-
The study of synchronizations in coupled oscillators is very important for understanding the occurrence of self-organized behaviors in complex systems. In the traditional Kuramoto model that has been extensively applied to the study of synchronous dynamics of coupled oscillators, the interaction function among oscillators is pairwise. The multiplex interaction mechanism that describes triple or multiple coupling functions has been a research focus in recent years. When the multiplex coupling dominates the interactions among oscillators, the phase oscillator systems can exhibit the typical abrupt desynchronization transitions. In this paper, we extensively investigate the synchronous dynamics of the Kuramoto model with mean-field triple couplings. We find that the abrupt desynchronization transition is irreversible, i.e. the system may experience a discontinuous transition from coherent state to incoherent state as the coupling strength deceases adiabatically, while the reversed transition cannot occur by adiabatically increasing the coupling. Moreover, the coherent state strongly depends on initial conditions. The dynamical mechanism of this irreversibility is theoretically studied by using the self-consistency approach. The neutral stability of ordered state is also explained through analyzing the linear-stability of the incoherent state. Further studies indicate that the system may experience a cascade of desynchronized standing-wave transitions when the width of the distribution function of natural frequencies of oscillators is changed. At the critical coupling, the motion of coupled oscillators in high-dimensional phase space becomes unstable through the saddle-node bifurcation and collapses into a stable low-dimensional invariant torus, which corresponds to the standing-wave state. The above conclusions and analyses are further extended to the case of multi-peak natural-frequency distributions. The results in this work reveal various collective synchronous states and the mechanism of the transitions among these macroscopic states brought by multiplex coupling. This also conduces to the in-depth understanding of transitions among collective states in other complex systems.
-
Keywords:
- synchronization /
- multiple coupling /
- abrupt desynchronization transitions /
- desynchronized standing wave transition
[1] Pikovsky A, Rosenblum M, Kurths J 2001 Synchronization, A Universal Concept in Nonlinear Sciences (New York: Cambridge University Press) pp1−24
[2] Strogatz S 2003 Sync: The Emerging Science of Spontaneous Order (London: Pengiun Press Science) pp103−152
[3] 郑志刚 2004 耦合非线性系统的时空动力学与合作行为 (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第53—85页
Zheng Z G 2004 Space-time Dynamics and Cooperative Behavior of Coupled Nonlinear Systems (Beijing: Higher Education Press) pp53−85 (in Chinese)
[4] Rohen M, Sorge A, Timme M, Witthaut D 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 064101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mikhailov A S, Calenbuhr V, 2002 From Cells to Societies: Models of Complex Coherent Action (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag) pp127−154
[6] Glass L, Mackay M C 1988 From Clocks to Chaos: The Rhythms of Life (Princeton: Princeton University Press) p10
[7] Montbrió E, Pazó D 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 244101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 吴玉喜, 黄霞, 高建, 郑志刚 2007 56 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y X, Huang X, Gao J, Zheng Z G 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu C, Gao J, Sun Y, Huang X, Zheng Z G 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 12039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Winfree A T 1967 J. Theor. Biol. 16 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kuramoto Y 1975 Self-entrainment of a Population of Coupled Non-linear Oscillators, in: International Symposium on Mathematical Problems in Theoretical Physics (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag) pp420−428
[12] Rodrigues F A, Peron M TKD, Ji P, Kurths J 2016 Phys. Rep. 610 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kuramoto Y 1984 Chemical Oscillations, Waves and Turbulence (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag) pp60–66
[14] Kuramoto Y, Nishikawa I 1987 J. Stat. Phys. 49 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郑志刚 2019 复杂系统的涌现动力学: 从同步到集体输运 (北京: 科学出版社) 第95 −176页
Zheng Z G 2019 Emergence Dynamics in Complex Systems: From Synchronization to Collective Transport (Beijing: Science Press) pp95−176 (in Chinese)
[16] Tanaka T, Aoyagi T 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Komarov M, Pikovsky A 2015 Phys. Rev. E 92 020901(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bick C, Ashwin P, Rodrigues A 2016 Chaos 26 094814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xu C, Xiang H, Gao J, Zheng Z G 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 31133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Millán A P, Torres J J, Bianconi G 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 9910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Millán A P, Torres J J, Bianconi G 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 022307
[22] Petri G, Expert P, Turkheimer F, Carhart-Harris R, Nutt D, Hellyer P J, Vaccarino F 2014 J. R. Soc. Interface 11 20140873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Giusti C, Ghrist R, Bassett D S 2016 J. Comput. Neurosci. 41 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sizemore A E, Giusti C, Kahn A, Vettel J M, Betzel R, Bassett D S 2018 J. Comput. Neurosci. 44 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Skardal P S, Arenas A 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 248301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fell J, Axmacher N 2011 Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Skardal P S, Ott E, Restrepo J G 2011 Phys. Rev. E 84 036208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang J W, Rong L L, Deng Q H, Zhang J Y 2010 Eur. Phys. J. B 77 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zheng Z G, Hu G, Hu B 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 5318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 朱廷祥, 吴晔, 肖井华 2012 62 040502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu T X, Wu Y, Xiao J H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 040502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Daido H 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 1406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Crawford J D 1994 J. Statist.Phys. 74 1047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 郑志刚, 翟云 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 010505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z G, Zhai Y 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys., Mech. Astron. 50 010505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Komarov M, Pikovsky A 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 204101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Omel’chenko O E, Wolfrum M 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 164101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Omel’chenko O E, Wolfrum M 2013 Physica D 263 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Xu C, Wang X B, Skardal P S 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 023281
-
图 2 (a) 当
${\omega _0} = 1$ 时不同自然频率分布半宽度$\gamma $ 对应的$f(q)$ 曲线; (b) 当${\omega _0} = 1$ ,$\gamma = 0.2$ ,$\eta = 1$ 时,$F(q) = (2\eta - 1) f(q)$ 和$G(q) = 1/\sqrt K $ 两条曲线的交点随着耦合强度K变化的示意图Figure 2. (a)
$f(q)$ curves when${\omega _0} = 1$ ; (b) the intersection of curves$F(q) = (2\eta - 1)f(q)$ and$G(q) = 1/\sqrt K $ for different couplings K, where${\omega _0} = 1$ ,$\gamma = 0.2$ ,$\eta = 1$ .图 3 自然频率为双峰Lorentz分布且
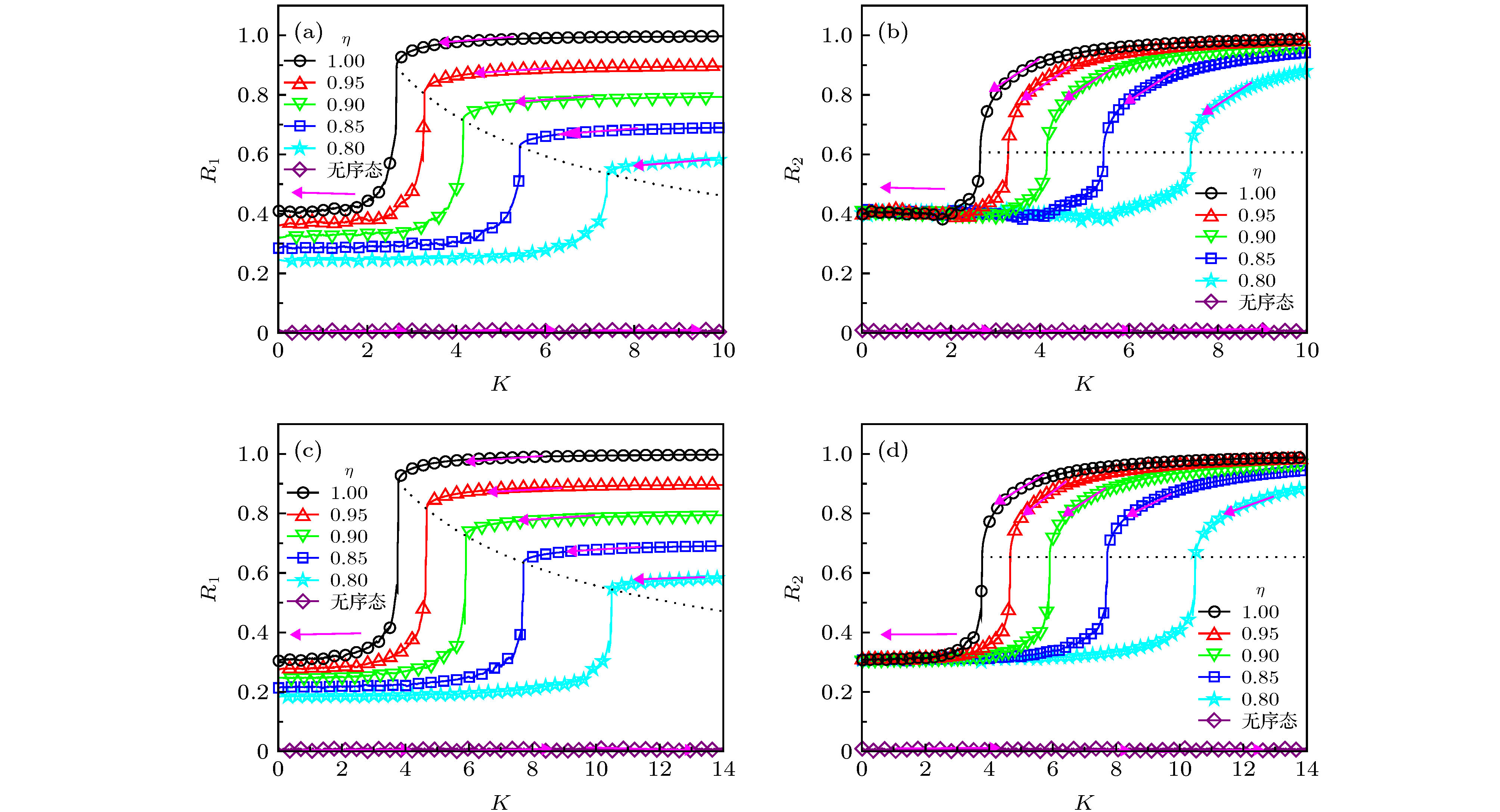
${\omega _0} = 1$ 时不同分布半宽$\gamma $ 对应的系统序参量${R_1}$ ,${R_2}$ 随耦合强度K的变化 (a), (d)$\gamma = 0$ ; (b), (e)$\gamma = 0.5$ ; (c), (f)$\gamma = 1$ . 图中实线和符号标记分别对应于理论预测和数值结果($N = {10^5}$ 个耦合相振子), 对于每一个$\eta $ , 系统的初始相位分别按概率$\eta $ 和$1 - \eta $ 随机设置为$0$ 和$\pi $ Figure 3. The order parameters
${R_1}$ [(a)—(c)] and${R_2}$ [(d)—(f)] varying against the coupling strength K for different γ and${\omega _0} = 1$ , when the natural frequency obeys a bimodal Lorentz distribution: (a), (d)$\gamma = 0$ ; (b), (e)$\gamma = 0.5$ ; (c), (f)$\gamma = 1$ . Theoretical predictions and numerical results are labeled as solid lines and symbols, respectively ($N = {10^5}$ ). For every η, the initial phase is set as 0 and π for η and 1–η.图 4 当
$\eta = 1$ ,${\omega _0} = 1$ ,$\gamma = 0$ 时不同耦合强度K对应的序参量${R_{1, 2}}(t)$ 的周期振荡图像($N = {10^5}$ 个耦合振子) (a), (b)$K = 1.5 < {K_{\rm{c}}}$ ; (c), (d)$K = 0.5 < {K_{\rm{c}}}$ Figure 4. Oscillatory behaviors of the order parameter
${R_{1, 2}}(t)$ for different coupling strengths K, where$\eta = 1$ ,${\omega _0} = 1$ ,$\gamma = 0$ , and$N = {10^5}$ : (a), (b)$K = 1.5 < {K_{\rm{c}}}$ ; (c), (d)$K = 0.5 < {K_{\rm{c}}}$ .图 6 当
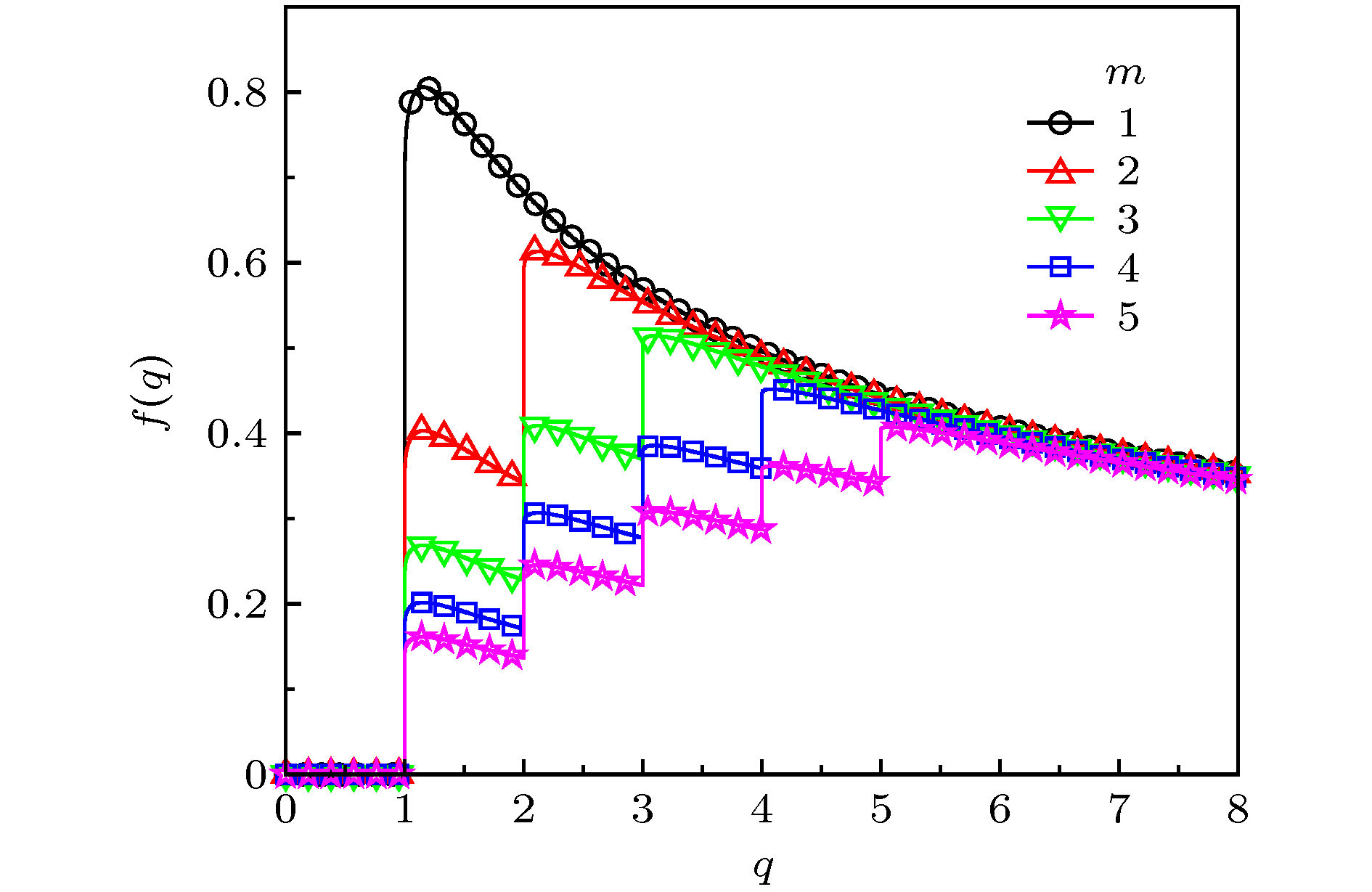
${\omega _0} = 1$ 时, 不同m对应的序参量${R_{1, 2}}$ 随耦合强度K的变化 (a), (b) m = 2; (c), (d) m = 3. 标记有图形的实线表示数值模拟结果, 黑色虚线表示ADT临界值理论预测结果(40)式Figure 6. The order parameters
${R_1}$ [(a), (c)] and${R_2}$ [(b), (d)] varying against the coupling strength K for different m and${\omega _0} = 1$ : (a), (b)$m = 2$ ; (c), (d)$m = 3$ . Theoretical predictions and numerical results are labeled as solid lines and symbols, respectively. The dotted lines are the theoretical predictions of the critical values of ADT given in (40). -
[1] Pikovsky A, Rosenblum M, Kurths J 2001 Synchronization, A Universal Concept in Nonlinear Sciences (New York: Cambridge University Press) pp1−24
[2] Strogatz S 2003 Sync: The Emerging Science of Spontaneous Order (London: Pengiun Press Science) pp103−152
[3] 郑志刚 2004 耦合非线性系统的时空动力学与合作行为 (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第53—85页
Zheng Z G 2004 Space-time Dynamics and Cooperative Behavior of Coupled Nonlinear Systems (Beijing: Higher Education Press) pp53−85 (in Chinese)
[4] Rohen M, Sorge A, Timme M, Witthaut D 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 064101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mikhailov A S, Calenbuhr V, 2002 From Cells to Societies: Models of Complex Coherent Action (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag) pp127−154
[6] Glass L, Mackay M C 1988 From Clocks to Chaos: The Rhythms of Life (Princeton: Princeton University Press) p10
[7] Montbrió E, Pazó D 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 244101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 吴玉喜, 黄霞, 高建, 郑志刚 2007 56 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y X, Huang X, Gao J, Zheng Z G 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 3803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu C, Gao J, Sun Y, Huang X, Zheng Z G 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 12039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Winfree A T 1967 J. Theor. Biol. 16 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kuramoto Y 1975 Self-entrainment of a Population of Coupled Non-linear Oscillators, in: International Symposium on Mathematical Problems in Theoretical Physics (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag) pp420−428
[12] Rodrigues F A, Peron M TKD, Ji P, Kurths J 2016 Phys. Rep. 610 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kuramoto Y 1984 Chemical Oscillations, Waves and Turbulence (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag) pp60–66
[14] Kuramoto Y, Nishikawa I 1987 J. Stat. Phys. 49 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郑志刚 2019 复杂系统的涌现动力学: 从同步到集体输运 (北京: 科学出版社) 第95 −176页
Zheng Z G 2019 Emergence Dynamics in Complex Systems: From Synchronization to Collective Transport (Beijing: Science Press) pp95−176 (in Chinese)
[16] Tanaka T, Aoyagi T 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Komarov M, Pikovsky A 2015 Phys. Rev. E 92 020901(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bick C, Ashwin P, Rodrigues A 2016 Chaos 26 094814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xu C, Xiang H, Gao J, Zheng Z G 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 31133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Millán A P, Torres J J, Bianconi G 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 9910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Millán A P, Torres J J, Bianconi G 2019 Phys. Rev. E 99 022307
[22] Petri G, Expert P, Turkheimer F, Carhart-Harris R, Nutt D, Hellyer P J, Vaccarino F 2014 J. R. Soc. Interface 11 20140873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Giusti C, Ghrist R, Bassett D S 2016 J. Comput. Neurosci. 41 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sizemore A E, Giusti C, Kahn A, Vettel J M, Betzel R, Bassett D S 2018 J. Comput. Neurosci. 44 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Skardal P S, Arenas A 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 248301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fell J, Axmacher N 2011 Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Skardal P S, Ott E, Restrepo J G 2011 Phys. Rev. E 84 036208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang J W, Rong L L, Deng Q H, Zhang J Y 2010 Eur. Phys. J. B 77 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zheng Z G, Hu G, Hu B 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 5318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 朱廷祥, 吴晔, 肖井华 2012 62 040502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu T X, Wu Y, Xiao J H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 040502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Daido H 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 1406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Crawford J D 1994 J. Statist.Phys. 74 1047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 郑志刚, 翟云 2020 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 50 010505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z G, Zhai Y 2020 Sci. Sin. Phys., Mech. Astron. 50 010505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Komarov M, Pikovsky A 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 204101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Omel’chenko O E, Wolfrum M 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 164101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Omel’chenko O E, Wolfrum M 2013 Physica D 263 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Xu C, Wang X B, Skardal P S 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 023281
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12840
- PDF Downloads: 317
- Cited By: 0




















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: