-
The entropy-modulated material has been a hot topic due to its unique design concept and excellent properties. However, previous studies of entropy-modulated materials mainly focused on the alloys with simple face-centered cubic, or body-centered cubic, or hexagonal close-packed structures. In this work, the design concept of entropy-modulation is introduced into Gd2Co17 based intermetallic compound, and the effect of high configuration entropy on the structural stabilization and room-temperature magnetic properties of Gd2Co17 based intermetallic compound are studied systematically. The samples are prepared by vacuum Arc melting technology in an ultrahigh-purity Ar atmosphere and followed by annealing at 1000 ℃ for 8 days and finally by quenching in cool water. The fine powders are prepared by grinding the ingots in an agate mortar. The powder XRD and SEM-EDS are used to check the crystal structures and chemical compositions. To study the magnetic properties, the column-like samples are prepared by mixing the fine powder and epoxy with a weight ratio of 1∶1, and then aligned under an applied field of 1 T at room temperature. The high configuration entropy is found to play an important role in the structural stabilization and magnetic properties of Gd2Co17 based medium- and high-entropy intermetallic compounds. The XRD patterns and Rietveld structural refinement results confirm that all the samples are single-phase. The structure depends on the effective atomic radius RA, the structure of entropized Gd2Co17 based intermetallics can be stabilized into rhombohedral Th2Zn17-type with RA > 1.416 or hexagonal Th2Ni17-type with RA < 1.4105. According to thermodynamic calculations of entropized Gd2Co17 intermeatllics, the atomic radius difference Δr ranges from 0.55% to 1.81%, and the mixing enthalpy $ \Delta {{\boldsymbol{H}}}_{{\rm{m}}{\rm{i}}{\rm{x}}} $ is corresponding to 0 for the rare earth site, –4 to –1 kJ/mol for the transition metal site, and –8.54 to –5.13 kJ/mol between rare earth and transition metal sites. It is suggested that all the thermodynamic parameters meet the criteria for the formation of single-phase medium- and high-entropy intermetallic compounds. The configuration entropy changes from 0.69R to 1.39R. The room temperature magnetic properties are significantly improved by the modulation of entropized design at rare earth and transition metal sublattices. The entropization enhances the saturation moments of all samples, which can be explained with a modified magnetic valence model. The value of${N}_{{\rm{sp}}}^{\uparrow }$ (the number of the electrons in the unpolarized sp conduction bands) increases from 0.3 to 0.4 after entropization, the indirect interaction between rare earth and transition metal sublattice is increased, the spin moment of s conducting electron as a medium of two sublattices is enhanced, and the magnetic moment is increased. The entropization also induces magnetic anisotropy to transform from basal plane to easy axis for the entropized design at transition metal sublattice and the coercivity of rare earth to increase.-
Keywords:
- Gd2Co17 /
- high entropy intermetallic compound /
- Rietveld refinement /
- magnetic valence model
[1] Yin L H, Guo Y Q, Guo X P 2022 Inorg. Chem. 61 2402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Shen B G, Cheng Z H, Liang B, Guo H Q, Zhang J X, Gong H Y, Wang F W, Yan Q W, Zhan W S 1995 Appl. Phys. Lett. 67 1621
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Coey J M D, Sun H 1990 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 87 L251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 易健宏, 彭元东 2004 稀有金属材料与工程 33 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi J H, Peng Y D 2004 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 33 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng Z H, Shen B G, Liang B, Zhang J X, Wang F W, Zhang S Y, Zhao J G, Zhan W S 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hasebe A, Imai T, Otsuki E 1994 Electr. Eng. Jpn. 114 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Girt E, Altounian Z, Swainson I P 1997 Phys. B Condens. Matter 234 637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Girt E, Guillot M, Swainson I P, Krishnan K M, Altounian Z, Thomas G 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 5323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liang J K, Huang Q, Santoro A, Liu Q L, Chen X L 1999 J. Appl. Phys. 86 1226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang S, Fang Y K, Song K K, Zhu X Y, Wang L, Sun W, Pan W, Zhu M G, Li W 2020 J. Rare Earths 38 1224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 文雪萍, 易健宏, 彭元东, 李丽娅, 叶途明, 夏庆林 2005 粉末冶金材料科学与工程 10 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen X P, Yi J H, Peng Y D, Li L Y, Ye T M, Xia Q L 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng. Powder Metall. 10 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, Gan J Y, Chin T S, Shun T T, Tsau C H, Chang S Y 2004 Adv. Eng. Mater. 6 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cantor B, Chang I T H, Knight P, Vincent A J B 2004 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 申天展, 宋海洋, 安敏荣 2021 70 186201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen T Z, Song H Y, An M R 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 186201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou N X, Jiang S C, Huang T, Qin M D, Hu T, Luo J 2019 Sci. Bull. 64 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Y, Yang X, Liaw P K 2012 JOM 64 830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang J, Zhang Y, Xiao H X, Li L Y, Kou H C, Li J S 2019 Mater. Lett. 240 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 鲁一荻, 张骁勇, 侯硕, 何卫锋, 王辉, 吕昭平 2021 稀有金属材料与工程 50 333
Lu Y D, Zhang X Y, Hou S, He W F, Wang H, Lü Z P 2021 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 50 333
[19] 李蕊轩, 张勇 2017 66 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R X, Zhang Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Rost C M, Sachet E, Borman T, Moballegh A, Dickey E C, Hou D, Jones J L, Curtarolo S, Maria J P 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 8485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yadav T P, Mukhopadhyay S, Mishra S S, Mukhopadhyay N K, Srivastava O N 2017 Philos. Mag. Lett. 97 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang T, Zhao Y L, Tong Y, Jiao Z B, Wei J, Cai J X, Han X D, Chen D, Hu A, Kai J J, Lu K, Liu Y, Liu C T 2018 Science 362 933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] He Q, Guo Y Q, Zheng Z Z 2013 Appl. Mech. Mater. 455 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yin L H, Guo Y Q, Guo X P 2022 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 563 169883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 郭新鹏, 郭永权, 王京南, 殷林瀚 2021 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版) 53 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo X P, Guo Y Q, Wang J N, Yin L H 2021 J. South China Norm. Univ. , Nat. Sci. Ed. 53 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cheng Z H, Shen B G, Zhang J X, Liang B, Guo H Q, Kronmüller H 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 70 3467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wei X Z, Hu S J, Zeng D C, Liu Z Y, Brück E, Klaasse J C P, de Boer F R, Buschow K H J 1999 Phys. B Condens. Matter 266 249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sun Z G, Zhang S Y, Zhang H W, Shen B G 2001 J. Alloys Compd. 322 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fuquan B, Tegus O, Dagula W, Brück E, Klaasse J C P, Buschow K H J 2007 J. Alloys Compd. 431 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang X, Zhang Y 2012 Mater. Chem. Phys. 132 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guo Y Q, Li W, Feng W C, Luo J, Liang J K, He Q J, Yu X J 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 192513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Bean C P, Livingston J D, Rodbell D S 1959 J. Phys. Radium 20 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Buschow K H J 1980 Handb. Ferromagn. Mater. (Vol. 1)(Amsterdam: Elsevier) pp297–414
[34] Gu Z F, Zeng D C, Liu Z Y, Liang S Z, Klaasse J C P, Bru E, de Boer F R, Buschow K H J 2001 Physica B 304 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang J Y, Shen B G, Zhang S Y, Sun Z G, Zhan W S 1999 J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 32 2371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Guo Y Q, Feng W C, Li W, Luo J, Liang J K 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 023919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 熵调控Gd2Co17系列样品XRD图谱 (a) Gd2Co17; (b) Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (d) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17; (e) (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17; (f) (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17; (g) (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17
Figure 1. The XRD patterns of the entropized Gd2Co17 intermetallic compounds: (a) Gd2Co17; (b) Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (d) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17; (e) (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17; (f) (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17; (g) (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17.
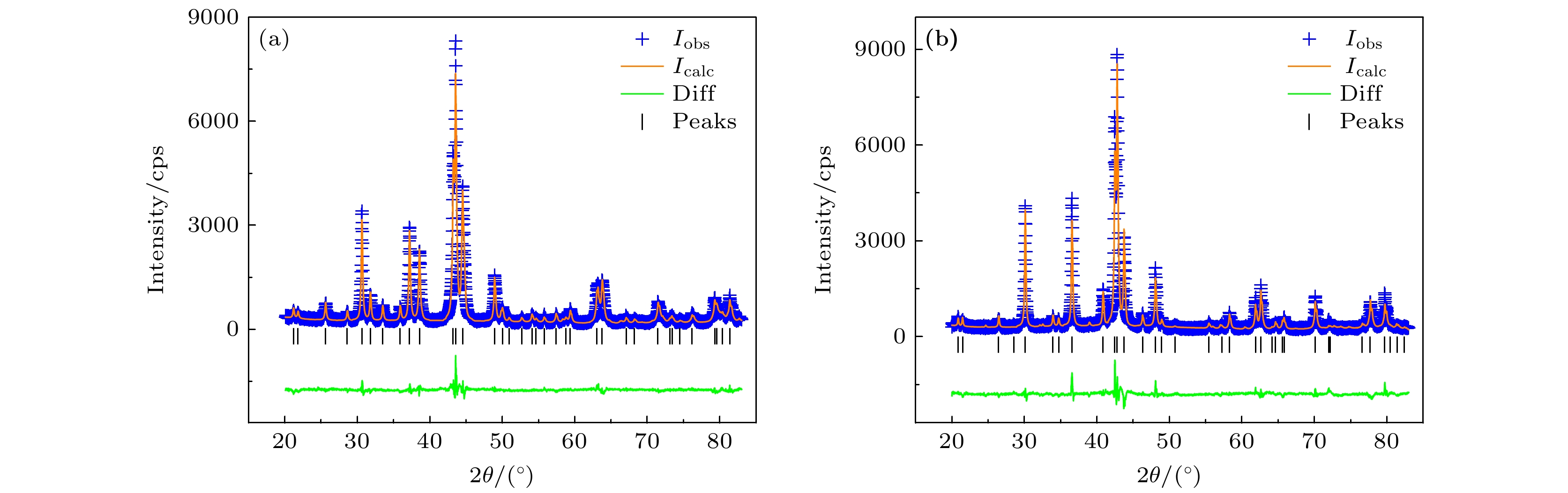
图 4 Gd2(T1, T2, ···, Tn)17系列取向样品XRD图谱 (a) Gd2Co17; (b) Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (d) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17
Figure 4. XRD patterns of aligned Gd2(T1, T2, ···, Tn)17 intermetallic compounds: (a) Gd2Co17; (b) Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (d) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17.
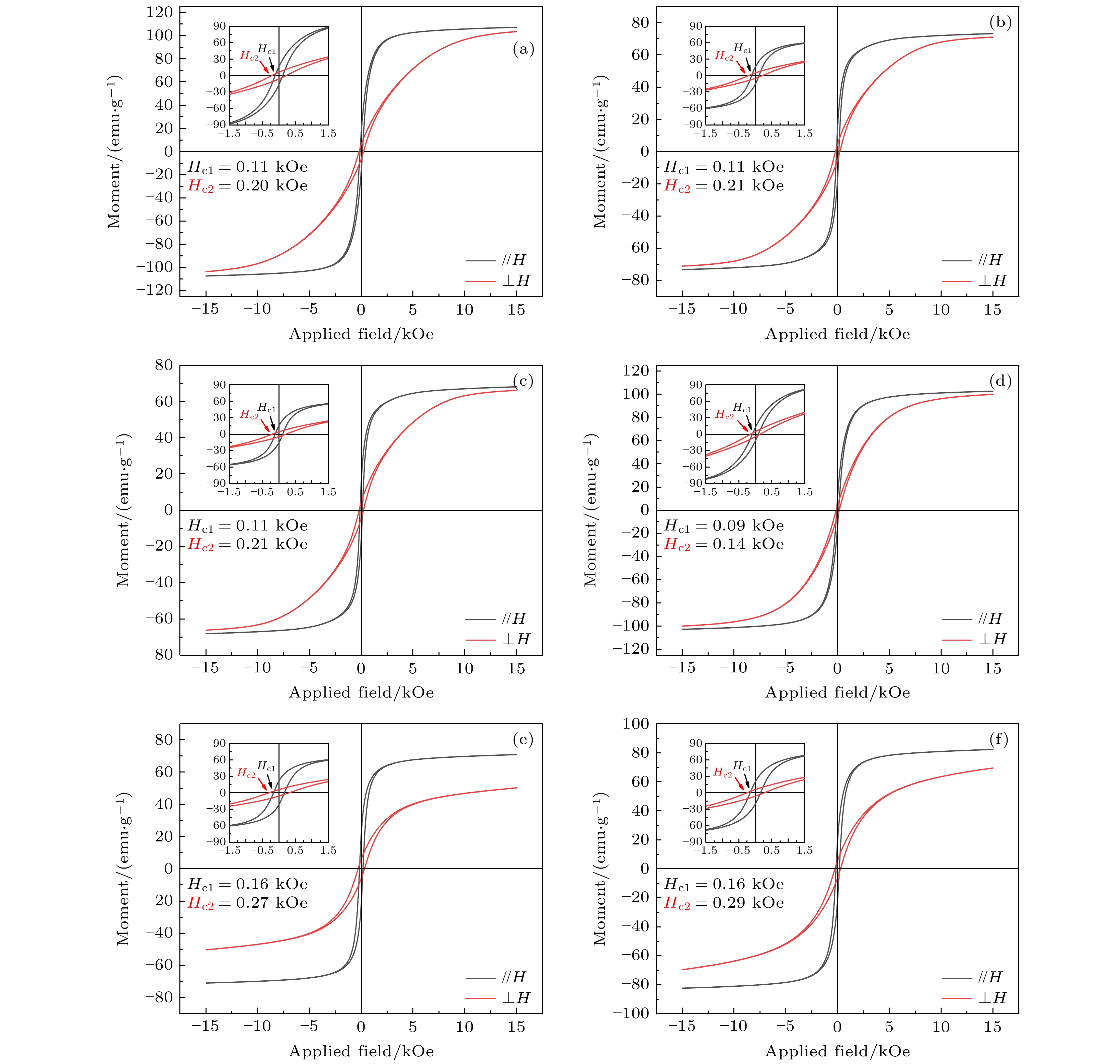
图 6 熵调控Gd2Co17系列取向样品平行和垂直于外加磁场方向的磁滞回线 (a)Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17; (b) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17; (d) (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17; (e) (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17; (f) (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17
Figure 6. Hysteresis loops of entropized Gd2Co17 samples with magnetic aligned direction parallel and perpendicular to the direction of applied magnetic field: (a) Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17; (b) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17; (d) (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17; (e) (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17; (f) (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17.
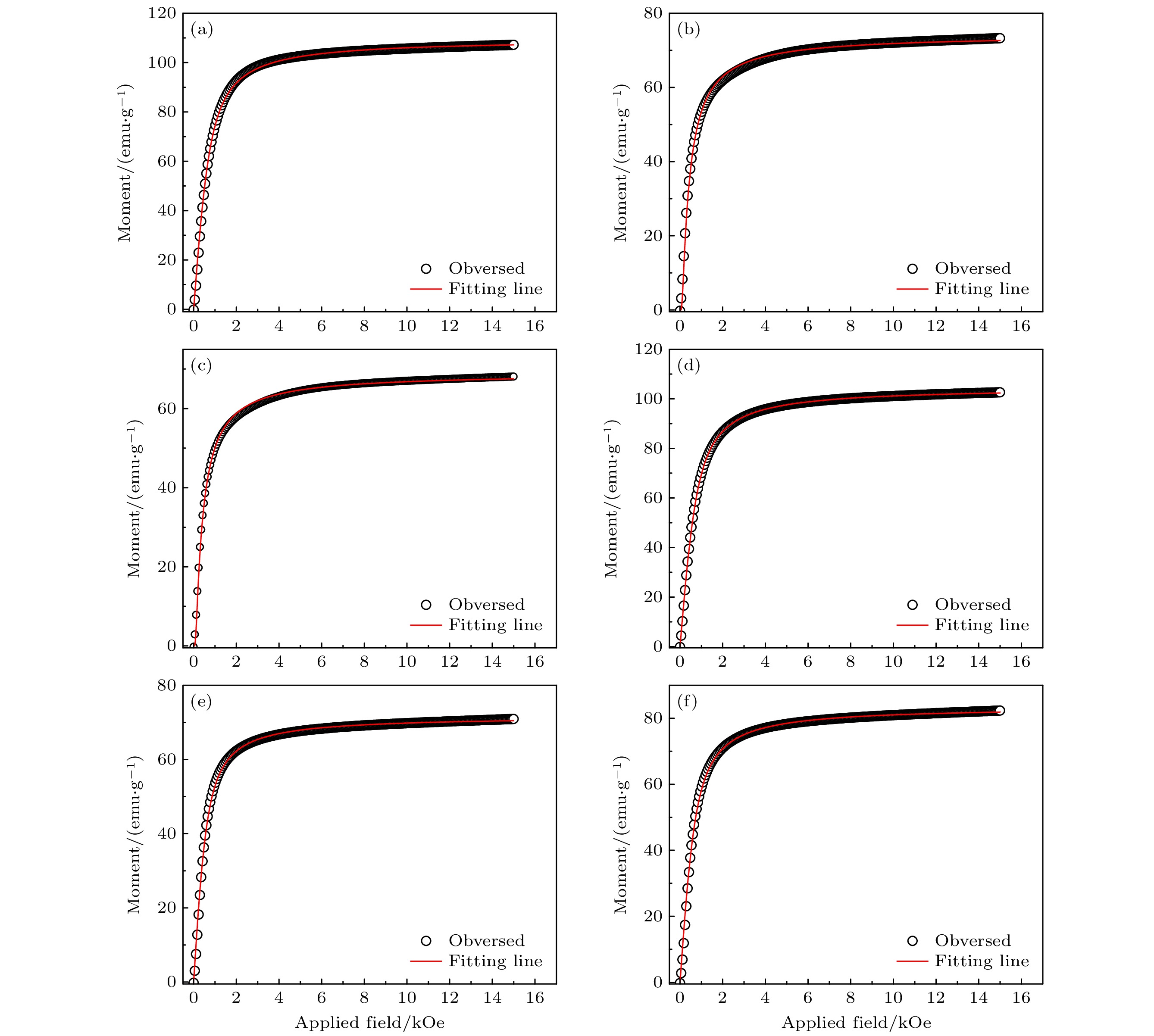
图 8 Gd2Co17系列取向样品的拟合磁化曲线 (a) Gd2(Fe1/2Co1/2)17; (b) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17; (d) (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17; (e) (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17; (f) (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17
Figure 8. Fitted magnetization curves of field aligned entropized Gd2Co17: (a) Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17; (b) Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17; (c) Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17; (d) (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17; (e) (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17; (f) (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17.
表 1 熵调控Gd2Co17系列样品热力学参数
Table 1. Thermodynamic parameters of entropized Gd2Co17 intermetallic compounds.
样品 原子半径差 ${{\Delta } }r$/% ${\rm{混} }{\rm{合} }{\rm{焓} }\Delta {{\boldsymbol{H}}}_{ {\rm{m} }{\rm{i} }{\rm{x} } }$/(kJ·mol–1) 混合熵 $\Delta {S}_{ {\rm{mix} } } /R$ 稀土位 金属位 稀土位-金属位 Gd2Co17 — — — –8.29 0 Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17 0.79 — –1.00 –5.13 0.69 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 0.99 — –1.33 –7.85 1.10 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 1.81 — –4.00 –8.38 1.39 (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17 0.55 0 — –8.48 0.69 (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17 0.69 0 — –8.54 1.10 (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17 0.83 0 — –8.48 1.39 表 2 熵调控Gd2Co17系列样品晶格参数、品质因子和可信度因子
Table 2. Lattice parameter, merit factors M and smith factor F of entropized Gd2Co17 intermetallic compounds.
样品 a/Å c/Å V/Å3 M(20) F(20) Gd2Co17 8.378(0) 12.206(6) 742.0(0) 28 27 Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17 8.458(0) 12.409(6) 768.8(2) 17 14 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 8.444(4) 12.254(1) 756.6(7) 23 23 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 8.507(0) 8. 267(8) 518.1(7) 49 39 (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17 8.332(3) 8.133(1) 489.0(1) 46 52 (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17 8.363(1) 12.203(0) 739.1(5) 28 28 (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17 8.333(6) 8.125(6) 488.7(1) 44 45 表 3 选取样品的元素组成
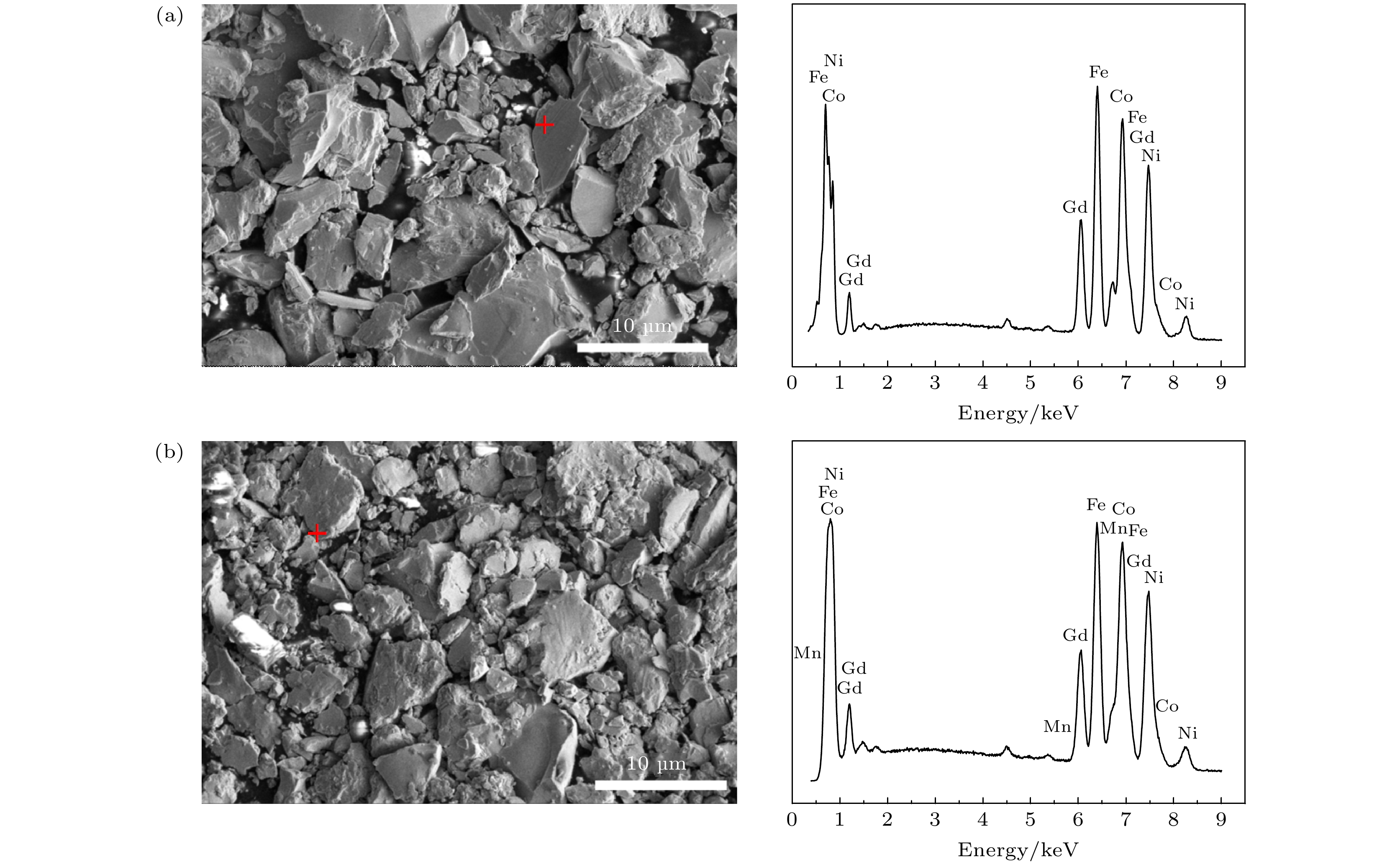
Table 3. Element compositions of typical samples.
元素 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 质量百分比/% 原子百分比/% 质量百分比/% 原子百分比/% Gd 24.5 10.6 26.0 11.3 Co 26.1 30.3 18.9 21.9 Fe 24.0 29.4 16.9 20.7 Ni 25.4 29.6 20.1 23.4 Mn — — 18.1 22.7 表 4 具有菱方结构的样品的精修晶体学数据
Table 4. Refined crystallographic data of samples with rhombohedral structure.
样品 Gd2Co17 Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17 空间群 ${R}\bar3{m}$ ${R}\bar3{m}$ ${R}\bar{\text{3} }{m}$ ${R}\bar3{m}$ a/Å 8.375(2) 8.454(5) 8.444(7) 8.358(0) c/Å 12.200(4) 12.413(7) 12.254(3) 12.185(7) V/Å3 741.131(2) 768.436(1) 756.817(0) 737.200(9) 稀土位 Gd Gd Gd Gd, Tb, Dy 6c (0, 0, z) (z = 0.34369) (z = 0.34188) (z = 0.33731) (z = 0.34197) 占位率/% 100 100 100 各33.33 金属位 Co Co, Fe Fe, Co, Ni Co 6c (0, 0, z) (z = 0.09431) (z = 0.08016) (z = 0.08100) (z = 0.09567) 占位率/% 100 各50 各33.33 100 9d (1/2, 0, 1/2) — — — — 占位率/% 100 各50 各33.33 100 18f (x, 0, 0) (x = 0.28942) (x = 0.30352) (x = 0.30607) (x = 0.29175) 占位率/% 100 各50 各33.33 100 18h (x, 1–x, z) (x = 0.16826; z = 0.48728) (x = 0.50226; z = 0.15830) (x = 0.16629; z = 0.49090) (x = 0.16783; z = 0.48701) 占位率/% 100 各50 各33.33 100 Rp/% 5.144 8.110 8.830 5.605 RWP/% 6.865 10.611 12.690 7.057 表 5 具有六方结构的样品的精修晶体学数据
Table 5. Refined crystallographic data of samples with hexagonal structure.
样品 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17 (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17 空间群 P63/mmc P63/mmc P63/mmc a/Å 8.501(6) 8.329(5) 8.332(9) c/Å 8.265(3) 8.130(4) 8.124(4) V/Å3 517.357(3) 488.512(1) 488.561(0) 稀土位 Gd Gd, Tb Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho 2b (0, 0, 1/4) — — — 占位率/% 100 各50 各25 2d (1/3, 2/3, 3/4) — — — 占位率/% 100 各50 各25 金属位 Fe, Co, Ni, Mn Co Co 4f (1/3, 2/3, z) (z = 0.14285) (z = 0.12127) (z = 0.13757) 占位率/% 各25 100 100 6g (1/2, 0, 0) — — — 占位率/% 各25 100 100 12j (x, y, 1/4) (x = 0.32333; y = –0.02248) (x = 0.33032; y = 0.96090) (x = 0.32409; y = 0.96806) 占位率/% 各25 100 100 12k (x, 2x, z) (x = 0.16182; z = –0.11890) (x = 0.16585; z = 0.98326) (x = 0.16655; z = 0.98716) 占位率/% 各25 100 100 Rp/% 7.006 8.07 9.07 RWP/% 8.942 10.50 11.80 表 6 熵调控Gd2Co17系列样品有效原子半径RA
Table 6. Effective radius ratio RA of entropized Gd2Co17 intermetallic compounds.
样品 晶体结构 有效原子半径RA Gd2Co17 菱方 1.4262 Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17 菱方 1.4330 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 菱方 1.4334 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 六方 1.3996 (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17 六方 1.4166 (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17 菱方 1.4105 (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17 六方 1.4056 表 7 熵调控Gd2Co17系列取向样品磁化曲线拟合参数
Table 7. Results of fitted magnetization parameters of field aligned entropized Gd2Co17.
取向样品 拟合度 Nμ/(emu·g–1) Nμ/μB Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17 0.99887 109.56395±0.02882 25.30 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 0.99630 74.23084±0.03279 17.19 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 0.99644 68.97675±0.02946 15.87 (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17 0.99985 104.73245±0.01038 24.71 (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17 0.99844 71.71314±0.01977 16.96 (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17 0.99837 83.60305±0.02565 19.81 表 8 R2T17金属间化合物的室温磁性能
Table 8. Magnetic properties of R2T17 at room temperature.
二元R2T17 晶体结构 饱和磁矩Nμ/μB 居里温度Tc/K 磁各向异性 Gd2Co17 菱方 13.5—14.4 1209—1240 基面 Gd2Fe17 六方 21—21.5 460—485 基面 Gd2Ni17 六方 8.8—9.36 187—205 — Tb2Co17 菱方 8.4—10.7 1180—1195 基面 Dy2Co17 六方 7—8.3 1152—1188 基面 Ho2Co17 六方 5.8—7.7 1173—1183 基面 熵调控Gd2Co17 晶体结构 饱和磁矩Nμ/μB 理论磁矩Nμ/μB 磁各向异性 Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17 菱方 25.30 17.25—17.95 易轴 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 菱方 17.19 14.43—15.09 易轴 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 六方 15.87 — 易轴 (Gd1/2Tb1/2)2Co17 六方 24.71 10.95—12.55 基面 (Gd1/3Tb1/3Dy1/3)2Co17 菱方 16.96 9.63—12.87 基面 (Gd1/4Tb1/4Dy1/4Ho1/4)2Co17 六方 19.81 8.68—10.28 基面 表 9 熵调控Gd2Co17系列样品饱和磁矩计算结果
Table 9. Calculated moments of entropized Gd2Co17 intermetallic.
样品 实验
磁矩/μB理论
磁矩/μB$ {N}_{{\rm{s}}{\rm{p}}}^{\uparrow } $ Gd2Co17 13.5—14.4 14.40 0.30 Gd2(Co1/2Fe1/2)17 25.30 26.70 0.40 Gd2(Co1/3Fe1/3Ni1/3)17 17.19 18.20 0.40 Gd2(Co1/4Fe1/4Ni1/4Mn1/4)17 15.87 13.95 0.40 -
[1] Yin L H, Guo Y Q, Guo X P 2022 Inorg. Chem. 61 2402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Shen B G, Cheng Z H, Liang B, Guo H Q, Zhang J X, Gong H Y, Wang F W, Yan Q W, Zhan W S 1995 Appl. Phys. Lett. 67 1621
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Coey J M D, Sun H 1990 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 87 L251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 易健宏, 彭元东 2004 稀有金属材料与工程 33 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi J H, Peng Y D 2004 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 33 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng Z H, Shen B G, Liang B, Zhang J X, Wang F W, Zhang S Y, Zhao J G, Zhan W S 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 1385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hasebe A, Imai T, Otsuki E 1994 Electr. Eng. Jpn. 114 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Girt E, Altounian Z, Swainson I P 1997 Phys. B Condens. Matter 234 637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Girt E, Guillot M, Swainson I P, Krishnan K M, Altounian Z, Thomas G 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 5323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liang J K, Huang Q, Santoro A, Liu Q L, Chen X L 1999 J. Appl. Phys. 86 1226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang S, Fang Y K, Song K K, Zhu X Y, Wang L, Sun W, Pan W, Zhu M G, Li W 2020 J. Rare Earths 38 1224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 文雪萍, 易健宏, 彭元东, 李丽娅, 叶途明, 夏庆林 2005 粉末冶金材料科学与工程 10 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen X P, Yi J H, Peng Y D, Li L Y, Ye T M, Xia Q L 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng. Powder Metall. 10 236
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, Gan J Y, Chin T S, Shun T T, Tsau C H, Chang S Y 2004 Adv. Eng. Mater. 6 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cantor B, Chang I T H, Knight P, Vincent A J B 2004 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 申天展, 宋海洋, 安敏荣 2021 70 186201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen T Z, Song H Y, An M R 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 186201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou N X, Jiang S C, Huang T, Qin M D, Hu T, Luo J 2019 Sci. Bull. 64 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang Y, Yang X, Liaw P K 2012 JOM 64 830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang J, Zhang Y, Xiao H X, Li L Y, Kou H C, Li J S 2019 Mater. Lett. 240 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 鲁一荻, 张骁勇, 侯硕, 何卫锋, 王辉, 吕昭平 2021 稀有金属材料与工程 50 333
Lu Y D, Zhang X Y, Hou S, He W F, Wang H, Lü Z P 2021 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 50 333
[19] 李蕊轩, 张勇 2017 66 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R X, Zhang Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Rost C M, Sachet E, Borman T, Moballegh A, Dickey E C, Hou D, Jones J L, Curtarolo S, Maria J P 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 8485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yadav T P, Mukhopadhyay S, Mishra S S, Mukhopadhyay N K, Srivastava O N 2017 Philos. Mag. Lett. 97 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang T, Zhao Y L, Tong Y, Jiao Z B, Wei J, Cai J X, Han X D, Chen D, Hu A, Kai J J, Lu K, Liu Y, Liu C T 2018 Science 362 933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] He Q, Guo Y Q, Zheng Z Z 2013 Appl. Mech. Mater. 455 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yin L H, Guo Y Q, Guo X P 2022 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 563 169883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 郭新鹏, 郭永权, 王京南, 殷林瀚 2021 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版) 53 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo X P, Guo Y Q, Wang J N, Yin L H 2021 J. South China Norm. Univ. , Nat. Sci. Ed. 53 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cheng Z H, Shen B G, Zhang J X, Liang B, Guo H Q, Kronmüller H 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 70 3467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wei X Z, Hu S J, Zeng D C, Liu Z Y, Brück E, Klaasse J C P, de Boer F R, Buschow K H J 1999 Phys. B Condens. Matter 266 249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sun Z G, Zhang S Y, Zhang H W, Shen B G 2001 J. Alloys Compd. 322 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fuquan B, Tegus O, Dagula W, Brück E, Klaasse J C P, Buschow K H J 2007 J. Alloys Compd. 431 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang X, Zhang Y 2012 Mater. Chem. Phys. 132 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guo Y Q, Li W, Feng W C, Luo J, Liang J K, He Q J, Yu X J 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 192513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Bean C P, Livingston J D, Rodbell D S 1959 J. Phys. Radium 20 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Buschow K H J 1980 Handb. Ferromagn. Mater. (Vol. 1)(Amsterdam: Elsevier) pp297–414
[34] Gu Z F, Zeng D C, Liu Z Y, Liang S Z, Klaasse J C P, Bru E, de Boer F R, Buschow K H J 2001 Physica B 304 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang J Y, Shen B G, Zhang S Y, Sun Z G, Zhan W S 1999 J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 32 2371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Guo Y Q, Feng W C, Li W, Luo J, Liang J K 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 023919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7297
- PDF Downloads: 90
- Cited By: 0

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: