-
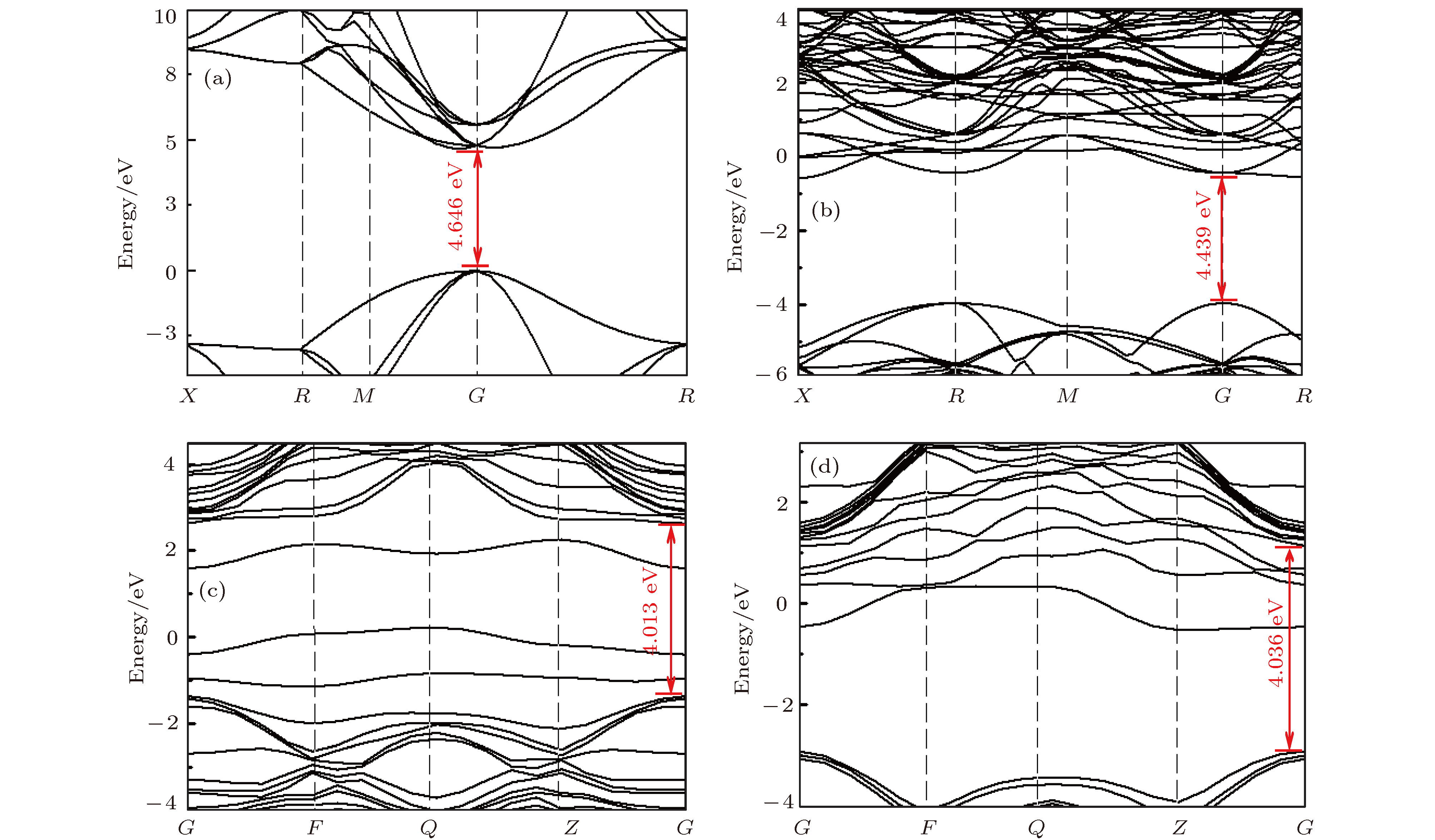
FeNiMnCo-C体系中, 在压力6.5 GPa、温度1280—1300 ℃的极端物理条件下, 采用温度梯度法成功合成了硼(B)、硫(S)协同掺杂金刚石大单晶. 通过傅里叶红外光谱测试对高温高压所制备金刚石中的杂质进行了表征. 借助霍尔效应对典型金刚石样品的电输运性能进行了测试, 测试结果表明: 硼硫协同掺杂有利于提高p型金刚石的电导率, 而且硼硫在合成体系中的添加比例可以决定金刚石的p, n特性. 此外, 第一性原理计算结果表明, 合成体系中不同比例的硼硫协同掺杂对金刚石的p, n特性以及电导率有着直接的影响, 计算结果与实验测试结果相吻合.As is well known, diamond is extensively used in many fields, because of its excellent properties, such as its hardness, high thermal conductivity, high electron and hole mobility, high breakdown field strength and large band gap (5.4 eV). However, its application in semiconductor area needs to be further understood, because it is irreplaceable by conventional semiconductor materials, especially in the extreme working conditions. Furthermore, the preparation of n-type diamond semiconductors is still an unsolved problem. The reason is that an effective donor element has not yet been found. Recently, both the theoretical and experimental studies show that it is difficult to obtain n-type diamond semiconductor with excellent properties by doping single element in the synthetic system. In this paper, diamond single crystals co-doped with B and S are successfully synthesized in FeNiMnCo-C system at a pressure of 6.5 GPa and temperature ranging from 1280 ℃ to 1300 ℃, by using temperature gradient method. The impurity defects in the synthesized diamond single crystals are characterized by Fourier infrared absorption spectra and the results indicate that the corresponding characteristic absorption peaks of B and S are located at 1298 cm–1 and 847 cm–1, respectively. Furthermore, the absorption attributed to B-S group is not detected. The N concentration of the synthesized diamond crystals decreases to 195 ppm, resulting from the incorporation of B and S impurities into the diamond lattices. Additionally, the electrical properties of the typical diamond single crystals are measured in virtue of Hall effects at room temperature. The measurement results display that the electrical conductivity of the diamond doped with B is obviously enhanced, resulting from the involvement of the S when B addition amount is fixed in the synthesis system. Hall mobility of the corresponding diamond crystals increases from 12.5 cm–2·V–1·s–1 to 760.87 cm–2·V–1·s–1. And then, the relative proportion of S and B will determine the p/n properties of the obtained diamond. In order to further study the electrical properties of diamond, first-principles calculations are adopted and the theoretical calculation results show that the impurity elements involved in the obtained diamond can affect the band structures of the synthetic diamond crystals, which is consistent with the experimental result.
-
Keywords:
- high pressure and high temperature /
- co-doped /
- diamond /
- electrical properties
[1] 王君卓, 李尚升, 宿太超, 胡美华, 胡强, 吴玉敏, 王健康, 韩飞, 于昆鹏, 高广进, 郭明明, 贾晓鹏, 马红安, 肖宏宇 2018 67 168101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J Z, Li S S, Su T C, Hu M H, Hu Q, Wu Y M, Wang J K, Han F, Yu K P, Gao G J, Guo M M, Jia X P, Ma H A, Xiao H Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 168101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘银娟, 贺端威, 王培, 唐明君, 许超, 王文丹, 刘进, 刘国端, 寇自力 2017 66 038103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y J, He D W, Wang P, Tang M J, Xu C, Wang W D, Liu J, Liu G D, Kou Z L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 038103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li Y, Zhou Z X, Guan X M, Li S S, Wang Y, Jia X P, Ma H A 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 028101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Banerjee A, Bernoulli D, Zhang H T, Yuen M F, Liu J B, Dong J C, Ding F, Lu J, Dao M, Zhang W J, Lu Y, Suresh S 2018 Science 360 300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang J K, Li S S, Jiang Q W, Song Y L, Yu K P, Han F, Su T C, Hu M H, H Q, Ma H A, Jia X P, Xiao H Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 088102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ekimov E A, Sidorov1 V A, Bauer E D, Mel'nik N N, Curro N J, Thompson J D, Stishov1 S M 2004 Nature 428 542
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Prawer S, Uzan-Sanay C, Braunstein G 1993 Appl. Phys. Lett. 63 2502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jackson K, Pederson M R, Harrison J G 1990 Phys. Rev. B 41 12641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cao G Z, Driessen F A J M, Bauhuis C J 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 3125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gong C S, Li S S, Zhang H R, Su T C, Hu M H, Ma H A, Jia X P, Li Y 2017 Int. J. Refract. Metals and Hard Mater. 66 116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yan B M, Jia X P, Sun S S, Zhou Z X, Fang C, Chen N, Li Y D, Li Y, Ma H A 2015 Int. J Refract. Metals and Hard Mater. 48 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fang C, Jia X P, Sun S S, Yan B M, Li Y D, Chen N, Li Y, Ma H A 2016 High Pressure Res. 36 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Katayama Yoshida H, Nishimatsu T, Yamamoto T, Orita N 2001 J. Phys.: Cond. Matter 13 8901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li Y, Jia X P, Ma H A, Zhang J, Wang F B, Chen N, Feng Y G 2014 CrystEngComm 16 7547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 肖宏宇, 秦玉琨, 隋永明, 梁中翥, 刘利娜, 张永胜 2016 65 070705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao H Y, Qin Y K, Sui Y M, Liang Z Z, Liu L N, Zhang Y S, 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 070705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 秦杰明, 张莹, 曹建明, 田立飞, 董中伟, 李岳 2011 60 036105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qin J M, Zhang Y, Cao J M, Tian L F, Dong Z W, Li Y 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 036105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sumiya H, Toda N, Nishibayashi Y, Satoh S 1997 J. Crystal Growth 178 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liang Z Z, Jia X P, Ma H A, Zang C Y, Zhu P W, Guan Q F, Kanda H 2005 Diamond Relat. Mater. 14 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma L Q, Ma H A, Xiao H Y, Li S S, Li Y, Jia X P 2010 Chin. Sci. Bull. 55 677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang J Q, Ma H A, Jiang Y P, Liang Z Z, Tian Y, Jia X P 2007 Diamond Relat. Mater. 16 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李勇, 李宗宝, 宋谋胜, 王应, 贾晓鹏, 马红安 2016 65 118103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Li Z B, Song M S, Wang Y, Jia X P, Ma H A 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 118103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王应, 李勇, 李宗宝 2016 65 087101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Li Y, Li Z B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 087101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
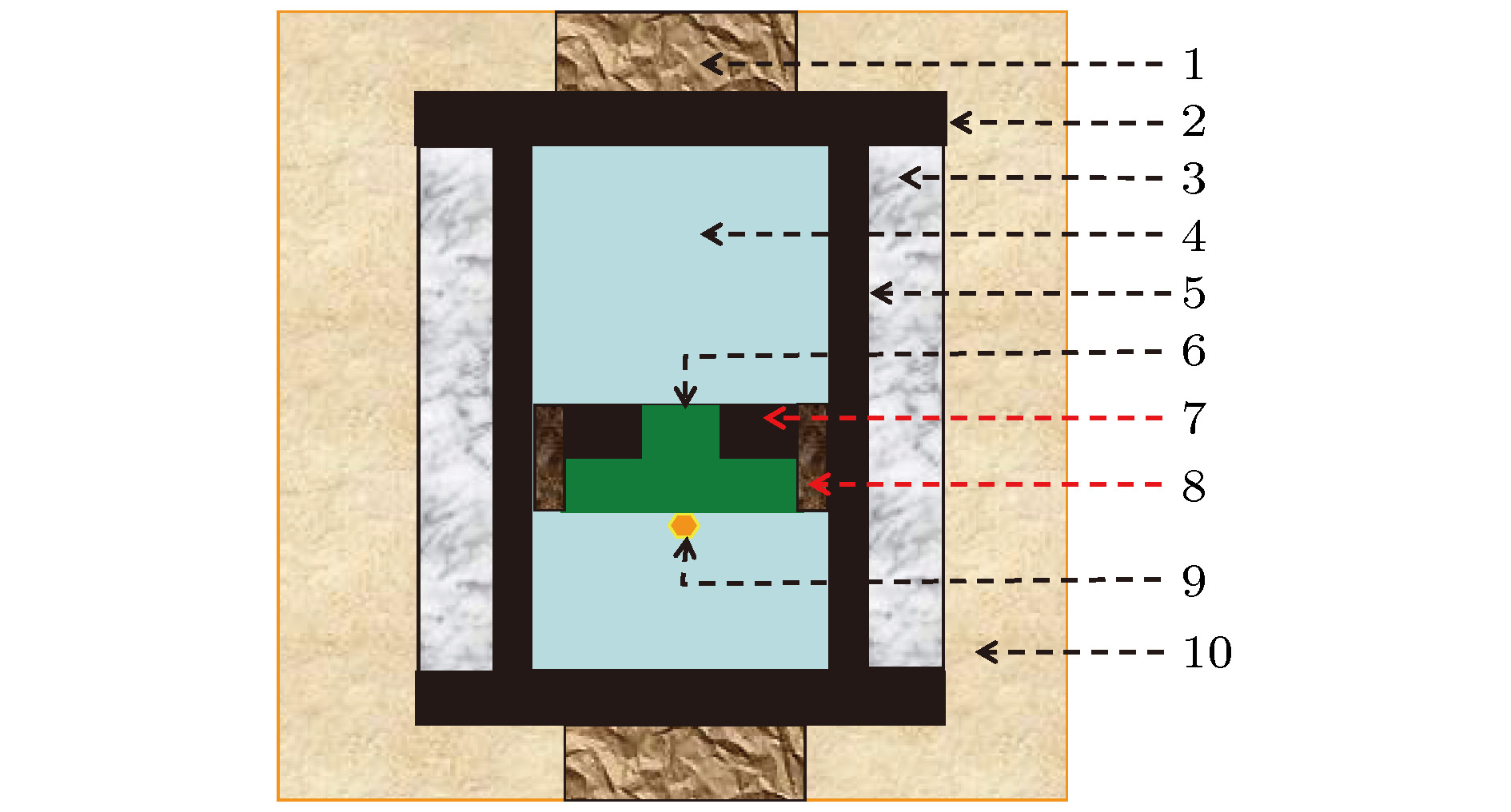
图 1 金刚石合成腔体示意图(1, 钢帽; 2, 石墨片; 3, 氯化钠管; 4, 陶瓷堵头; 5, 石墨加热管; 6, 触媒; 7, 碳源; 8, 绝缘管; 9, 晶种; 10, 叶蜡石)
Fig. 1. Schematic of the cell for diamond synthesis (1, conductive ring; 2, graphite sheet; 3, NaCl tube; 4, ceramic cylinder and cover; 5, graphite heater; 6, catalyst; 7, carbon source; 8, insulation tube; 9, seed crystal; 10, pyrophyllite).
表 1 金刚石合成参数
Table 1. Parameters of the synthetic experiments of diamond performed at 6.5 GPa in the FeNiMnCo-C system.
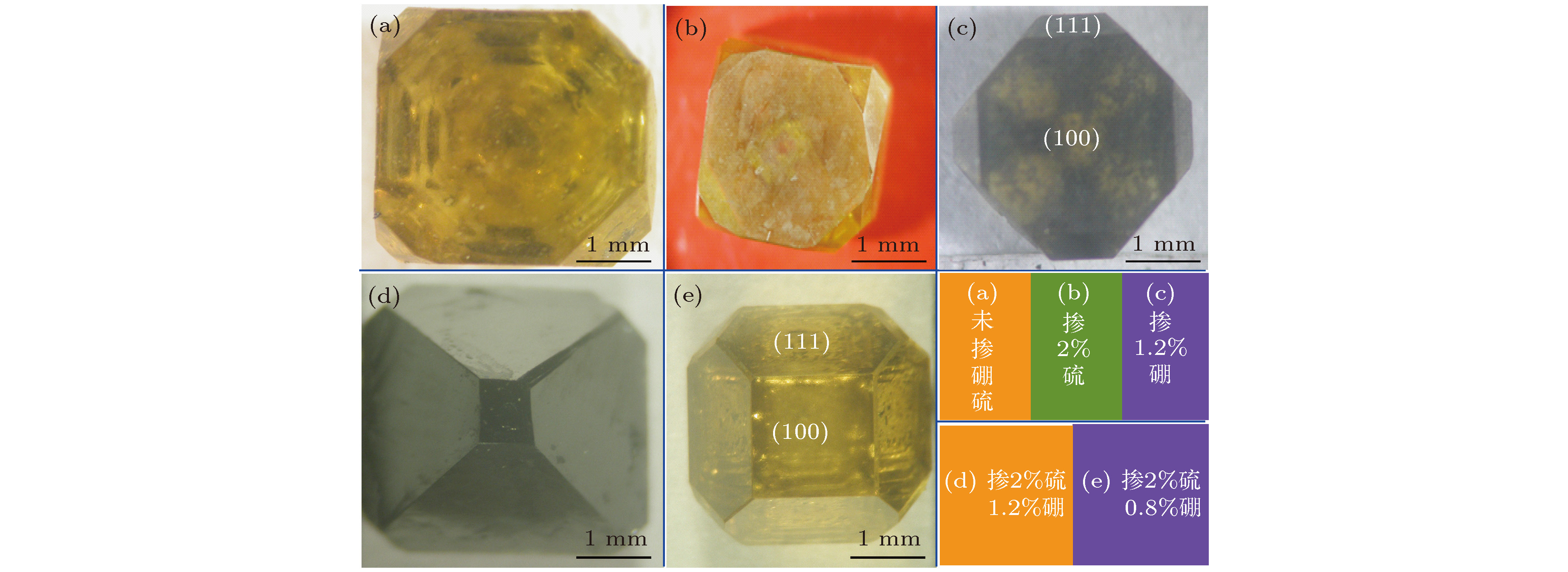
Sample B/% S/% 温度/℃ 颜色 (a) — — 1280 黄色 (b) — 2.0 1280 黄色 (c) 1.2 — 1280 黄黑色 (d) 1.2 2.0 1300 黑色 (e) 0.8 2.0 1290 黄色 表 2 金刚石样品的电学性能参数((a)未添加硼与硫, (b)添加2.0%硫, (c)添加1.2%硼, (d)添加1.2%硼和2.0%硫, (e)添加0.8%硼和2.0 %硫)
Table 2. Electrical performance parameters of the diamond samples measured at room temperature ((a) without B or S additives, (b) with 2.0 wt.% S additive, (c) with 1.2% B additive, (d) with 1.2% B and 2.0% S additives, (e) with 0.8% B and 2.0% S additives).
Sample 电阻率/Ω·cm 载流子浓度/cm–3 迁移率/cm–2·V–1·s–1 Hall系数 (a) > 108 — — — (b) 4.417 × 106 5.383 × 109 262.853 –1.151 × 109 (c) 3.665 × 103 1.364 × 1016 12.5 4.586 × 104 (d) 8.510 6.652 × 1014 760.870 6.475 × 103 (e) 1.262 × 106 8.738 × 1010 56.680 –7.153 × 107 -
[1] 王君卓, 李尚升, 宿太超, 胡美华, 胡强, 吴玉敏, 王健康, 韩飞, 于昆鹏, 高广进, 郭明明, 贾晓鹏, 马红安, 肖宏宇 2018 67 168101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J Z, Li S S, Su T C, Hu M H, Hu Q, Wu Y M, Wang J K, Han F, Yu K P, Gao G J, Guo M M, Jia X P, Ma H A, Xiao H Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 168101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘银娟, 贺端威, 王培, 唐明君, 许超, 王文丹, 刘进, 刘国端, 寇自力 2017 66 038103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y J, He D W, Wang P, Tang M J, Xu C, Wang W D, Liu J, Liu G D, Kou Z L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 038103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li Y, Zhou Z X, Guan X M, Li S S, Wang Y, Jia X P, Ma H A 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 028101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Banerjee A, Bernoulli D, Zhang H T, Yuen M F, Liu J B, Dong J C, Ding F, Lu J, Dao M, Zhang W J, Lu Y, Suresh S 2018 Science 360 300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang J K, Li S S, Jiang Q W, Song Y L, Yu K P, Han F, Su T C, Hu M H, H Q, Ma H A, Jia X P, Xiao H Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 088102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ekimov E A, Sidorov1 V A, Bauer E D, Mel'nik N N, Curro N J, Thompson J D, Stishov1 S M 2004 Nature 428 542
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Prawer S, Uzan-Sanay C, Braunstein G 1993 Appl. Phys. Lett. 63 2502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jackson K, Pederson M R, Harrison J G 1990 Phys. Rev. B 41 12641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cao G Z, Driessen F A J M, Bauhuis C J 1995 J. Appl. Phys. 78 3125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gong C S, Li S S, Zhang H R, Su T C, Hu M H, Ma H A, Jia X P, Li Y 2017 Int. J. Refract. Metals and Hard Mater. 66 116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yan B M, Jia X P, Sun S S, Zhou Z X, Fang C, Chen N, Li Y D, Li Y, Ma H A 2015 Int. J Refract. Metals and Hard Mater. 48 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fang C, Jia X P, Sun S S, Yan B M, Li Y D, Chen N, Li Y, Ma H A 2016 High Pressure Res. 36 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Katayama Yoshida H, Nishimatsu T, Yamamoto T, Orita N 2001 J. Phys.: Cond. Matter 13 8901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li Y, Jia X P, Ma H A, Zhang J, Wang F B, Chen N, Feng Y G 2014 CrystEngComm 16 7547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 肖宏宇, 秦玉琨, 隋永明, 梁中翥, 刘利娜, 张永胜 2016 65 070705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao H Y, Qin Y K, Sui Y M, Liang Z Z, Liu L N, Zhang Y S, 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 070705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 秦杰明, 张莹, 曹建明, 田立飞, 董中伟, 李岳 2011 60 036105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qin J M, Zhang Y, Cao J M, Tian L F, Dong Z W, Li Y 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 036105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sumiya H, Toda N, Nishibayashi Y, Satoh S 1997 J. Crystal Growth 178 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liang Z Z, Jia X P, Ma H A, Zang C Y, Zhu P W, Guan Q F, Kanda H 2005 Diamond Relat. Mater. 14 1932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma L Q, Ma H A, Xiao H Y, Li S S, Li Y, Jia X P 2010 Chin. Sci. Bull. 55 677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang J Q, Ma H A, Jiang Y P, Liang Z Z, Tian Y, Jia X P 2007 Diamond Relat. Mater. 16 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李勇, 李宗宝, 宋谋胜, 王应, 贾晓鹏, 马红安 2016 65 118103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Li Z B, Song M S, Wang Y, Jia X P, Ma H A 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 118103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 王应, 李勇, 李宗宝 2016 65 087101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Li Y, Li Z B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 087101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11441
- PDF下载量: 117
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: