-
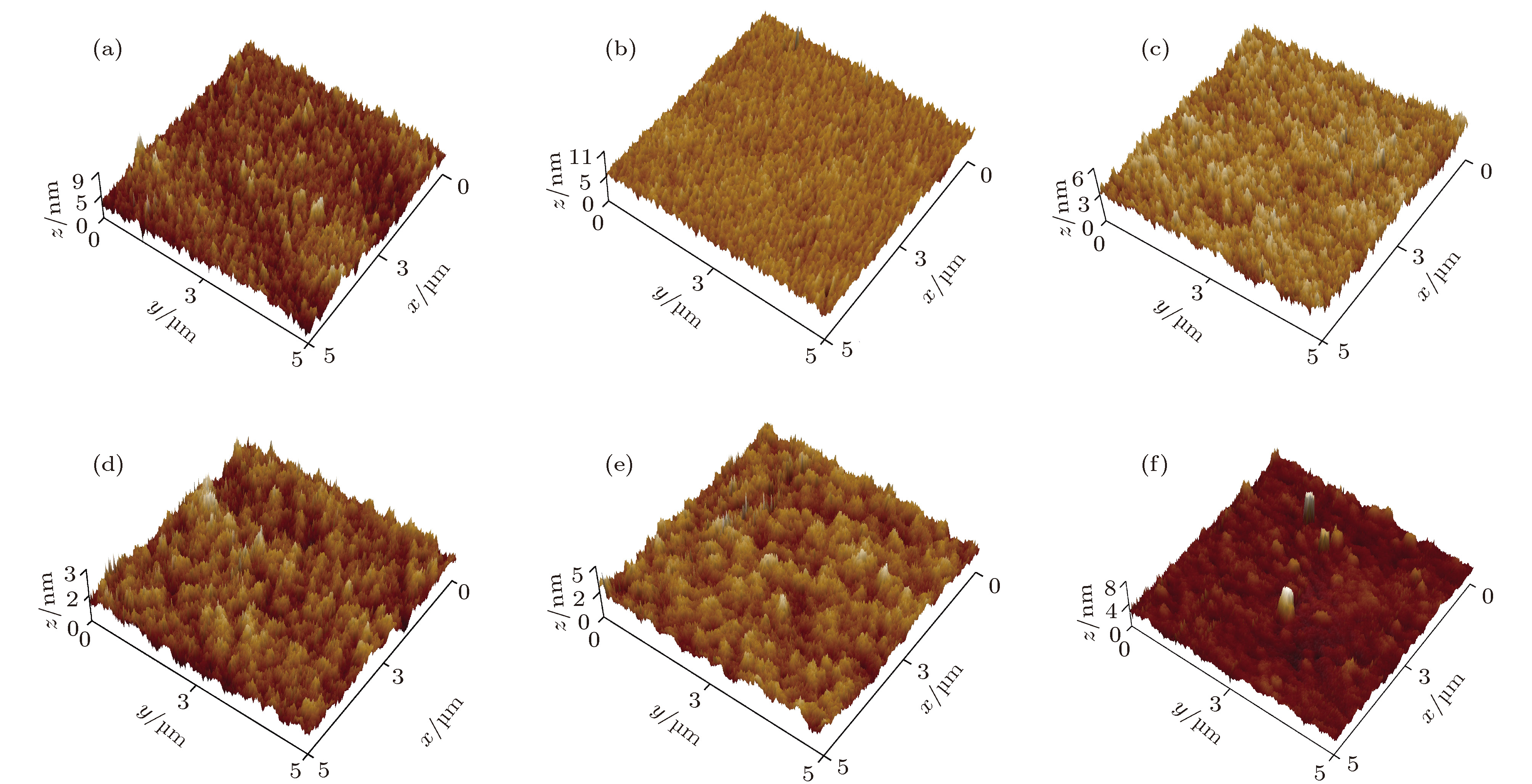
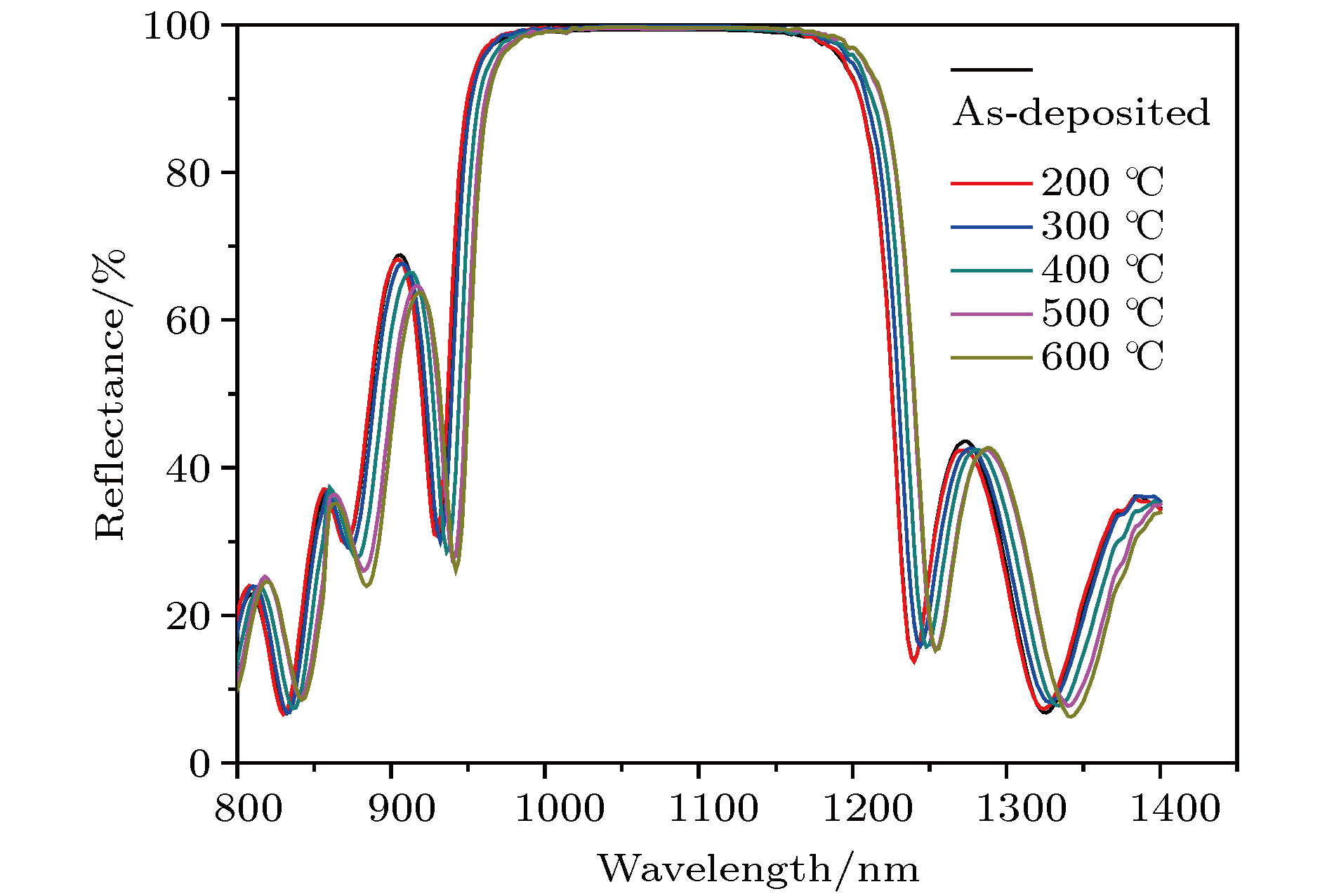
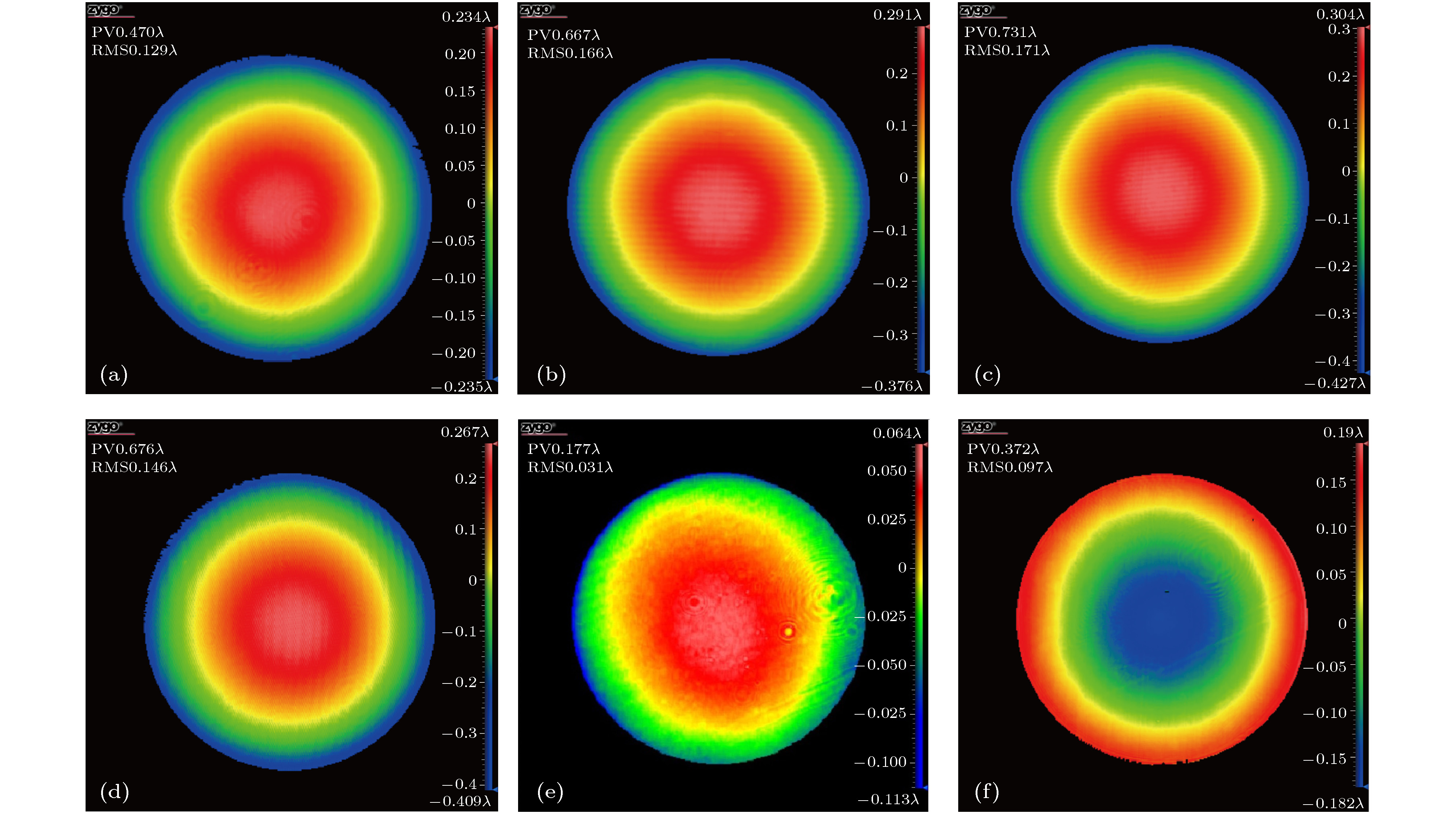
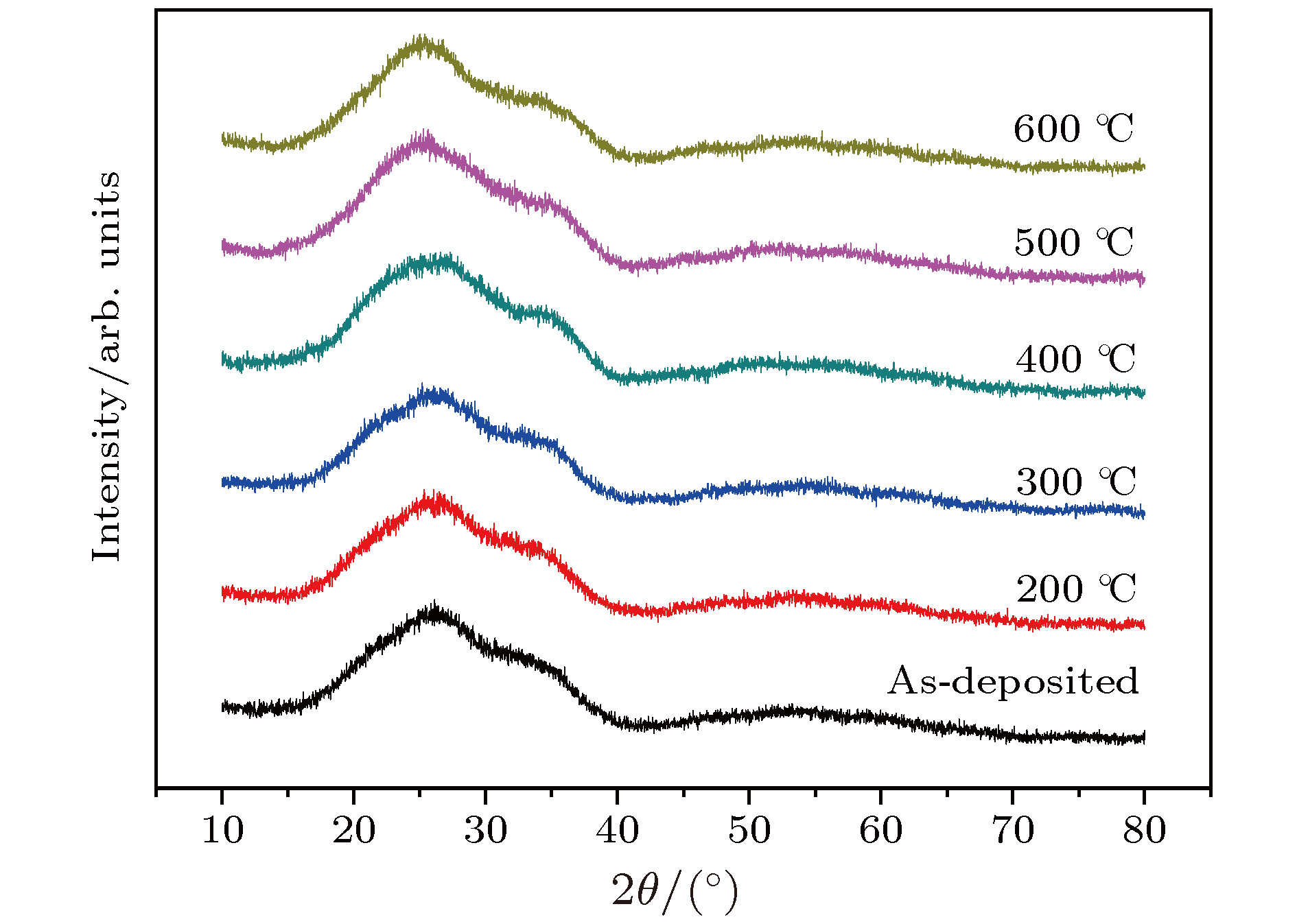
In the optical system of spaceborne laser altimeter, dielectric mirror is an indispensable optical film element. Its surface shape quality directly affects the resolution and accuracy of distance measurement of the detection system. It is pressing and necessary to carry out research on the surface shape control technology of dielectric mirror to eliminate or reduce the effect of film stress on surface shape. The Ta2O5/SiO2 multilayer reflective coatings are deposited on quartz substrates by using the ion beam assisted electron beam evaporation (IBE), and then annealed in air in a temperature range from 200 to 600 ℃. The effect of annealing temperature on the structure, optical and stress properties of Ta2O5/SiO2 multilayer reflective coatings are systemically investigated by using x-ray diffraction, atomic force microscope, spectrophotometer and laser interferometer. The results show that all the Ta2O5/SiO2 multilayer reflective coatings, after being annealed, are amorphous in structure. The annealing temperature has a great influence on the surface roughness of reflective coating. With the increase of annealing temperature, the surface roughness of reflective coating first decreases and then gradually increases, but is still smaller than that of as-deposited sample. After being annealed, the reflectance spectrum of reflective coating shifts slightly toward the long-wave direction, and the reflectivity increases a little. When being annealed at 500-600 ℃, the compressive stress of reflective coating could be transformed into tensile stress, and the surface is changed from convex to concave shape. It can be concluded that annealing at an appropriate temperature can effectively release residual stress of Ta2O5/SiO2 multilayer reflective coating and eliminate the deformation of substrate caused by film stress, and thus improving the surface shape quality of dielectric mirror., After being annealed, the reflective coating still possesses the stable structure and spectral properties, so that dielectric mirror can meet the application requirements of spaceborne laser altimeter. In this paper, the experimental results are of great significance for applying the annealing technology to the surface shape control technology of dielectric mirrors.
-
Keywords:
- optical thin films /
- Ta2O5/SiO2 multilayer reflective coatings /
- annealing /
- residual stress
[1] 唐新明, 谢俊峰, 付兴科, 莫凡, 李少宁, 窦显辉 2017 测绘学报 46 714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang X M, Xie J F, Fu X K, Mo F, Li S N, Dou X H 2017 Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 46 714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘斌, 张军, 鲁敏, 滕书华, 马燕新, 张文广 2015 激光与红外 54 5104
Liu B, Zhang J, Lu M, Teng S H, Ma Y X, Zhang W G 2015 Laser Infr. 54 5104
[3] 刘豪, 舒嵘, 洪光烈, 郑龙, 葛烨, 胡以华 2014 63 104214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H, Shu R, Hong G L, Zheng L, Ge Y, Hu Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schiltz D, Patel D, Baumgarten C, Reagan B A, Rocca J J, Menoni C S 2017 Appl. Opt. 5 6
[5] Kumar S, Shankar A, Kishore N, Mukherjee C, Kamparath R, Thakur S 2019 Optik 176 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qiao Z, Pu Y T, Liu H, Luo K, Wang G, Liu Z C, Ma P 2015 Thin Solid Films 592 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ailloud Q, Zerrad M, Amra C 2018 Opt. Express 26 13264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 马跃, 阳凡林, 易洪, 李松 2015 红外与激光工程 44 2401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma Y, Yang F L, Yi H, Li S 2015 Infrar. Laser Eng. 44 2401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 庞志海, 樊学武, 陈钦芳, 马臻, 邹刚毅 2013 光学学报 33 186
Pang Z H, Fan X W, Chen Q F, Ma Z, Zou G Y 2013 Acta Opt. Sin. 33 186
[10] Wang L S, Liu H S, Jiang Y G, Yang X, Liu D D, Ji Y Q, Zhang F, Chen D Y 2017 Optik 142 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sertel T, Sonmez N A, Cetin S S, Ozcelik S 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li S D, Liu H S, Jiang Y G, He J H, Wang L S, Ji Y Q 2019 Optik 181 695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bischoff M, Nowitzki T, Voß O, Wilbrandt S, Stenzel O 2014 Appl. Opt. 5 3
[14] Jena S, Tokas R B, Rao K D, Thakur S, Sahoo N K 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 6108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Çetinörgü-Goldenberg E, Klemberg-Sapieha J E, Martinu L 2012 Appl. Opt. 51 6498
[16] 季一勤, 姜玉刚, 刘华松, 王利栓, 刘丹丹, 姜承慧, 羊亚平, 樊荣伟, 陈德应 2013 红外与激光工程 42 418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji Y Q, Jiang Y G, Liu H S, Wang L S, Liu D D, Jiang C H, Yang Y P, Fan R W, Chen D Y 2013 Infrar. Laser Eng. 42 418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 冷健, 季一勤, 刘华松, 庄克文, 刘丹丹 2018 红外与激光工程 47 196
Leng J, Ji Y Q, Liu H S, Zhuang K W, Liu D D 2018 Infrar. Laser Eng. 47 196
[18] Shen Y M, Han Z X, Shao J D, Shao S Y, He H B 2008 Chin. Opt. Lett. 6 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Stoney G G 1909 Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 82 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 黄才华, 薛亦渝, 彭桦, 夏志林, 郭培涛 2009 中国激光 36 364
Huang C H, Xue Y Y, Peng H, Xia Z L, Guo P T 2009 Chin. J. Lasers 36 364
[21] 申雁鸣2008 博士学位论文(上海: 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所)
Shen Y M 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
-
表 1 经不同温度退火后Ta2O5/SiO2多层反射膜基片变形和残余应力值
Table 1. Substrate deflection and residual stress of annealed Ta2O5/SiO2 multilayer reflective coatings.
Annealing temperature/℃ Substrate deflection/nm Residual stress/MPa Before coating After coating After annealing After coating After annealing As-deposited 31.6 –282.8 –282.8 –90.9 –90.9 200 29.5 –281.6 –375.3 –89.9 –117.0 300 31.4 –278.4 –363.9 –89.5 –114.3 400 30.2 –282.8 –320.2 –90.5 –101.3 500 31.8 –284.1 –67.1 –92.3 –28.6 600 30.5 –280.3 213.3 –89.8 52.9 表 2 Ta2O5/SiO2多层反射膜在500—600 ℃退火后基片变形和残余应力值
Table 2. Substrate deflection and residual stress of Ta2O5/SiO2 multilayer reflective coatings annealed at the temperature range from 500 to 600 ℃
Annealing temperature/℃ Substrate deflection/nm Residual stress/MPa Before coating After coating After annealing After coating After annealing 525 31.2 –279.8 16.4 –89.9 –4.3 550 29.6 –283.6 60.1 –90.5 8.8 575 30.8 –281.5 112.6 –90.3 23.6 -
[1] 唐新明, 谢俊峰, 付兴科, 莫凡, 李少宁, 窦显辉 2017 测绘学报 46 714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang X M, Xie J F, Fu X K, Mo F, Li S N, Dou X H 2017 Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 46 714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘斌, 张军, 鲁敏, 滕书华, 马燕新, 张文广 2015 激光与红外 54 5104
Liu B, Zhang J, Lu M, Teng S H, Ma Y X, Zhang W G 2015 Laser Infr. 54 5104
[3] 刘豪, 舒嵘, 洪光烈, 郑龙, 葛烨, 胡以华 2014 63 104214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H, Shu R, Hong G L, Zheng L, Ge Y, Hu Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schiltz D, Patel D, Baumgarten C, Reagan B A, Rocca J J, Menoni C S 2017 Appl. Opt. 5 6
[5] Kumar S, Shankar A, Kishore N, Mukherjee C, Kamparath R, Thakur S 2019 Optik 176 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Qiao Z, Pu Y T, Liu H, Luo K, Wang G, Liu Z C, Ma P 2015 Thin Solid Films 592 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ailloud Q, Zerrad M, Amra C 2018 Opt. Express 26 13264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 马跃, 阳凡林, 易洪, 李松 2015 红外与激光工程 44 2401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma Y, Yang F L, Yi H, Li S 2015 Infrar. Laser Eng. 44 2401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 庞志海, 樊学武, 陈钦芳, 马臻, 邹刚毅 2013 光学学报 33 186
Pang Z H, Fan X W, Chen Q F, Ma Z, Zou G Y 2013 Acta Opt. Sin. 33 186
[10] Wang L S, Liu H S, Jiang Y G, Yang X, Liu D D, Ji Y Q, Zhang F, Chen D Y 2017 Optik 142 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sertel T, Sonmez N A, Cetin S S, Ozcelik S 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li S D, Liu H S, Jiang Y G, He J H, Wang L S, Ji Y Q 2019 Optik 181 695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bischoff M, Nowitzki T, Voß O, Wilbrandt S, Stenzel O 2014 Appl. Opt. 5 3
[14] Jena S, Tokas R B, Rao K D, Thakur S, Sahoo N K 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 6108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Çetinörgü-Goldenberg E, Klemberg-Sapieha J E, Martinu L 2012 Appl. Opt. 51 6498
[16] 季一勤, 姜玉刚, 刘华松, 王利栓, 刘丹丹, 姜承慧, 羊亚平, 樊荣伟, 陈德应 2013 红外与激光工程 42 418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji Y Q, Jiang Y G, Liu H S, Wang L S, Liu D D, Jiang C H, Yang Y P, Fan R W, Chen D Y 2013 Infrar. Laser Eng. 42 418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 冷健, 季一勤, 刘华松, 庄克文, 刘丹丹 2018 红外与激光工程 47 196
Leng J, Ji Y Q, Liu H S, Zhuang K W, Liu D D 2018 Infrar. Laser Eng. 47 196
[18] Shen Y M, Han Z X, Shao J D, Shao S Y, He H B 2008 Chin. Opt. Lett. 6 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Stoney G G 1909 Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 82 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 黄才华, 薛亦渝, 彭桦, 夏志林, 郭培涛 2009 中国激光 36 364
Huang C H, Xue Y Y, Peng H, Xia Z L, Guo P T 2009 Chin. J. Lasers 36 364
[21] 申雁鸣2008 博士学位论文(上海: 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所)
Shen Y M 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 15103
- PDF Downloads: 230
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: