-
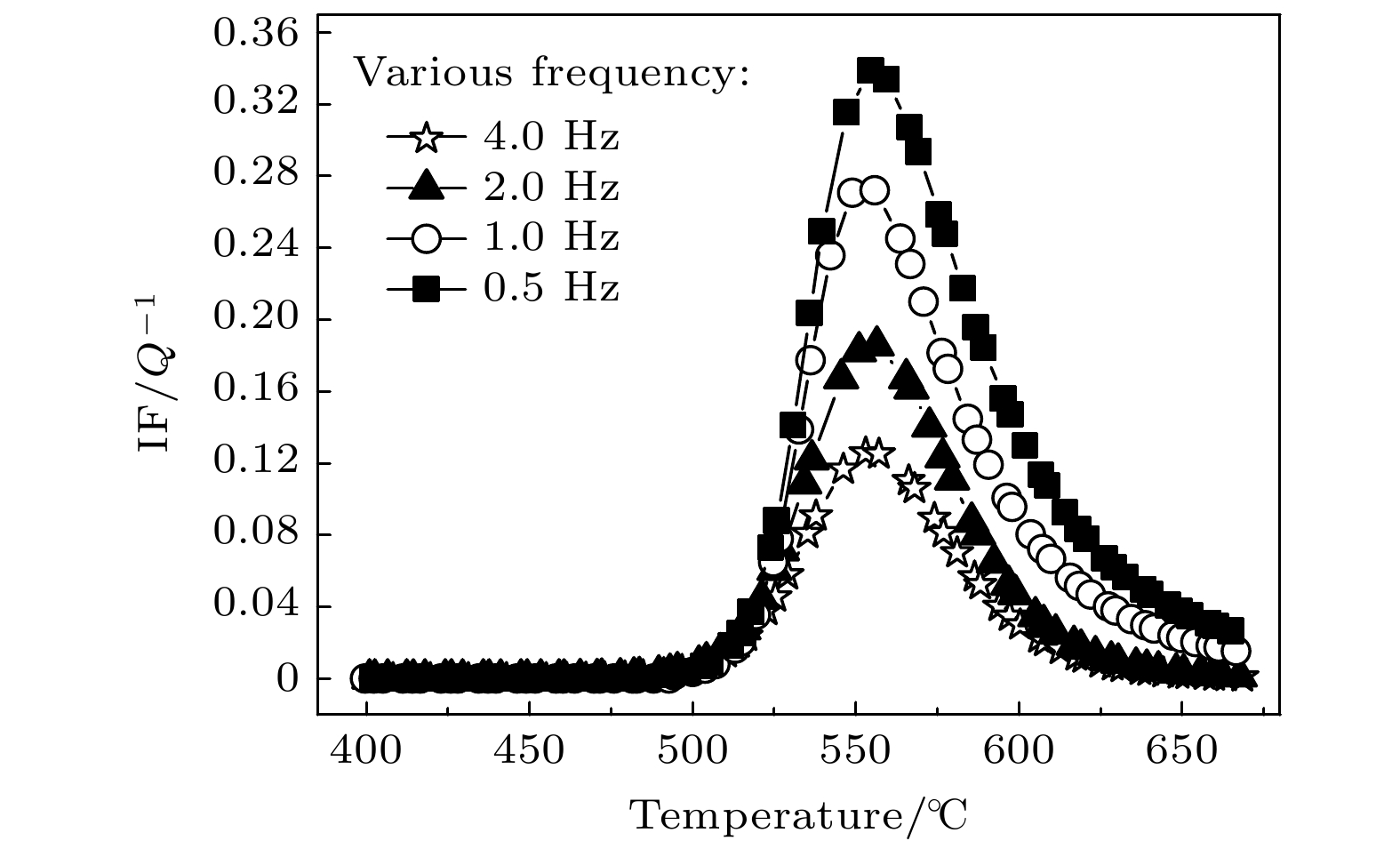
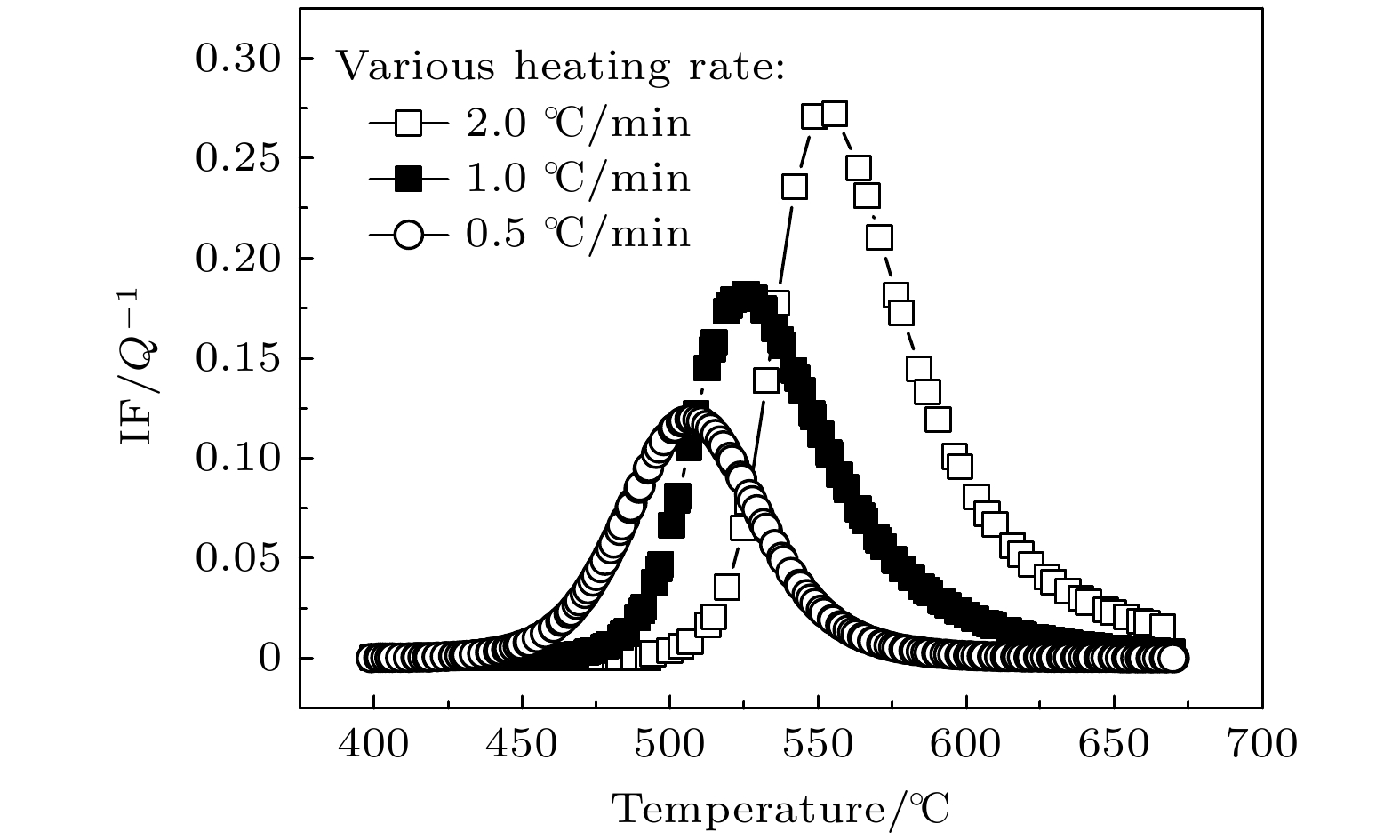
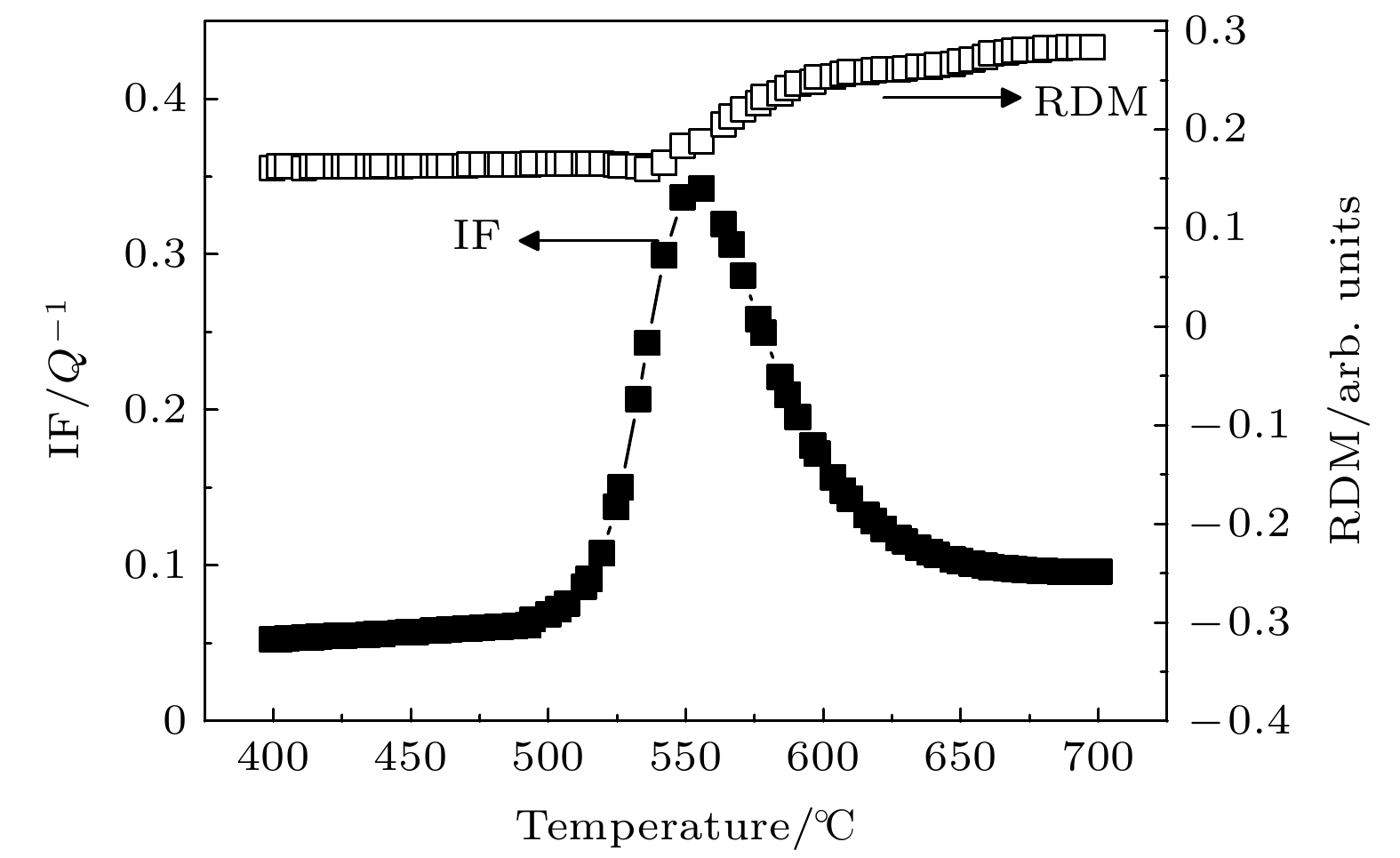
The Ni-Al intermetallic compounds, as important high-temperature structural materials, have clear target requirements in a number of fields. Powder metallurgy is an important candidate for preparing the Ni-Al intermetallic compounds. Clarifying the formation and transformation process of Ni-Al intermetallic compounds in sintering process and determining the solid diffusion reaction temperature and types of intermetallic compounds are greatly important for tailoring sintering process and optimizing product quality. In this paper, the internal friction behaviors of Ni-Al powder mixture compacts in the sintering process are systematically investigated by the internal friction technique. A typical internal friction peak is observed in the internal friction-temperature spectrum. The peak height decreases with the measuring frequency increasing, but the peak temperature is independent of frequency. Moreover, the internal friction peak shifts toward higher temperature and the peak height increases as the heating rate increases. It is reasonable that the internal friction peak belongs to the typical phase transformation internal friction peak which is associated with the formation of intermetallic compounds NiAl3 and Ni2Al3 in the heating process. Furthermore, the microstructure of the Ni-Al powder mixture can be tailored by mechanical ball-milling. The internal friction peak shifts toward lower temperature and the peak height decreases with the ball-milling time increasing, which indicates that the solid diffusion reaction can be activated at lower temperature with a slower reaction rate. This decrease is related to the refinement of powder particles, the lamellar formation of powder mixture, the enhancement of solid solution degree and surface energy, and the shortened atomic diffusion distance due to the mechanical ball-milling. It is also indicated that the mechanical ball-milling can effectively reduce the initial temperature of solid diffusion reaction, thus lowering sintering temperature.
-
Keywords:
- Ni-Al intermetallic compounds /
- internal friction /
- mechanical ball-milling /
- solid diffusion reaction
[1] Camagu S T, Mathabathe N M, Motaung D E, Muller T F G, Arendse C J, Bolokang A S 2019 Vacuum 169 108919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Moshksar M M, Mirzaee M 2004 Intermetallics 12 1361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Mashreghi A, Moshksar M M 2009 J. Alloys Compd. 484 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen T, Hampikia J M, Thadhani N N 1999 Acta Mater. 47 2567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Enayati M H, Karimzadeh F, Anvari S Z 2008 J. Mater. Process. Technol. 200 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mirale D B 1993 Acta Mater. 41 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chmielewski M, Nosewicz S, Pietrzak K, Rojek J, Strojny-Nedza A, Mackiewicz S, Dutkiewicz J 2014 J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nuria C, Carlos R C L, Jose M G 2013 J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Movahedi B 2014 Adv. Powde. Technol. 25 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xiang Z D, Rose S R, Datta P K 2008 Scr. Mater. 59 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo J T, Wang Z S, Sheng L Y, Zhou L Z, Yuan C, Chen Z G, Li Song 2012 Prog. Nat. Sci. 22 414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hadjiafxenti A, Gunduz I E, Tsotsos C, Kyratsi T, Aouadi S M, Doumanidis C C, Rebholz C 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 505 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hadjiafxenti A, Gunduz I E, Kyratsi T, Doumanidis C C, Rebholz C 2013 Vacuum 96 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hao G L, Li Y C, Wang X F, Wang W G, Wang X F, Wang D, Li X Y 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 036102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ivanov E, Grigorieva T, Golubkova G, Boldyrev V, Fasman A B, Mikailenko S D, Kalinina O T 1988 Mater. Lett. 7 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Mchael A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Maric R, Ishihara K N, Shingu P H 1996 J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 15 1180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 郝刚领, 许巧平, 李先雨, 王伟国 2019 68 126101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao G L, Xu Q P, Li X Y, Wang W G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 126101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Han F S, Zhu Z G and Gao J C 1999 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30 771
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nowich A S, Berry B S, 1972 Anelastic Relaxation in Crystalline Solids (New York and London: Academic Press) p454
[21] 方前锋 1996 金属学报 32 565
Fang Q F 1996 Acta Metall. Sin. 32 565
[22] 冯端 1999 金属物理学 (第三卷) (北京: 科学出版社) 第196−200页
Feng D 1999 Metal Physics (Vol. 3) (Beijing: Science Press) pp196−200 (in Chinese)
[23] 王清周 2006 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学院固体物理研究所)
Wang Q Z 2006 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: Institute of Solid State Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[24] Zheng L Q, Fang Q F 2001 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 13 3411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Charlot F, Gaffet E, Zeghmati B, Bernard F, Niepce J C 1999 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 262 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 张宇文, 邓永和, 文大东, 赵鹤平, 高明 2020 69 136601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y W, Deng Y H, Wen D D, Zhao H P, Gao M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 136601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Schwarz R B, Johnson W L 1983 Phys. Rev. Lett. 51 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
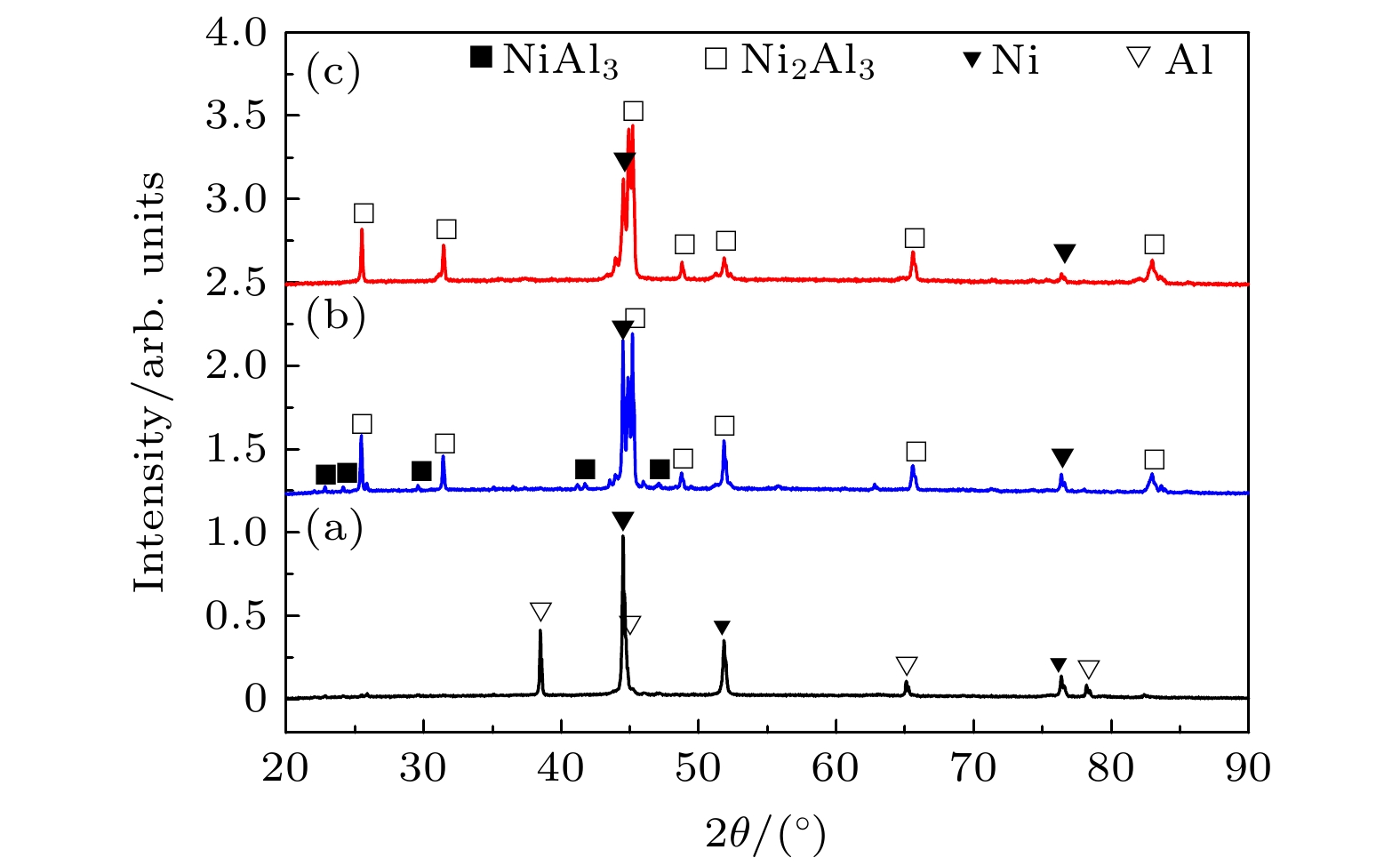
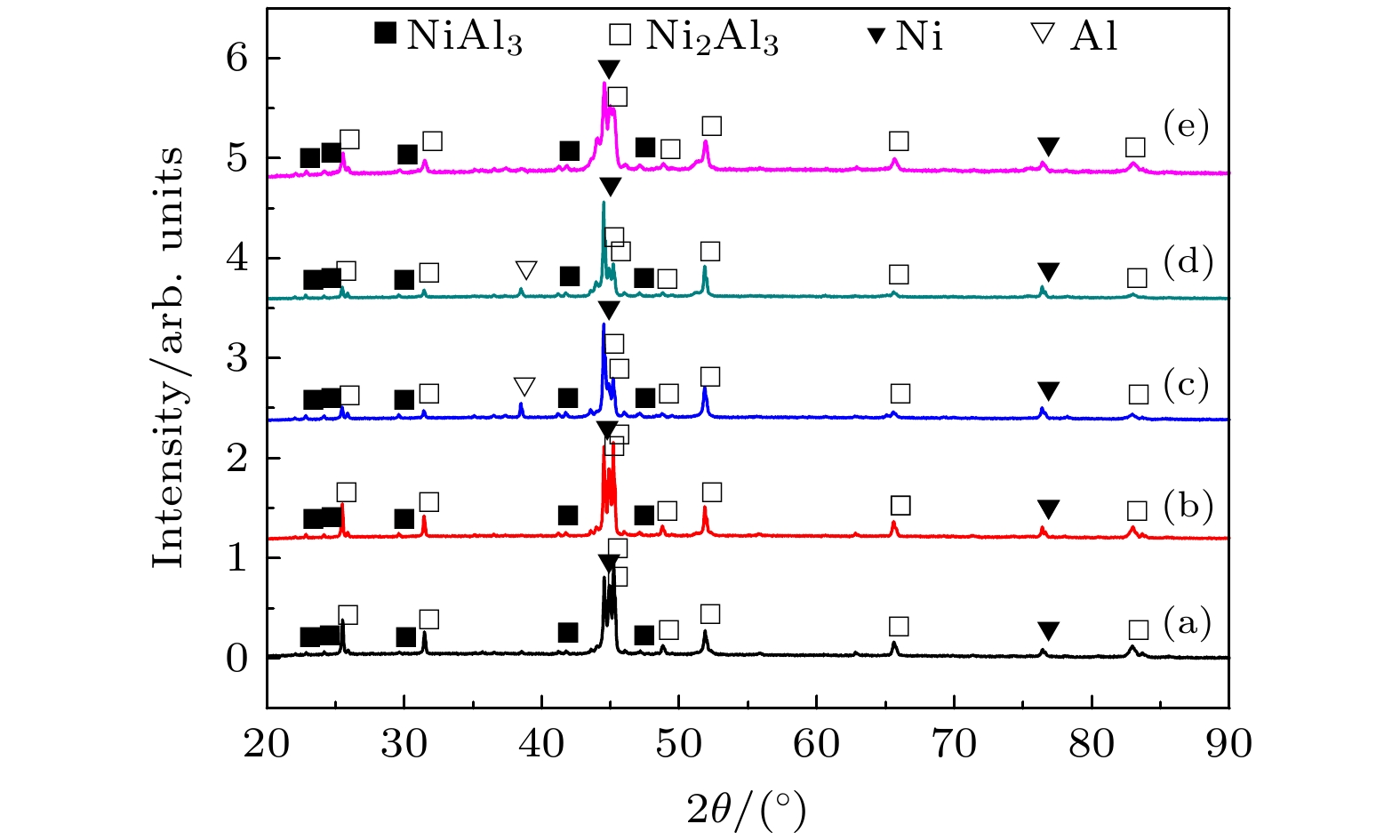
图 4 不同温度热处理的Ni-Al粉末压坯XRD图谱 (a) 492 ℃; (b) 556 ℃; (c) 675 ℃ (三个温度分别对应于内耗峰起始温度、峰值温度和结束温度)
Figure 4. XRD patterns of Ni-Al powder compact milled for 1 h after heat treatment at different temperature: (a) 492 ℃; (b) 556 ℃; (c) 675 ℃ (three temperatures respectively corresponding to start temperature, peak temperature and end temperature of the internal friction peak).
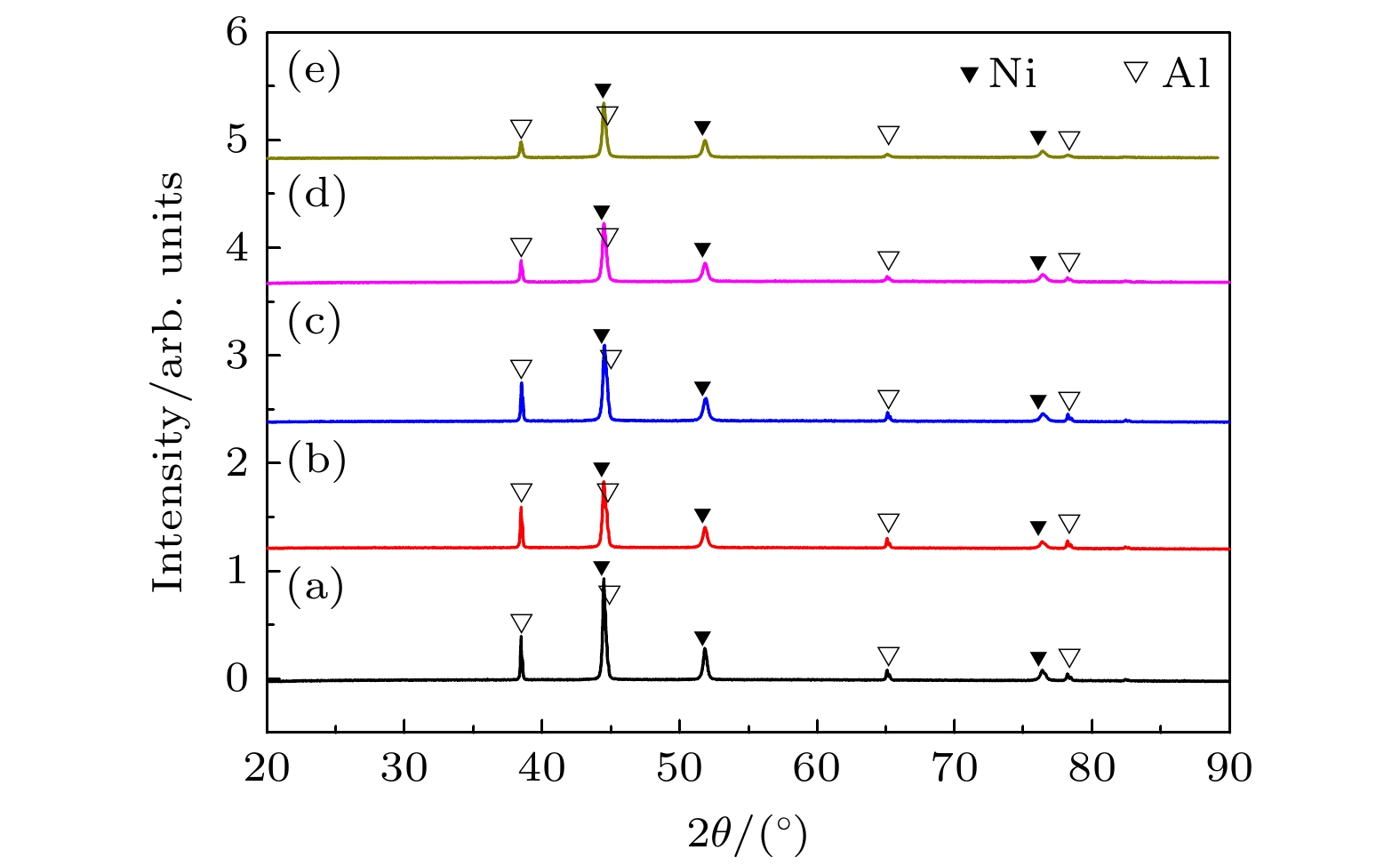
图 8 球磨时间不同的Ni-Al粉末压坯热处理后XRD图谱 (a) 0 h, 559 ℃; (b) 1 h, 556 ℃; (c) 2 h, 533 ℃; (d) 10 h, 483 ℃; (e) 20 h, 434 ℃(热处理温度对应于球磨时间不同的样品的内耗峰的峰温)
Figure 8. XRD patterns of Ni-Al powder compact after heat treatment for the sample processing ball-milling for different time: (a) 0 h, 559 ℃; (b) 1 h, 556 ℃; (c) 2 h, 533 ℃; (d) 10 h, 483 ℃; (e) 20 h, 434 ℃ (the heat treatment temperatures corresponding to internal friction peak temperatures of ball-milled samples for different time).
图 9 球磨时间不同的Ni-Al粉末压坯热处理后XRD图谱 (a) 0 h, 700 ℃; (b) 1 h, 675 ℃; (c) 2 h, 660 ℃; (d) 10 h, 625 ℃; (e) 20 h, 575 ℃ (热处理温度对应于球磨时间不同的样品的内耗峰的结束温度)
Figure 9. XRD patterns of Ni-Al powder compact after heat treatment for the sample processing ball-milling for different time: (a) 0 h, 700 ℃; (b) 1 h, 675 ℃; (c) 2 h, 660 ℃; (d) 10 h, 625 ℃; (e) 20 h, 575 ℃ (the heat treatment temperatures corresponding to end temperature of internal friction peak of ball-milled samples for different time).
-
[1] Camagu S T, Mathabathe N M, Motaung D E, Muller T F G, Arendse C J, Bolokang A S 2019 Vacuum 169 108919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Moshksar M M, Mirzaee M 2004 Intermetallics 12 1361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Mashreghi A, Moshksar M M 2009 J. Alloys Compd. 484 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen T, Hampikia J M, Thadhani N N 1999 Acta Mater. 47 2567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Enayati M H, Karimzadeh F, Anvari S Z 2008 J. Mater. Process. Technol. 200 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mirale D B 1993 Acta Mater. 41 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chmielewski M, Nosewicz S, Pietrzak K, Rojek J, Strojny-Nedza A, Mackiewicz S, Dutkiewicz J 2014 J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nuria C, Carlos R C L, Jose M G 2013 J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Movahedi B 2014 Adv. Powde. Technol. 25 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xiang Z D, Rose S R, Datta P K 2008 Scr. Mater. 59 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo J T, Wang Z S, Sheng L Y, Zhou L Z, Yuan C, Chen Z G, Li Song 2012 Prog. Nat. Sci. 22 414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hadjiafxenti A, Gunduz I E, Tsotsos C, Kyratsi T, Aouadi S M, Doumanidis C C, Rebholz C 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 505 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hadjiafxenti A, Gunduz I E, Kyratsi T, Doumanidis C C, Rebholz C 2013 Vacuum 96 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hao G L, Li Y C, Wang X F, Wang W G, Wang X F, Wang D, Li X Y 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 036102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ivanov E, Grigorieva T, Golubkova G, Boldyrev V, Fasman A B, Mikailenko S D, Kalinina O T 1988 Mater. Lett. 7 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Mchael A 1990 Phys. Rev. Lett. 64 487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Maric R, Ishihara K N, Shingu P H 1996 J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 15 1180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 郝刚领, 许巧平, 李先雨, 王伟国 2019 68 126101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao G L, Xu Q P, Li X Y, Wang W G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 126101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Han F S, Zhu Z G and Gao J C 1999 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30 771
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nowich A S, Berry B S, 1972 Anelastic Relaxation in Crystalline Solids (New York and London: Academic Press) p454
[21] 方前锋 1996 金属学报 32 565
Fang Q F 1996 Acta Metall. Sin. 32 565
[22] 冯端 1999 金属物理学 (第三卷) (北京: 科学出版社) 第196−200页
Feng D 1999 Metal Physics (Vol. 3) (Beijing: Science Press) pp196−200 (in Chinese)
[23] 王清周 2006 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学院固体物理研究所)
Wang Q Z 2006 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: Institute of Solid State Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[24] Zheng L Q, Fang Q F 2001 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 13 3411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Charlot F, Gaffet E, Zeghmati B, Bernard F, Niepce J C 1999 Mater. Sci. Eng., A 262 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 张宇文, 邓永和, 文大东, 赵鹤平, 高明 2020 69 136601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y W, Deng Y H, Wen D D, Zhao H P, Gao M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 136601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Schwarz R B, Johnson W L 1983 Phys. Rev. Lett. 51 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7011
- PDF Downloads: 60
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: