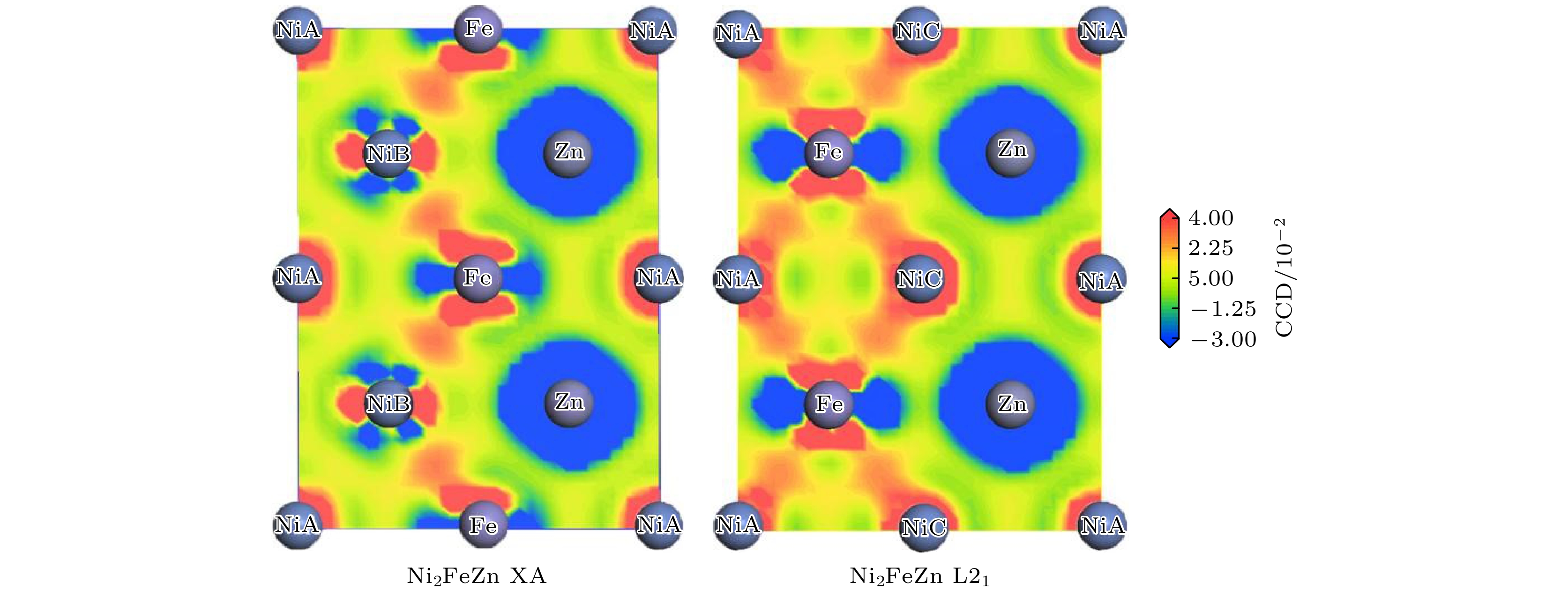
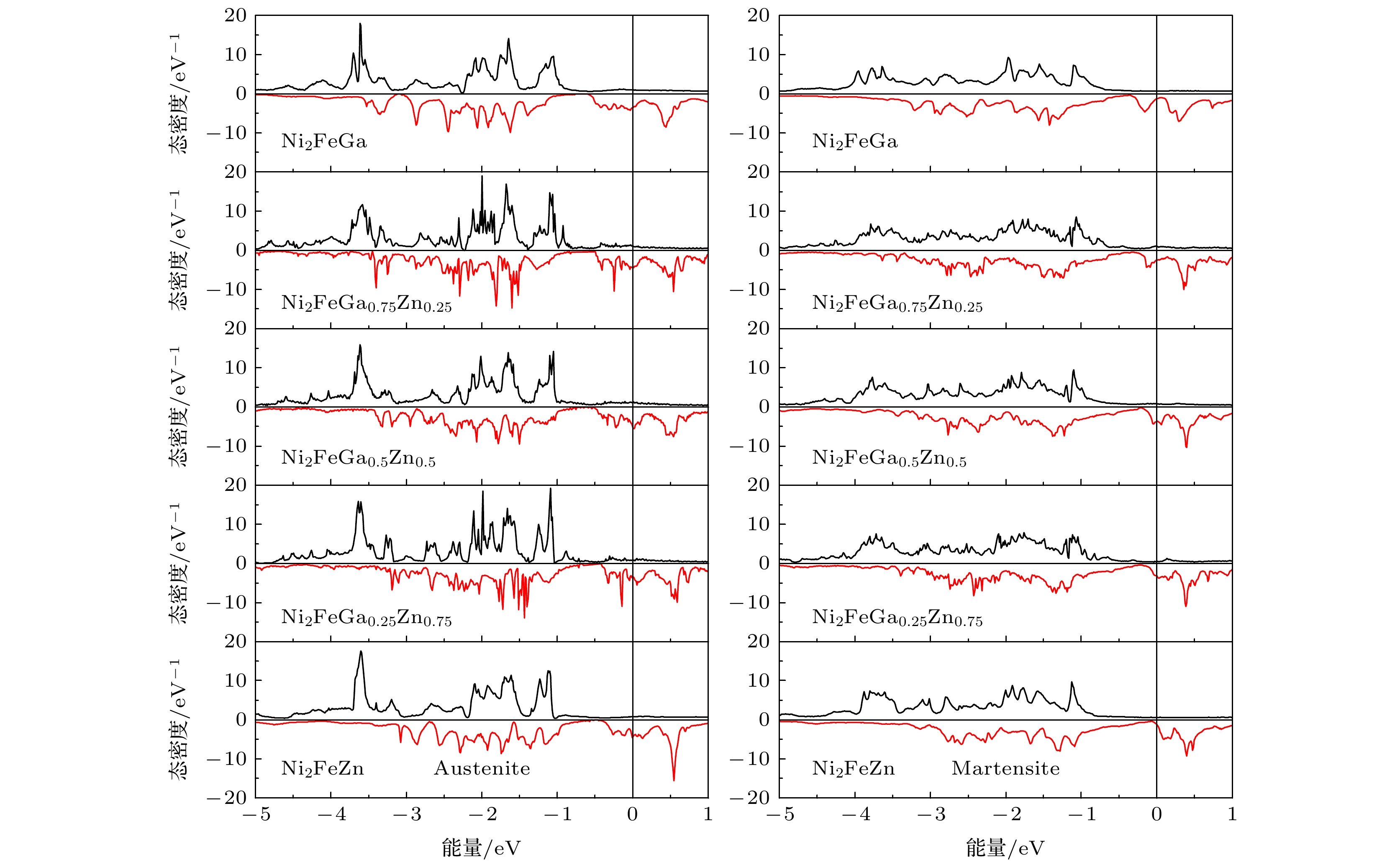
-
The magnetic shape memory alloys (MSMAs) have both martensitic transformation and ferromagnetism in the same material, thus external magnetic field can be used to induce/control the phase transformation or the reorientation of martensite variant. MSMAs have received considerable attention for their interesting properties and wide applications in different fields. For practical applications, the martensitic transformation temperature TM is an important factor and a high TM is preferable. Recently, Zn-doping has been found to be a possible way to elevate the value of TM of Ni-Mn based MSMA, but this effect on other kinds of MSMAs is not very clear yet. Heusler alloy Ni2FeGa is a typical MSMA with unique properties, however, its TM is relatively low. So it can be meaningful to find possible ways to increase its phase transition temperature. In this paper, the influences of Zn-doping on the electronic structure, martensitic transformation and magnetic properties of Heusler-type magnetic shape memory alloy Ni2FeGa are investigated by first-principle calculations. Total energy calculation and charge density difference indicate that Zn atom prefers to occupy the Ga (D) site when substituting for Ga in Ni2FeGa1–xZnx (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1). This main-group-element-like behavior is related to the closed 3d shell of Zn. Due to the similar atomic radii of Ga and Zn, Zn-doping does not lead the lattice constant to change greatly. The variation of the energy difference ΔEM between the martensite and austenite with Zn content increasing is calculated, and the result shows that ΔEM increases with Zn-doping increasing, and thus conducing to increasing the stability of the martensite phase and to evaluating the transformation temperature TM in Ni2FeGa1–xZnx. This trend can be explained by the Jahn-Teller effect observed in the DOS structure. The Zn-doping does not change the magnetic structure of Ni2FeGa. A ferromagnetic coupling between Fe spin moment and Ni spin moment can be observed within the whole range studied. The calculated total spin moment increases with Zn content increasing. The variation of formation energy Ef with Zn-doping is investigated. In Ni2FeGa1–xZnx a negative Ef is retained within the whole range studied, though it increases slightly with the doping of Zn. It is also found that the Zn-doping can increase the stability of L21 Heusler phase in Ni2FeGa1–xZnx and suppress the formation of the FCC L12 phase.
-
Keywords:
- Heusler alloys /
- magnetic shape memory alloys /
- electronic structure /
- martensitic transformation
[1] Dunand D C, Müllner P 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gottschall T, Skokov K P, Scheibel F, Acet M, Ghorbani Zavareh M, Skourski Y, Wosnitza J, Farle M, Gutfleisch O 2016 Phys. Rev. Appl. 5 024013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ghosh S, Ghosh A, Mandal K 2018 J. Alloys Compd. 746 200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ullakko K, Huang J K, Kanter C, Kokorin V V, O’Handley R C 1996 Appl. Phys. Lett. 69 1966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu Z H, Zhang M, Cui Y T, Zhou Y Q, Wang W H, Wu G H, Zhang X X 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Karaca H E, Karaman I, Lagoudas D C, Maier H J, Chumlyakov Y I 2003 Scr. Mater. 49 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kainuma R, Imano Y, Ito W, Sutou Y, Morito H, Okamoto S, Kitakami O, Oikawa K, Fujita A, Kanomata T, Ishida K 2006 Nature 439 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Omori T, Watanabe K, Umetsu R, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 082508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Webster P J, Ziebeck K R A, Town S L, Peak M S 1984 Philos. Mag. B 49 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu G D, Chen J L, Liu Z H, Dai X F, Wu G H, Zhang B, Zhang X X 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 262504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Han Z D, Wang D H, Zhang C L, Xuan H C, Zhang J R, Gu B X, Du Y W 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 104 053906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Algethami Obaidallah A, 李歌天, 柳祝红, 马星桥 2020 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Algethami O A, Li T G, Liu Z H, Ma X Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang H H, Qian M F, Zhang X X, Wei L S, Cao F Y, Xing D W, Cui X P, Sun J F, Geng L 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 689 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Luo H Z, Meng F B, Jiang Q X, Liu H Y, Liu E K, Wu G H, Wang Y X 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Barton L S, Lazott R T, Marsten E R 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 17A908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ni Z N, Guo X M, Li Q S, Liang Z Y, Luo H Z, Meng F B 2018 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 464 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Janovec J, Straka L, Sozinov A, Heczko O, Zelený M 2020 Mater. Res. Express 7 026101
[18] Ghotbi Varzaneh A, Kameli P, Abdolhosseini Sarsari I, Ghorbani Zavareh M, Salazar M C, Amiri T, Skourski Y, Luo J L, Etsell T H, Chernenko V A 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 134403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Payne M C, Teter M P, Allan D C, Arias T A, Joannopoulos J D 1992 Rev. Mod. Phys. 64 1065
[20] Segall M D, Lindan P L D, Probert M J, Pickard C J, Hasnip P J, Clark S J, Payne M C 2002 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 14 2717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kandpal H C, Fecher G H, Felser C 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 1507
[24] Zhang R F, Veprek S, Argon A S 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 172103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gilleßen M, Dronskowski R 2010 J. Comput. Chem. 31 612
[26] Zhang Y J, Wang W H, Zhang H G, Liu E K, Ma R S, Wu G H 2013 Physica B 420 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cordero B, Gomez V, Platero-Prats A E, Reves M, Echeverría J, Cremades E, Barragan F, Alvarez S 2008 Dalton Trans. 21 2832
[28] 赵建涛, 赵昆, 王家佳, 余新泉, 于金, 吴三械 2012 61 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao J T, Zhao K, Wang J J, Yu X Q, Yu J, Wu S X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wollmann L, Chadov S, Kübler J, Felser C 2011 Phys. Rev. B 92 064417
[30] Paul S, Ghosh S 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 063523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Luo H Z, Meng F B, Liu G D, Liu H Y, Jia P Z, Liu E K, Wang W H, Wu G H 2013 Intermetallics 38 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Barman S R, Chakrabarti A, Singh S, Banik S, Bhardwaj S, Paulose P L, Chalke B A, Panda A K, Mitra A, Awasthi A M 2008 Phys. Rev. B 78 134406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Entel P, Dannenberg A, Siewert M, Herper H C, Gruner M E, Buchelnikov V D, Chernenko V A 2011 Mater. Sci. Forum 684 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Winterlik J, Chadov S, Gupta A, Alijani V, Gasi T, Filsinger K, Balke B, Fecher G H, Jenkins C A, Casper F, Kubler J, Gao L, Parkin S S P, Felser C 2012 Adv. Mater. 24 6283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Faleev S V, Ferrante Y, Jeong J, Samant M G, Jones B, Parkin S S P 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 034022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Brown P J, Bargawi A Y, Crangle J, Neumann K U, Ziebeck K R A 1999 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 11 4715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Barman S R, Banik S, Shukla A K, Kamal C, Chakrabart A 2007 EPL 80 57002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Soykan C, Özdemir Kart S, Sevik C, Çağın T 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 611 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 计算得到的Ni2FeGa1–xZnx(x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1)合金立方奥氏体相的平衡晶格常数a, 形成能Ef和磁性参数
Table 1. The calculated equilibrium lattice constant a, formation energy Ef and magnetic properties of Ni2FeGa1–xZnx (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1) alloys in cubic austenitic state.
x 0.00 0.25 0.5 0.75 1.00 a/Å 5.76 5.76 5.75 5.74 5.74 Ef/(eV·f.u.–1) –0.75 –0.64 –0.54 –0.43 –0.34 Mt
(μB/f.u.)3.40 3.50 3.61 3.72 3.82 MNi/μB 0.16 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 MFe/μB 3.11 3.13 3.15 3.16 3.17 MGa/μB –0.03 –0.02 –0.01 0.00 — MZn/μB — –0.06 –0.06 –0.05 –0.04 表 2 计算得到的Ni2FeGa1–xZnx (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1)合金在马氏体状态下的马氏体与奥氏体之间能量差ΔEM, c/a比值和磁性参数
Table 2. The calculated energy difference ΔEM between the martensite and austenite, c/a ratio and magnetic properties of Ni2FeGa1–xZnx (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1) alloys in tetragonal martensitic state.
x 0.00 0.25 0.5 0.75 1.00 ΔEM/(eV·f.u.–1) –0.110 –0.119 –0.128 –0.144 –0.151 c/a 1.36 1.36 1.34 1.33 1.32 Mt/(μB·f.u.–1) 3.38 3.48 3.63 3.73 3.85 MNi/μB 0.28 0.32 0.35 0.38 0.41 MFe/μB 2.92 3.00 3.02 3.06 3.11 MGa/μB –0.11 –0.10 –0.08 –0.07 — MZn/μB — –0.13 –0.11 –0.10 –0.09 -
[1] Dunand D C, Müllner P 2011 Adv. Mater. 23 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gottschall T, Skokov K P, Scheibel F, Acet M, Ghorbani Zavareh M, Skourski Y, Wosnitza J, Farle M, Gutfleisch O 2016 Phys. Rev. Appl. 5 024013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ghosh S, Ghosh A, Mandal K 2018 J. Alloys Compd. 746 200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ullakko K, Huang J K, Kanter C, Kokorin V V, O’Handley R C 1996 Appl. Phys. Lett. 69 1966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu Z H, Zhang M, Cui Y T, Zhou Y Q, Wang W H, Wu G H, Zhang X X 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Karaca H E, Karaman I, Lagoudas D C, Maier H J, Chumlyakov Y I 2003 Scr. Mater. 49 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kainuma R, Imano Y, Ito W, Sutou Y, Morito H, Okamoto S, Kitakami O, Oikawa K, Fujita A, Kanomata T, Ishida K 2006 Nature 439 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Omori T, Watanabe K, Umetsu R, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 082508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Webster P J, Ziebeck K R A, Town S L, Peak M S 1984 Philos. Mag. B 49 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu G D, Chen J L, Liu Z H, Dai X F, Wu G H, Zhang B, Zhang X X 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 262504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Han Z D, Wang D H, Zhang C L, Xuan H C, Zhang J R, Gu B X, Du Y W 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 104 053906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Algethami Obaidallah A, 李歌天, 柳祝红, 马星桥 2020 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Algethami O A, Li T G, Liu Z H, Ma X Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang H H, Qian M F, Zhang X X, Wei L S, Cao F Y, Xing D W, Cui X P, Sun J F, Geng L 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 689 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Luo H Z, Meng F B, Jiang Q X, Liu H Y, Liu E K, Wu G H, Wang Y X 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Barton L S, Lazott R T, Marsten E R 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 17A908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ni Z N, Guo X M, Li Q S, Liang Z Y, Luo H Z, Meng F B 2018 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 464 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Janovec J, Straka L, Sozinov A, Heczko O, Zelený M 2020 Mater. Res. Express 7 026101
[18] Ghotbi Varzaneh A, Kameli P, Abdolhosseini Sarsari I, Ghorbani Zavareh M, Salazar M C, Amiri T, Skourski Y, Luo J L, Etsell T H, Chernenko V A 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 134403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Payne M C, Teter M P, Allan D C, Arias T A, Joannopoulos J D 1992 Rev. Mod. Phys. 64 1065
[20] Segall M D, Lindan P L D, Probert M J, Pickard C J, Hasnip P J, Clark S J, Payne M C 2002 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 14 2717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kandpal H C, Fecher G H, Felser C 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 1507
[24] Zhang R F, Veprek S, Argon A S 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 172103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gilleßen M, Dronskowski R 2010 J. Comput. Chem. 31 612
[26] Zhang Y J, Wang W H, Zhang H G, Liu E K, Ma R S, Wu G H 2013 Physica B 420 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cordero B, Gomez V, Platero-Prats A E, Reves M, Echeverría J, Cremades E, Barragan F, Alvarez S 2008 Dalton Trans. 21 2832
[28] 赵建涛, 赵昆, 王家佳, 余新泉, 于金, 吴三械 2012 61 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao J T, Zhao K, Wang J J, Yu X Q, Yu J, Wu S X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 213102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wollmann L, Chadov S, Kübler J, Felser C 2011 Phys. Rev. B 92 064417
[30] Paul S, Ghosh S 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 063523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Luo H Z, Meng F B, Liu G D, Liu H Y, Jia P Z, Liu E K, Wang W H, Wu G H 2013 Intermetallics 38 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Barman S R, Chakrabarti A, Singh S, Banik S, Bhardwaj S, Paulose P L, Chalke B A, Panda A K, Mitra A, Awasthi A M 2008 Phys. Rev. B 78 134406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Entel P, Dannenberg A, Siewert M, Herper H C, Gruner M E, Buchelnikov V D, Chernenko V A 2011 Mater. Sci. Forum 684 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Winterlik J, Chadov S, Gupta A, Alijani V, Gasi T, Filsinger K, Balke B, Fecher G H, Jenkins C A, Casper F, Kubler J, Gao L, Parkin S S P, Felser C 2012 Adv. Mater. 24 6283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Faleev S V, Ferrante Y, Jeong J, Samant M G, Jones B, Parkin S S P 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 034022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Brown P J, Bargawi A Y, Crangle J, Neumann K U, Ziebeck K R A 1999 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 11 4715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Barman S R, Banik S, Shukla A K, Kamal C, Chakrabart A 2007 EPL 80 57002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Soykan C, Özdemir Kart S, Sevik C, Çağın T 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 611 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5719
- PDF Downloads: 89
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: