-
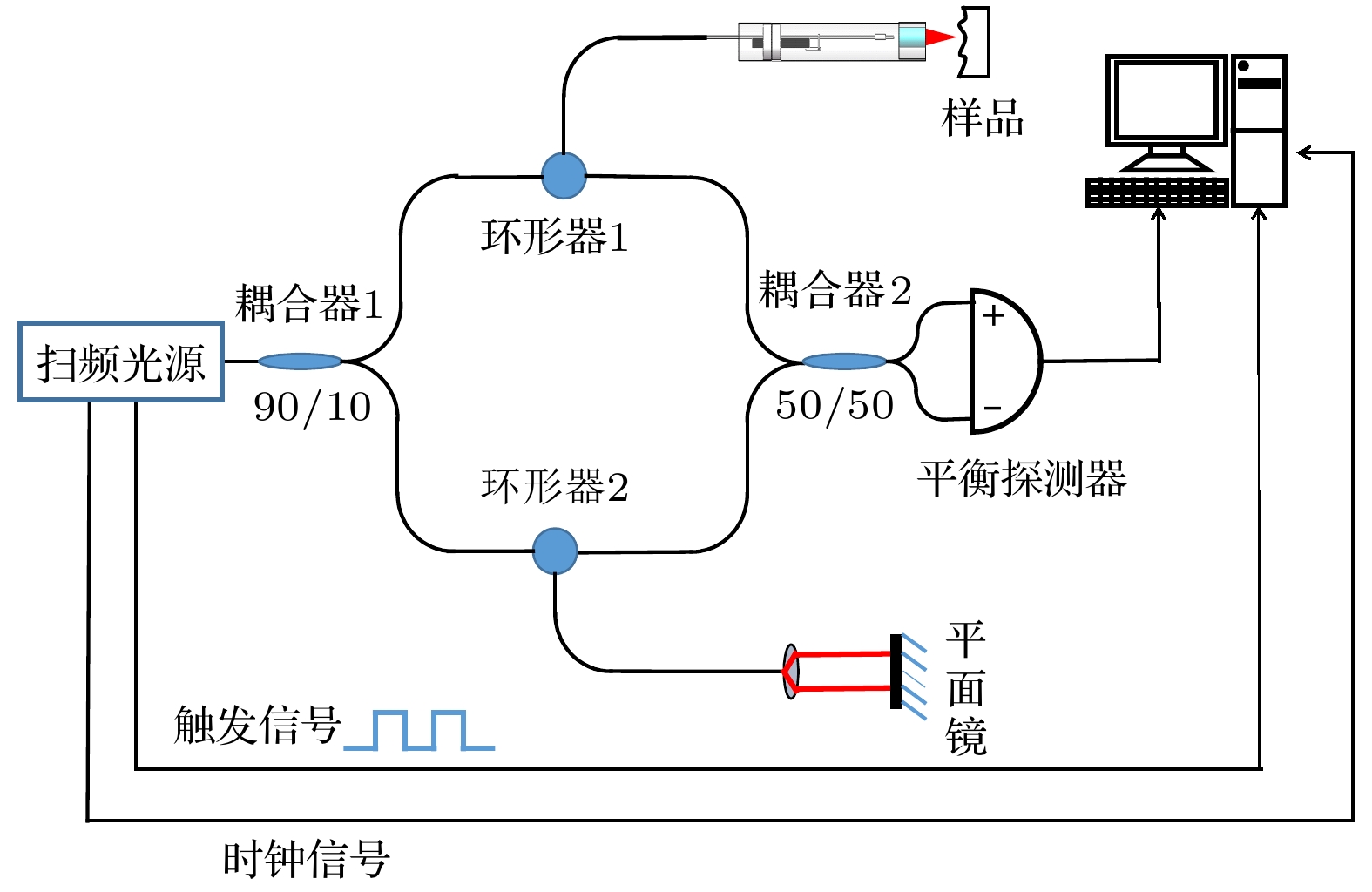
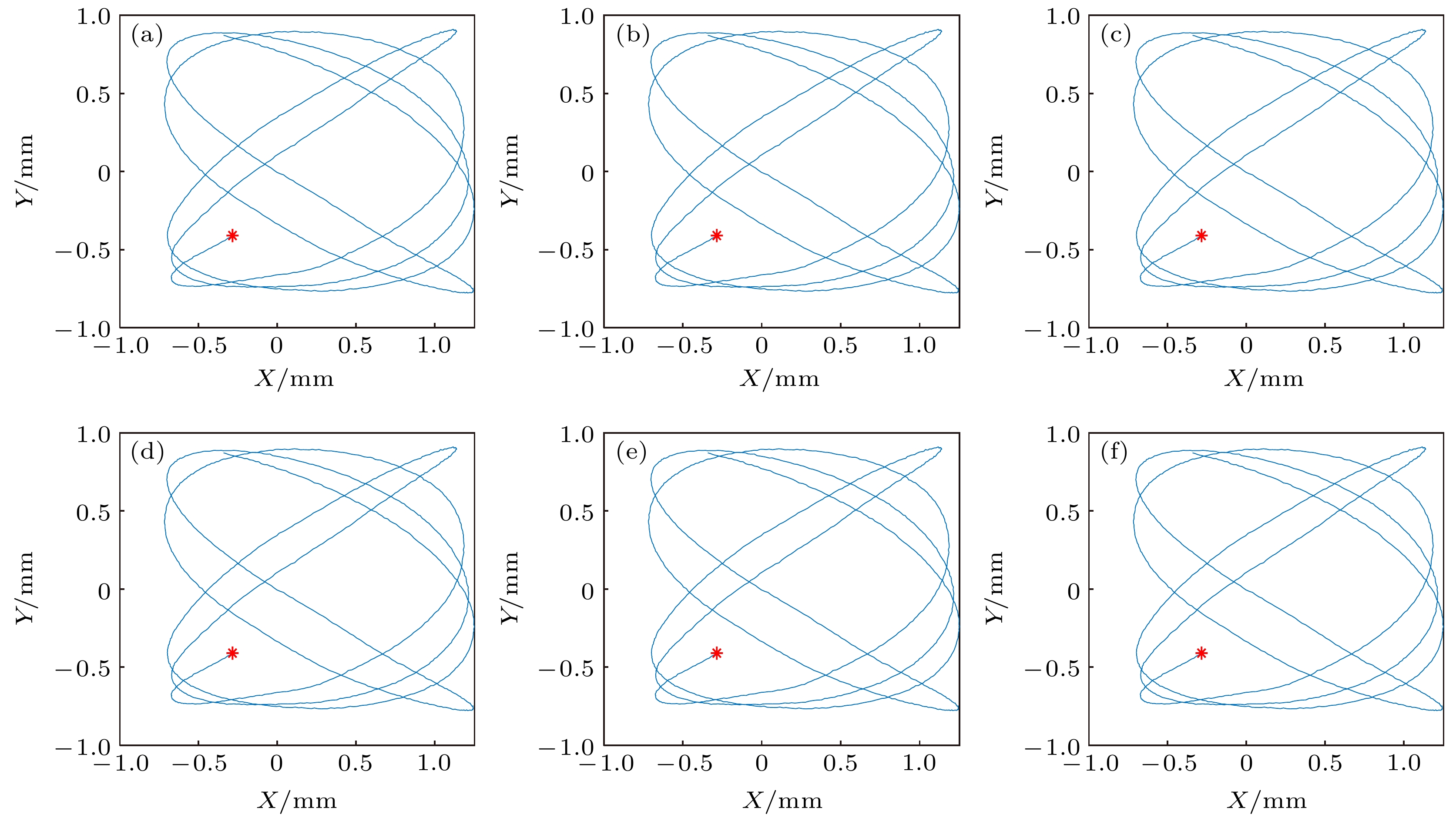
基于非对称光纤悬臂结构的Lissajous扫描光纤探头可实现低电压驱动下的大范围扫描成像. 本文研究了全封装的小型化预标定Lissajous扫描光纤探头. 通过优化设计与数值仿真, 选择了能实现高填充率Lissajous扫描的正交谐振频率, 确定了非对称光纤悬臂的结构参数. 全封装探头在5 mm工作距离处的焦点直径为25 μm, 视场大小达到1.5 mm × 1.5 mm, 总刚性长度和外径分别为35 mm和3.5 mm. 研究了全封装探头扫描轨迹的稳定性、可重复性与扫描成像的旋转稳定性. 结合实验室搭建的50 kHz扫频光学相干层析(OCT)系统, 对硬币和生物组织进行高质量成像, 验证了用于内窥OCT成像的小型化预标定Lissajous扫描光纤探头具有良好的成像性能.
-
关键词:
- 光学相干层析成像 /
- Lissajous扫描 /
- 内窥成像
In this paper we present a miniaturized pre-calibration based forward-viewing Lissajous scanning fiber probe for endoscopic optical coherence tomography (OCT). The probe is based on an asymmetric fiber cantilever driven by the piezoelectric bender to realize the two-dimensional (2D) Lissajous scanning, which can realize a relatively large scanning range under a low driving voltage. A capillary metal tube is mounted at the end of the main fiber to reduce the resonant frequency of the fiber cantilever. The relationship between the filling rate and the side-lobe number of the Lissajous scanning pattern is studied, and a method of selecting the orthogonal resonant frequency of the Lissajous scanning is proposed. Through the numerical simulation by COMSOL software, the structural parameters of the asymmetric fiber cantilever are determined. The orthogonal resonant frequencies of the asymmetric fiber cantilever are 169 Hz and 122 Hz. The lengths of the main imaging fiber, the auxiliary fiber and the metal capillary tube are 15.94 mm, 4.49 mm and 2 mm, respectively. The probe is fully packaged in a metal tube for endoscopic imaging. The focal spot and the working distance are 25 µm and 5 mm, respectively. The field of view is larger than 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm. The total rigid length and the outer diameter of the probe are 35 mm and 3.5 mm, respectively. The stability and repeatability of the Lissajous scanning trajectory, and the imaging stability with the rotation of the probe are investigated and verified. The probe is incorporated into a 50 kHz swept source OCT system. The axial resolution of the endoscopic OCT is 10.3 μm, and the imaging frame rate is 1 FPS (frames per second). The maximum signal-to-noise ratio of the imaging system is 110 dB. The imaging performance of the probe is validated by the 2D en-face and three-dimensional volumetric OCT imaging of the high scattering sample and the biological tissue. The probe can be used for the endoscopic imaging of the human tooth. From the result we can distinguish the dental enamel, dental essence and the dental calculus. The developed forward-viewing Lissajous scanning fiber probe is expected to be used in dental applications such as early calculus detection.-
Keywords:
- optical coherence tomography /
- Lissajous scanning /
- endoscopic imaging
[1] Huang D, Swanson E A, Lin C P, Schuman J S, Stinson W G, Chang W, Hee M R, Flotte T, Gregory K, Puliafito C A, Fujimoto J G 1991 Science 254 1178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 贾亚青, 梁艳梅, 朱晓农 2007 56 3861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia Y Q, Liang Y M, Zhu X N 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 3861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 黄良敏, 丁志华, 洪威, 王川 2011 61 023401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L M, Ding Z H, Hong W, Wang C 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 023401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li X D, Chudoba C, Ko T, Pitris C, Fujimoto J G 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 1520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu J, Conry M, Gu C, Wang F, Yaqoob Z, Yang C 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 1265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pan Y, Xie H, Fedder G K 2001 Opt. Lett. 26 1966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Park H C, Song C, Kang M, Jeong Y, Jeong K H 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 2673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Y, Bachman M, Li G P, Guo S, Wong B J F, Chen Z 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Min E J, Na J, Ryu S Y, Lee B H 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 1897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang K, Huang Y, and Kang J U 2011 Opt. Eng. 50 119002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu X M, Cobb J, Chen Y, Kimmey M B, Li X 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Huo L, Xi J, Wu Y, Li X 2010 Opt. Express 18 14375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Min E J, Shin J G, Kim Y, Lee B H 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang N, Tsai T H, Ahsen O O, Liang K, Lee H C, Xue P, Li X, Fujimoto J G 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vilches S, Kretschmer S, Çağlar A, Zappe H 2017 J. Micromech. Microeng. 27 105015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hinnerk S H, Pfeiffer T, Eixmann T, Lohmann S, Ahrens M, Rehra J, Draxinger W, KÖNIG P, Huber R, Hüttmann G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Helmchen F, Fee M S, Tank D W, Denk W 2001 Neuron 31 903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu T, Ding Z H, Wang K, Chen M, Wang C 2009 Opt. Express 17 13819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Moon S, Lee S, Rubinstein M, Wong B J F, Chen Z 2010 Opt. Express 18 21183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Park H C, Seo Y H, Jeong K H 2014 Opt. Express 22 5818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Seo Y H, Hwang K, Park H C, Jeong K H 2016 Opt. Express 24 3903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liang W, Murari K, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Li M J, Li X 2012 J. Biomed. Opt. 17 021108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hwang K, Seo Y H, Ahn J, Kim P, Jeong K H 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 14075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
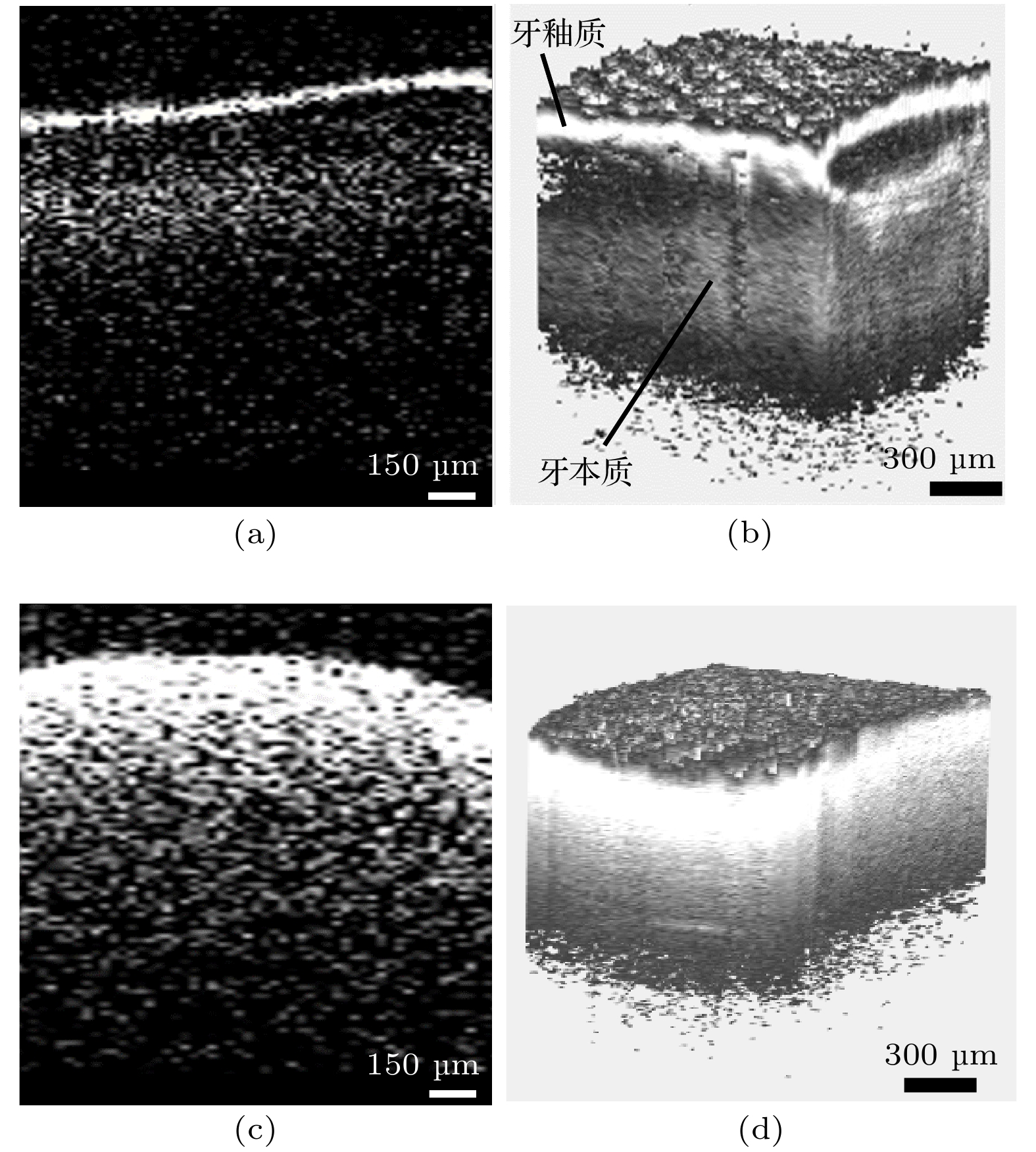
图 10 (a)磨牙的二维OCT横截面图像; (b)磨牙的三维OCT图像; (c)牙结石的二维OCT横截面图像; (d)牙结石的三维OCT图像
Fig. 10. (a) Two-dimensional OCT cross sectional image of the health molar tooth tissue; (b) three-dimensional OCT image of the health molar tooth tissue; (c) two-dimensional OCT cross sectional image of the dental calculus; (d) three-dimensional OCT image of the dental calculus.
-
[1] Huang D, Swanson E A, Lin C P, Schuman J S, Stinson W G, Chang W, Hee M R, Flotte T, Gregory K, Puliafito C A, Fujimoto J G 1991 Science 254 1178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 贾亚青, 梁艳梅, 朱晓农 2007 56 3861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia Y Q, Liang Y M, Zhu X N 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 3861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 黄良敏, 丁志华, 洪威, 王川 2011 61 023401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L M, Ding Z H, Hong W, Wang C 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 023401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li X D, Chudoba C, Ko T, Pitris C, Fujimoto J G 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 1520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu J, Conry M, Gu C, Wang F, Yaqoob Z, Yang C 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 1265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pan Y, Xie H, Fedder G K 2001 Opt. Lett. 26 1966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Park H C, Song C, Kang M, Jeong Y, Jeong K H 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 2673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Y, Bachman M, Li G P, Guo S, Wong B J F, Chen Z 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Min E J, Na J, Ryu S Y, Lee B H 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 1897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang K, Huang Y, and Kang J U 2011 Opt. Eng. 50 119002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu X M, Cobb J, Chen Y, Kimmey M B, Li X 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1763
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Huo L, Xi J, Wu Y, Li X 2010 Opt. Express 18 14375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Min E J, Shin J G, Kim Y, Lee B H 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang N, Tsai T H, Ahsen O O, Liang K, Lee H C, Xue P, Li X, Fujimoto J G 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vilches S, Kretschmer S, Çağlar A, Zappe H 2017 J. Micromech. Microeng. 27 105015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hinnerk S H, Pfeiffer T, Eixmann T, Lohmann S, Ahrens M, Rehra J, Draxinger W, KÖNIG P, Huber R, Hüttmann G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Helmchen F, Fee M S, Tank D W, Denk W 2001 Neuron 31 903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu T, Ding Z H, Wang K, Chen M, Wang C 2009 Opt. Express 17 13819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Moon S, Lee S, Rubinstein M, Wong B J F, Chen Z 2010 Opt. Express 18 21183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Park H C, Seo Y H, Jeong K H 2014 Opt. Express 22 5818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Seo Y H, Hwang K, Park H C, Jeong K H 2016 Opt. Express 24 3903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liang W, Murari K, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Li M J, Li X 2012 J. Biomed. Opt. 17 021108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hwang K, Seo Y H, Ahn J, Kim P, Jeong K H 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 14075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7803
- PDF下载量: 120
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: