-
Energetic charged-particle beams produced from ultrashort ultra-intense laser plasma interactions play a vital role in charged-particle radiography. When such an energetic beam penetrates through a foil target, its energy loss is negligible, and the main physics process is small-angle scattering. Owing to this scattering effect, charged-particle radiography of a target with a transversely distributed steep density gradient region will produce a modulation structure in the fluence distribution on the detection plane, which could be used to diagnose the steep density gradient region. In the past, the theoretical work on the scattering effect and the resulting modulation structure was done with Monte-Carlo simulations, which cost a lot of computing time and the studied parameter range was limited. In the present work, an analytical model is developed to deal with the scattering effect inside the target and the modulation structure on the detection plane in radiography, which can quickly present the results that coincide with Monte-Carlo simulations very well. By using this analytical model, the characteristics of modulation structures are analyzed. A dimensionless characteristic parameter related to radiography conditions is put forward, and its range determines different modulation structures and also the probability of diagnosing a steep density gradient region with a width
$\lesssim $ 2 μm.-
Keywords:
- scattering /
- radiography /
- charged-particle beam
[1] Zohuri B 2017 Inertial Confinement Fusion Driven Thermonuclear Energy (Cham: Springer International Publishing AG)
[2] Lindl J 1995 Phys. Plasmas 2 3933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen B, Yang Z, Wei M, Pu Y, Hu X, Chen T, Liu S, Yan J, Huang T, Jiang S, Ding Y 2014 Phys. Plasmas. 21 122705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 陆中伟, 王晓方 2019 68 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Z W, Wang X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Marshall F J, Ivancic S T, Mileham C, Nilson P M, Ruby J J, Stoeckl C, Scheiner B S, Schmitt M J 2021 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92 033701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Higginson A, Gray R J, King M, et al. 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gonsalves A J, Nakamura K, Daniels J, et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 084801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li C K, Séguin F H, Frenje J A, et al. 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 135003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Du B, Wang X F 2018 AIP Adv. 8 125328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mackinnon A J, Patel P K, Borghesi M, et al. 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cobble J A, Johnson R P, Cowan T E, Renard-Le Galloudec N, Allen M 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 92 1775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 温树槐, 丁永坤 2012 激光惯性约束聚变诊断学 (北京: 国防工业出版社)
Wen S H, Ding Y K 2012 Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Diagnostics (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) (in Chinese)
[13] 滕建, 洪伟, 赵宗清, 巫顺超, 秦孝尊, 何颖玲, 谷渝秋, 丁永坤 2009 58 1635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Teng J, Hong W, Zhao Z Q, Wu S C, Qin X Z, He Y L, Gu Y Q, Ding Y K 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 肖渊, 王晓方, 滕建, 陈晓虎, 陈媛, 洪伟 2012 61 234102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao Y, Wang X F, Teng J, Chen X H, Chen Y, Hong W 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 234102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈媛, 王晓方, 邵光超 2015 64 154101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y, Wang X F, Shao G C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 154101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bethe H A 1953 Phys. Rev. 89 1256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Highland V L 1975 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 129 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Shao G, Wang X 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 092703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Y, Wang X 2020 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 62 095023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu X J, Wang X F, Chen X H 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ferrari A, Sala P R, Fassò A, Ranft J, Siegen U 2005 FLUKA: A Multi-particle Transport Code No. SLAC-R-773 Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC)
[22] Jackson J D 2005 Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) (Beijing: Higher Education Press)
[23] 汪晓莲, 李澄, 邵明, 陈宏芳 2009 粒子探测技术 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社)
Wang X L, Li C, Shao M, Chen H F 2009 The Technique of Particle Detection (Hefei: USTC Press) (in Chinese)
-
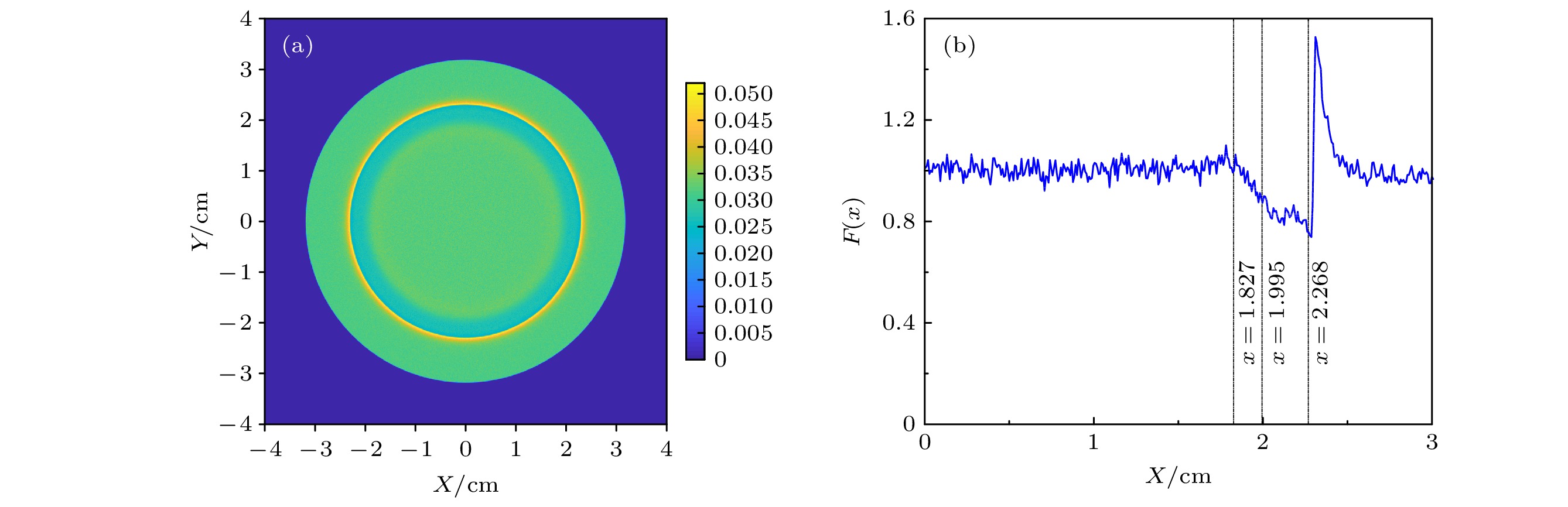
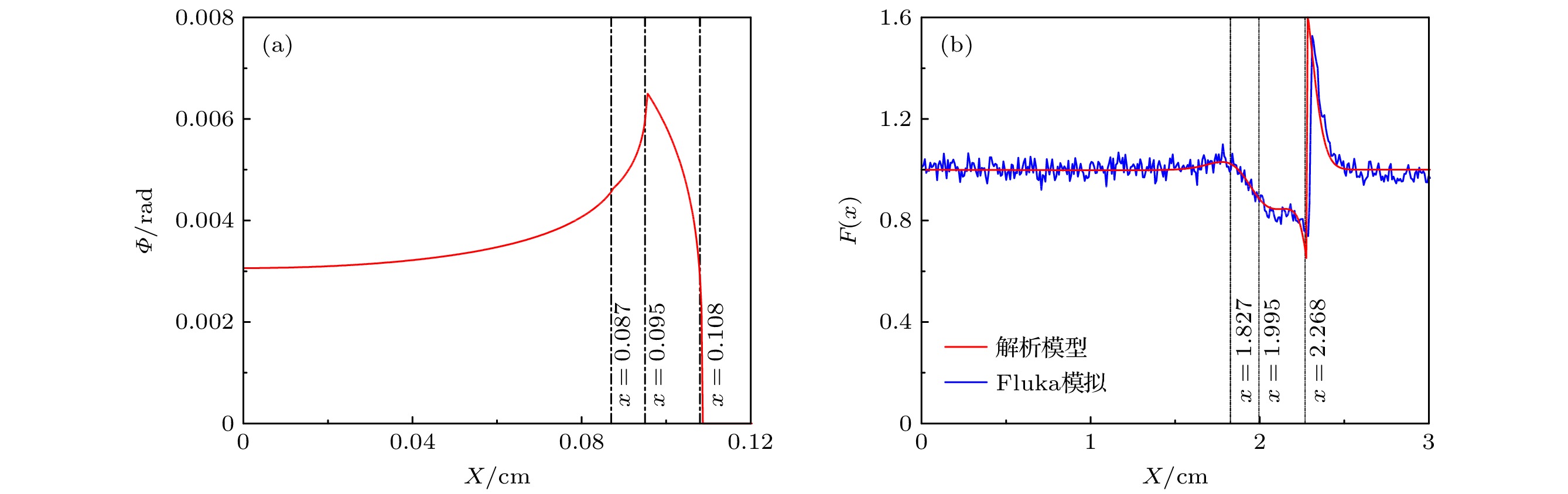
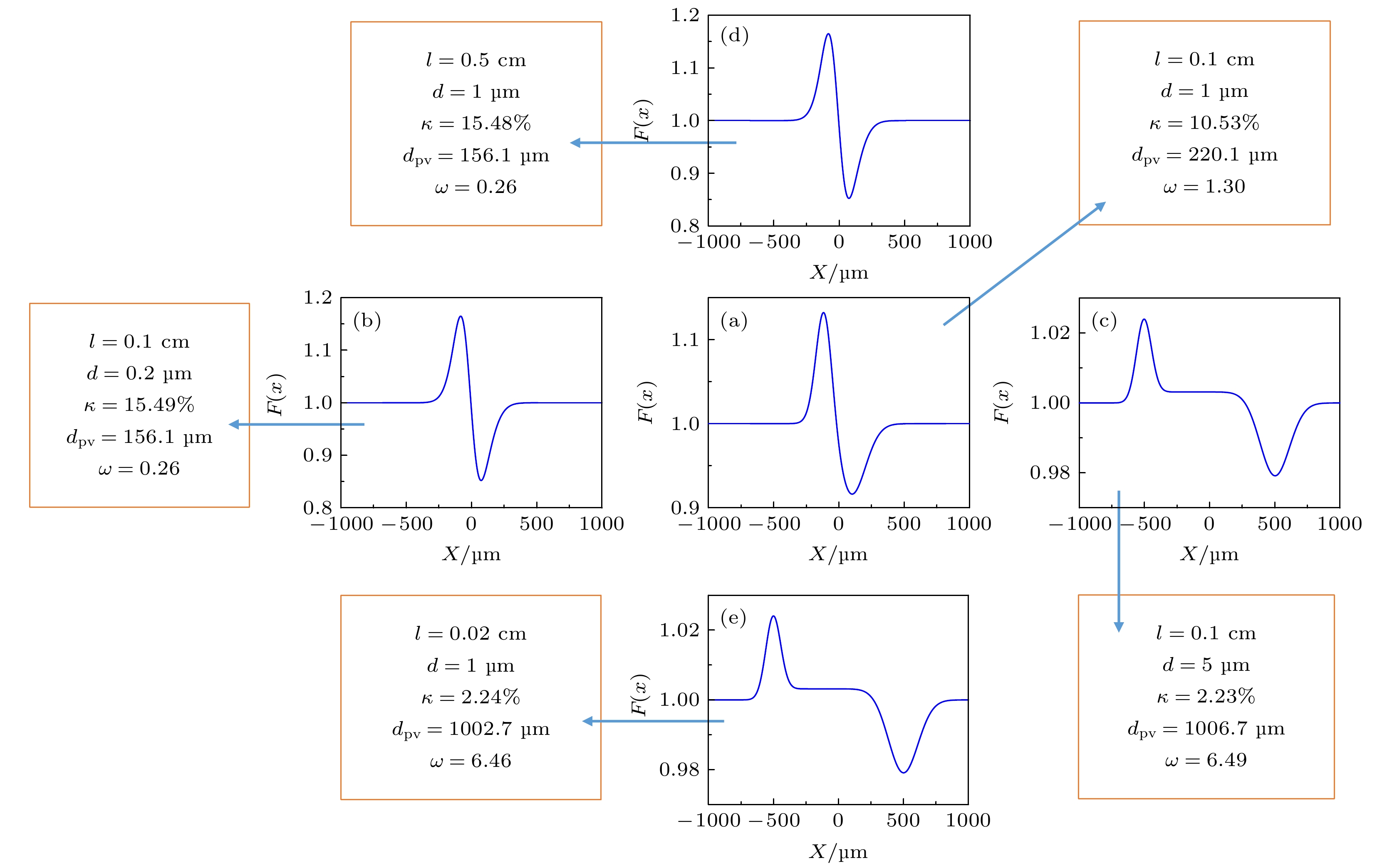
图 9 调制信号特征量和ω随照相参数的变化 (a) 点源发散束情况下改变梯度区宽度; (b) 改变点源与靶的间距; (c) 点源发散束和平行束条件下改变靶与探测面距离; (d) 无量纲的调制信号特征量随ω的变化关系
Figure 9. Dependence of the characteristic quantities and ω on the change of: (a) Density gradient width by using a point-source beam for radiography; (b) point source-to-target distance; (c) target-to-detection plane distance by using a parallel beam or a point-source beam for radiography, respectively; (d) the relation of the dimensionless characteristic quantities to ω.
-
[1] Zohuri B 2017 Inertial Confinement Fusion Driven Thermonuclear Energy (Cham: Springer International Publishing AG)
[2] Lindl J 1995 Phys. Plasmas 2 3933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen B, Yang Z, Wei M, Pu Y, Hu X, Chen T, Liu S, Yan J, Huang T, Jiang S, Ding Y 2014 Phys. Plasmas. 21 122705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 陆中伟, 王晓方 2019 68 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Z W, Wang X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Marshall F J, Ivancic S T, Mileham C, Nilson P M, Ruby J J, Stoeckl C, Scheiner B S, Schmitt M J 2021 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92 033701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Higginson A, Gray R J, King M, et al. 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gonsalves A J, Nakamura K, Daniels J, et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 084801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li C K, Séguin F H, Frenje J A, et al. 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 135003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Du B, Wang X F 2018 AIP Adv. 8 125328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mackinnon A J, Patel P K, Borghesi M, et al. 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 045001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cobble J A, Johnson R P, Cowan T E, Renard-Le Galloudec N, Allen M 2002 J. Appl. Phys. 92 1775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 温树槐, 丁永坤 2012 激光惯性约束聚变诊断学 (北京: 国防工业出版社)
Wen S H, Ding Y K 2012 Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Diagnostics (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) (in Chinese)
[13] 滕建, 洪伟, 赵宗清, 巫顺超, 秦孝尊, 何颖玲, 谷渝秋, 丁永坤 2009 58 1635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Teng J, Hong W, Zhao Z Q, Wu S C, Qin X Z, He Y L, Gu Y Q, Ding Y K 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 肖渊, 王晓方, 滕建, 陈晓虎, 陈媛, 洪伟 2012 61 234102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao Y, Wang X F, Teng J, Chen X H, Chen Y, Hong W 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 234102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈媛, 王晓方, 邵光超 2015 64 154101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y, Wang X F, Shao G C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 154101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bethe H A 1953 Phys. Rev. 89 1256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Highland V L 1975 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 129 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Shao G, Wang X 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 092703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Y, Wang X 2020 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 62 095023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu X J, Wang X F, Chen X H 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ferrari A, Sala P R, Fassò A, Ranft J, Siegen U 2005 FLUKA: A Multi-particle Transport Code No. SLAC-R-773 Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC)
[22] Jackson J D 2005 Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) (Beijing: Higher Education Press)
[23] 汪晓莲, 李澄, 邵明, 陈宏芳 2009 粒子探测技术 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社)
Wang X L, Li C, Shao M, Chen H F 2009 The Technique of Particle Detection (Hefei: USTC Press) (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6354
- PDF Downloads: 88
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: