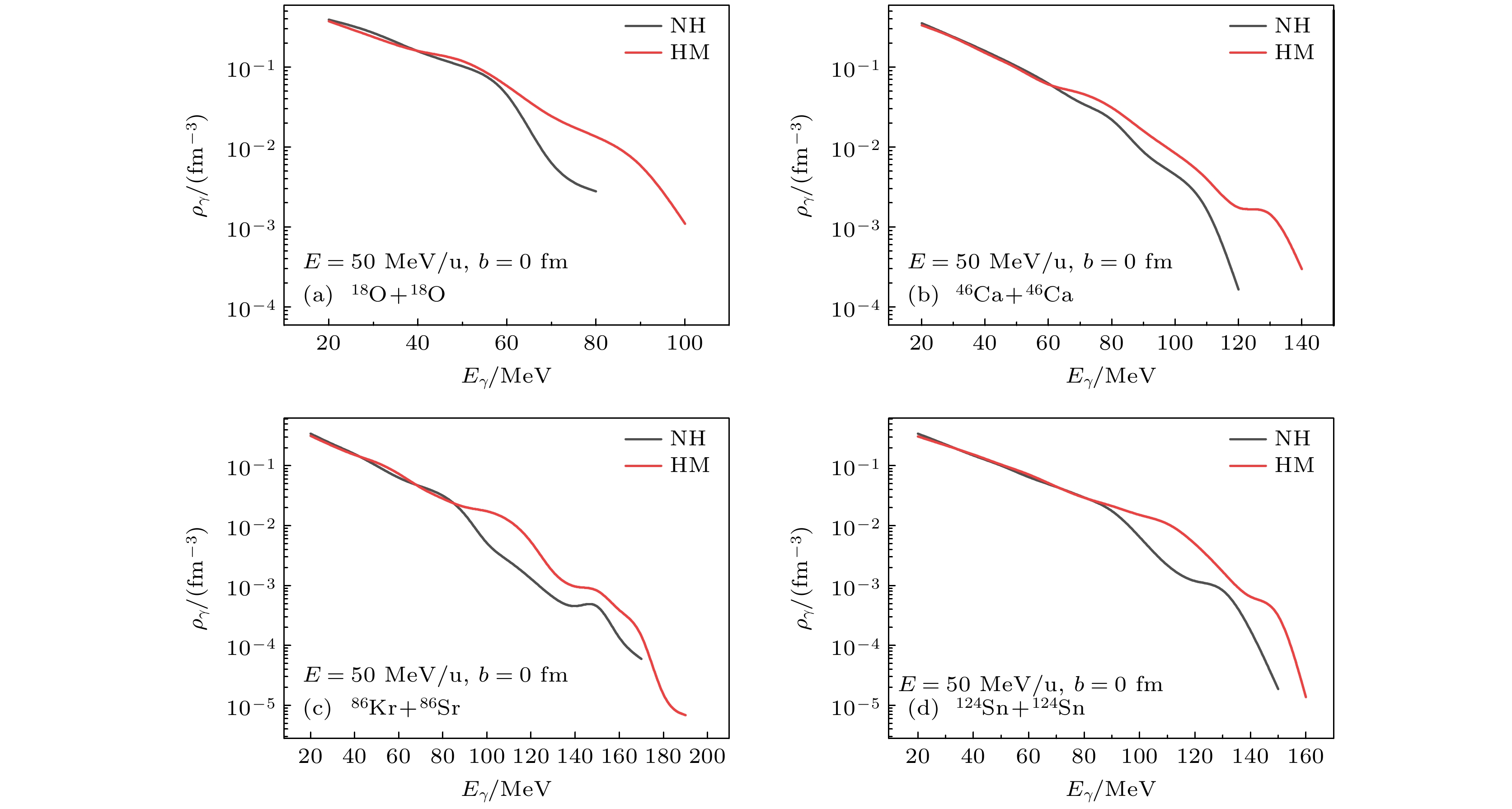
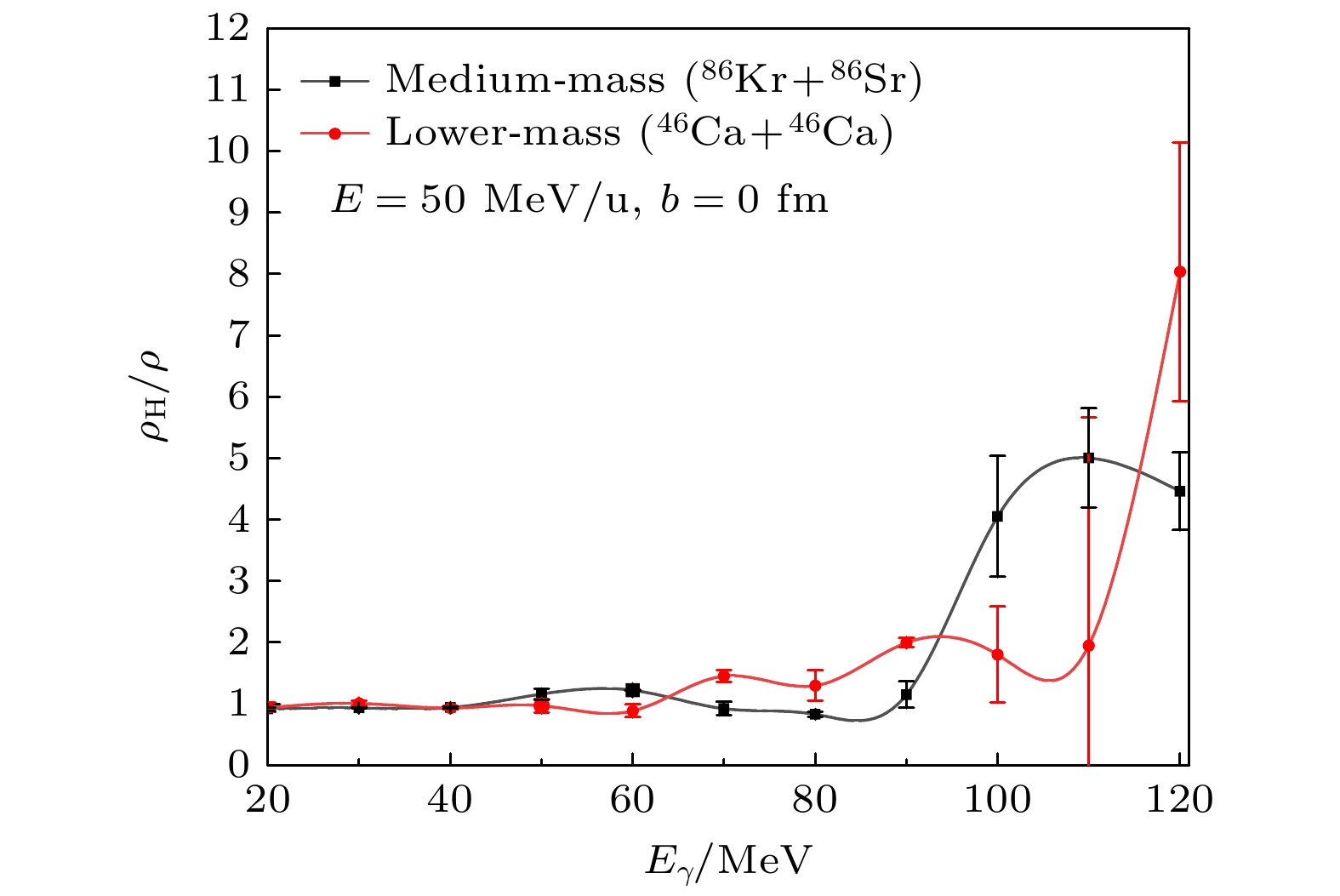
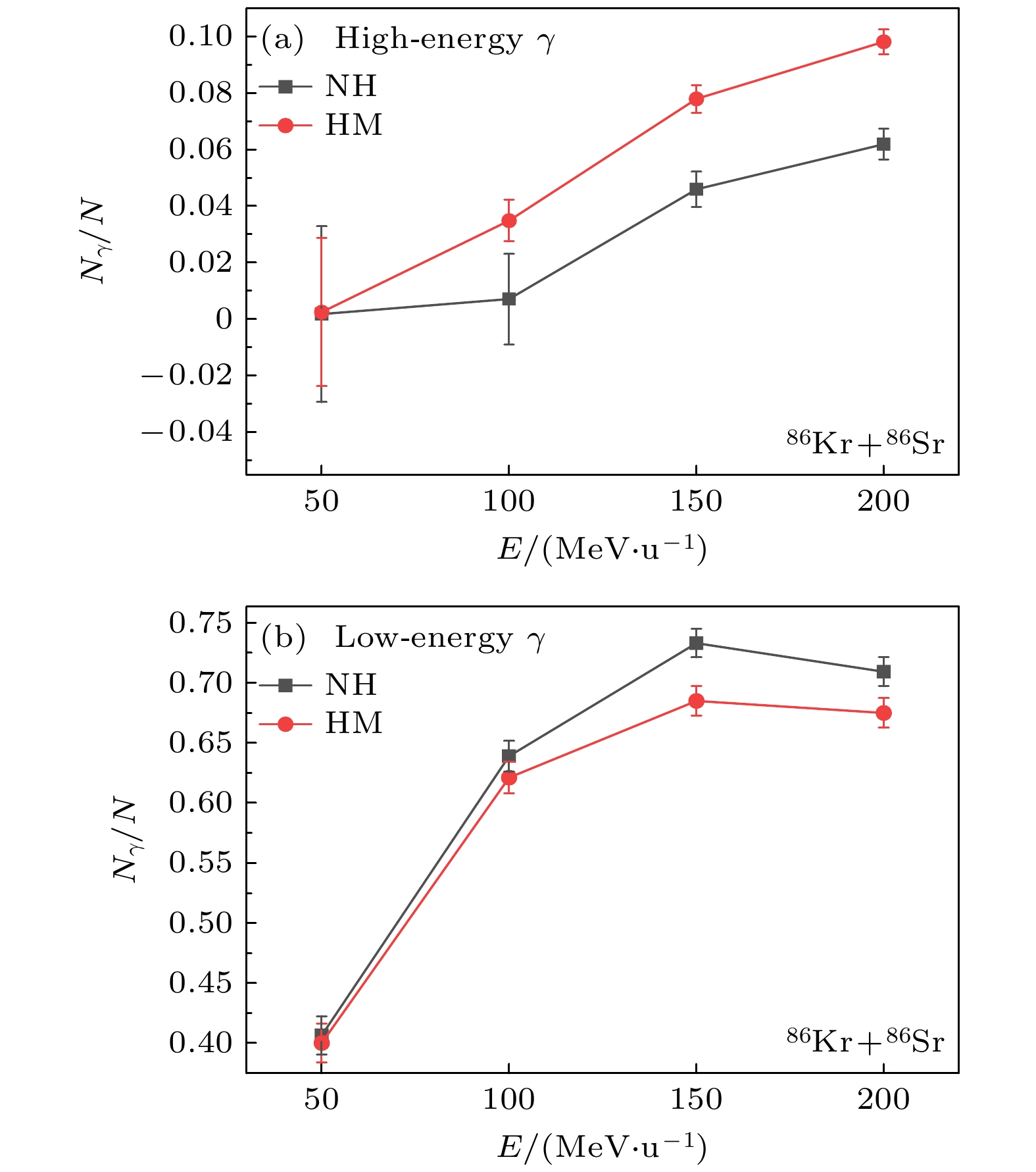
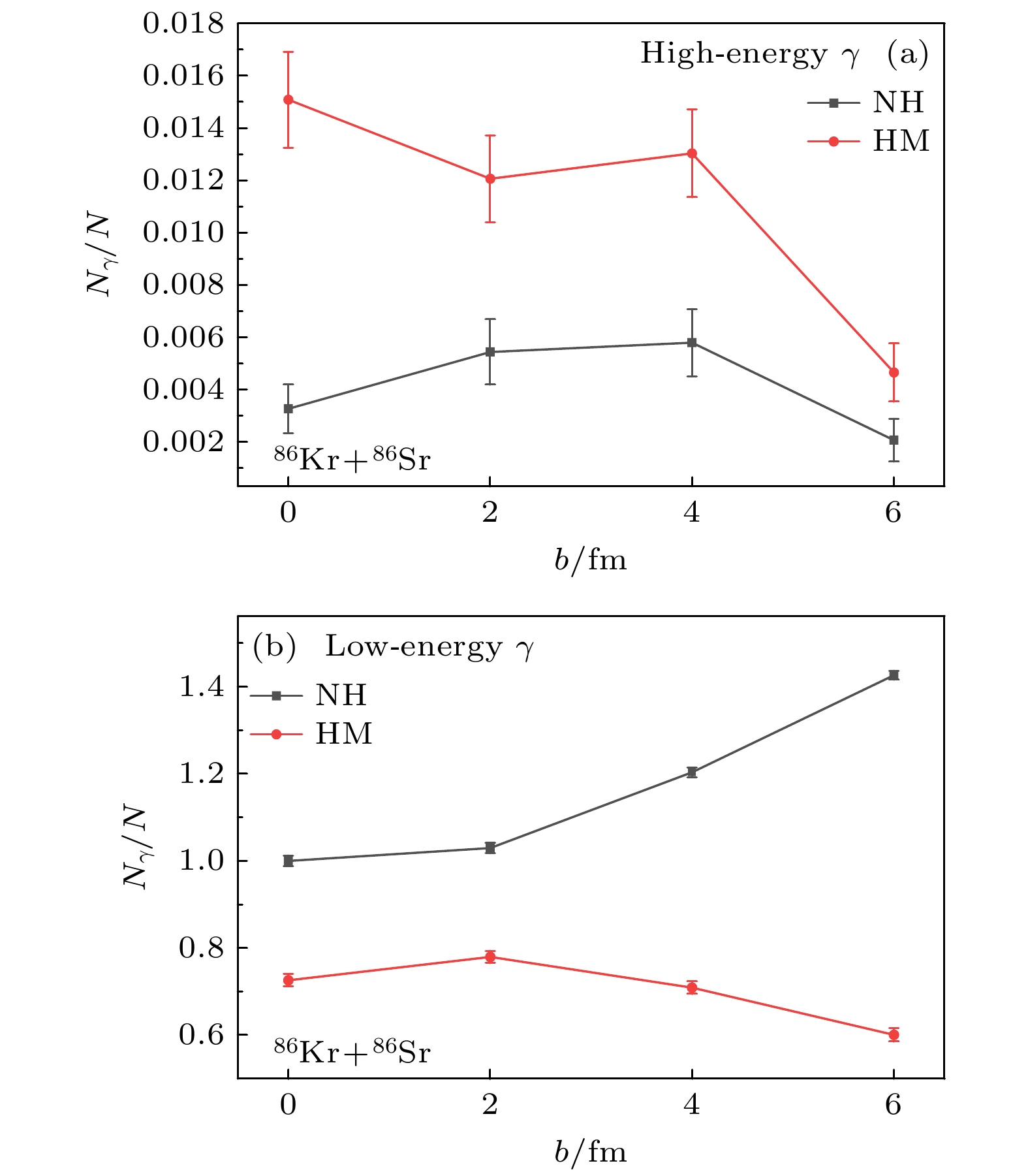
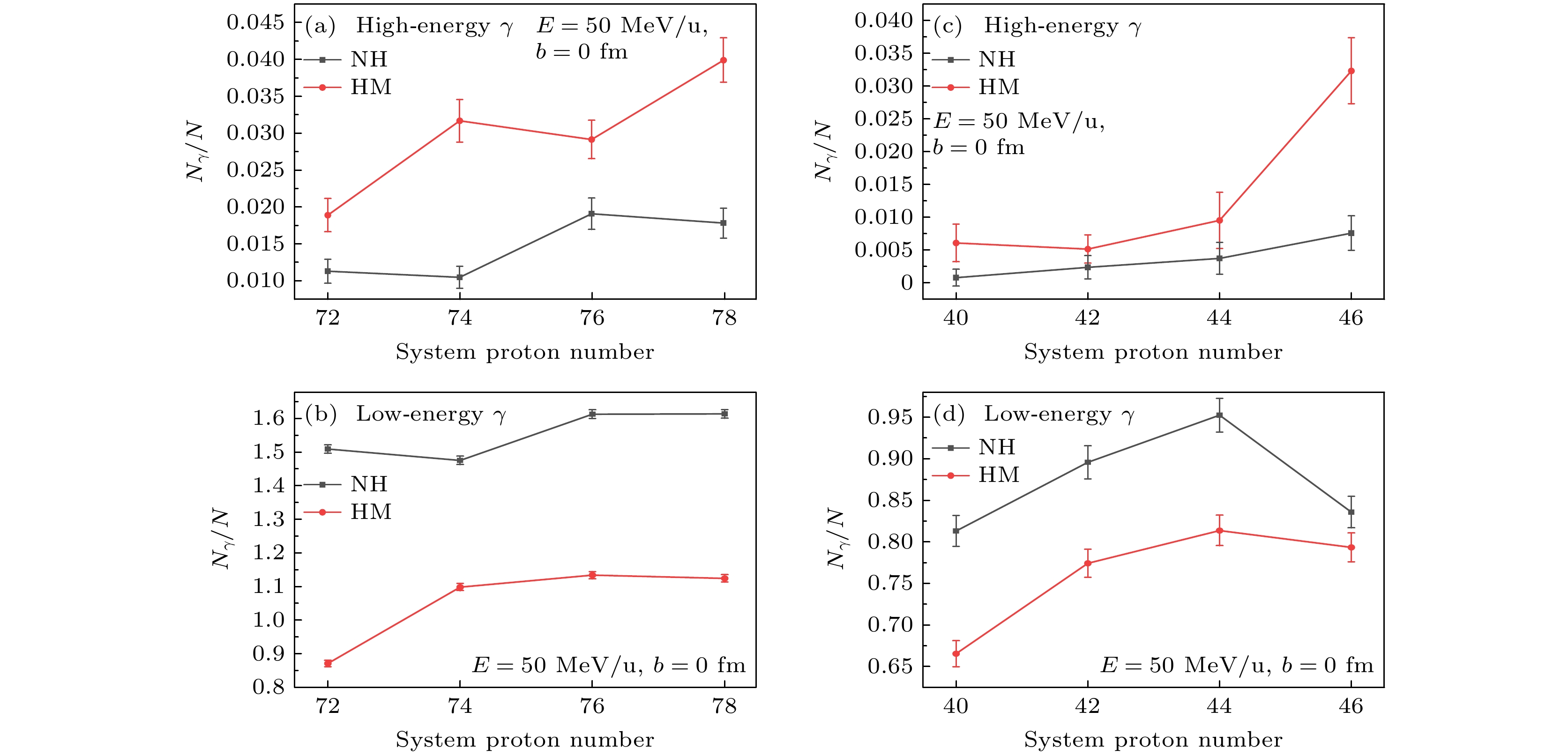
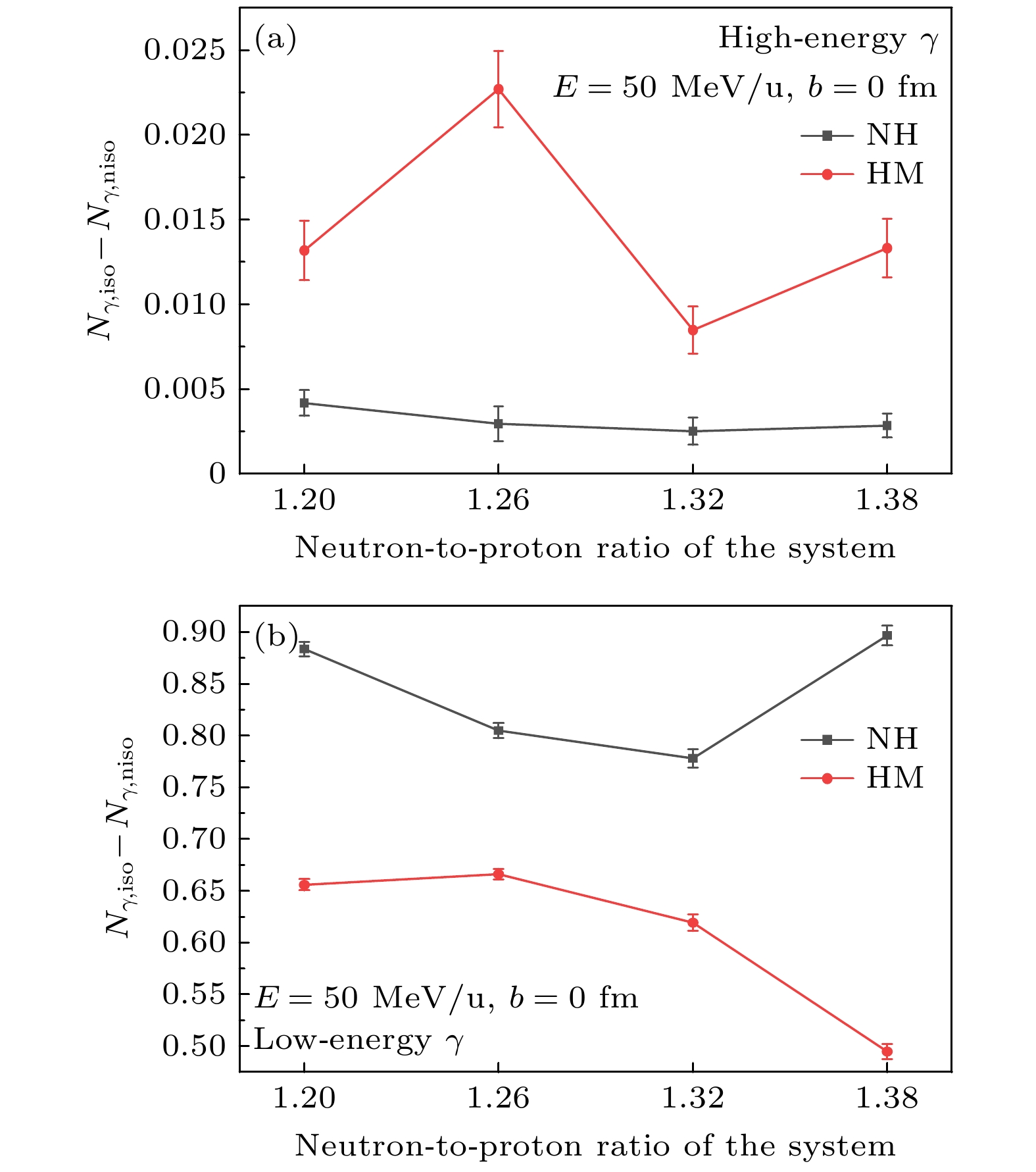
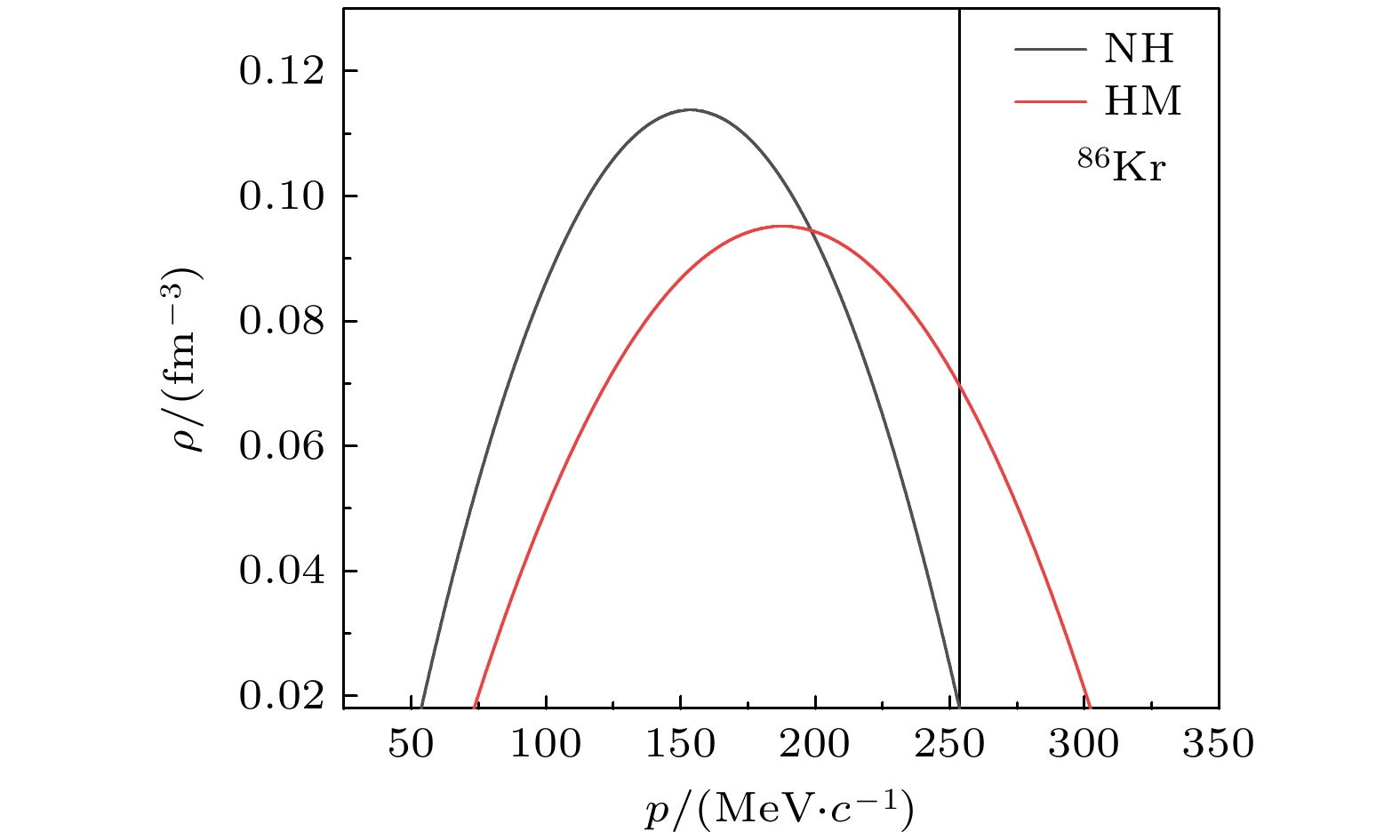
基于量子分子动力学模型, 以核子轫致辐射光子为探针, 系统研究了高动量分布(HMT)对核反应系统的影响, 并探讨了这种影响与入射能量、碰撞参数及同位旋相关核子-核子碰撞截面的关系. 研究结果表明: 在入射能量为50 MeV/u时, 从轻到重的反应系统, 含HMT的系统在高能区的光子密度均显著高于无HMT的系统, 而在低能区两者差异不明显. 此外, 在对心碰撞中光子能量改变现象随入射能量的增加而增强, 并在E = 150 MeV/u时达到峰值. 这一由HMT引起的能量移动现象在碰撞参数b = 0—6 fm范围内普遍存在. 进一步分析表明, 同位旋相关核子-核子碰撞截面的引入会改变系统的碰撞概率, 而HMT通过影响核子间相互作用进一步调制了这一过程. 综上所述, HMT对核反应系统具有重要影响, 其效应与入射能量和同位旋相关核子-核子碰撞截面密切相关.In this work, semi-classical quantum molecular dynamics is used to investigate the influence of high momentum distribution on nuclear reaction systems by using photons produced by nucleon bremsstrahlung as indicators. The research examines the relationship between this influence and the incident energy, collision parameters, and the differences in isotopic spin cross-sections. Under the condition of a 20% high-momentum distribution and ensuring the conservation of nuclear energy, a system different from traditional configurations is constructed by sampling neutrons and protons using the Monte Carlo method, with the selected nucleons exhibiting characteristics of high-momentum nucleons. The influence of high-momentum distribution within the nucleus on bremsstrahlung photons is analyzed through the collision results of heavy ions in nuclear systems spanning from light to heavy species. The results indicate that, at an incident energy value of 50 MeV/u, the collision system studied in this work exhibits higher photon density in the high-energy region of high momentum distribution system than traditional system for nuclear systems ranging from light-mass system (18O+18O), lower-mass system (46Ca+46Ca), and medium-mass system (86Kr+86Sr) to heavy-mass system (124Sn+124Sn), than those, while there is no significant difference in photon density in the low-energy region. At a collision parameter b = 0 fm, the energy shift phenomenon of photons produced by collisions becomes more pronounced with the increase of incident energy, peaking at E = 150 MeV/u. This energy transfer phenomenon induced by high momentum distribution typically exists within the collision parameter range from b = 0 fm to b = 6 fm. When considering isotopic spin cross-sections, high momentum distribution can affect the collision probability of the system. Therefore, high momentum distribution has a significant influence on nuclear reaction system, closely related to incident energy and isotopic spin cross-section.
-
Keywords:
- high-momentum distribution /
- heavy-ion collision /
- spectrum /
- isospin effect
[1] Subedi R, Shneor R, Monaghan P, et al. 2008 Science 320 1476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hen O, Sargsian M, Weinstein L B, et al. 2014 Science 346 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hen O, Li B A, Guo W J, Weinstein L B, Piasetzky E 2015 Phys. Rev. C 91 025803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yong G C, Li B A 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 064614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li S, Cruz-Torres R, Santiesteban N, et al. 2022 Nature 609 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li B A, Guo W J, Shi Z 2015 Phys. Rev. C 91 044601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bulgac A 2023 Phys. Rev. C 107 L061602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Pazy E 2023 Phys. Rev. C 107 054308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hong B, Ren Z Z, Wu C, Mu X 2023 Classical Quantum Gravity 40 125007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yong G C 2022 Phys. Rev. C 105 L011601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rodrigues E H, Dutra M, Lourenço O 2023 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 523 4859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang R, Ma N N, Wang T F 2023 Chin. Phys. C 47 044103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Weinstein L B, Piasetzky E, Higinbotham D W, Gomez J, Hen O, Shneor R 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 052301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dutra M, Lenzi C H, Lourenço O 2022 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 517 4265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lourenço O, Lenzi C H, Frederico T, Dutra M 2022 Phys. Rev. D 106 043010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sedrakian A 2024 Phys. Rev. Lett. 133 171401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lopes L L 2024 Phys. Rev. C 110 015805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tews I, Lattimer J M, Ohnishi A, Kolomeitsev E E 2017 Astrophys. J. 848 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Aichelin J, Bertsch G F 1985 Phys. Rev. C 31 1370
[20] Aichelin J, Stocker H 1986 Phys. Lett. B 176 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Aichelin J, Peilert G, Bohnet A, et al. 1988 Phys. Rev. C 37 2451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bass S A, Belkacem M, Bleicher M, et al. 1998 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 41 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Germain M, Hartnack C, Laville J L, Aichelin J, Belkacem M, Suraud E 1998 Phys. Lett. B 437 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] d’Enterria D G, Martínez G, Aphecetche L, Delagrange H, Fernández F, Löhner H, Ortega R, Ostendorf R W, Schutz Y, Wilschut H W 2002 Phys. Lett. B 538 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Guo W M, Li B A, Yong G C 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 034603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yong G C, Zuo W, Zhang X C 2011 Phys. Lett. B 705 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Subedi R, Shneor R, Monaghan P, et al. 2008 Science 320 1476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hen O, Sargsian M, Weinstein L B, et al. 2014 Science 346 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hen O, Li B A, Guo W J, Weinstein L B, Piasetzky E 2015 Phys. Rev. C 91 025803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yong G C, Li B A 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 064614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li S, Cruz-Torres R, Santiesteban N, et al. 2022 Nature 609 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li B A, Guo W J, Shi Z 2015 Phys. Rev. C 91 044601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bulgac A 2023 Phys. Rev. C 107 L061602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Pazy E 2023 Phys. Rev. C 107 054308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hong B, Ren Z Z, Wu C, Mu X 2023 Classical Quantum Gravity 40 125007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yong G C 2022 Phys. Rev. C 105 L011601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rodrigues E H, Dutra M, Lourenço O 2023 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 523 4859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang R, Ma N N, Wang T F 2023 Chin. Phys. C 47 044103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Weinstein L B, Piasetzky E, Higinbotham D W, Gomez J, Hen O, Shneor R 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 052301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dutra M, Lenzi C H, Lourenço O 2022 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 517 4265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lourenço O, Lenzi C H, Frederico T, Dutra M 2022 Phys. Rev. D 106 043010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sedrakian A 2024 Phys. Rev. Lett. 133 171401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lopes L L 2024 Phys. Rev. C 110 015805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tews I, Lattimer J M, Ohnishi A, Kolomeitsev E E 2017 Astrophys. J. 848 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Aichelin J, Bertsch G F 1985 Phys. Rev. C 31 1370
[20] Aichelin J, Stocker H 1986 Phys. Lett. B 176 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Aichelin J, Peilert G, Bohnet A, et al. 1988 Phys. Rev. C 37 2451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bass S A, Belkacem M, Bleicher M, et al. 1998 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 41 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Germain M, Hartnack C, Laville J L, Aichelin J, Belkacem M, Suraud E 1998 Phys. Lett. B 437 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] d’Enterria D G, Martínez G, Aphecetche L, Delagrange H, Fernández F, Löhner H, Ortega R, Ostendorf R W, Schutz Y, Wilschut H W 2002 Phys. Lett. B 538 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Guo W M, Li B A, Yong G C 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 034603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yong G C, Zuo W, Zhang X C 2011 Phys. Lett. B 705 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 922
- PDF下载量: 32
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: