-
Kiselev black hole possesses the two horizons, i.e. the inner horizon and outer horizon. In some cases, the so-called outer horizon of black hole is actually a cosmic horizon. In this paper, Kiselev space-time with black hole horizon and cosmic horizon is considered. The radius of black hole horizon and the radius of cosmic horizon are approximately obtained to be
$r_{\rm B} \approx 2M \left[ 1 + \left(2M/{\lambda}\right)^{-(3w_{\rm {\rm q}}+1)} \right]$ and$r_{\rm C} \approx \lambda + \dfrac{2M} {3w_{\rm {\rm q}}+1}$ with$M \ll \lambda$ and$w_{\rm q}$ a parameter. The energy density of the Kiselev spacetime near the cosmic horizon is approximately proportional to$w_{\rm q}$ , so the energy densities with some different$ w_{\rm q}$ have the same order of magnitude in the range$-1<w_{\rm q} < - 1/3$ . Near the black hole horizon, it increases rapidly with the increase of$w_{\rm q}$ . The thermodynamic properties of the systems with black hole horizon and cosmic horizon as boundary are studied. The first law of thermodynamics for the two systems is given in a unified way. Similarly, Smarr relation for the mass of Kiselev black hole is also obtained. For$M \ll \lambda $ , the work done by the fluid on the cosmic horizon and the thermal energy flux flowing into the cosmic horizon of Kiselev spacetime are calculated approximately. In the range of$-1 < w_{\rm q} < - 1/3 $ , the thermal energy always flows out of the cosmic horizon. The work done by the fluid on the black hole horizon is much smaller than the change in the energy of black hole,$\Delta w_{\rm B} \ll \Delta r_{\rm B}$ . This indicates that the energy increase of black hole comes mainly from the thermal energy flowing into the black hole through its outer horizon. The problem of accreting the pressureless fluid into Kiselev black hole is discussed. One can find that there are the zero gravity surfaces between the black hole horizon and cosmic horizon of Kiselev spacetime, the radii of which increase with the decrease of$w_{\rm q}$ . For$w_{\rm q}=-\dfrac{2}{3}$ and$w_{\rm q}=-1$ , the accretion radii of Kiselev black hole are respectively determined to be$r_0 \approx 1.6 \times 10^{4}$ (l.y.) and$r_0 \approx 1.2 \times 10^{6}$ (l.y.). On condition that the accretion energy density is proportional to the background energy density,$\rho_{\rm {mB}} = \eta_{\rm B} \rho_{\rm B}$ with$\eta_{\rm B}$ being a proportionality coefficient, the accretion rate of Kiselev black hole is given as$\chi_{\rm B} = - \dfrac{3 \eta_{\rm B} w_{\rm q}} {2} \left(\dfrac{2M}{\lambda}\right)^{-(3w_{\rm q} + 1)}$ . For$w_{\rm q}= - 2/3 $ , the accretion rate of the black hole takes its maximum$\chi_{\rm max} \approx 1.2 \times 10^{- 6} \eta_{\rm B} $ ; for$w_{\rm q}= - 1$ , the accretion rate takes its minimum$\chi_ {\rm {min}} \approx 1.2 \times 10 ^ {-8} \eta_{\rm B} $ . On the assumption that$\eta_{\rm B}$ changes slowly enough with$w_{\rm q}$ , the accretion rate of Kiselev black hole increases with the increase of$w_{\rm q}$ .-
Keywords:
- Kiselev black hole /
- matter accretion /
- thermodynamic properties
[1] Riess A G, Filippenko A V, Challis P, et al. 1998 Astron. J. 116 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Perlmutter S, Aldering G, Goldhaber G, et al. 1999 Astrophys. J. 517 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Garnavich P M, Kirshner R P, Challis P, et al. 1998 Astrophys. J. 493 L53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kiselev V V 2003 Class. Quant. Grav. 20 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Majeed B, Jamil M, Pradhan P 2015 Adv. High Energy Phys. 2015 124910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Azreg-Aïnou M, Rodrigues M E 2013 J. High Energy Phys. 2013 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bondi H, Hoyle F 1944 Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 104 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bondi H 1952 Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 112 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Michel F C 1972 Astrophys. Space Sci. 15 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Begelman M 1978 Astron. Astrophys. 70 583
[11] Malec E 1999 Phys. Rev. D 60 104043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jawad A, Shahzad M U 2016 Eur. Phys. J. C 76 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Karkowski J, Malec E 2013 Phys. Rev. D 87 044007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Babichev E, Dokuchaev V, Eroshenko Y 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 021102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Babichev E, Dokuchaev V, Eroshenko Y 2005 J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 100 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jamil M, Rashid M A, Qadir A 2008 Eur. Phys. J. C 58 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao C, Chen X, Faraoni V, Shen Y G 2008 Phys. Rev. D 78 024008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Babichev E, Chernov S, Dokuchaev V, Eroshenko Y 2008 Phys. Rev. D 78 104027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kumar R, Ghosh S G 2017 Eur. Phys. J. C 77 577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Paik B, Gangopadhyay S 2018 Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 33 1850084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ahmed A K, Camci U, Jamil M 2016 Class. Quantum Grav. 33 215012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sharif M, Iftikhar S 2016 Eur. Phys. J. C 76 147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jiao L, Yang R J 2017 J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 9 023
[24] Jiao L, Yang R J 2017 Eur. Phys. J. C 77 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sahoo P K, Mahanta K L, Goit D, Sihna A K, Xulu S S, Das U R, Prasad A, Prasad R 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 020402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
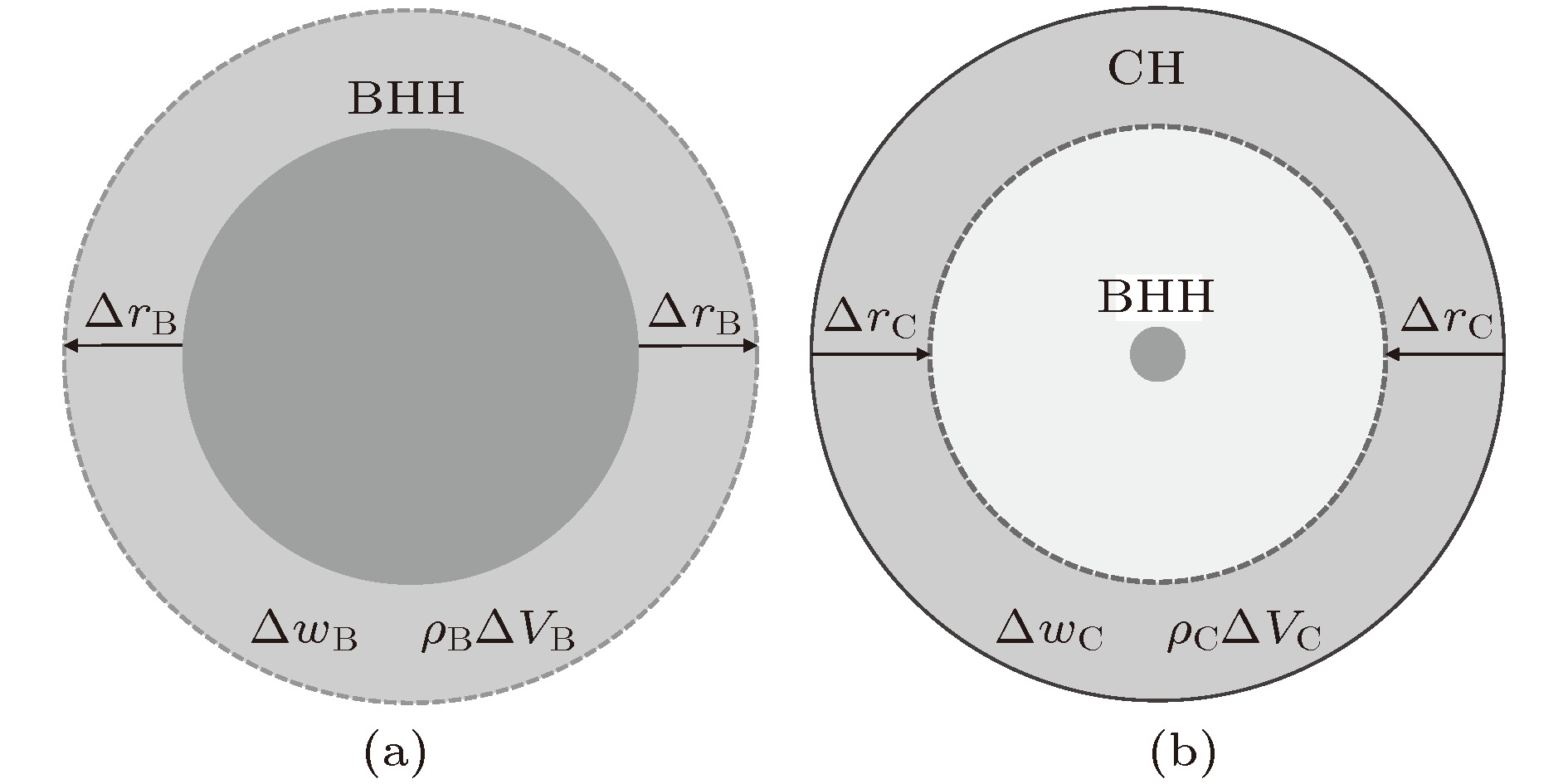
图 1 (a)黑洞视界做功示意图; (b)宇宙视界做功示意图; 其中BHH和CH分别表示黑洞视界和宇宙视界,
$ \Delta r_{\rm {B, C}} $ 表示黑洞视界和宇宙视界半径的微小变化, 虚线表示变化后的黑洞视界和宇宙视界Figure 1. (a) Doing work of black hole horizon; (b) doing work of cosmic horizon. BHH and CH stand for the black hole horizon and the cosmic horizon, respectively.
$ \Delta r_{\rm {B, C}} $ denotes a small change of the radii of black hole horizon and cosmic horizon. The dotted lines represent the changed black hole horizon and the changed cosmic horizon.图 3 在
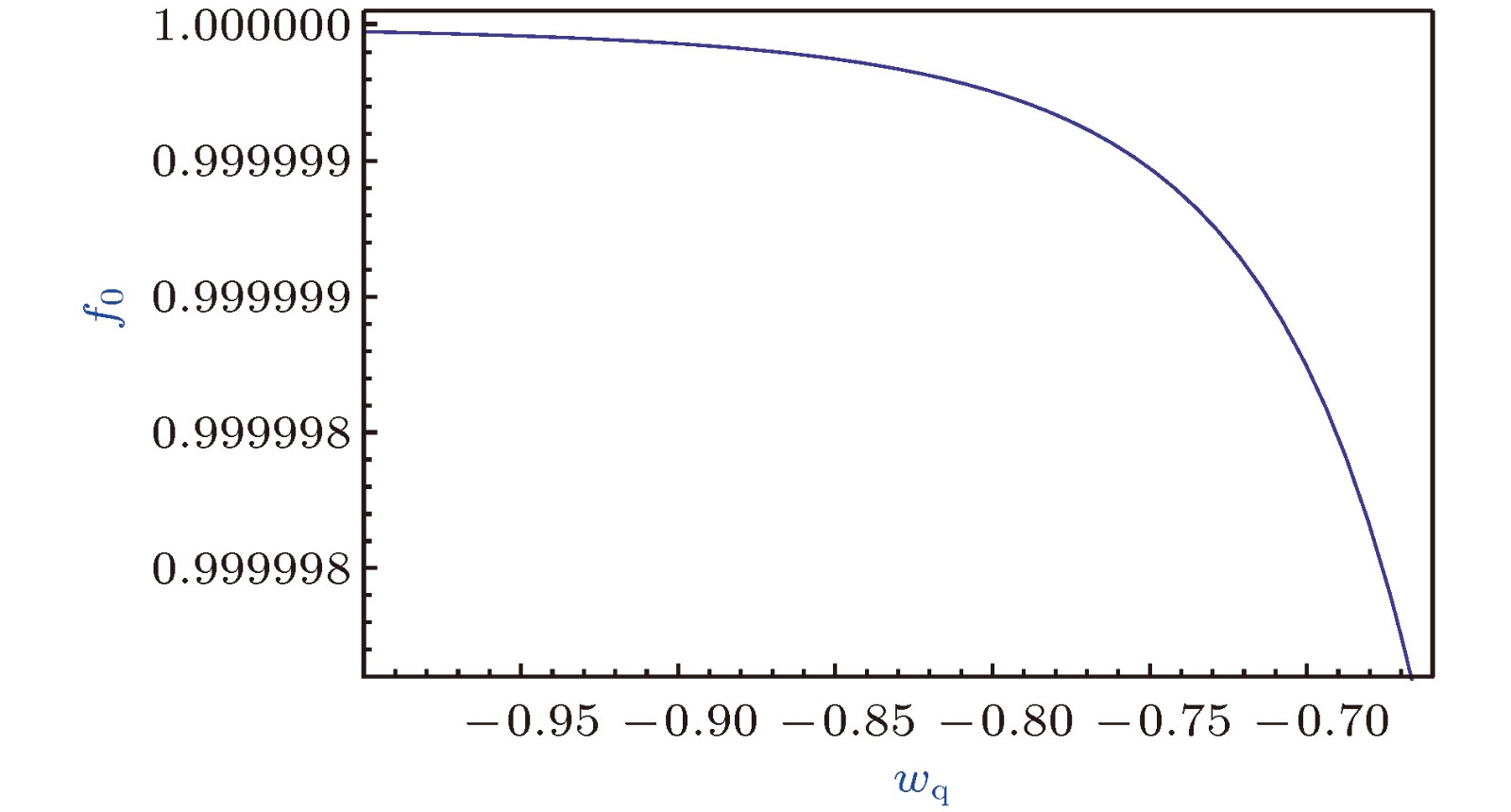
$M = 10 ^{-2}$ l.y.和$\lambda = 1.378 \times 10 ^{10}$ l.y.条件下的$f_0\text{-}w_{\rm q} $ 曲线, 对于$w_{\rm q} =-\frac{2}{3}$ 和$ -1$ , 分别有$f_{0}\approx $ 0.999998和0.99999998Figure 3. The
$f_0\text{-}w_{\rm q}$ curve ($M = 10 ^{-2}$ l.y. and$\lambda = 1.378 \; \times$ $10 ^{10}$ l.y.). For$w_{\rm q}=-\frac{2}{3}$ and$ -1$ , the metric function$f_{0}\approx 0.999998$ and 0.99999998, respectively.图 4 黑洞吸积率
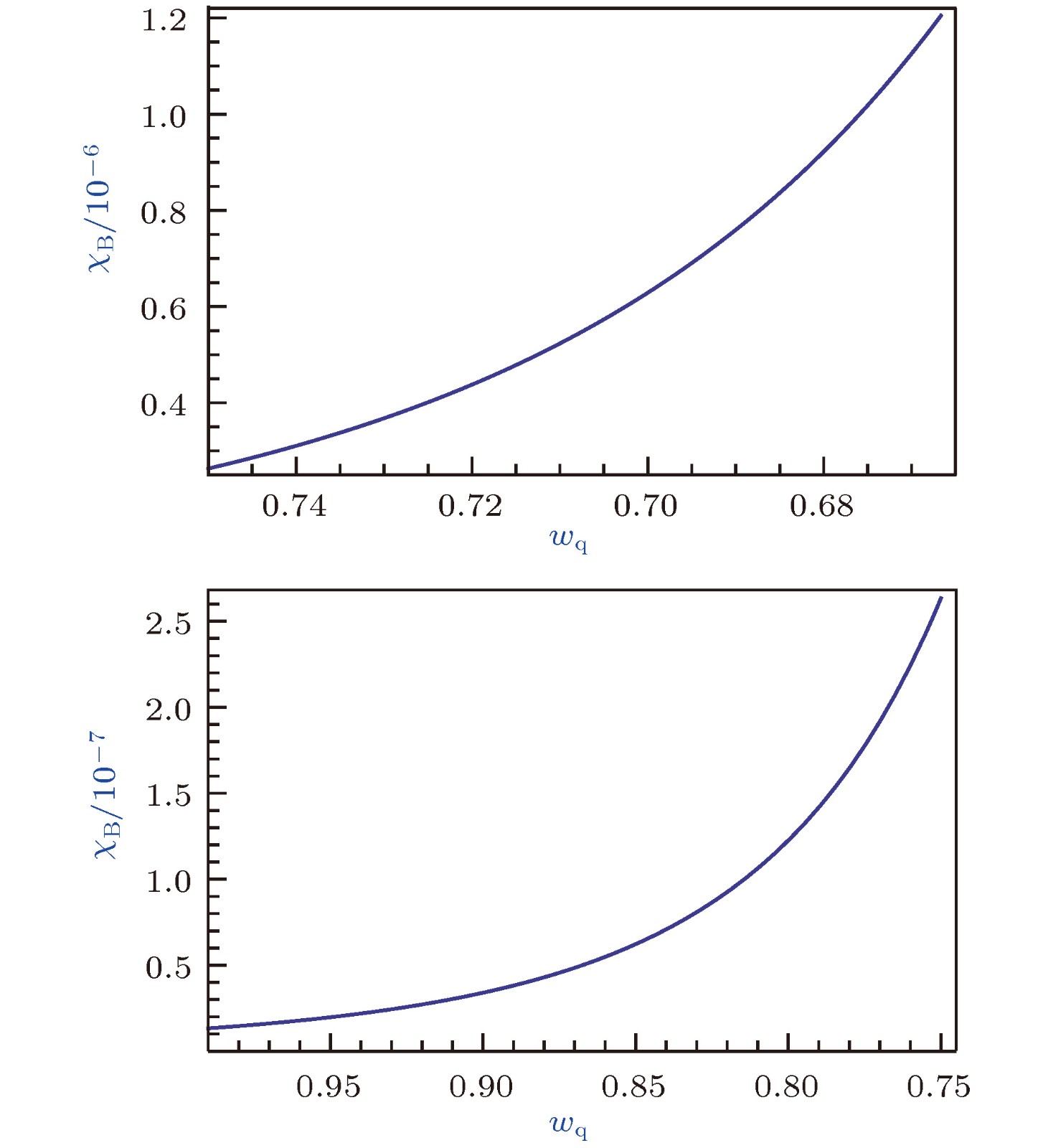
$\chi_{\rm B}$ (单位$\eta_{\rm B}$ )与$w_{\rm q}$ 的关系图(M =$ 10 ^{-2}$ l.y.和$\lambda = 1.378 \times 10 ^{10}$ l.y.)Figure 4. Relationship between black hole accretion rate
$\chi_{\rm B} $ (unit$\eta_{\rm B}$ ) and$ w_{\rm q}$ ($M = 10 ^{-2}\; {\rm l.y.}$ and$\lambda = 1.378 \; \times $ 1010 l.y.).表 1 黑洞视界附近背景时空的能量密度
Table 1. Energy density of spacetime near the horizon of black hole
$w_{\rm q}$ $-2/3$ $-0.8$ $-0.9$ $-0.99$ $-0.999$ $-0.9999$ $\rho_{\rm B}\left(\dfrac{3} {8{\text{π}} \lambda^2}\right)$ $4.59333\times10^{11}$ $1.01396\times10^7$ $3204.12$ $2.24275$ 1.08413 1.00811 -
[1] Riess A G, Filippenko A V, Challis P, et al. 1998 Astron. J. 116 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Perlmutter S, Aldering G, Goldhaber G, et al. 1999 Astrophys. J. 517 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Garnavich P M, Kirshner R P, Challis P, et al. 1998 Astrophys. J. 493 L53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kiselev V V 2003 Class. Quant. Grav. 20 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Majeed B, Jamil M, Pradhan P 2015 Adv. High Energy Phys. 2015 124910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Azreg-Aïnou M, Rodrigues M E 2013 J. High Energy Phys. 2013 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bondi H, Hoyle F 1944 Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 104 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bondi H 1952 Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 112 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Michel F C 1972 Astrophys. Space Sci. 15 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Begelman M 1978 Astron. Astrophys. 70 583
[11] Malec E 1999 Phys. Rev. D 60 104043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jawad A, Shahzad M U 2016 Eur. Phys. J. C 76 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Karkowski J, Malec E 2013 Phys. Rev. D 87 044007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Babichev E, Dokuchaev V, Eroshenko Y 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 021102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Babichev E, Dokuchaev V, Eroshenko Y 2005 J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 100 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jamil M, Rashid M A, Qadir A 2008 Eur. Phys. J. C 58 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao C, Chen X, Faraoni V, Shen Y G 2008 Phys. Rev. D 78 024008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Babichev E, Chernov S, Dokuchaev V, Eroshenko Y 2008 Phys. Rev. D 78 104027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kumar R, Ghosh S G 2017 Eur. Phys. J. C 77 577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Paik B, Gangopadhyay S 2018 Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 33 1850084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ahmed A K, Camci U, Jamil M 2016 Class. Quantum Grav. 33 215012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sharif M, Iftikhar S 2016 Eur. Phys. J. C 76 147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jiao L, Yang R J 2017 J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 9 023
[24] Jiao L, Yang R J 2017 Eur. Phys. J. C 77 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sahoo P K, Mahanta K L, Goit D, Sihna A K, Xulu S S, Das U R, Prasad A, Prasad R 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 020402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8122
- PDF Downloads: 73
- Cited By: 0





































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: