-
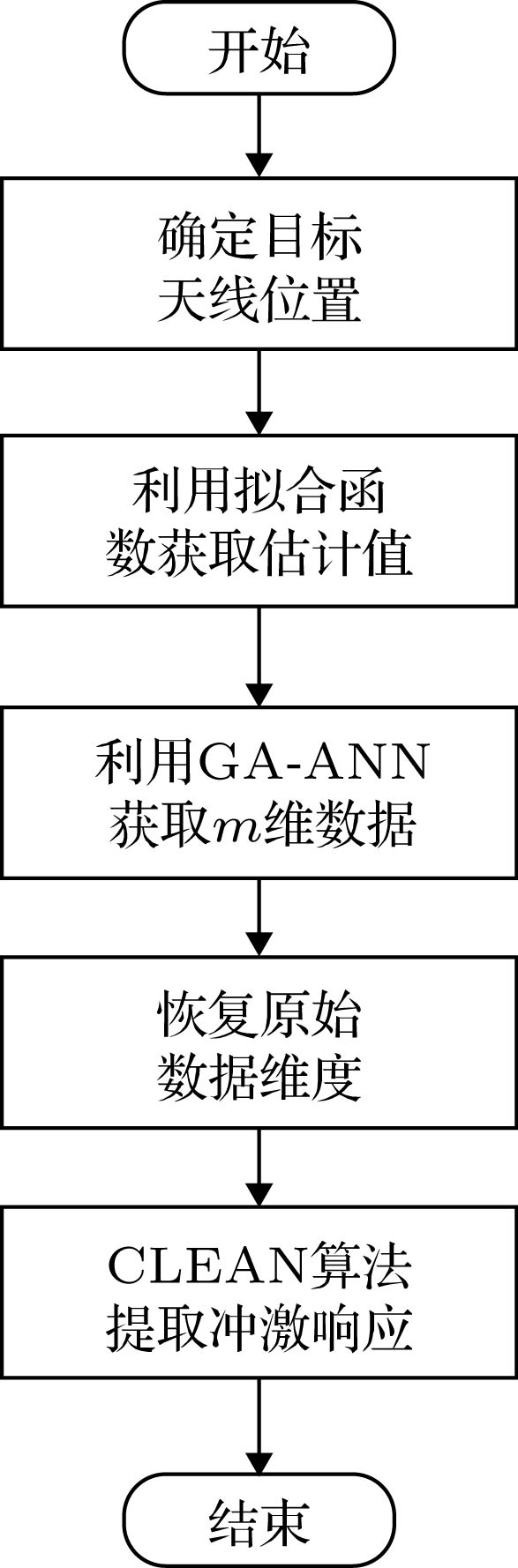
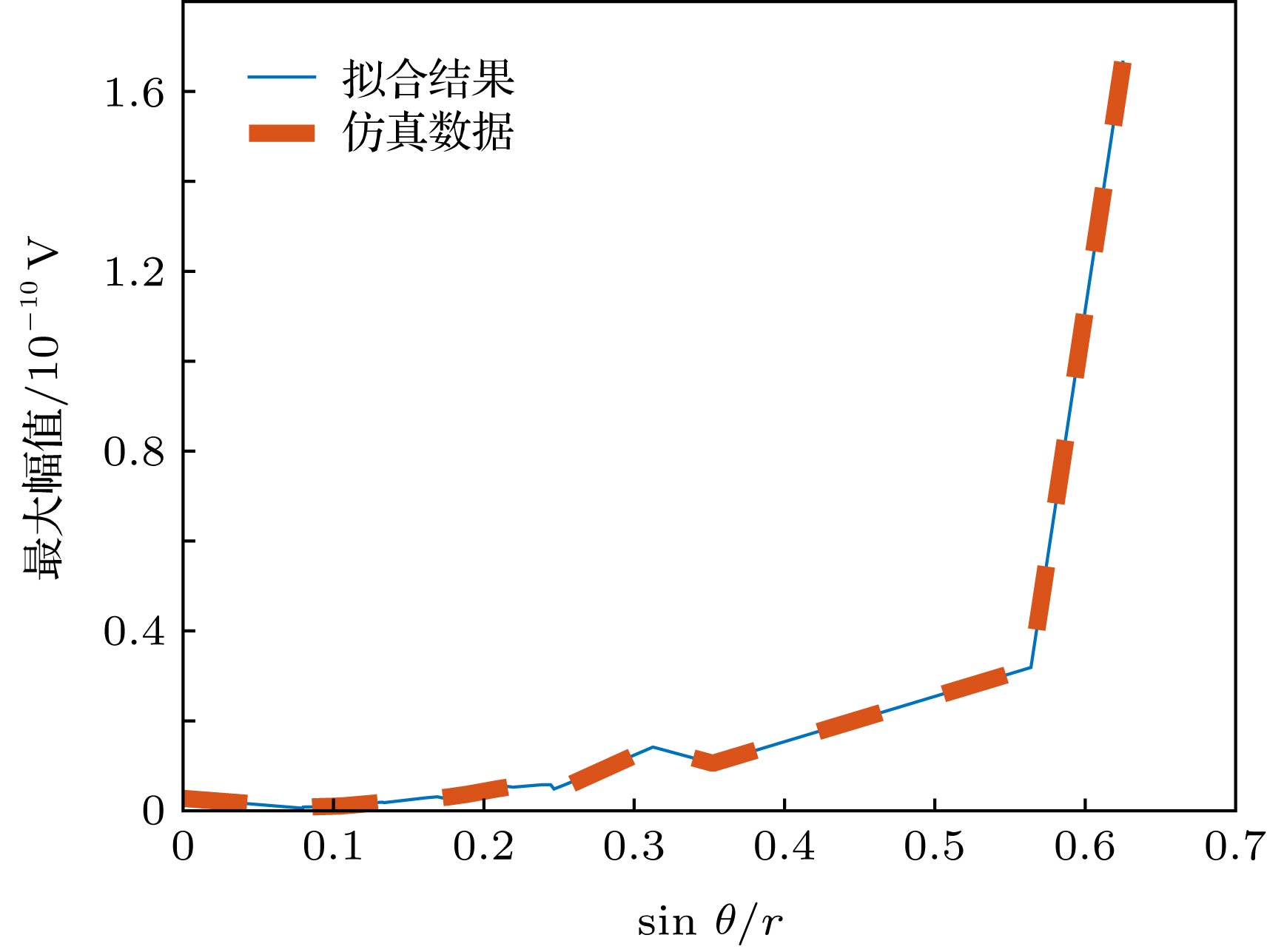
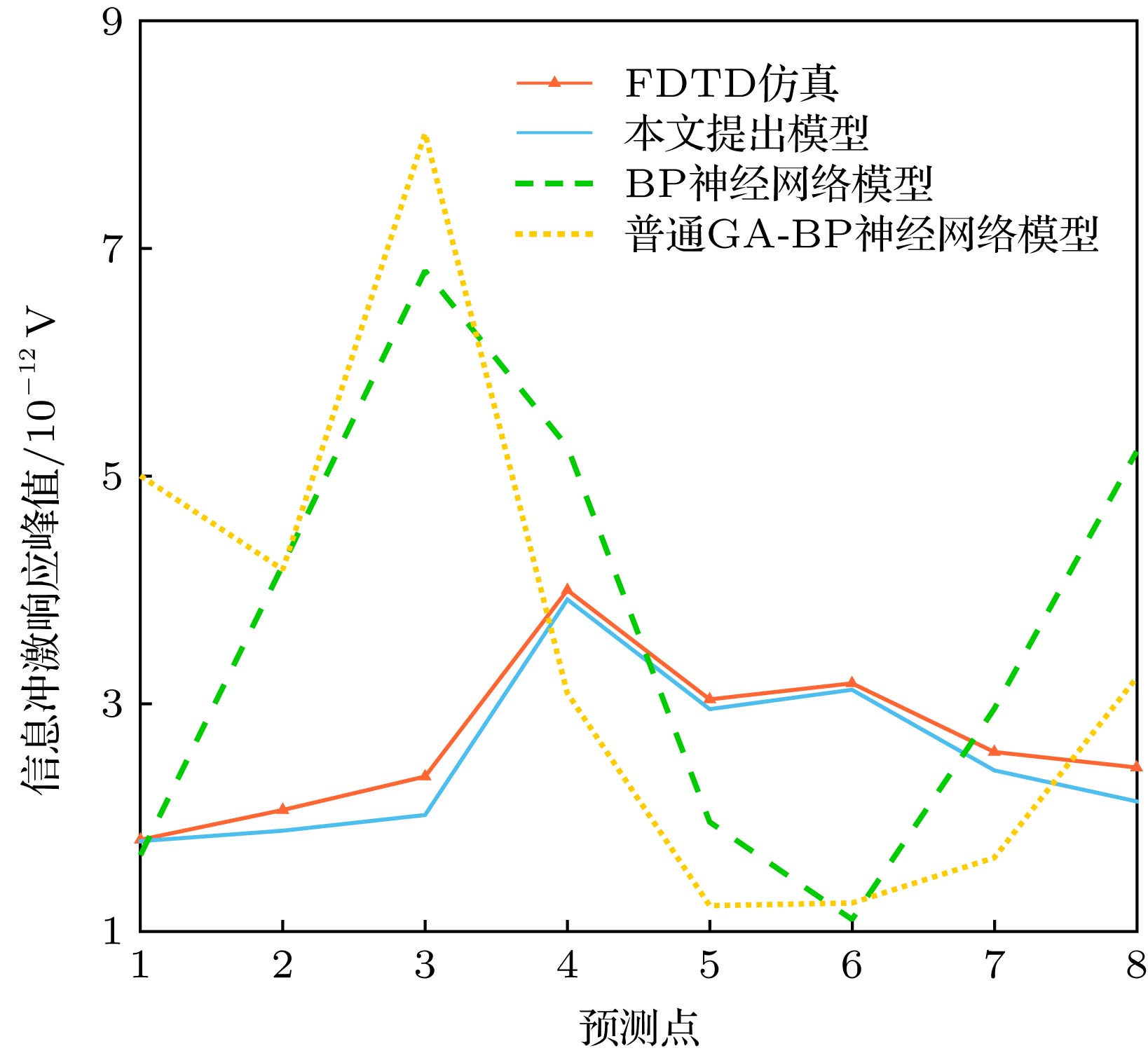
Because of the strong non-linear fitting capability, the artificial neural network (ANN) can be used to establish the mapping relationship between the terminal position and the received signal for obtaining the channel characteristics at different locations. The accuracy of an ANN model is, in general, determined by the number of the training sets used in constructing the model. The more the training sets, the better the accuracy is. However, getting a large number of training sets by deterministic model is expensive. Therefore, under the same number of training sets, improving the accuracy of the model is crucial to develop an effective time reversal (TR) modeling method based on ANN. In this paper, a new TR channel modeling method based on the back propagation neural network is proposed. Genetic algorithm (GA) with excellent global search capability is used to optimize the weight and threshold of the ANN to avoid the possibility of the ANN falling into local minimum. According to the basic principle of time reversal, the peak characteristics are obtained by the fitting method. In order to improve the accuracy of the model, the peak value characteristics are integrated into the GA as empirical knowledge to change the fitness function. Meanwhile, the principal component analysis technology is utilized to process data, which reduces the data dimension and the training time of ANN while data characteristics are ensured. Once the terminal antenna positions are input to the proposed model, the accurate TR received signals can be quickly obtained. Finally, the deconvolution operation of the received signal is performed by the clean algorithm to obtain the channel characteristics. A simple indoor TR scenario is used as an example to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results show that the three channel characteristics obtained by the model, i.e., channel impulse response peak value, 15 dB multipath number, and average delay, have high accuracy. Furthermore, the proposed model has more excellent performance than the other two ANN models under the condition of the same number of training samples. Based on the basic principle of TR technology, the electromagnetic waves have better focusing effect in more complex environments. Therefore, the proposed method is also applicable to more complicated environments than the simple indoor scenario.
-
Keywords:
- time reversal /
- channel modeling /
- artificial neural network /
- empirical knowledge
[1] Hoefer W J R 2015 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 63 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rosny J, Lerosey G, Fink M 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58 3139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lerosey G, Rosny J, Tourin A, Derode A, Fink M 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 154101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bellizzi G G, Bevacqua M T, Crocco L, Isernia T 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 4380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Carminati R, Pierrat R, Rosny J, Fink M 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Malyuskin O, Fusco V 2010 IET Microw. Antenna. P. 4 1140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 臧锐, 王秉中, 丁帅, 龚志双 2016 65 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zang R, Wang B Z, Ding S, Gong Z S 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 龚志双, 王秉中, 王任, 臧锐, 王晓华 2017 66 044101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong Z S, Wang B Z, Wang R, Zang R, Wang X H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ge G D, Wang B Z, Wang D, Zhao D S, Ding S 2011 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 59 4345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Abduljabbar A M, Yavuz M E, Costen F, Himeno R, Yokota H 2016 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 64 3636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Naqvi I H, Zein G, Lerosey G, Rosny J, Besnier P, Tourin A, Fink M 2010 IET Microw. Antenna. P. 4 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang Y, Wang B Z, Ding S 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 050101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ding S, Fang Y, Zhu J F, Yang Y, Wang B Z 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 1386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 朱江, 王雁, 杨甜 2018 67 050201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J, Wang Y, Yang T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 050201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Talebi F, Pratt T 2016 IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65 499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sarestoniemi M, Hamalainen M, Iinatti J 2017 IEEE Access 5 10622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Naqvi I H, Besnier P, Zein G 2011 IET Microw. Antenna P. 5 468
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Naqvi I H, Aleem S A, Usman O, Ali S B, Besnier P, Zein G 2012 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Shanghai, China, April 1−4, 2012 p37
[19] Kim H, Sui C, Cai K, Sen B, Fan J 2018 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 60 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Popoola S I, Misra S, Atayero A A 2018 Wireless Pers. Commun. 99 441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qiu R C, Zhou C M, Guo N, Zhang J Q 2006 IEEE Antenn. Wirel. Pr. 5 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王秉中, 臧锐, 周洪澄 2013 微波学报 29 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B Z, Zang R, Zhou H C 2013 J. Microw. 29 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tse D, Viswanath P 2005 Fundamentals of Wireless Communication (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p12
[24] Cramer J M, Scholtz R A, Win M Z 2002 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 50 561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen J F, Li Y H, Wang J Q, Li Y J, Zhang Y L 2015 IET Image Process. 9 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kaina N, Dupre M, Lerosey G, Fink M 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 6693
-
表 1 TRM天线位置
Table 1. Location of the TRM antennas.
X/cm Y/cm Z/cm TRM1 2.5 0 0 TRM2 –2.5 0 0 TRM3 7.5 0 0 TRM4 –7.5 0 0 表 2 终端天线的位置
Table 2. Location of the terminal antenna.
坐标最小值/cm 坐标最大值/cm X 10 30 Y 10 30 Z 0 30 表 3 CPU时间及计算机性能
Table 3. CPU time and computer performance.
本模型 FDTD软件仿真 CST仿真软件 CPU时间 约2 min 11 s 约23 h 约25 h 计算平台 Intel i5-4430 3.00 GHz 16 GB(台式机) E5-2690v3 2.60 GHz 128 GB(服务器) E5-2690v3 2.60 GHz 128GB(服务器) -
[1] Hoefer W J R 2015 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 63 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rosny J, Lerosey G, Fink M 2010 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58 3139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lerosey G, Rosny J, Tourin A, Derode A, Fink M 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 154101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bellizzi G G, Bevacqua M T, Crocco L, Isernia T 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 4380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Carminati R, Pierrat R, Rosny J, Fink M 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Malyuskin O, Fusco V 2010 IET Microw. Antenna. P. 4 1140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 臧锐, 王秉中, 丁帅, 龚志双 2016 65 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zang R, Wang B Z, Ding S, Gong Z S 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 204102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 龚志双, 王秉中, 王任, 臧锐, 王晓华 2017 66 044101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong Z S, Wang B Z, Wang R, Zang R, Wang X H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ge G D, Wang B Z, Wang D, Zhao D S, Ding S 2011 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 59 4345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Abduljabbar A M, Yavuz M E, Costen F, Himeno R, Yokota H 2016 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 64 3636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Naqvi I H, Zein G, Lerosey G, Rosny J, Besnier P, Tourin A, Fink M 2010 IET Microw. Antenna. P. 4 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang Y, Wang B Z, Ding S 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 050101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ding S, Fang Y, Zhu J F, Yang Y, Wang B Z 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 1386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 朱江, 王雁, 杨甜 2018 67 050201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J, Wang Y, Yang T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 050201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Talebi F, Pratt T 2016 IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65 499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sarestoniemi M, Hamalainen M, Iinatti J 2017 IEEE Access 5 10622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Naqvi I H, Besnier P, Zein G 2011 IET Microw. Antenna P. 5 468
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Naqvi I H, Aleem S A, Usman O, Ali S B, Besnier P, Zein G 2012 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Shanghai, China, April 1−4, 2012 p37
[19] Kim H, Sui C, Cai K, Sen B, Fan J 2018 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 60 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Popoola S I, Misra S, Atayero A A 2018 Wireless Pers. Commun. 99 441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qiu R C, Zhou C M, Guo N, Zhang J Q 2006 IEEE Antenn. Wirel. Pr. 5 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王秉中, 臧锐, 周洪澄 2013 微波学报 29 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B Z, Zang R, Zhou H C 2013 J. Microw. 29 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tse D, Viswanath P 2005 Fundamentals of Wireless Communication (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p12
[24] Cramer J M, Scholtz R A, Win M Z 2002 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 50 561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen J F, Li Y H, Wang J Q, Li Y J, Zhang Y L 2015 IET Image Process. 9 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kaina N, Dupre M, Lerosey G, Fink M 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 6693
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 16640
- PDF Downloads: 90
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: