-
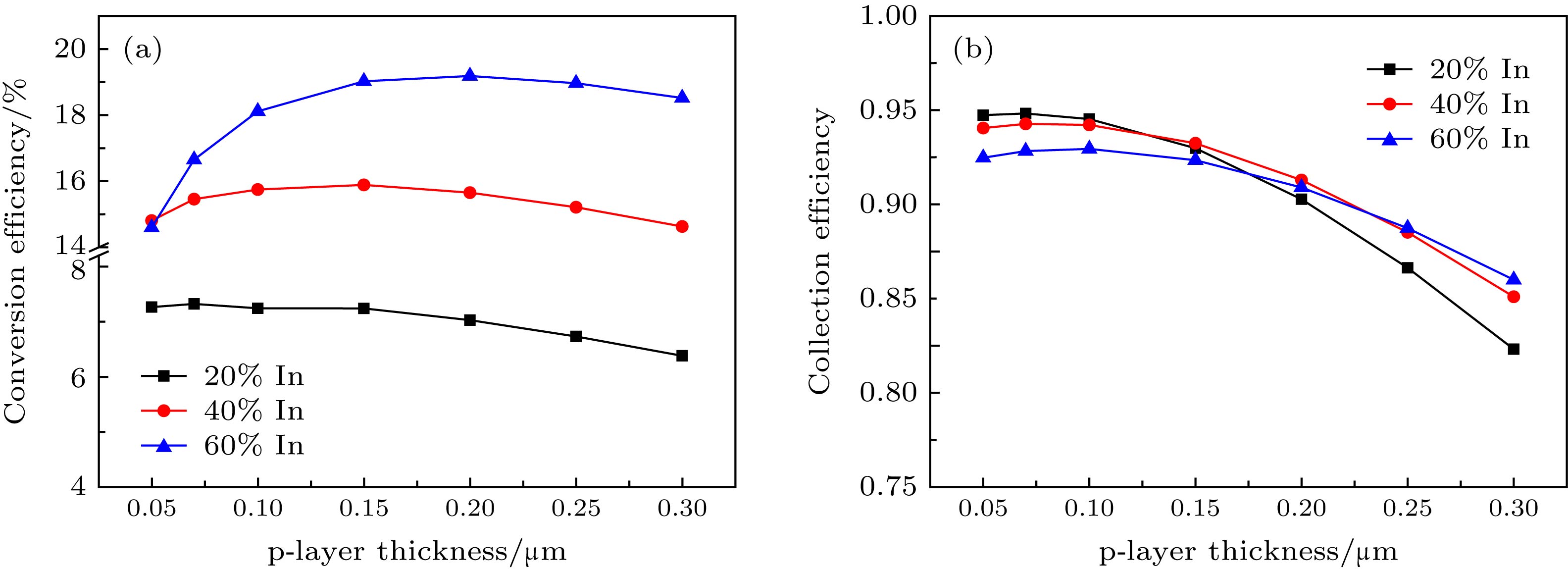
In this paper, the effects of p-layer hole concentration and p-layer thickness on the performances of InGaN p-i-n homojunction solar cells with different indium components and their intrinsic mechanisms are investigated by numerical simulations. it is found that the conversion efficiency of solar cells first increases and then decreases slightly with the increase of p-layer hole concentration and p-layer thickness. Moreover, the change of p-layer hole concentration and p-layer thickness will cause great changes of the conversion efficiency of the solar cells, especially as the indium composition increases. In order to better clarify and understand the physical mechanism of this phenomenon, the collection efficiency, I-V characteristic, built-in electric field and carrier transport of solar cells are analyzed in this paper. When the hole concentration is insufficient, the build-in electric filed is not strong enough to separate the most of the electric-hole pairs. This will reduce the collection efficiency. In addition, the lower the hole concentration, the higher the series resistance of solar cells will be and the more the power loss. So a conclusion can be drawn that the lower hole concentration of p-layer would be accompanied by the reduction of collection efficiency and the increase of series resistance, thus resulting in a lower conversion efficiency. With the increase of the hole concentration which is below an optimal value, the built-in electric field reaches the threshold, which can improve the collection efficiency. At the same time, although the series resistance is reduced to a certain extent, it still reduces the effective output power and limits the conversion efficiency. When the hole concentration is higher than the optimal value, the carrier mobility becomes the main factor limiting the conversion efficiency. As for the p-layer thickness, the simulation results indicate that the lateral transport of carriers from the p-layer to the anode electrodes becomes more obstructive with the thinning of p-layer thickness. This is because when the p-layer thickness decreases, thus causing the p-layer sectional area to decrease, the lateral series resistance becomes higher. It is clear that when the p-layer is too thin, the lateral series resistance is one of the main limiting factors affecting the conversion efficiency of solar cells.
-
Keywords:
- numerical simulation /
- InGaN /
- homojunction /
- solar cell
[1] Jain S C, Willander M, Narayan J, Overstraeten R V 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ambacher O 1998 J. Phys. D 31 2653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Strite S T, Morkoc H 1998 JVST B 10 1237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mohammad S N, Morkoç H 1996 Prog. Quant. Electron. 20 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang H L, Zhang X H, Wang H X, Li B, Chen C, Li Y X, Yan H, Wu Z S, Jiang H 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 127805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, Iii J W A, Haller E E, Hai L, Schaff W J, Saito Y, Nanishi Y 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 3967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bhuiyan A G, Sugita K, Hashimoto A, Yamamoto A 2012 IEEE J. Photovolt. 2 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Muth J F, Lee J H, Shmagin I K, Kolbas R M, Casey H C, Keller B P, Mishra U K, Denbaars S P 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 2572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Nanishi Y, Saito Y, Yamaguchi T 2003 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 2549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu Y, Sun X J, Jia Y P, Li D B 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 126101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tran B T, Chang E Y, Trinh H D, Lee C T, Sahoo K C, Lin K L, Huang M C, Yu H W, Luong T T, Chung C C 2012 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 102 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, Shan W, Ager J W, Haller E E, Hai L, Schaff W J, Metzger W K, Kurtz S 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 6477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Fabien C A M, Moseley M, Gunning B, Doolittle W A, Ponce F A 2014 IEEE J. Photovolt. 4 601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Cai X M, Zeng S W, Zhang B P 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 183516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Islam M R, Kaysir M R, Islam M J, Hashimoto A, Yamamoto A 2013 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shim J P, Choe M, Jeon S R, Seo D, Lee T, Lee D S 2011 Appl. Phys. Express 4 1166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen X, Matthews K D, Hao D, Schaff W J, Eastman L F 2008 Phys. Status Solidi 205 1103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Feng S W, Lai C M, Chen C H, Sun W C, Tu L W 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 093118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu S, Cheng L, Wang Q 2018 Superlattice Microst. 119 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 周梅, 赵德刚 2015 发光学报 36 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou M, Zhao D G 2015 Chin. J. Lumin. 36 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Benmoussa D, Hassane B, Abderrachid H 2013 International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC) Ouarzazate, Morocco, March 7−9, 2013 p23
[22] Mesrane A, Rahmoune F, Mahrane A, Oulebsir A 2015 Int. J. Photoenergy 2015 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Holec D, Costa P M F J, Kappers M J, Humphreys C J 2007 J. Cryst. Growth 303 314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Michael S, Bates A, Green M 2005 Conference Record of the Thirty-first IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference 2005 Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, Jan. 3-7, 2005 p719
[25] Fischer S, Wetzel C, Haller E E, Meyer B K 1995 Appl. Phys. Lett. 67 1298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Bhattacharyya A, Li W, Cabalu J, Moustakas T D, Smith D J, Hervig R L 2004 Appl. Phys. Lett. 85 4956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chao L, Ren Z, Xin C, Zhao B, Wang X, Yin Y, Li S 2014 IEEE Photono. Tchnol. Lett. 26 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Fabien C A M, Doolittle W A 2014 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 130 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shen Y C, Mueller G O, Watanabe S, Gardner N F, Krames M R 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Chang J Y, Yen S H, Chang Y A, Kuo Y K 2013 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 49 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wu J, Walukiewicz W 2003 Superlattice Microst. 34 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, Ager J W, Haller E E, Lu H, Schaff W J 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 4741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Walukiewicz W, Iii J W A, Yu K M, Liliental-Weber Z, Wu J, Li S X, Jones R E, Denlinger J D 2006 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Brown G F, Iii J W A, Walukiewicz W, Wu J 2010 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94 478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kuo Y K, Chang J Y, Shih Y H 2012 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 48 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Brown G F, Ager J W, Walukiewicz W, Schaff W J, Wu J 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 6477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] King P D C, Veal T D, Jefferson P H, Mcconville C F, Lu H, Schaff W J 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 115312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Neufeld C J, Toledo N G, Cruz S C, Iza M, Denbaars S P, Mishra U K 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 1571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 (a) In0.2Ga0.8N, (c) In0.4Ga0.6N和(e) In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n同质结在零偏压及光照下, 不同空穴浓度(NA+)下的内建电场; (b) In0.2Ga0.8N, (d) In0.4Ga0.6N和(f) In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n同质结在不同空穴浓度(NA+)下的I-V曲线
Fig. 3. Under AM1.5 illumination and zero bias, electric-field of (a) In0.2Ga0.8N, (c) In0.4Ga0.6N and (e) In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n homojunction solar cells with various hole concentration (NA+); I-V curves of (b) In0.2Ga0.8N, (d) In0.4Ga0.6N and (f) In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n homojunction solar cells with various hole concentration (NA+), respectively.
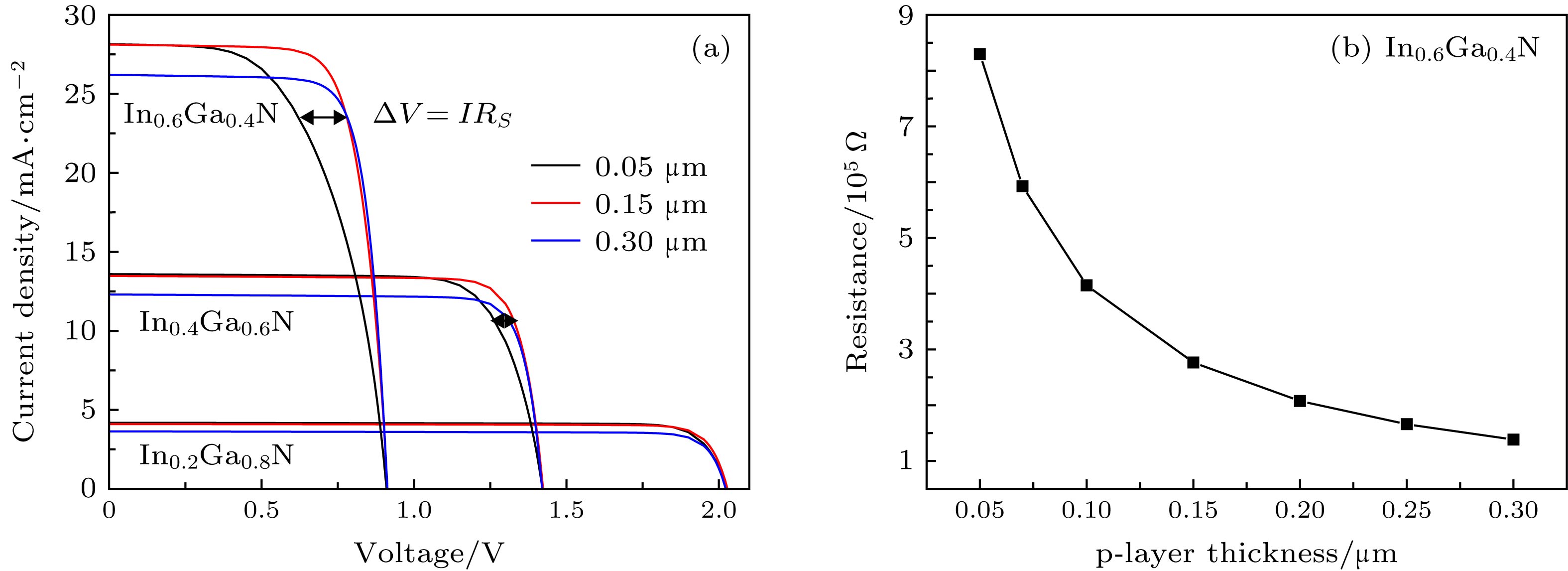
图 6 (a) In0.2Ga0.8N, In0.4Ga0.6N和In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n同质结电池在不同p层厚度下的I-V曲线; (b)不同p层厚度下In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n同质结电池p层的横向电阻
Fig. 6. (a) I-V curves of In0.2Ga0.8N, In0.4Ga0.6N and In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n homojunction solar cells with various p-layer thickness and (b) the lateral resistance of p-layer for In0.6Ga0.4N p-i-n homojunction solar cells.
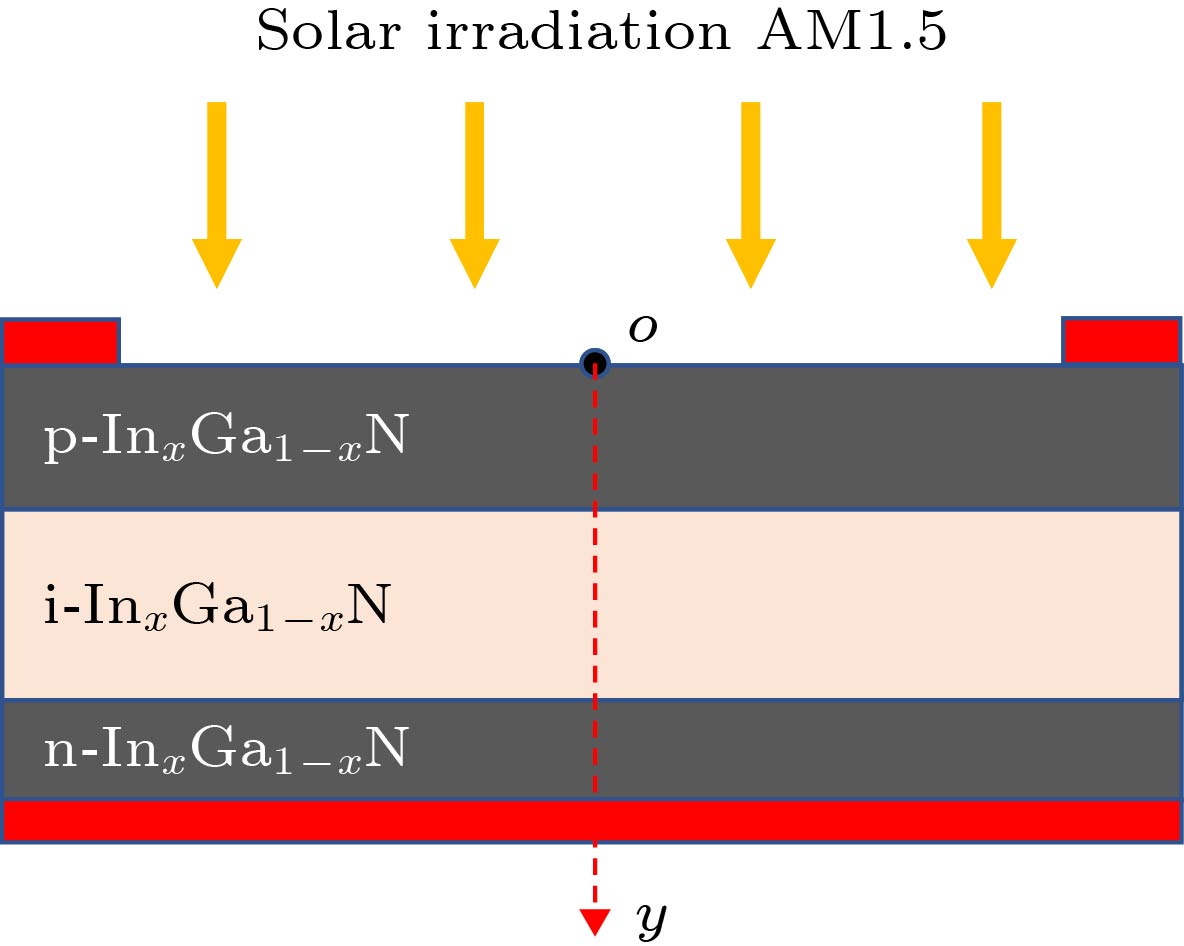
表 1 InxGa1–xN p-i-n同质结器件中的基准参数
Table 1. Parameters of baseline for InxGa1–xN p-i-n homojunction solar cells.
参数 基准值 铟组分/% 20, 40, 60 少子寿命/ns 1 p层掺杂激活浓度/cm–3 5 × 1017 i层掺杂浓度/cm–3 1 ×1017 n层掺杂浓度/cm–3 5 × 1017 p层厚度/μm 0.2 i层厚度/μm 0.4 n层厚度μm 2 表面复合速度/cm·s–1 1 ×104 -
[1] Jain S C, Willander M, Narayan J, Overstraeten R V 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ambacher O 1998 J. Phys. D 31 2653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Strite S T, Morkoc H 1998 JVST B 10 1237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mohammad S N, Morkoç H 1996 Prog. Quant. Electron. 20 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang H L, Zhang X H, Wang H X, Li B, Chen C, Li Y X, Yan H, Wu Z S, Jiang H 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 127805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, Iii J W A, Haller E E, Hai L, Schaff W J, Saito Y, Nanishi Y 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 3967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bhuiyan A G, Sugita K, Hashimoto A, Yamamoto A 2012 IEEE J. Photovolt. 2 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Muth J F, Lee J H, Shmagin I K, Kolbas R M, Casey H C, Keller B P, Mishra U K, Denbaars S P 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 2572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Nanishi Y, Saito Y, Yamaguchi T 2003 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 2549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu Y, Sun X J, Jia Y P, Li D B 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 126101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tran B T, Chang E Y, Trinh H D, Lee C T, Sahoo K C, Lin K L, Huang M C, Yu H W, Luong T T, Chung C C 2012 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 102 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, Shan W, Ager J W, Haller E E, Hai L, Schaff W J, Metzger W K, Kurtz S 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 6477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Fabien C A M, Moseley M, Gunning B, Doolittle W A, Ponce F A 2014 IEEE J. Photovolt. 4 601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Cai X M, Zeng S W, Zhang B P 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 183516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Islam M R, Kaysir M R, Islam M J, Hashimoto A, Yamamoto A 2013 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shim J P, Choe M, Jeon S R, Seo D, Lee T, Lee D S 2011 Appl. Phys. Express 4 1166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen X, Matthews K D, Hao D, Schaff W J, Eastman L F 2008 Phys. Status Solidi 205 1103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Feng S W, Lai C M, Chen C H, Sun W C, Tu L W 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 093118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu S, Cheng L, Wang Q 2018 Superlattice Microst. 119 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 周梅, 赵德刚 2015 发光学报 36 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou M, Zhao D G 2015 Chin. J. Lumin. 36 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Benmoussa D, Hassane B, Abderrachid H 2013 International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC) Ouarzazate, Morocco, March 7−9, 2013 p23
[22] Mesrane A, Rahmoune F, Mahrane A, Oulebsir A 2015 Int. J. Photoenergy 2015 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Holec D, Costa P M F J, Kappers M J, Humphreys C J 2007 J. Cryst. Growth 303 314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Michael S, Bates A, Green M 2005 Conference Record of the Thirty-first IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference 2005 Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, Jan. 3-7, 2005 p719
[25] Fischer S, Wetzel C, Haller E E, Meyer B K 1995 Appl. Phys. Lett. 67 1298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Bhattacharyya A, Li W, Cabalu J, Moustakas T D, Smith D J, Hervig R L 2004 Appl. Phys. Lett. 85 4956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chao L, Ren Z, Xin C, Zhao B, Wang X, Yin Y, Li S 2014 IEEE Photono. Tchnol. Lett. 26 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Fabien C A M, Doolittle W A 2014 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 130 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shen Y C, Mueller G O, Watanabe S, Gardner N F, Krames M R 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Chang J Y, Yen S H, Chang Y A, Kuo Y K 2013 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 49 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wu J, Walukiewicz W 2003 Superlattice Microst. 34 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, Ager J W, Haller E E, Lu H, Schaff W J 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 4741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Walukiewicz W, Iii J W A, Yu K M, Liliental-Weber Z, Wu J, Li S X, Jones R E, Denlinger J D 2006 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Brown G F, Iii J W A, Walukiewicz W, Wu J 2010 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94 478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kuo Y K, Chang J Y, Shih Y H 2012 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 48 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Brown G F, Ager J W, Walukiewicz W, Schaff W J, Wu J 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 6477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] King P D C, Veal T D, Jefferson P H, Mcconville C F, Lu H, Schaff W J 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 115312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Neufeld C J, Toledo N G, Cruz S C, Iza M, Denbaars S P, Mishra U K 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 1571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 13698
- PDF下载量: 103
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: