-
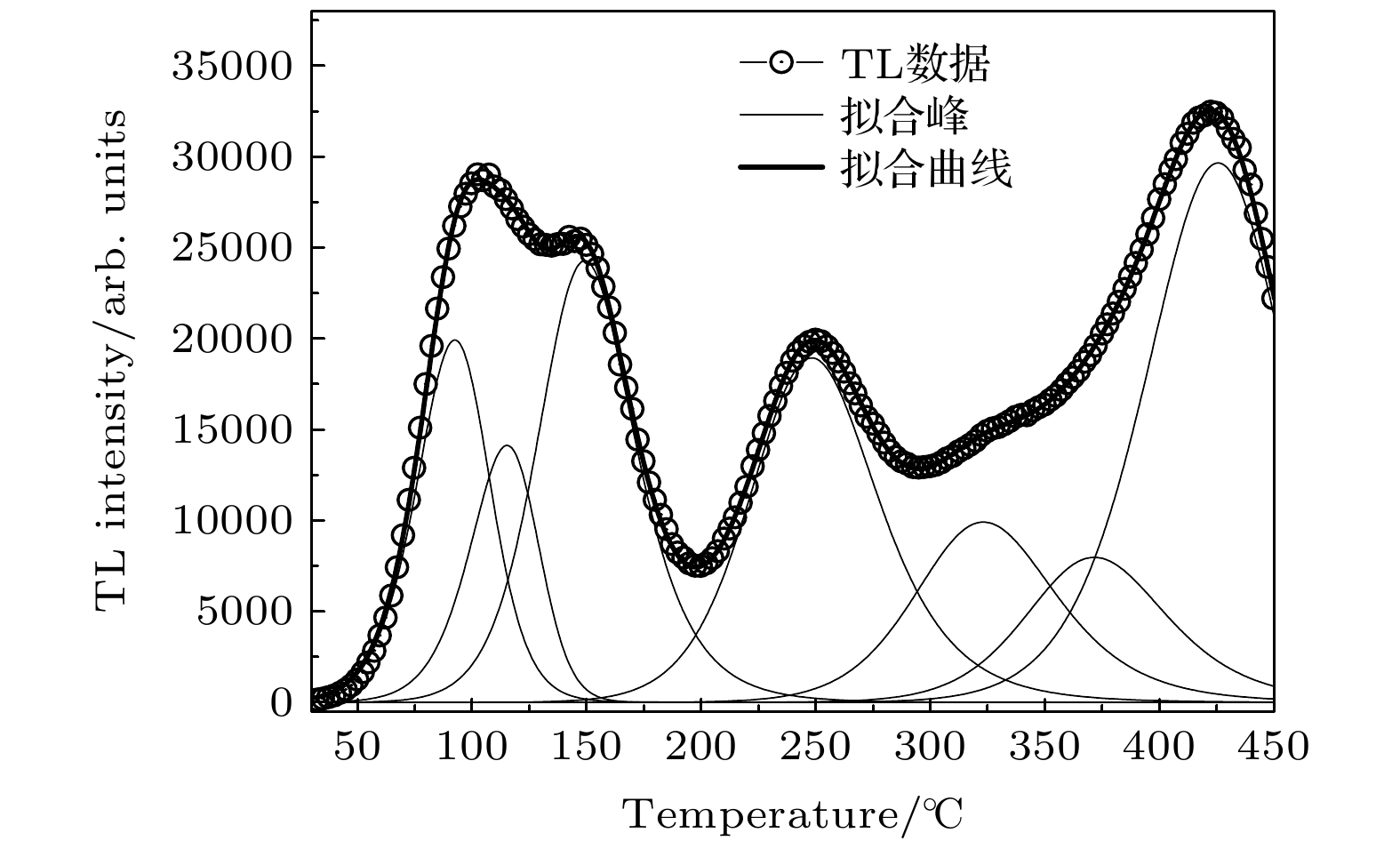
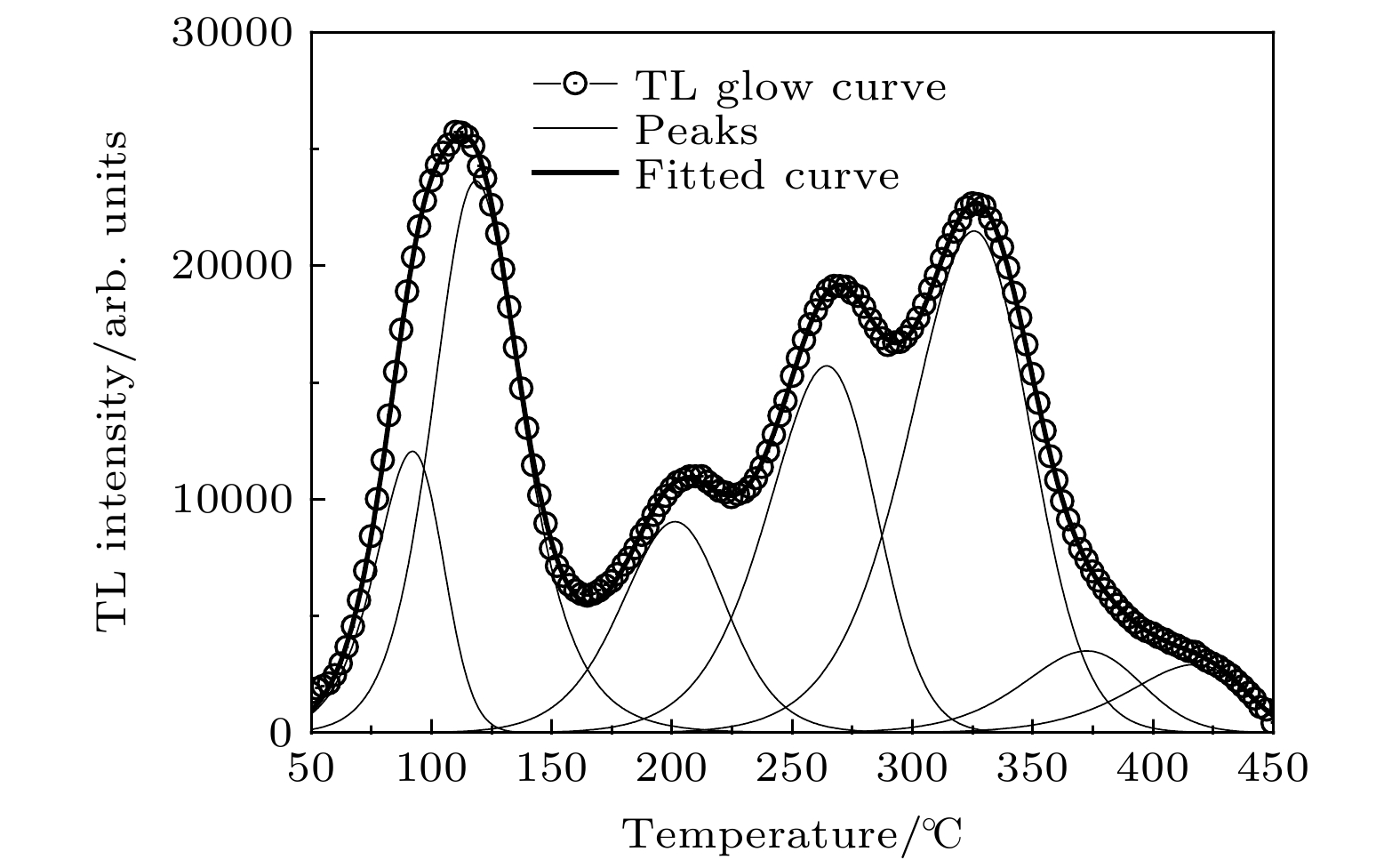
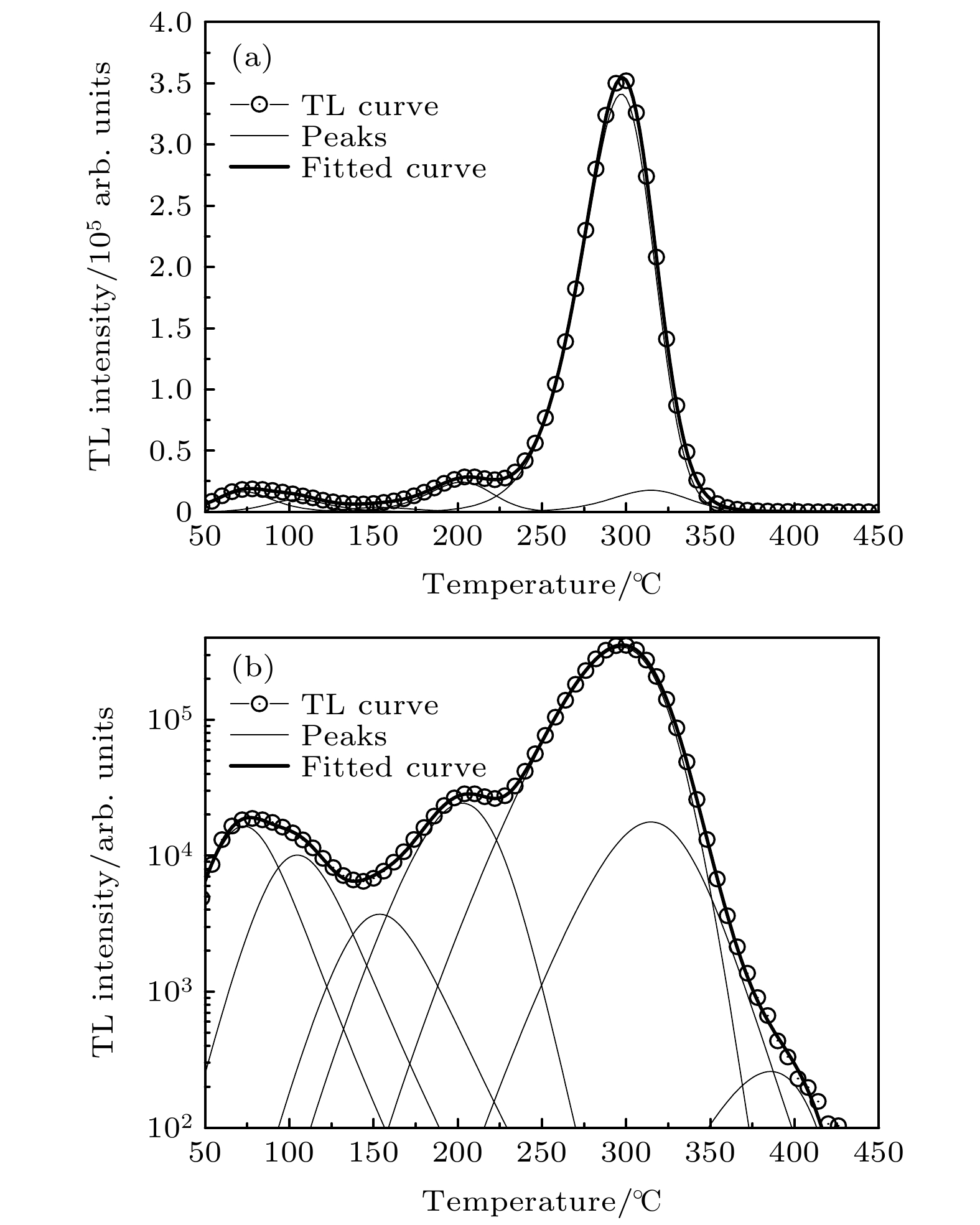
LiMgPO4 (LMP) phosphor doped with rare earth is a promising radiation dosimeter material. Thermoluminescence (TL) spectroscopy is an effective method to study the carrier traps and luminescence centers in materials. To study the luminescent mechanism of rare-earth-doped LMP phosphors, LMP phosphors doped with Tm and Tb (LMP:Tm, LMP:Tb and LMP:Tm, Tb) are prepared by high temperature solid state reaction. The TL glow curve and TL spectrum of the phosphors are measured by the linear heating method, and compared with the photoluminescence (PL) spectrum. The shape of the TL glow curve of LMP phosphor varies with the doping active impurities, but the TL glow curves can be fitted by seven TL peaks. Double-doping Tm3+ and Tb3+ in LMP phosphor can enhance the TL intensity of the fifth peak (E ~ 1.39 eV) and weaken the seventh TL peak (E ~ 1.70 eV). By comparing the PL spectra with TL spectra of the phosphors, it can be seen that the TL spectra are more complex than the PL spectra excited by ultraviolet light (λ = 352 nm). In the TL process, the electrons which are excited to the conduction band release the energy to recombination centers, and the released energy can more effectively excite the rare earth ions from the ground state to excited states, resulting in the more TL emitting peaks than in the the PL process. Although Tm3+ and Tb3+ can be the luminescent centers in LMP phosphors when Tm3+ and Tb3+ are doped in LMP simultaneously, Tb3+ ions are likely to act as sensitizers in LMP:Tm and LMP:Tb phosphor, and Tb3+ ions transfer energy to the low-energy Tm3+ ions, which makes the luminescent centers, Tm3+ ions, excited to the high-energy state and then de-excited with emitting light. This result is also proved by the fact that the luminescence decay of Tb3+ in phosphors increases with Tm3+ concentration increasing. The energy transfer through non-radiative transition is more significant at higher temperature. -
Keywords:
- LiMgPO4 /
- thermoluminescence /
- luminescence /
- energy transfer
[1] Daniels F, Boyd C A, Saunders D F 1953 Science 117 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xiong Z Y, Xu J Y, Zhao F L, Zhang Y, Liu J, Tang Q 2017 J. Lumin. 192 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] ZhangS, HuangY, Shi L, Seo H J 2010 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22 235402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gai M Q, Chen C Y, Fan Y W, Wang J H 2013 J. Rare Earths 31 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dhabekar B, Menon S N, Raja E A, Bakshi A K, Singh A K, Chougaonkar M P, Mayya Y S 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. A 269 1844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Singh A K, Menon S N, Dhabekar B, Kadam S, Chougaonkar M P, Mayya Y S 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. A 274 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bajaj N S, Palan C B, Koparkar K A, Kulkarni M S, Omanwar S K 2016 J. Lumin. 175 915
[8] 郭竞渊, 唐强, 唐桦明, 张纯祥, 罗达铃, 刘小伟 2017 66 107802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
GuoJ Y, Tang Q, Tang H M, Zhang C X, Luo D L, Liu X W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 107802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Baran A, Mahlik S, Grinberg M, Cai P, Kim S I, Seo H J 2014 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 26 85401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kumar M, Dhabekar B, Menon S N, Bakshi A K 2013 Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 155 410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kumar M, Dhabekar B, Menon S N, Chougaonkar M P, Mayya Y S 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 269 1849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Gieszczyk W, Bilski P, Osowski M K, Nowak T, Malinowski L 2018 Radiat. Meas. 113 1419
[13] Keskin I C, Türemis M, Kat M I, Gültekin S, Arslanlar Y T, Cetin A, Kibar R 2020 J. Lumin. 225 117276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tang H M, Lin L T, Zhang C X, Tang Q 2019 Inorg. Chem. 58 9698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郭竞渊, 唐强, 兰婷婷, 张纯祥, 罗达玲 2015 中国稀土学报 33 404
Guo J Y, Tang Q, Lan T T, Zhang C X, Luo D L 2015 J. Chin. Rare Earths Soc. 33 404
[16] Gieszczyk W, Marczewska B, Kosowski M, Mrozik A, Stoch P 2019 Materials 12 2861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hanic F, Handlovic M, Burdova K, Majling J 1982 J. Cryst. Spectrosc. 12 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 詹明亮, 陈瑶窈, 续卓, 熊正烨 2020 核技术 43 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan M L, Chen Y Y, Xu Z, Xiong Z Y 2020 Nucl. Tech. 43 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] McKeever S W S 1988 Thermoluminescence of Solids (London: Cambridge University Press) p75
[20] Liu X, Teng Y, Zhuang Y, Xie J, Qiao Y, Dong G, Chen D, Qiu J 2009 Opt. Lett. 22 3565
-
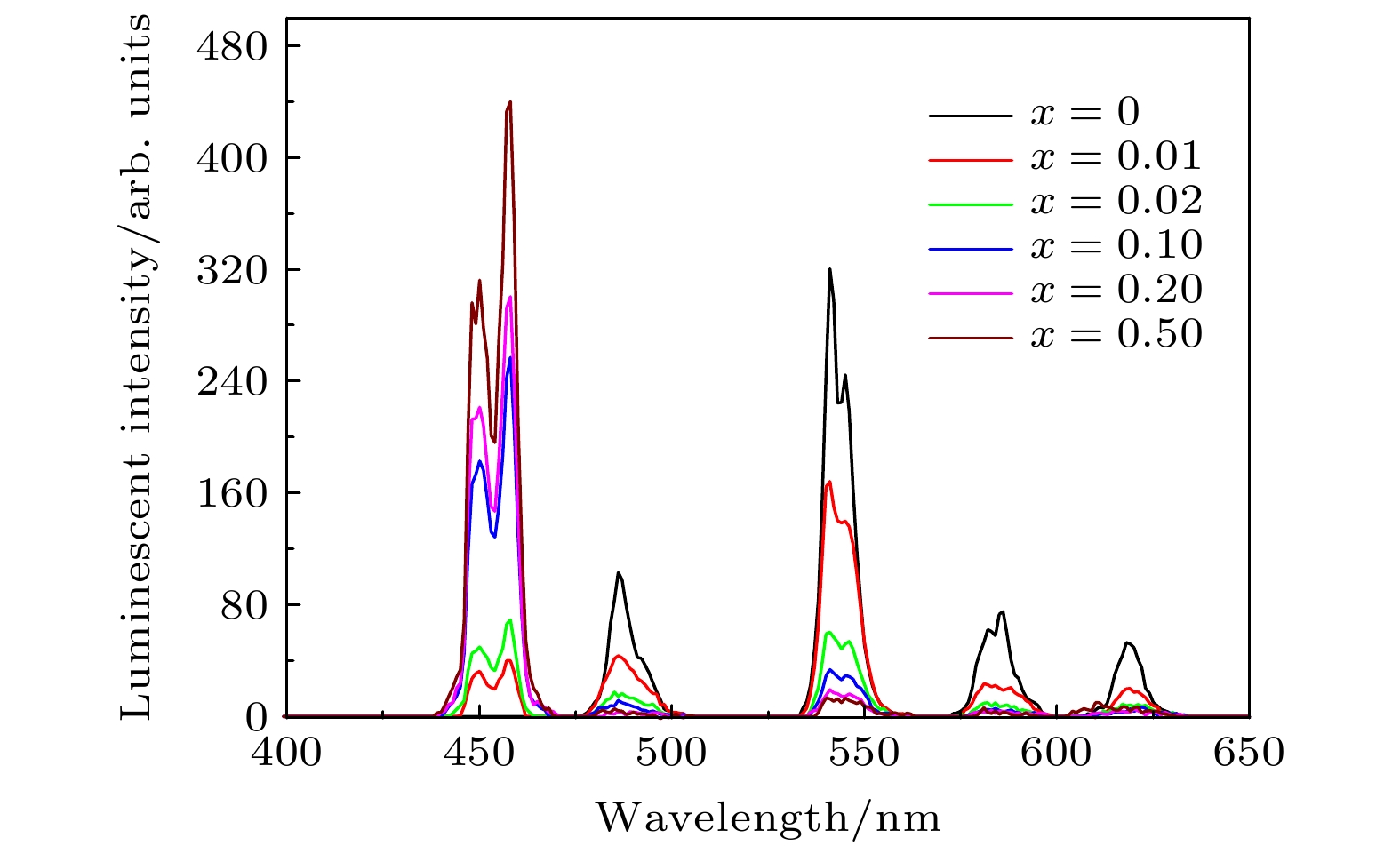
图 8 (a) LMP:Tb0.5at%磷光体不同温区的热释光谱 (b) LMP:Tm0.5at%磷光体不同温区的热释光谱 (c) LMP:Tm0.5at%, Tb0.5at%磷光体不同温区的热释光谱
Figure 8. (a). TL spectra of phosphors LMP:Tb0.5at% in different temperature ranges. (b). TL spectra of phosphors LMP:Tm0.5at% in different temperature ranges. (c). TL spectra of phosphors LMP:Tm0.5at%, Tb0.5at% in different temperature ranges.
表 1 LMP:Tb0.5at%磷光体的热释光陷阱参数
Table 1. TL trap’s parameters of LMP:Tb0.5at% phosphor.
峰序号 E/eV s/Hz n0 b 峰1 0.87 4.18 × 1011 1.68 × 105 1.5 峰2 0.99 2.28 × 1012 1.11 × 105 1.3 峰3 1.02 4.39 × 1011 2.76 × 105 2.0 峰4 1.17 4.88 × 1010 2.84 × 105 2.0 峰5 1.39 1.23 × 1011 1.64 × 105 2.0 峰6 1.64 1.32 × 1012 1.32 × 105 2.0 峰7 1.70 3.67 × 1011 4.84 × 105 1.6 表 2 LMP:Tm0.5at%磷光体的热释光陷阱参数
Table 2. TL trap’s parameters of LMP:Tm0.5at% phosphor.
峰序号 E/eV s/Hz n0 b 峰1 0.89 7.92 × 1011 8.83 × 104 1.2 峰2 1.01 3.31 × 1012 2.34 × 105 2.0 峰3 1.08 8.00 × 1010 1.04 × 105 1.5 峰4 1.20 4.27 × 1010 1.85 × 105 1.2 峰5 1.38 8.32 × 1010 2.83 × 105 1.3 峰6 1.63 1.17 × 1012 4.50 × 104 1.3 峰7 1.69 4.26 × 1011 3.67 × 104 1.0 表 3 LMP:Tb0.5at, Tm0.5at%磷光体的热释光陷阱参数
Table 3. TL trap’s parameters of LMP:Tb0.5at%, Tm0.5at% phosphor.
峰序号 E/eV s/Hz n0 b 峰1 0.85 9.30 × 1011 1.48 × 105 1.9 峰2 0.95 1.89 × 1012 9.83 × 104 2.0 峰3 1.09 2.74 × 1012 4.02 × 104 2.0 峰4 1.16 4.99 × 1011 2.48 × 105 1.4 峰5 1.40 6.26 × 1011 3.80 × 106 1.2 峰6 1.58 8.31 × 1012 2.13 × 105 1.5 峰7 1.70 2.18 × 1012 3.09 × 103 1.1 表 4 LMP:Tb0.5at%, Tm0.5at%磷光体中Tb3+向Tm3+的能量转移效率
Table 4. The efficiency of energy transfer from Tb3+ to Tm3+ in LMP:Tb0.5at%, Tm0.5at% phosphor.
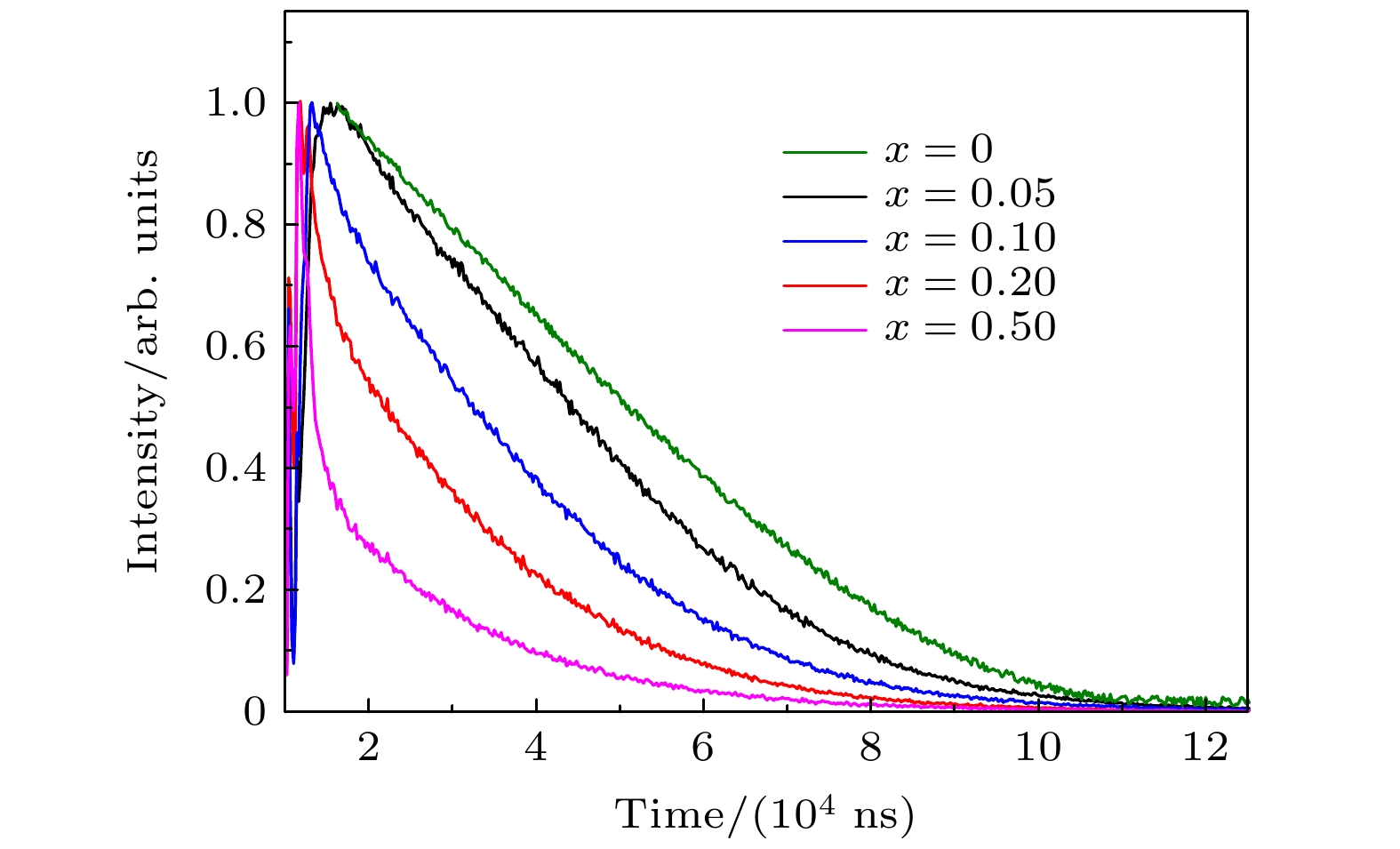
x τ/μs στ/μs ηET σηET 0 66.5 1.1 — — 0.05 33.3 0.3 49.9% 1.0% 0.10 26.6 0.2 60.0% 1.1% 0.20 20.3 0.2 69.5% 1.4% 1.00 13.4 0.3 79.8% 2.3% -
[1] Daniels F, Boyd C A, Saunders D F 1953 Science 117 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xiong Z Y, Xu J Y, Zhao F L, Zhang Y, Liu J, Tang Q 2017 J. Lumin. 192 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] ZhangS, HuangY, Shi L, Seo H J 2010 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22 235402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gai M Q, Chen C Y, Fan Y W, Wang J H 2013 J. Rare Earths 31 551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dhabekar B, Menon S N, Raja E A, Bakshi A K, Singh A K, Chougaonkar M P, Mayya Y S 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. A 269 1844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Singh A K, Menon S N, Dhabekar B, Kadam S, Chougaonkar M P, Mayya Y S 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. A 274 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bajaj N S, Palan C B, Koparkar K A, Kulkarni M S, Omanwar S K 2016 J. Lumin. 175 915
[8] 郭竞渊, 唐强, 唐桦明, 张纯祥, 罗达铃, 刘小伟 2017 66 107802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
GuoJ Y, Tang Q, Tang H M, Zhang C X, Luo D L, Liu X W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 107802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Baran A, Mahlik S, Grinberg M, Cai P, Kim S I, Seo H J 2014 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 26 85401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kumar M, Dhabekar B, Menon S N, Bakshi A K 2013 Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 155 410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kumar M, Dhabekar B, Menon S N, Chougaonkar M P, Mayya Y S 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 269 1849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Gieszczyk W, Bilski P, Osowski M K, Nowak T, Malinowski L 2018 Radiat. Meas. 113 1419
[13] Keskin I C, Türemis M, Kat M I, Gültekin S, Arslanlar Y T, Cetin A, Kibar R 2020 J. Lumin. 225 117276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tang H M, Lin L T, Zhang C X, Tang Q 2019 Inorg. Chem. 58 9698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郭竞渊, 唐强, 兰婷婷, 张纯祥, 罗达玲 2015 中国稀土学报 33 404
Guo J Y, Tang Q, Lan T T, Zhang C X, Luo D L 2015 J. Chin. Rare Earths Soc. 33 404
[16] Gieszczyk W, Marczewska B, Kosowski M, Mrozik A, Stoch P 2019 Materials 12 2861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hanic F, Handlovic M, Burdova K, Majling J 1982 J. Cryst. Spectrosc. 12 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 詹明亮, 陈瑶窈, 续卓, 熊正烨 2020 核技术 43 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan M L, Chen Y Y, Xu Z, Xiong Z Y 2020 Nucl. Tech. 43 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] McKeever S W S 1988 Thermoluminescence of Solids (London: Cambridge University Press) p75
[20] Liu X, Teng Y, Zhuang Y, Xie J, Qiao Y, Dong G, Chen D, Qiu J 2009 Opt. Lett. 22 3565
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8246
- PDF Downloads: 102
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: