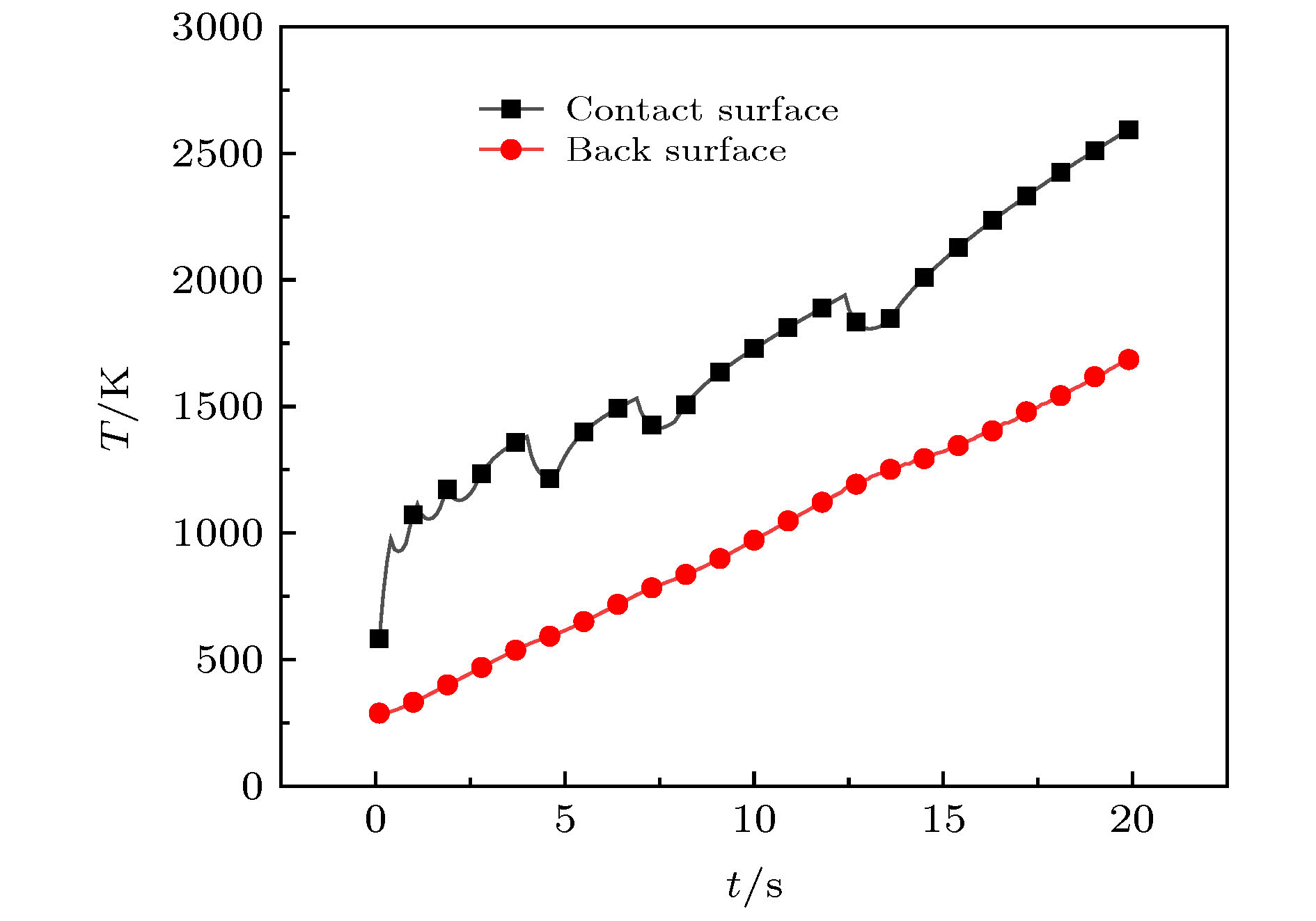
-
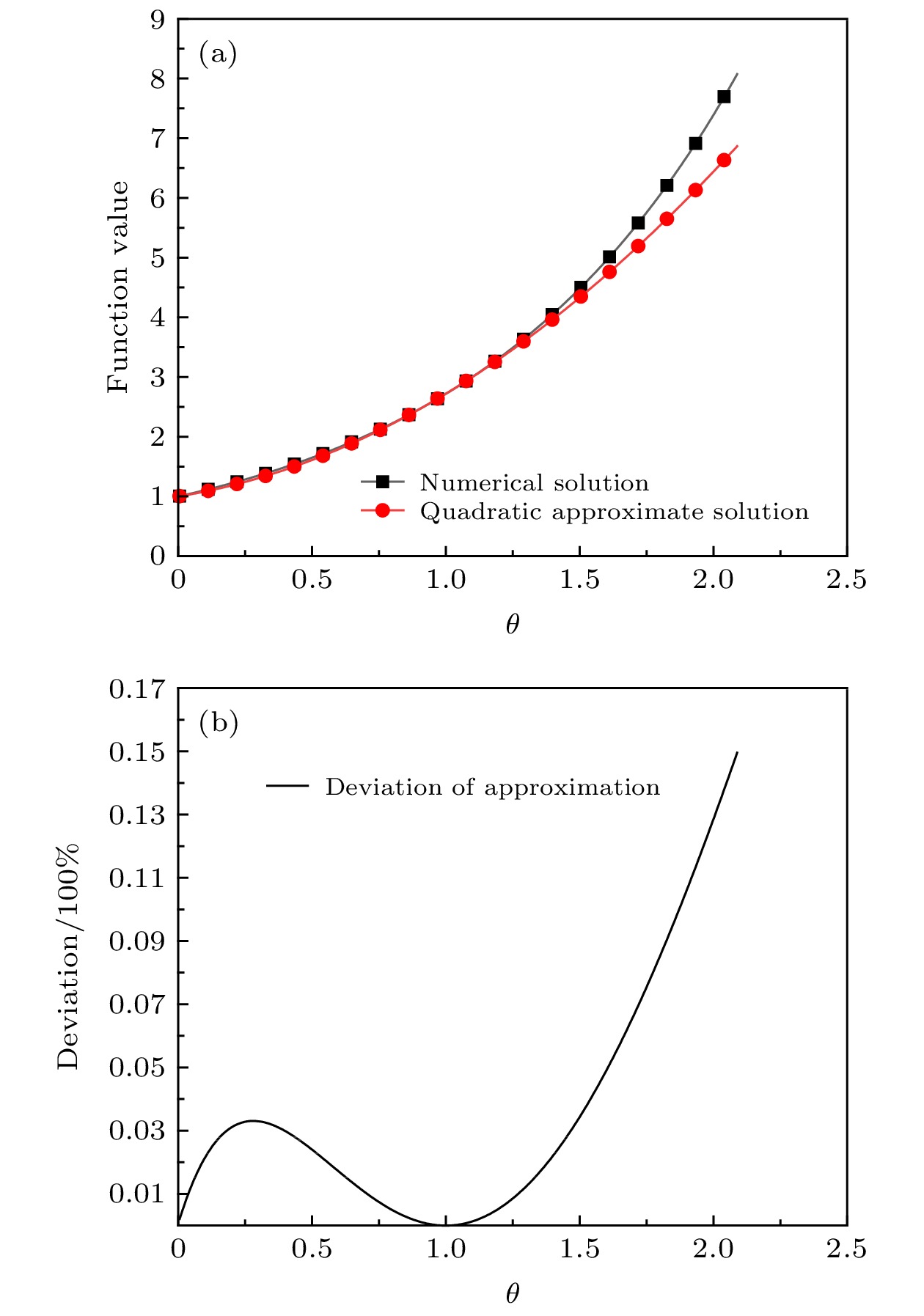
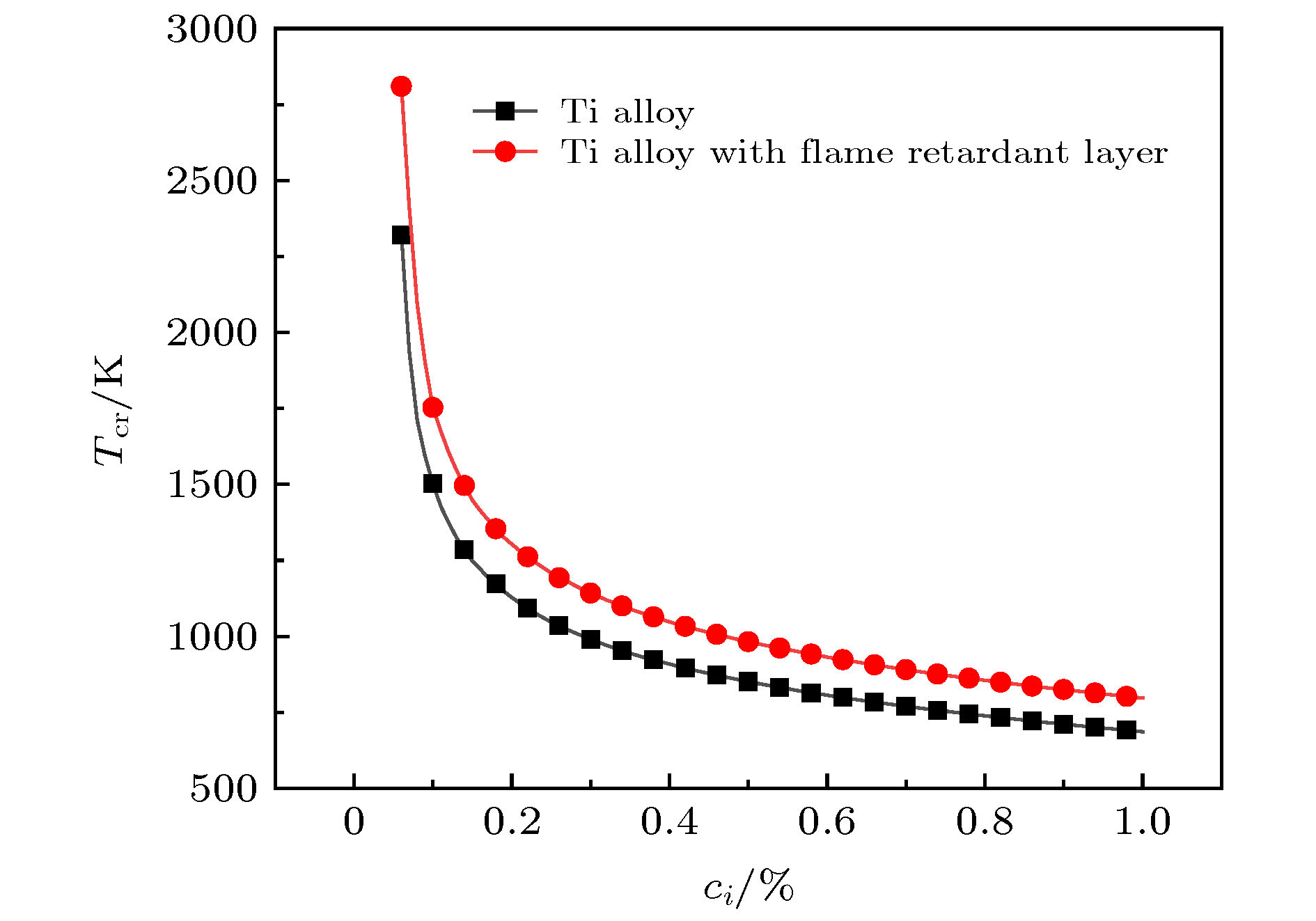
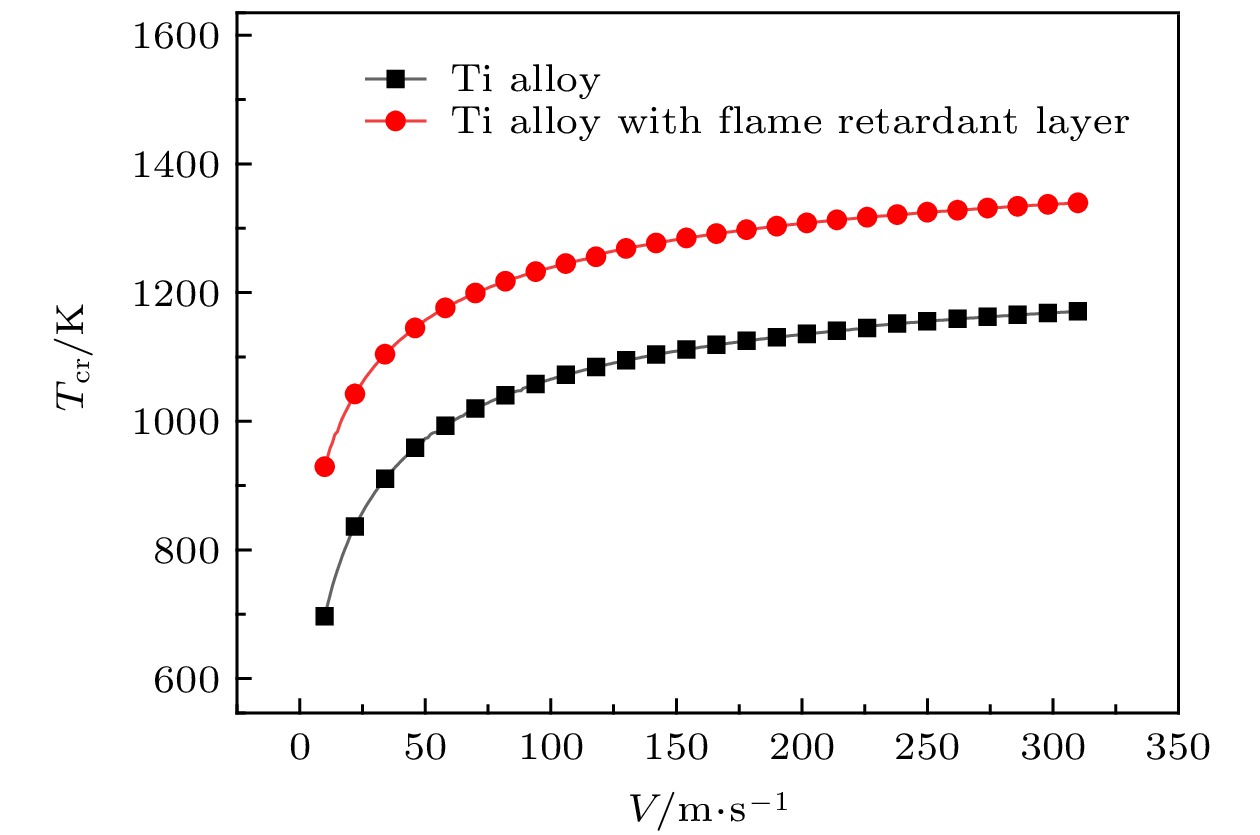
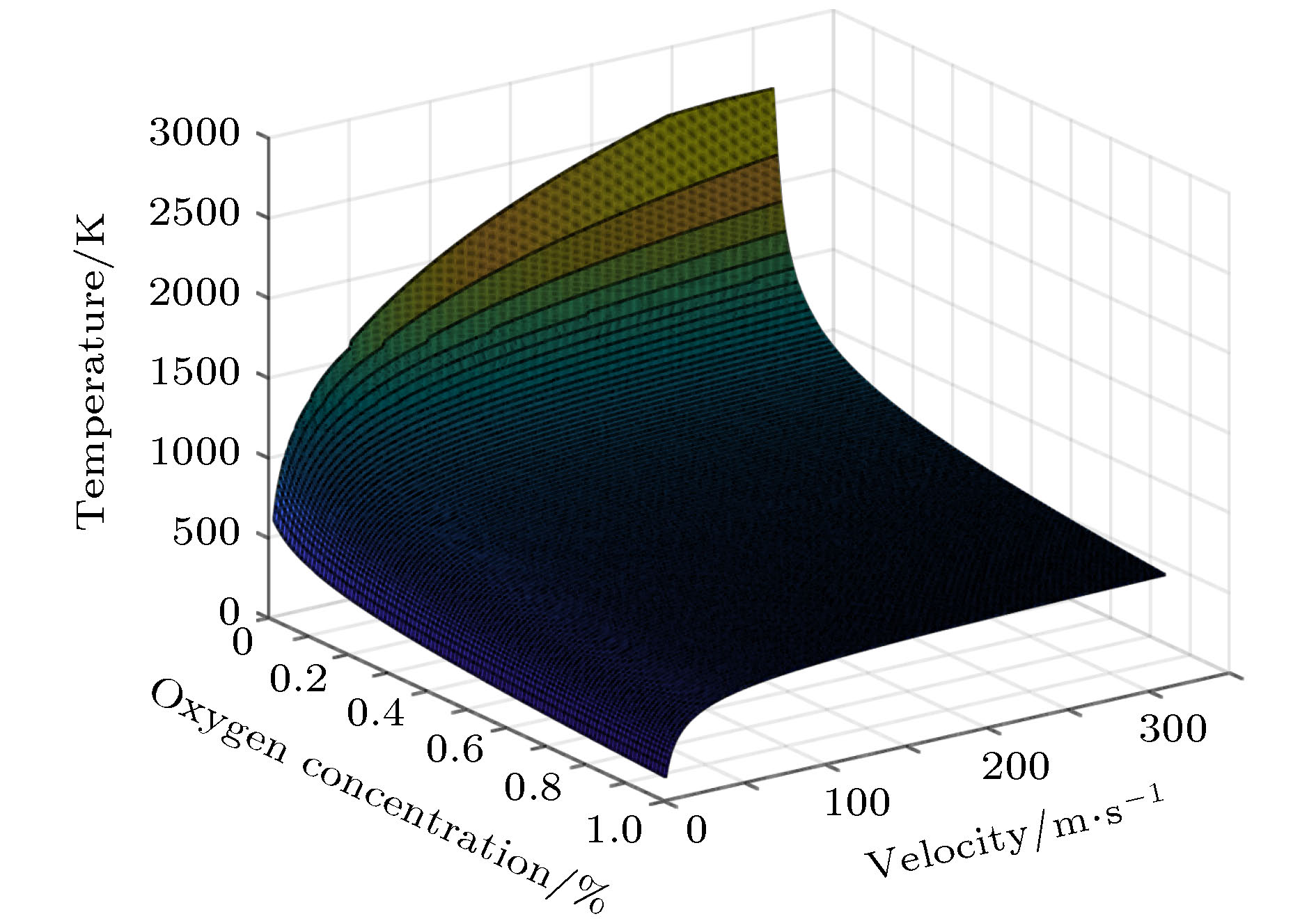
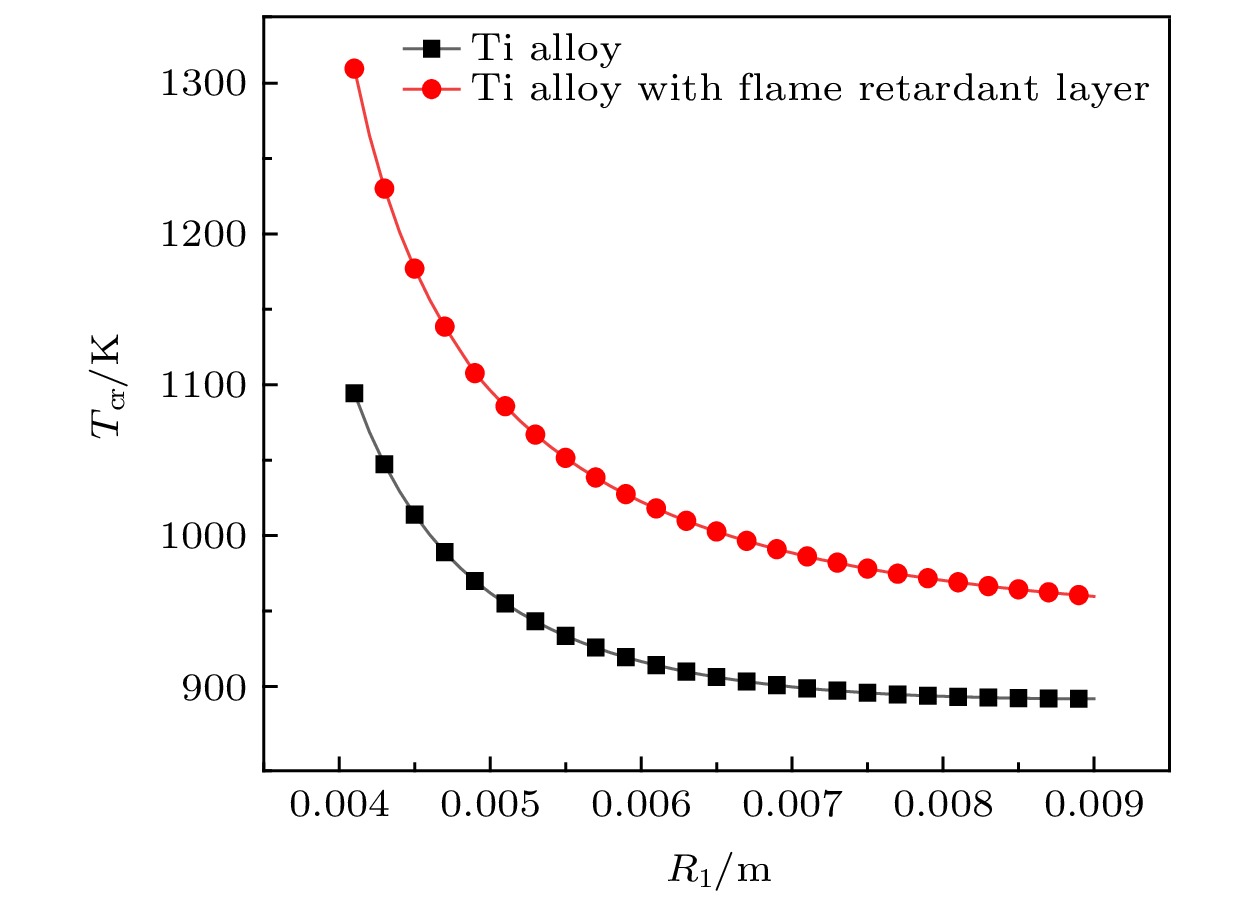
Combustion of titanium alloy is a typical catastrophic failure of modern aeroengine. The abnormal friction between compressor rotor and stator is the main ignition source. A thermal theory model with friction heat source of titanium alloy is established based on the theory of heterogeneous ignition. The corresponding equation of critical temperature and ignition delay time are derived. The difference between the frictional ignition model and the classic model is discussed. The concept of critical heat generation temperature is proposed. The difference from the heterogeneous ignition model, and the effects of friction coefficient, oxygen concentration, flow velocity, contact radius and flame retardant layer thickness on the ignition parameters are analyzed. The research result shows that when the instantaneous temperature of the contact surface is lower than the critical heat temperature, the heat generation process is dominated by frictional heat, and when the temperature is higher than the critical heat temperature, the heat generation process is dominated by chemical reaction heat, that reducing the coefficient of friction can dramatically increase the critical temperature, but the change of friction coefficient has very little effect on the ignition delay time which can be ignored, that the critical temperature decreases significantly with the increase of oxygen concentration and the decrease of flow velocity. When the oxygen concentration increases from 21% to 42% and the flow velocity decreases from 310 m/s to 50 m/s, the critical temperature decreases by about 213 K and 197 K, respectively. The relative error between the experimental result and the theoretical result is 8.3%, which verifies the reliability of the model. The contact area has an effect on friction heat generation, reaction heat generation, and surface heat dissipation, and has a great influence on the critical temperature. The critical temperature decreases exponentially with contact radius increasing. When the contact radius increases to 0.007 m, the ignition temperature of the titanium alloy and its flame retardant layer are 899 K and 988 K, respectively. The increase of the thickness of flame retardant layer can effectively improve the critical temperature and ignition delay time. The critical temperature of titanium alloy with flame retardant layer is increased by about 172 K, and the ignition delay time is increased by about 3 s.
-
Keywords:
- titanium alloy /
- ignition model with friction /
- heterogeneous reaction /
- fireproof
[1] Borisova E A, Sklyarov N M 2007 Aviation Materials and Technologists: Production Combustion and Fire Safety of Titanium Alloys (Moscow: VIAM) p21
[2] 弭光宝, 黄旭, 曹京霞, 王宝, 曹春晓 2016 65 056103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Huang X, Cao J X, Wang B, Cao C X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 056103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Frank-Kamenetskii D A 1955 Diffusion and Heat Exchange in Chemical Kinetics (Princeton: Princeton University Press) p288
[4] Merzhanov A G 1975 AIAA J. 13 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Elsayed S A 1996 J. Loss Prevent Proc. 9 393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Khaikin B I, Bloshenko V N 1970 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 6 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Aldushin A P, Bloshenko V N, Seplyarskii B S 1973 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 9 423
[8] Chernenko E V, Griva V A, Rozenband V I 1982 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 18 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shafirovich E, Teoh S K, Varma A 2008 Combust. Flame 152 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yuan C M, Amyotte P R, Hossain M N, Li C 2014 J. Hazard. Mater. 274 322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Breiter A L, Maltsev V M, Popov E I 1977 Phys. Combust. Explos. 13 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bolobov V I 2012 Phys. Combust. Explos. 48 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bolobov V I 2003 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 39 677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bolobov V I 2016 Phys. Combust. Explos. 52 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ouyang P X, Mi G B, Cao J X, Huang X, He L J, Li P J 2018 Mater. Today Commun. 16 364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 弭光宝, 欧阳佩旋, 李培杰, 曹京霞, 黄旭, 曹春晓 2019 航空材料学报 39 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Ouyang P X, Li P J, Cao J X, Huang X, Cao C X 2019 J. Aeron. Mater. 39 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 弭光宝, 黄旭, 曹京霞, 曹春晓 2014 金属学报 50 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Huang X, Cao J X, Cao C X 2014 Acta Metall. Sinica 50 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li W Y, Ma T, Li J 2010 Mater. Des. 31 1497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Darvazi A R, Iranmanesh M 2014 Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 75 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bohle M, Etling D, Muller U, Sreenivasan K R S, Riedel U, Warnatz J 2004 Prandtl’s Essentials of Fluid Mechanics (Heidelberg: Springer) (2nd Ed.) p428
[21] Thomas P H 1960 Trans. Faraday Soc. 56 833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gray P, Harper M J 1958 Sixth Symposium on Combustion New Haven, America, August 19–24, 1958 p425
[23] Boddington T, Feng C G, Gray P 1984 Proc. Roy. Soc. London 391 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 弭光宝, 曹春晓, 黄旭, 曹京霞, 王宝 2014 航空材料学报 34 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Cao C X, Huang X, Cao J X, Wang B 2014 J. Aeron. Mater. 34 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 中国航空材料手册编辑委员会 2001 中国航空材料手册(第4卷) (北京: 中国标准出版社) p147
China Aeronautical Materials Handbook Editorial Committee 2001 China Aeronautical Materials Handbook (Volume 4) (Beijing: China Standards Press) p147 (in Chinese)
[26] Wang L, Zhang Q Y, Li X X, Cui X H, Wang S Q 2014 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45 2284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen K M, Zhang Q Y, Li X X, Wang L, Cui X H, Wang S Q 2014 Tribo. Trans. 57 838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Elrod C W 1980 Proceedings of the Tri-Service Conference on Corrosion Boulder, America, November 5–7, 1980 p54
[29] 梁贤烨, 弭光宝, 李培杰, 曹京霞, 黄旭 2019 钛工业进展 36 1
Liang X Y, Mi G B, Li P J, Cao J X, Huang X 2019 Titanium Ind. Prog. 36 1
-
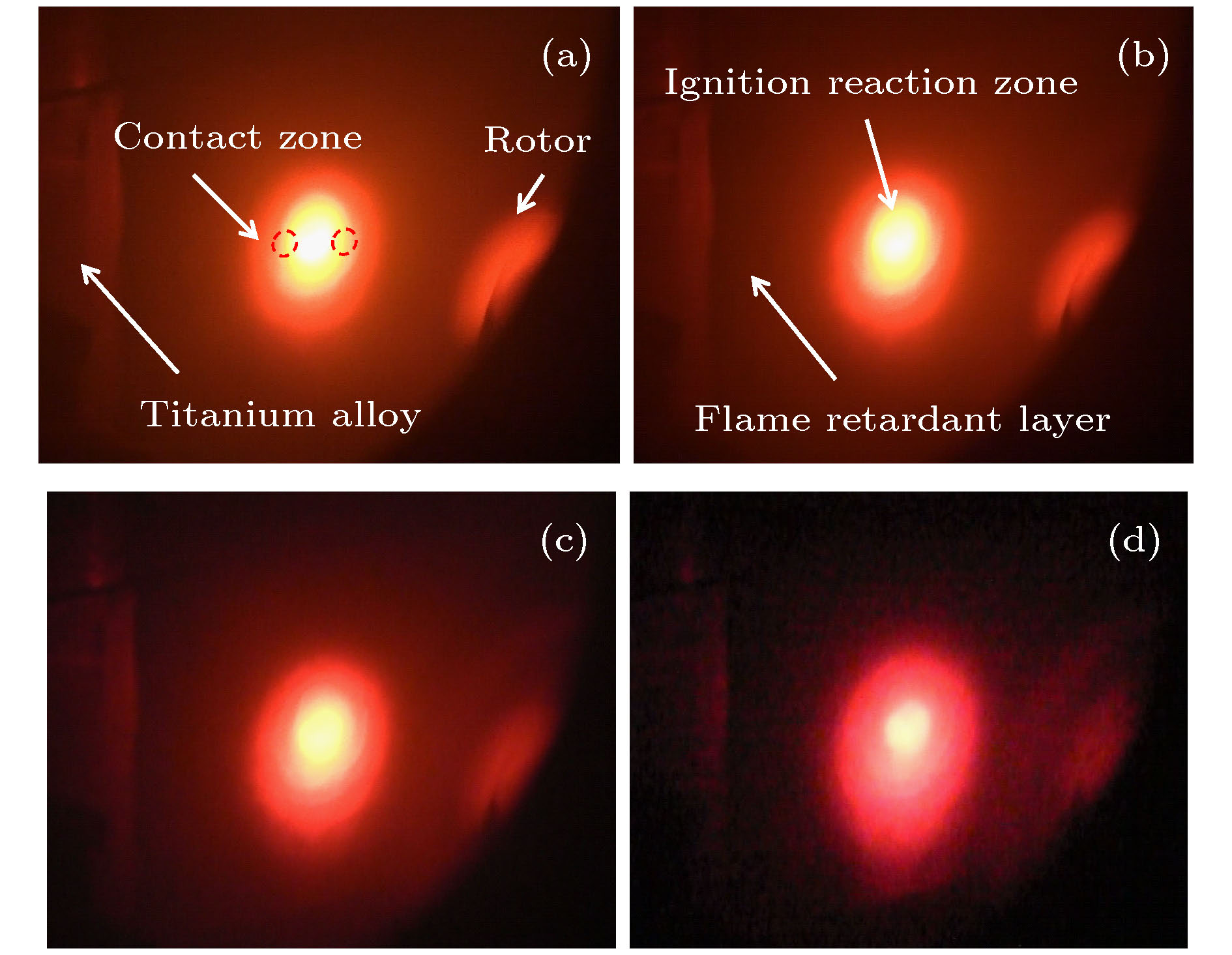
图 4 临界条件下摩擦着火过程的原位观察(I为静子背面反应区着火的镜像; II为反应区中心着火的放射状火花), 各子图分别对应摩擦结束后的不同时间 (a) 0.05 s; (b) 0.10 s; (c) 0.15 s; (d) 0.20 s; (e) 0.25 s; (f) 0.5 s
Figure 4. In-situ observation of friction ignition process under critical condition (I, mirror image of ignition of reaction zone; II, spark of micro-bump near the centre hole of reaction zone): (a) 0.05 s, (b) 0.10 s, (c) 0.15 s, (d) 0.20 s, (e) 0.25 s, (f) 0.5 s after the rubbing ends.
表 A1 术语表
Table A1. Nomenclature
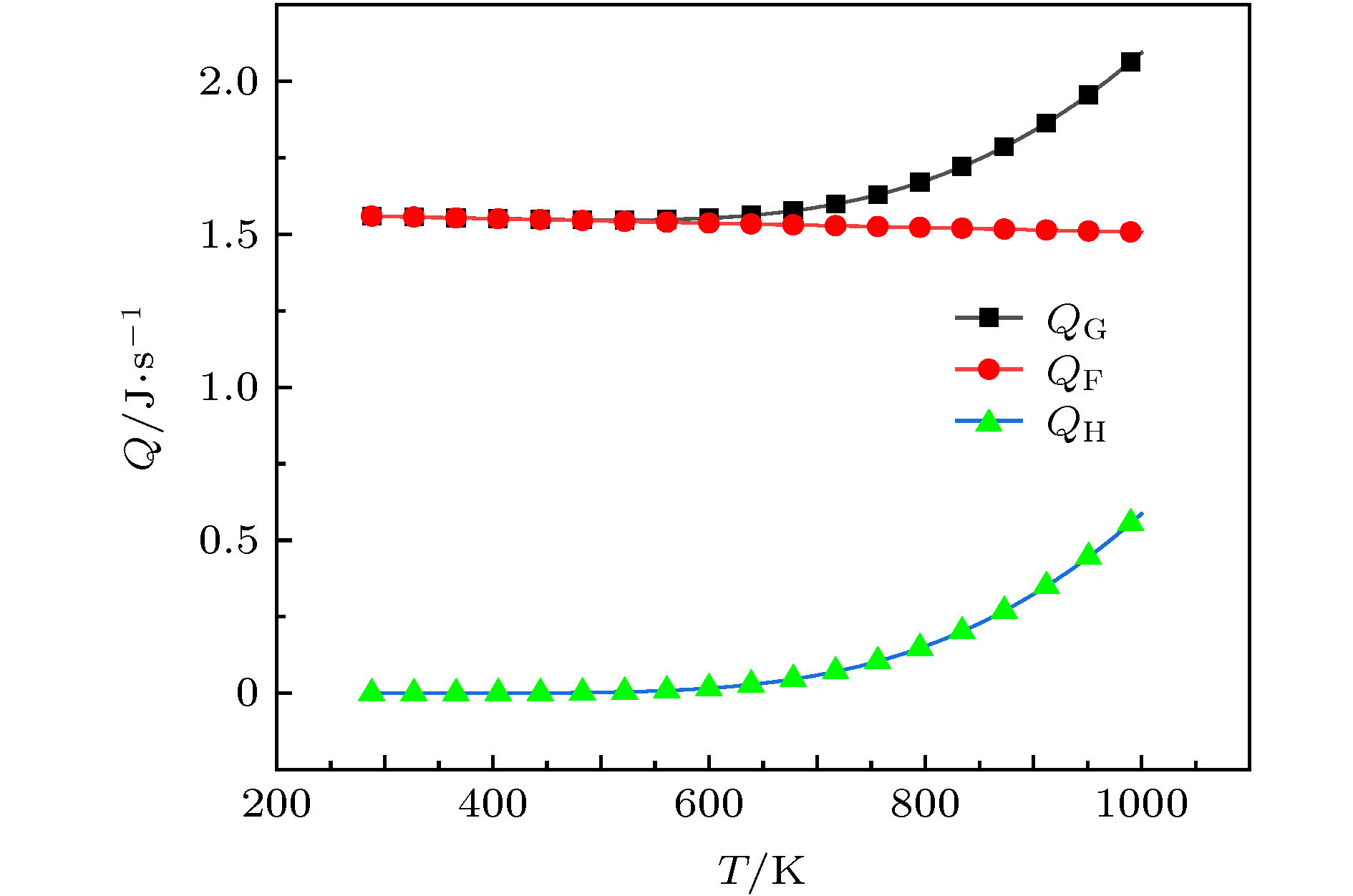
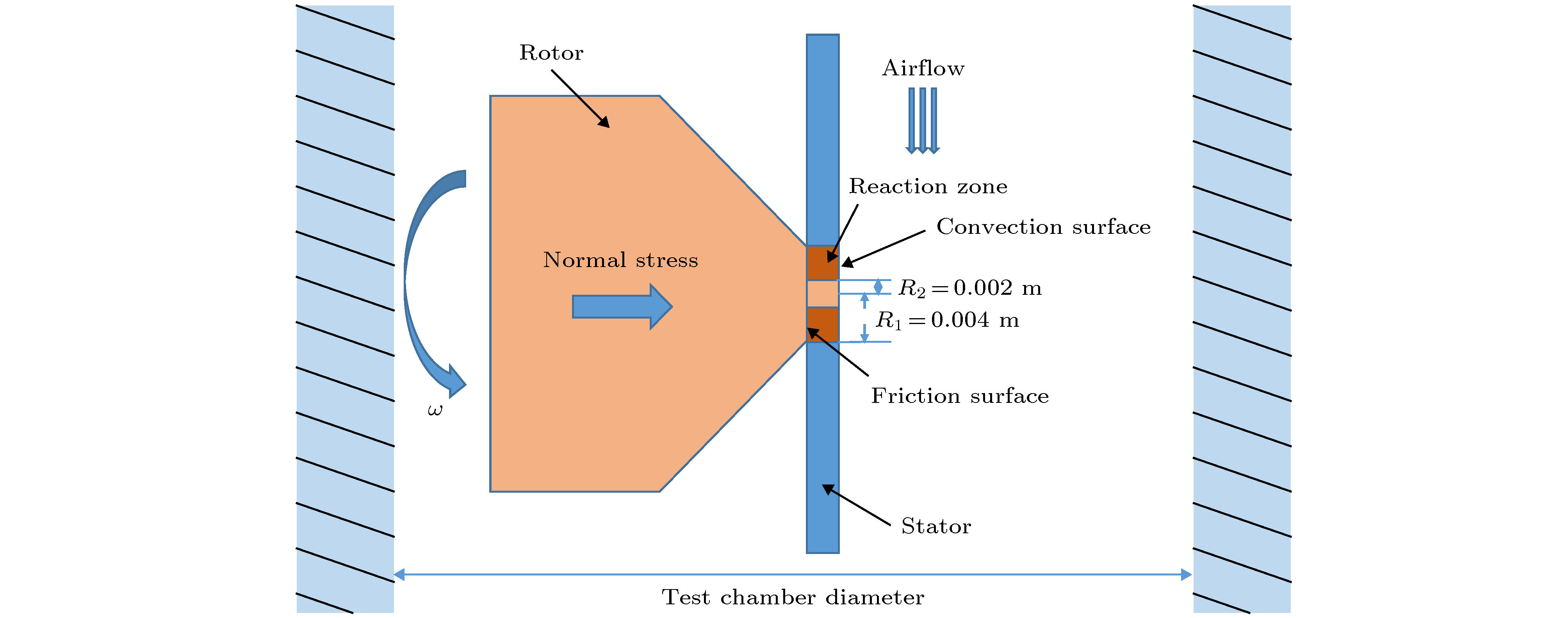
符号 物理意义 单位 λ 热传导系数 W·m–1·K–1 cp 比热 J·kg–1·K–1 q 单位反应热 MJ·kg–1 k 指前因子 kg·m–2·s–1 E 激活能 kJ·mol–1 f 摩擦应力 N·m–2 τ 着火延迟时间 s N 接触应力 N·m–2 φ 厚度 m d 试验舱直径 m R2 接触面内径 m R1 接触面外径 m ω 转子角速度 r·min–1 ci 氧浓度 100% v 流速 m·s QG 生热项 J·s–1 QH 反应热项 J·s–1 QC 对流散热项 J·s–1 QR 辐射散热项 J·s–1 μ 摩擦系数 / Sr 反应区面积 m2 a 吸附系数 / α 总传热系数 W·m–2·K–1 Nu 努塞尔数 / Pr 普朗特数 / Re 雷诺数 / 性能材料 密度
ρ/kg·m–3比热容
cp/J·kg–1·K–1反应热
q/MJ·kg–1指前因子
k/kg·m–2·s–1激活能
E/kJ·mol–1导热系数
λ/W·m–1·K–1吸附系数
a/MPa–0.5钛合金 4500 493 33 4.2 44.5 17.8 0.52 阻燃层 5600 560 — — — 0.62 — 初始摩擦正应力N/kPa 静子厚度φ/m 特征长度d/m 内半径R2/m 外半径R1/m 角速度ω/r·min–1 氧浓度ci/% 流速v/m·s–1 265 0.002 0.016 0.002 0.004 5000 21 50 -
[1] Borisova E A, Sklyarov N M 2007 Aviation Materials and Technologists: Production Combustion and Fire Safety of Titanium Alloys (Moscow: VIAM) p21
[2] 弭光宝, 黄旭, 曹京霞, 王宝, 曹春晓 2016 65 056103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Huang X, Cao J X, Wang B, Cao C X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 056103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Frank-Kamenetskii D A 1955 Diffusion and Heat Exchange in Chemical Kinetics (Princeton: Princeton University Press) p288
[4] Merzhanov A G 1975 AIAA J. 13 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Elsayed S A 1996 J. Loss Prevent Proc. 9 393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Khaikin B I, Bloshenko V N 1970 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 6 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Aldushin A P, Bloshenko V N, Seplyarskii B S 1973 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 9 423
[8] Chernenko E V, Griva V A, Rozenband V I 1982 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 18 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shafirovich E, Teoh S K, Varma A 2008 Combust. Flame 152 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yuan C M, Amyotte P R, Hossain M N, Li C 2014 J. Hazard. Mater. 274 322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Breiter A L, Maltsev V M, Popov E I 1977 Phys. Combust. Explos. 13 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bolobov V I 2012 Phys. Combust. Explos. 48 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bolobov V I 2003 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 39 677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bolobov V I 2016 Phys. Combust. Explos. 52 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ouyang P X, Mi G B, Cao J X, Huang X, He L J, Li P J 2018 Mater. Today Commun. 16 364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 弭光宝, 欧阳佩旋, 李培杰, 曹京霞, 黄旭, 曹春晓 2019 航空材料学报 39 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Ouyang P X, Li P J, Cao J X, Huang X, Cao C X 2019 J. Aeron. Mater. 39 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 弭光宝, 黄旭, 曹京霞, 曹春晓 2014 金属学报 50 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Huang X, Cao J X, Cao C X 2014 Acta Metall. Sinica 50 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li W Y, Ma T, Li J 2010 Mater. Des. 31 1497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Darvazi A R, Iranmanesh M 2014 Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 75 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bohle M, Etling D, Muller U, Sreenivasan K R S, Riedel U, Warnatz J 2004 Prandtl’s Essentials of Fluid Mechanics (Heidelberg: Springer) (2nd Ed.) p428
[21] Thomas P H 1960 Trans. Faraday Soc. 56 833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gray P, Harper M J 1958 Sixth Symposium on Combustion New Haven, America, August 19–24, 1958 p425
[23] Boddington T, Feng C G, Gray P 1984 Proc. Roy. Soc. London 391 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 弭光宝, 曹春晓, 黄旭, 曹京霞, 王宝 2014 航空材料学报 34 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mi G B, Cao C X, Huang X, Cao J X, Wang B 2014 J. Aeron. Mater. 34 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 中国航空材料手册编辑委员会 2001 中国航空材料手册(第4卷) (北京: 中国标准出版社) p147
China Aeronautical Materials Handbook Editorial Committee 2001 China Aeronautical Materials Handbook (Volume 4) (Beijing: China Standards Press) p147 (in Chinese)
[26] Wang L, Zhang Q Y, Li X X, Cui X H, Wang S Q 2014 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45 2284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen K M, Zhang Q Y, Li X X, Wang L, Cui X H, Wang S Q 2014 Tribo. Trans. 57 838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Elrod C W 1980 Proceedings of the Tri-Service Conference on Corrosion Boulder, America, November 5–7, 1980 p54
[29] 梁贤烨, 弭光宝, 李培杰, 曹京霞, 黄旭 2019 钛工业进展 36 1
Liang X Y, Mi G B, Li P J, Cao J X, Huang X 2019 Titanium Ind. Prog. 36 1
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9877
- PDF Downloads: 100
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: