-
Optical microresonators supporting whispering-gallery modes have been intensively studied in past decades due to their practical applications ranging from fundamental science to engineering physics. Among such microresonators, microsphere resonators have been demonstrated to possess ultra-high quality (Q) factor, however, their shapes usually become non-standard spherical body, leading to irregular resonant spectra. Microring resonators have unique potential in integraibility on chip, but the fabrication imperfection limits their Q-factor only to 106. In addition, the free spectral range (FSR) just depends on their radius. Due to the advantages of high Q-factor, standard shape, slender mode field distribution, the microbottle resonators are demonstrated to possess excellent performance in cavity quantum dynamics, nonlinear optics, high-sensitivity sensing, and micro-laser. In this paper, we carry out a systematic study on the spectral characteristics of prolate microbottle resonator theoretically and experimentally. First, theoretically, the field distribution theory of the microbottle resonator is studied in detail based on Helmholtz equation. Experimentally, prolate microbottle resonators are fabriated via arc discharge technology. Second, the radial modes and axial modes of the microbottles are efficiently excited with the help of a coupled tapered fiber waveguide. By adjusting the coupling gap between the microbottle and the waveguide, The controlling of three cupling states i.e. undercoupling, critical coupling and overcoupling are realized. In our experiment, the whispering-gallery modes excited are identifiable and recognizable. The resonant mode with an ultra-high Q-factor of up to 1.78 × 108 is achieved. The characteristic of ultra-high Q-factor makes the microbottle hold great potential in biochemical sensing, nonlinear optics, and micro-laser. The tuning stability is enhanced by keeping the waveguide in touch with the microbottle. We investigate the selective excitation of whispering-gallery modes by adjusting different coupling points. As a result, clean spectra with robust coupling are observed. The stable device is suitable for improving the sensing performance. Finally, Fano resonance effect is obtained by choosing the diameter of the tapered fiber waveguide. The results presented in this paper will be of great significance for enhancing the sensing, nonlinear optics and cavity quantum dynamics. -
Keywords:
- optical microresonator /
- microbottle resonator /
- whispering-gallery modes /
- mode selection /
- Fano resonance
[1] Vahala K J 2003 Nature 424 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang P, Ding M, Murugan G S, Bo L, Guang C, Semenova Y, Wu Q, Farrell G, Brambilla G 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 5208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王涛, 杨旭, 刘晓斐, 雷府川, 高铭, 胡蕴琪, 龙桂鲁 2015 64 164212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang T, Yang X, Liu X F, Lei F C, Gao M, Hu Y Q, Long G L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 164212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang M, Jin X, Li F, Cai B, Yang Y, Zeng S, Wang K 2019 Mater. Lett. 244 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lin G, Coikket A, Chembo Y K 2017 Adv. Opt. Photonics 9 828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shen Z, Zhou Z, Zhou C, Sun F, Guo G, Dong C, Guo G 2015 Photonics Res. 3 243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang S, Wang Y, Sun H 2015 Adv. Opt. Mater. 3 1136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bogaerts W, Heyn P D, Vaerenbergh T V, et al. 2012 Laser Photonics Rev. 6 47
[9] Wang T, He J, Lee C, Niu H 2012 Opt. Express 20 28119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gu G, Chen L, Fu H, Che K, Cai Z, Xu H 2013 Chin. Opt. Lett. 11 101401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sumetsky M 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Louyer Y, Meschede D, Rauschenbeutel A 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 031801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sumetsky M 2019 Prog. Quantum Electron. 64 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pöllinger M, O'Shea D, Warken F, Rauschenbeutel A 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 053901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Murugan G S, Wilkinson J S, Zervas M N 2009 Opt. Express 17 11816
[16] Murugan G S, Wilkinson J S, Zervas M N 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 1893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sumetsky M 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 163901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Dong Y, Jin X, Wang K 2015 App. Opt. 54 4016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gu F, Xie F, Lin X, Linghu S, Fang W, Zeng H, Tong L, Zhuang S 2017 Light Sci. Appl. 6 e17061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lu Q, Chen X, Xie S, Wu X 2018 Opt. Express 26 20183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yin Y, Niu Y, Ren M, Wu W, Zhao W, Nan J, Zheng Z, Zhang Y, Ding M 2018 Opt. Lett. 19 4715
[22] Stoian R, Kavine B K, Rosenberger A T 2019 Talanta 194 585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Asano M, Takeuchi Y, Ozdemir S K, Rikizo I, Yang L, Imoto N, Yamamoto T 2016 Opt. Express 24 12082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen Y, Zhou Z, Zou C, Shen Z, Guo G, Dong C 2017 Opt. Express 25 16879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yong Y, Ooka Y, Thompson R, Ward J, Chormaic S N 2018 Opt. Lett. 41 575
[26] Dong Y, Jin X, Wang K 2016 Opt. Commun. 372 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 杨睿, 於文华, 鲍洋, 张远宪, 普小云 2008 57 6412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang R, Yu W H, Bao Y, Zhang Y X, Pu X Y 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang K, Wang Y, Wu Y 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 2956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang M, Zeng S, Meng L, Yang Y, Jin X, Dong Y, Zhang L, Xu W, Wang K 2019 IEEE Photonics J. 11 7105412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liao J, Wu X, Liu L, Xu L 2016 Opt. Express 24 8574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang Z, Ng G I, Hu T, Qiu H, Guo X, Wang W, Rouifed M S, Liu C, Wang H 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 11 081105
[32] Chiba A, Fujiwara K, Hanamura R, Matsumoto T 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 261106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li B, Xiao Y, Zou C, Jiang X, Liu Y, Sun F, Li Y, Gong Q 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 021108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
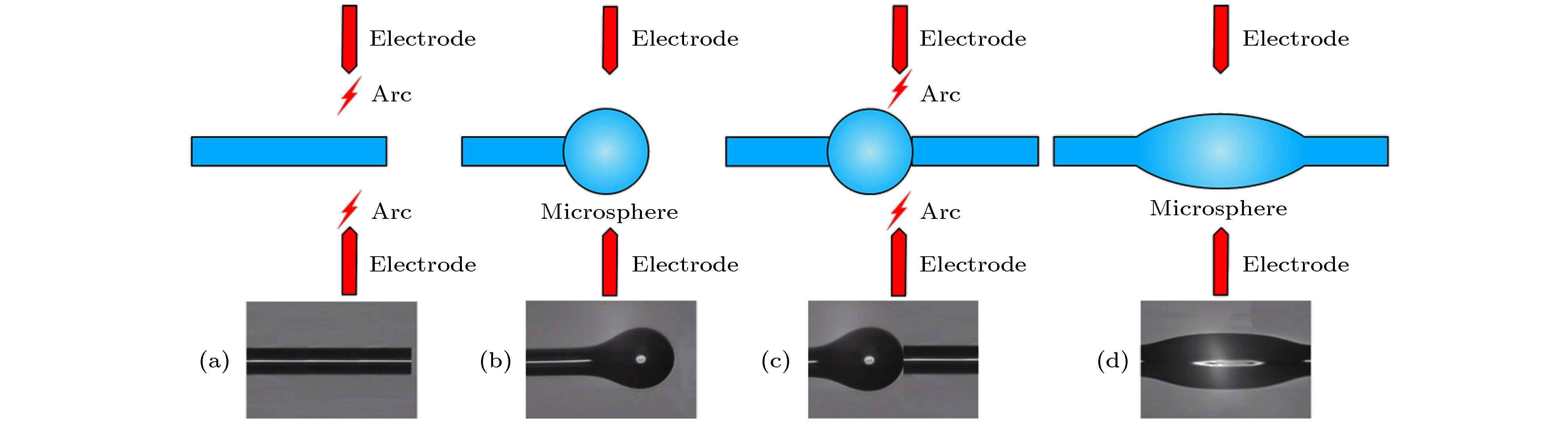
图 1 扁长型微瓶腔制备过程图 (a) 对单根光纤放电; (b) 微球腔形成; (c) 第二根光纤对齐; (d) 微瓶腔形成
Figure 1. The fabrication process of prolate microbottle resonator: (a) The single fiber is heated via electrical arc discharge; (b) the microsphere is formed; (c) another fiber is placed to align the microsphere; (d) the microbottle resonator is formed.
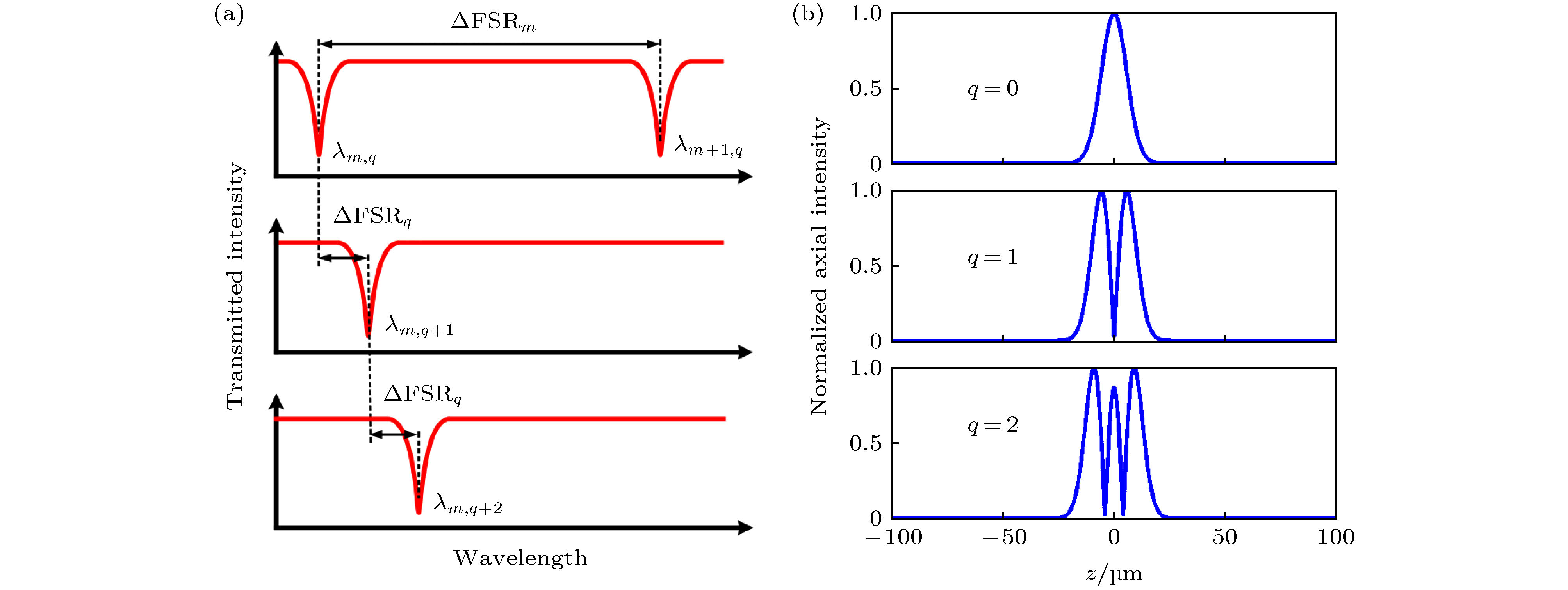
图 6 粗扫状态下得到的谐振光谱, 图中标记了一阶径向模式下的角向和轴向谐振模式及对应的角向模式FSR和轴向模式FSR
Figure 6. The resonance spectra of the microbottle resonator for different coupling gaps in coarse scanning, the angular and axial resonant mode in the first order radial mode, angular FSR (FSRq,i) and axial FSR (FSRm,i) are marked in the figure.
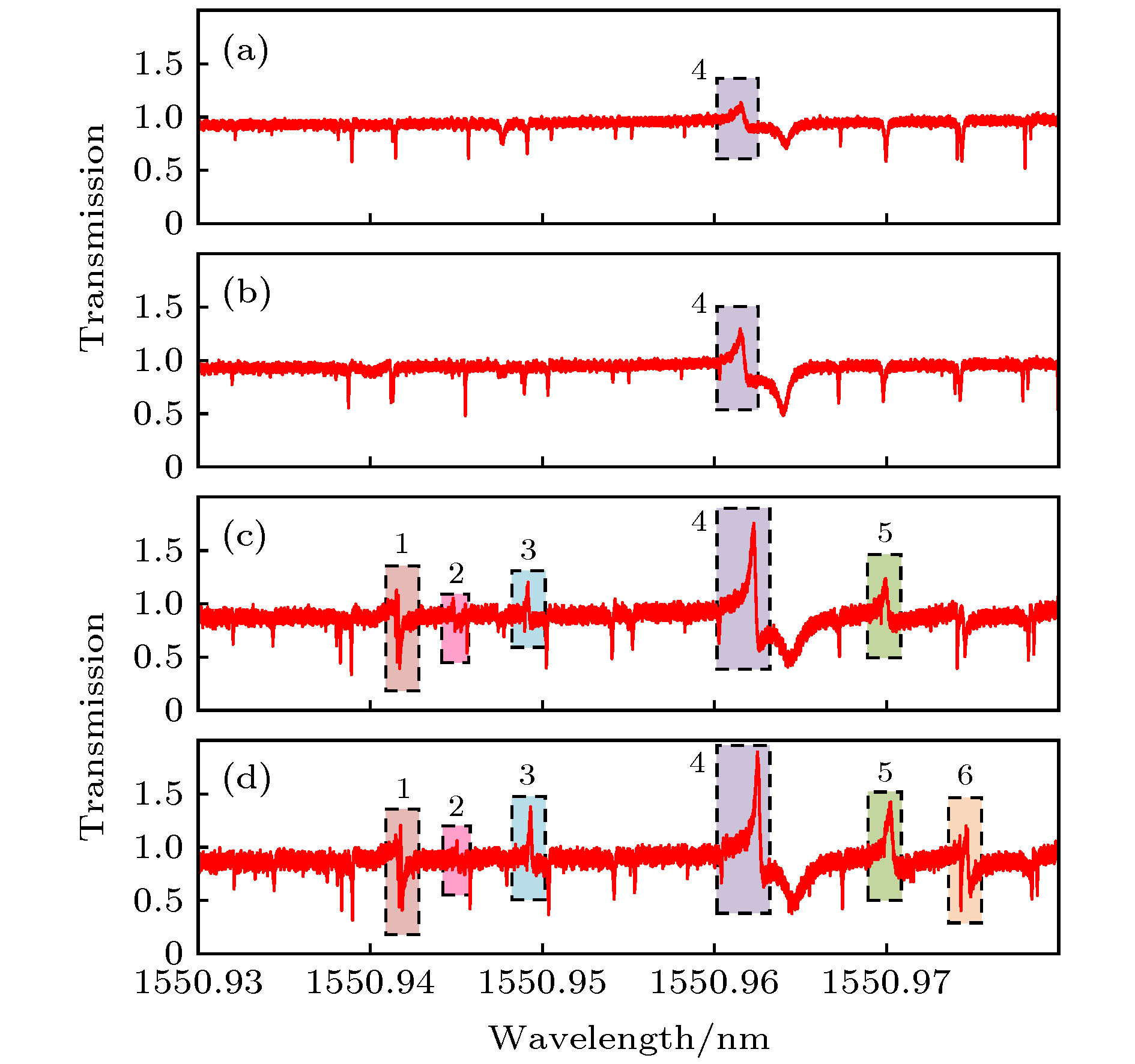
图 8 选择微瓶腔不同耦合点得到的谐振光谱 (a)实验操作示意图; (b)−(l)逐渐改变微瓶腔耦合点测得的谐振光谱图
Figure 8. The resonance spectra by choosing different coupling points of the microbottle resonator: (a) Schematic diagram of experimental operation; (b)−(l) the resonance spectra with the gradually changing coupling points of the microbottle.
表 1 实验测得的FSR值与理论计算得到的FSR值比较
Table 1. Comparison of FSR value of experimental data and theoretical data.
实验数据FSR/nm 理论数据FSR/nm 误差% 实验数据FSR/nm 理论数据FSR/nm 误差% FSRm,1 3.718 3.618 2.76 FSRq,1 1.232 1.204 2.33 FSRm,2 3.708 3.636 1.98 FSRq,2 1.241 1.206 2.59 FSRm,3 3.716 3.626 2.48 FSRq,3 1.239 1.208 2.57 FSRm,4 3.732 3.643 2.44 FSRq,4 1.238 1.210 2.31 FSRm,5 3.636 3.616 0.55 FSRq,5 1.237 1.212 2.06 FSRm,6 3.718 3.632 2.37 FSRq,6 1.239 1.214 2.06 -
[1] Vahala K J 2003 Nature 424 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang P, Ding M, Murugan G S, Bo L, Guang C, Semenova Y, Wu Q, Farrell G, Brambilla G 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 5208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王涛, 杨旭, 刘晓斐, 雷府川, 高铭, 胡蕴琪, 龙桂鲁 2015 64 164212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang T, Yang X, Liu X F, Lei F C, Gao M, Hu Y Q, Long G L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 164212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang M, Jin X, Li F, Cai B, Yang Y, Zeng S, Wang K 2019 Mater. Lett. 244 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lin G, Coikket A, Chembo Y K 2017 Adv. Opt. Photonics 9 828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shen Z, Zhou Z, Zhou C, Sun F, Guo G, Dong C, Guo G 2015 Photonics Res. 3 243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang S, Wang Y, Sun H 2015 Adv. Opt. Mater. 3 1136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bogaerts W, Heyn P D, Vaerenbergh T V, et al. 2012 Laser Photonics Rev. 6 47
[9] Wang T, He J, Lee C, Niu H 2012 Opt. Express 20 28119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gu G, Chen L, Fu H, Che K, Cai Z, Xu H 2013 Chin. Opt. Lett. 11 101401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sumetsky M 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Louyer Y, Meschede D, Rauschenbeutel A 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 031801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sumetsky M 2019 Prog. Quantum Electron. 64 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pöllinger M, O'Shea D, Warken F, Rauschenbeutel A 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 053901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Murugan G S, Wilkinson J S, Zervas M N 2009 Opt. Express 17 11816
[16] Murugan G S, Wilkinson J S, Zervas M N 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 1893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sumetsky M 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 163901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Dong Y, Jin X, Wang K 2015 App. Opt. 54 4016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gu F, Xie F, Lin X, Linghu S, Fang W, Zeng H, Tong L, Zhuang S 2017 Light Sci. Appl. 6 e17061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lu Q, Chen X, Xie S, Wu X 2018 Opt. Express 26 20183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yin Y, Niu Y, Ren M, Wu W, Zhao W, Nan J, Zheng Z, Zhang Y, Ding M 2018 Opt. Lett. 19 4715
[22] Stoian R, Kavine B K, Rosenberger A T 2019 Talanta 194 585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Asano M, Takeuchi Y, Ozdemir S K, Rikizo I, Yang L, Imoto N, Yamamoto T 2016 Opt. Express 24 12082
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen Y, Zhou Z, Zou C, Shen Z, Guo G, Dong C 2017 Opt. Express 25 16879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yong Y, Ooka Y, Thompson R, Ward J, Chormaic S N 2018 Opt. Lett. 41 575
[26] Dong Y, Jin X, Wang K 2016 Opt. Commun. 372 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 杨睿, 於文华, 鲍洋, 张远宪, 普小云 2008 57 6412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang R, Yu W H, Bao Y, Zhang Y X, Pu X Y 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang K, Wang Y, Wu Y 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 2956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang M, Zeng S, Meng L, Yang Y, Jin X, Dong Y, Zhang L, Xu W, Wang K 2019 IEEE Photonics J. 11 7105412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liao J, Wu X, Liu L, Xu L 2016 Opt. Express 24 8574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhang Z, Ng G I, Hu T, Qiu H, Guo X, Wang W, Rouifed M S, Liu C, Wang H 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 11 081105
[32] Chiba A, Fujiwara K, Hanamura R, Matsumoto T 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 261106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li B, Xiao Y, Zou C, Jiang X, Liu Y, Sun F, Li Y, Gong Q 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 021108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9109
- PDF Downloads: 224
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: