-
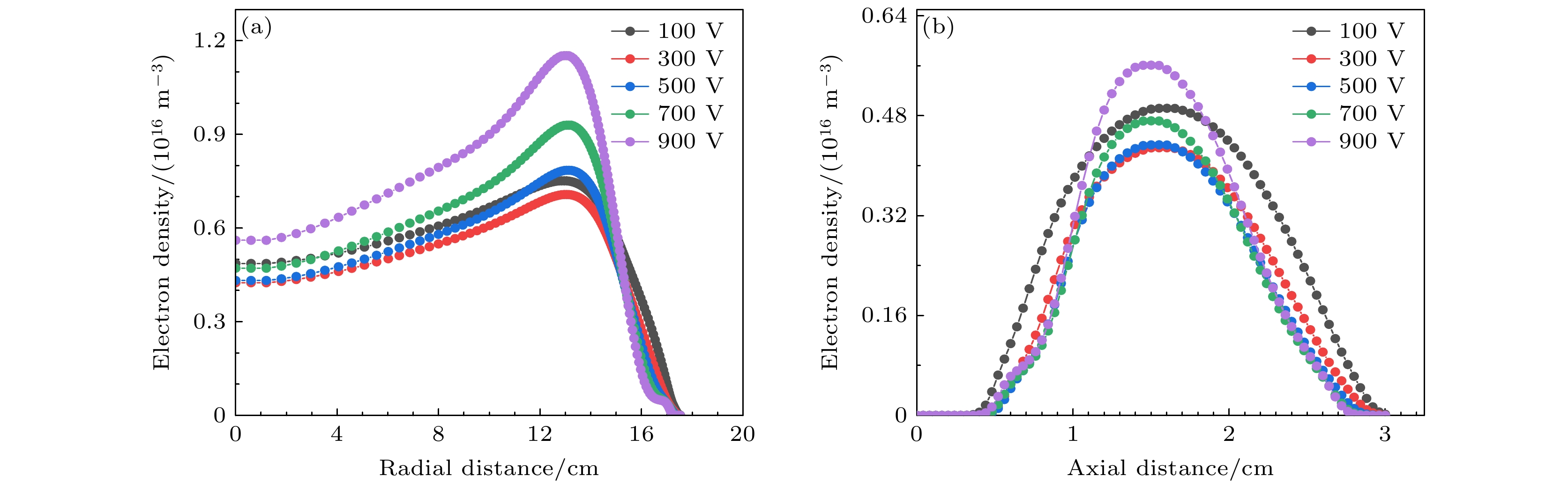
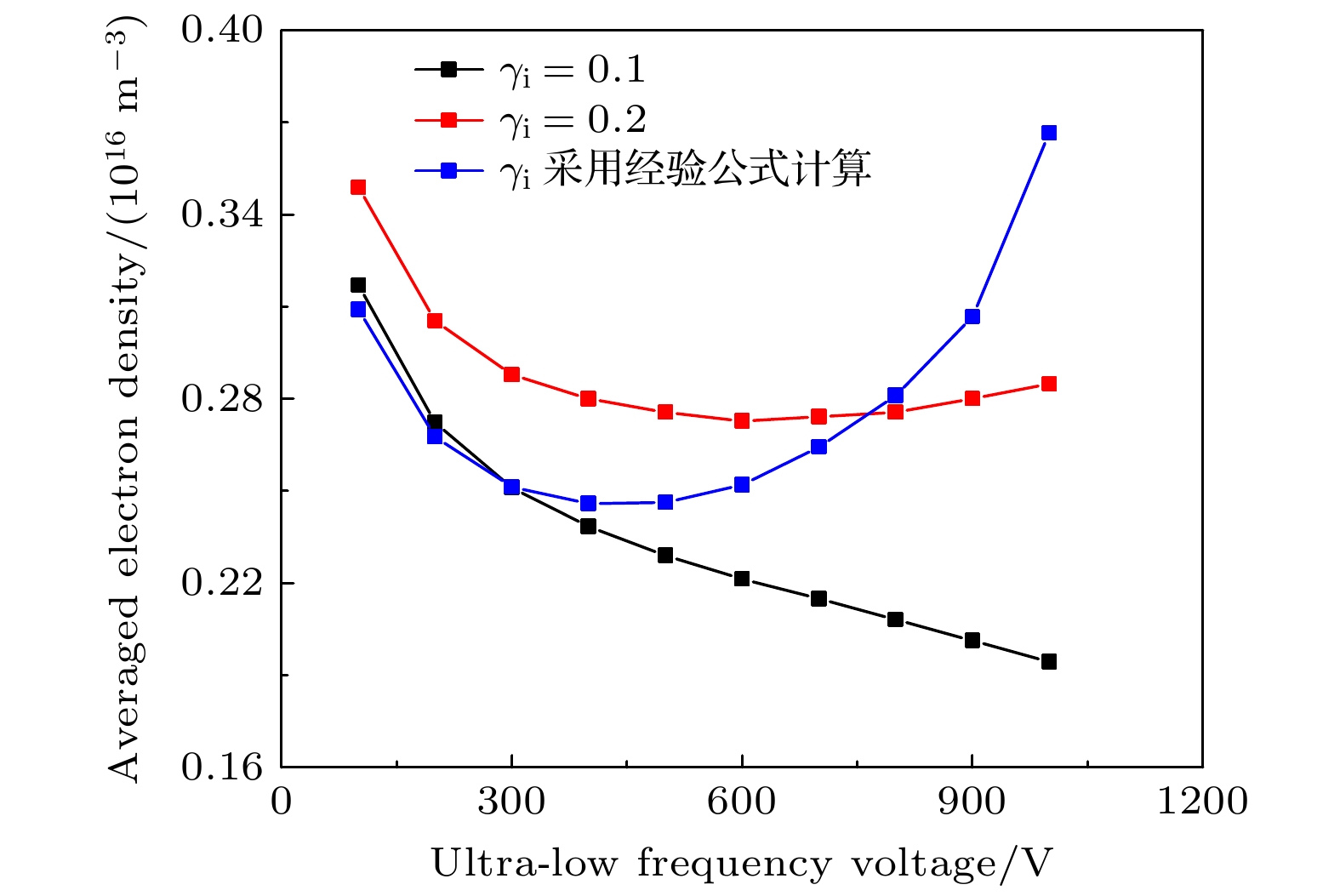
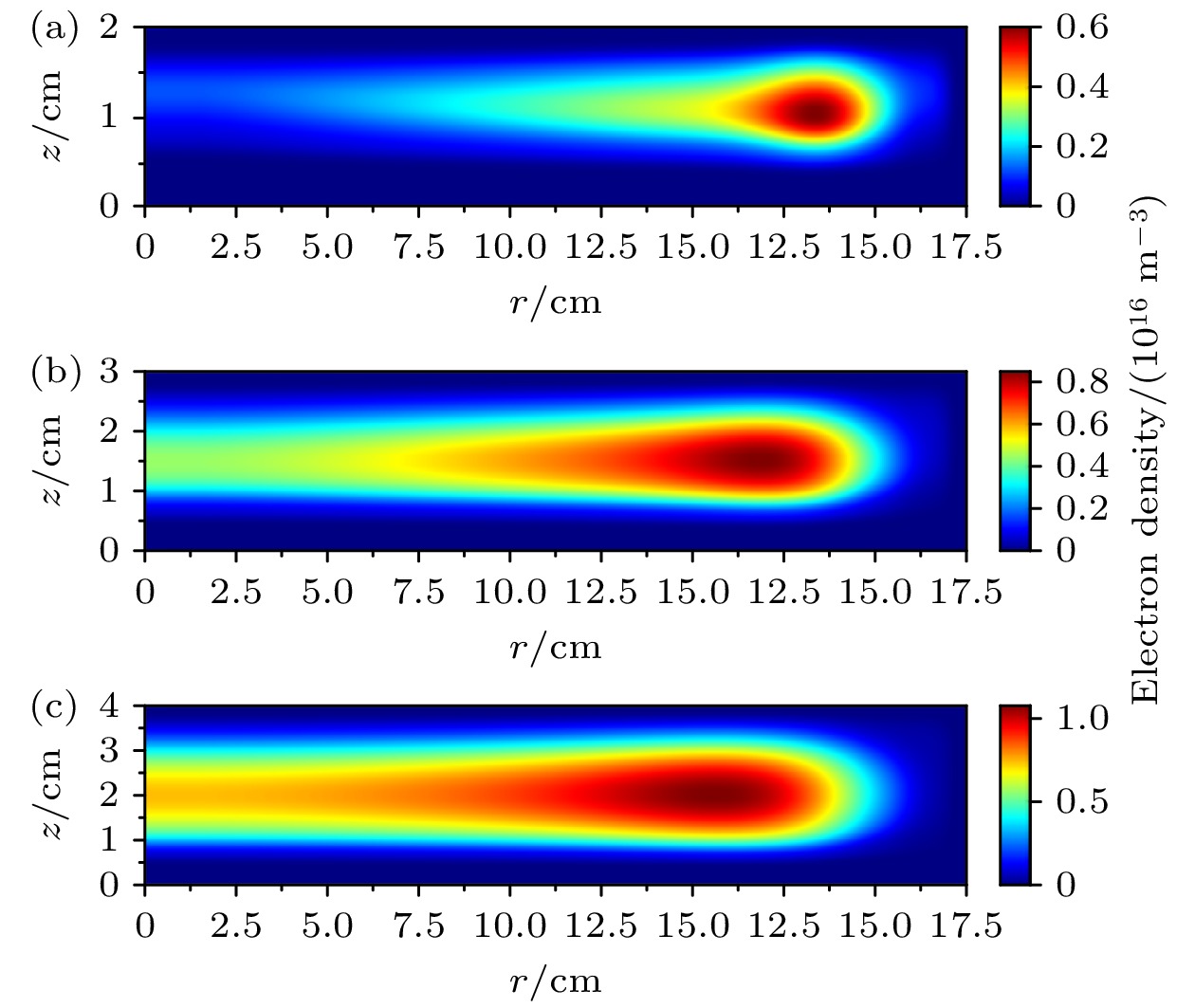
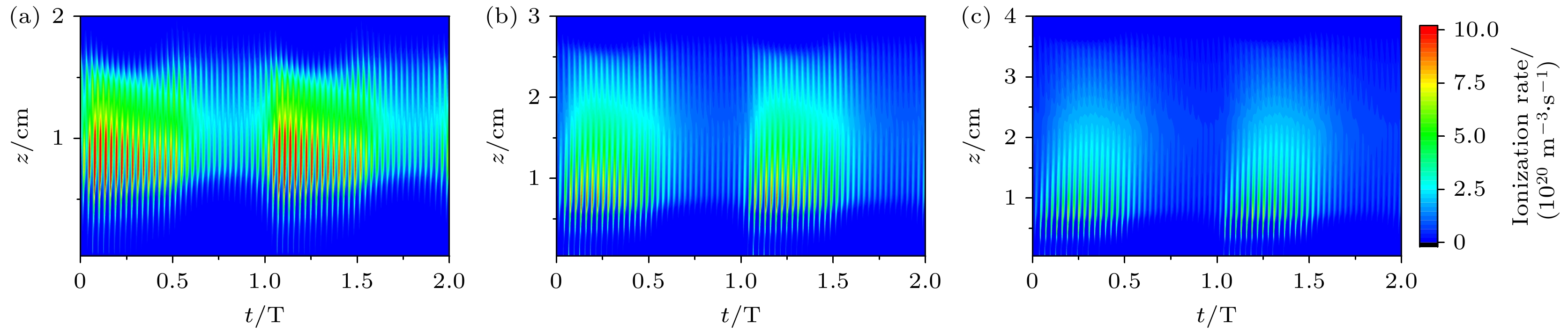
采用二维流体模型, 研究了不同的超低频电压、二次电子发射系数和极板间隙下, 二次电子对双频容性耦合等离子体特性的影响, 其中超低频源频率为400 kHz. 首先, 采用依赖离子能量的二次电子发射系数, 发现电子密度随超低频电压呈现出先降低后增高的趋势. 这是由于一方面, 较高的超低频电压会压缩有效放电体积; 另一方面, 极板发射的二次电子可以获得更多的能量, 进而增强电离过程. 通过与固定的二次电子发射系数的结果相比, 发现在较低的超低频电压下, 采用依赖能量的二次电子发射系数的结果接近于固定值为0.1的情况; 随着超低频电压的增加, 当采用依赖能量的发射系数时, 密度涨幅超过固定值为0.2的结果, 说明超低频电压对二次电子效应的增强效果并不是线性的. 最后, 对比了不同极板间隙下的等离子体特性, 发现随着极板间隙从2 cm增加到4 cm, 电离率的峰值有所下降, 但电子密度显著地增加, 等离子体的径向均匀性有所改善. 此外, 随着超低频电压的升高, 极板间隙对密度的影响越显著. 本文的研究结果有助于深入地理解超低频电源参数对于二次电子效应的影响, 并为等离子体工艺的优化提供一定的指导.In recent years, capacitively coupled plasmas driven by ultra-low frequency source have received increasing attention, because they are beneficial to generating ions with high energy and small scattering angle, which aligns well with the current trend in high aspect ratio etching. Since the sheath becomes thicker when an ultra-low frequency source is applied, the secondary electron emission becomes significant. Indeed, these energetic secondary electrons can enhance the ionization process and even affect the discharge mode. In this work, a two-dimensional fluid model is employed to study the influence of secondary electrons on the dual-frequency capacitively coupled plasma under different ultra-low frequency voltages, secondary electron emission coefficients and inter-electrode gaps. The high frequency is fixed at 13.6 MHz, and the ultra-low frequency is fixed at 400 kHz. First, by using the ion energy dependent secondary electron emission coefficient, it is shown that the electron density first decreases and then increases with ultra-low frequency voltage rising. This is because, on the one hand, the higher ultra-low frequency voltage leads to thicker sheath, and therefore, the effective discharge volume is compressed. On the other hand, secondary electrons emitted from electrodes can obtain more energy, thus enhancing the ionization process. By comparing with the results obtained with a fixed secondary electron emission coefficient, it is found that in the low voltage range, the evolution of the electron density is similar to that with a fixed coefficient of 0.1. While, in the high voltage range, the growth of the electron density is even more pronounced than that with a fixed coefficient of 0.2, indicating that the enhancement of the secondary electron effect by ultra-low frequency voltage is non-linear. Finally, the influence of discharge gap on the plasma properties is also discussed. It is shown that with the inter-electrode gap increasing from 2 to 4 cm, the maximum ionization rate becomes lower, but the electron density rises significantly, and the plasma radial uniformity is improved. When inter-electrode gap is large, secondary electrons can completely collide with neutral species, so their influence on the electron density at high ultra-low frequency voltage is more significant. The results obtained in this study contribute to understanding the influence of ultra-low frequency source on the secondary electron effect, and provide some guidance for optimizing plasma processing.
-
Keywords:
- capacitively coupled plasma /
- fluid model /
- ultra-low frequency power /
- secondary electron
[1] 戴忠玲, 毛明, 王友年 2006 物理 35 693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z L, Mao M, Wang Y N 2006 Physics 35 693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kim S S, Hamaguchi S, Yoon N S, Chang C S, Lee Y D, Ku S H 2001 Phys. Plasmas 8 1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 谭毅成, 伍尚华, 朱佐祥, 向其军, 朱祖云, 田卓 2018 人工晶体学报 47 1272
Tan Y C, Wu S H, Zhu Z X, Xiang Q J, Zhu Z Y, Tian Z 2018 J. Synth. Cryst. 47 1272
[4] Lieberman M A, Lichtenberg A J 2008 Principles of Plasma Discharges & Materials Processing 11 800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chabert P, Braithwaite N 2011 Physics of Radio-Frequency Plasmas (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[6] Lee J K, Manuilenko O V, Babaeva N Y, Kim H C, Shon J W 2005 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Han L, Kenney J, Rauf S, Korolov I, Schulze J 2023 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 32 115018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim H H, Shin J H, Lee H J 2023 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. , A 41 023004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y, Zhao K, Ma F F, Liu Y X, Gao F, Julian Schulze, Wang Y N 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 124 064102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Y, Zhao K, Ma F F, Sun J Y, Liu Y X, Gao F, Zhang Y R, Wang Y N 2025 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 34 035016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang J C, Tian P, Kenney J, Rauf S, Korolov I, Schulze J 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 075031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu J, Zhang Q Z, Liu Y X, Gao F, Wang Y N 2013 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46 235202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hartmann P, Korolov I, Escandon L J, Gennip W V, Buskes K, Schulze J 2022 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 31 055017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hartmann P, Wang L, Nosges K, Berger B, Wilczek S, Brinkmann R P, Mussenbrock T, Juhasz Z, Donko Z, Derzsi A, Lee E, Schulze J 2020 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 29 075014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu G H, Wang X Y, Liu Y X, Sun J Y, Wang Y N 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 064004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schulze J, Donko Z, Luggenholscher D, Czarnetzki U 2009 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18 034011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Takagi S, Chikata T, Sekine M 2021 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 60 SAAB07
[18] Donko Z, Schulze J, Hartmann P, Korolov I, Czarnetzki U, Schungel E 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 081501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schulze J, Donko Z, Schuengel E, Czarnetzki U 2011 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 20 045007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Saikia P, Bhuyan H, Yap S L, Escalona M, Favre M, Wyndham E, Schulze J 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 083505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张钰如, 高飞, 王友年 2021 70 095206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y R, Gao F, Wang Y N 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 095206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang Y R, Xiang X, Zhao S X, Bogaerts A, Wang Y N 2010 Phys. Plasma 17 113512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kurokawa M, Kitajima M, Toyoshima K, Kishino T 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 062717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] De Heer F J, Jansen R H J, Van Der Kaay W 1979 J. Phys. B: Atom. Mol. Phys. 12 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Tachibana K 1986 Phys. Rev. A 34 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rejoub R, Lindsay B G, Stebbings R F 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 042713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ali M A, Stone P M 2008 Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 271 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Phelps A V, Pitchford L C, Pedoussat C, Donko Z 1999 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 8 B1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Brinkmann R P 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 102 093303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Horvath B, Daksha M, Korolov I, Derzsi A, Schulze J 2017 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26 124001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Campanell M D, Khrabrov A V, Kaganovich I D 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 255001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Campanell M D 2013 Phys. Rev. E 88 033103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
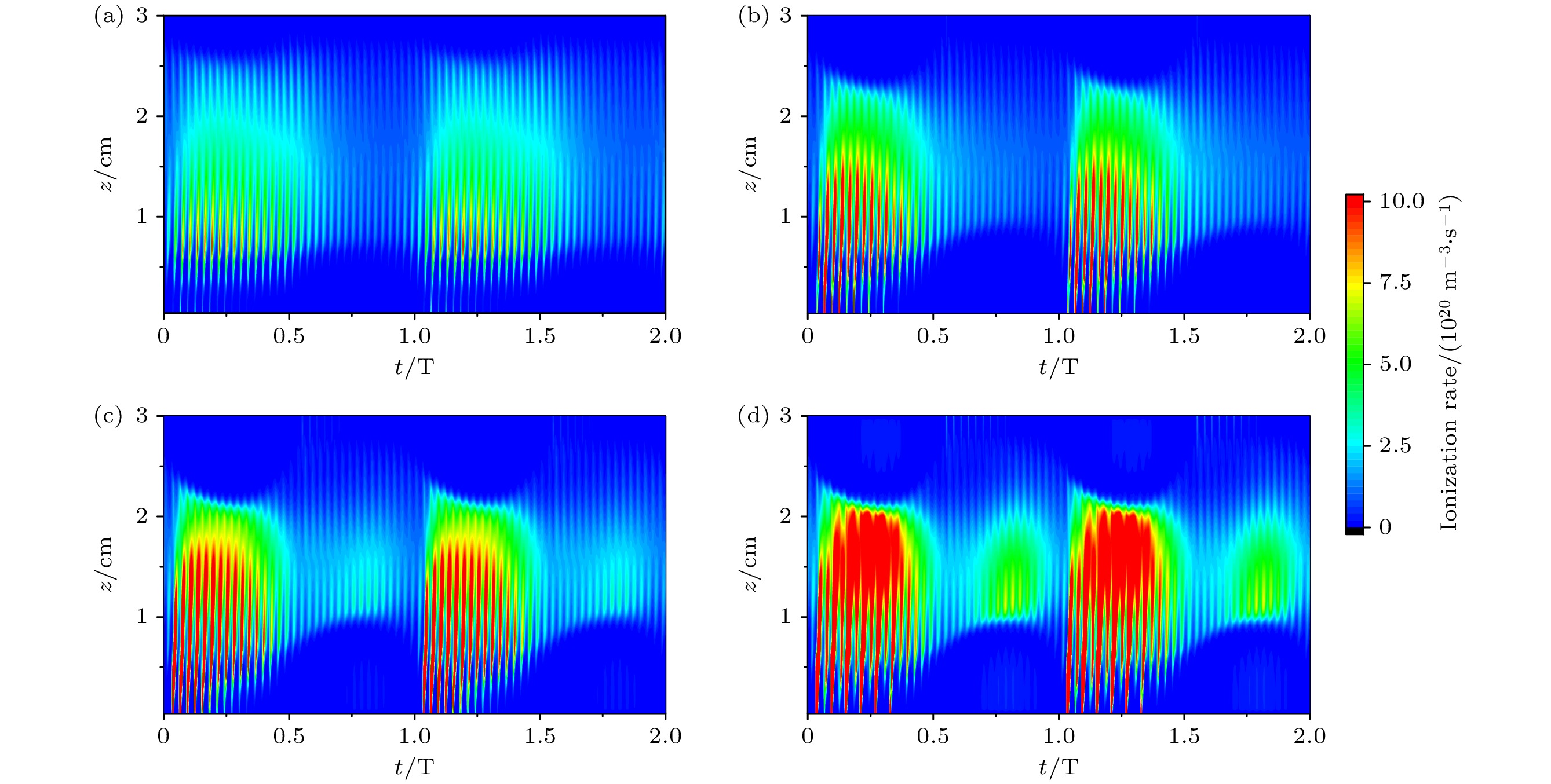
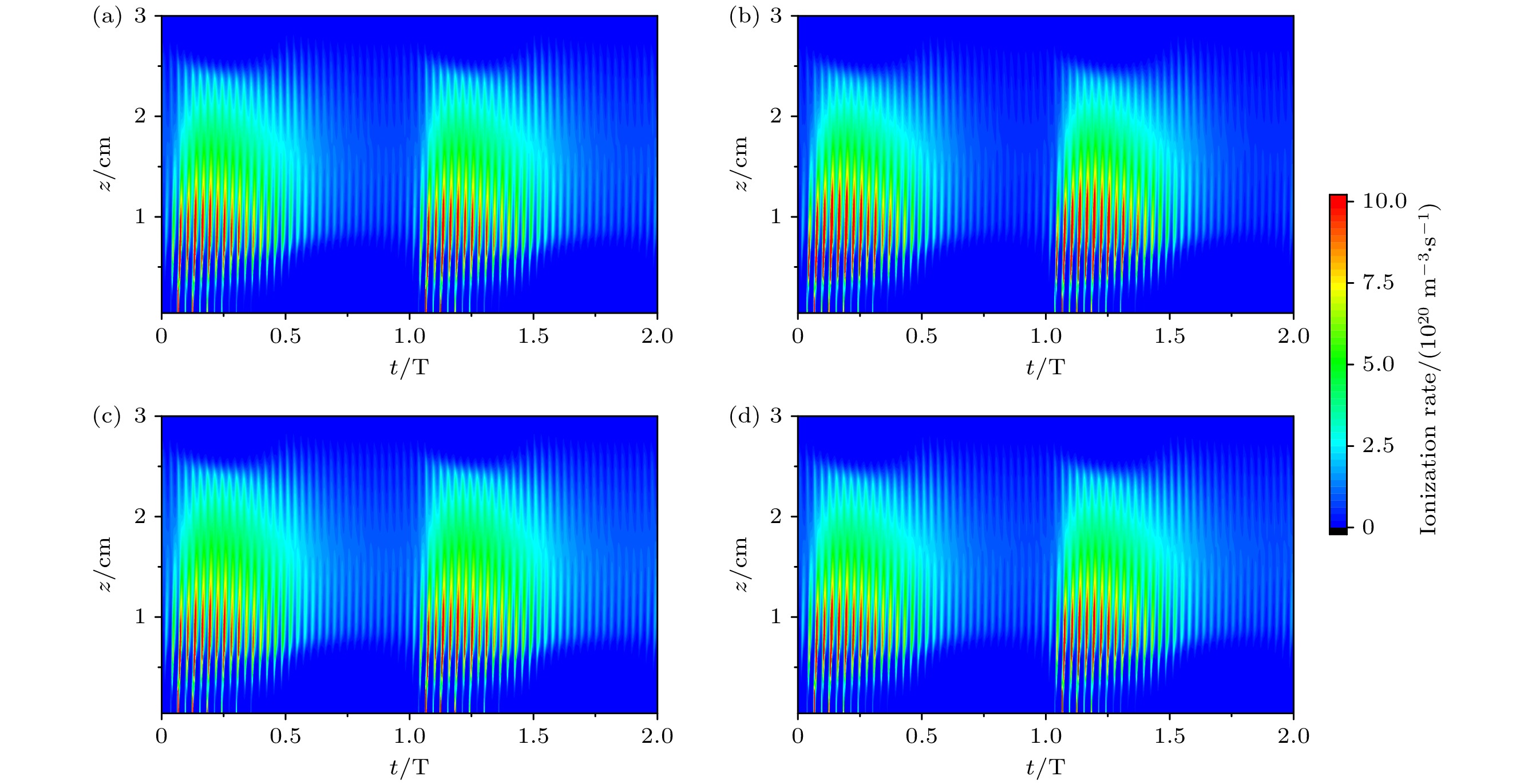
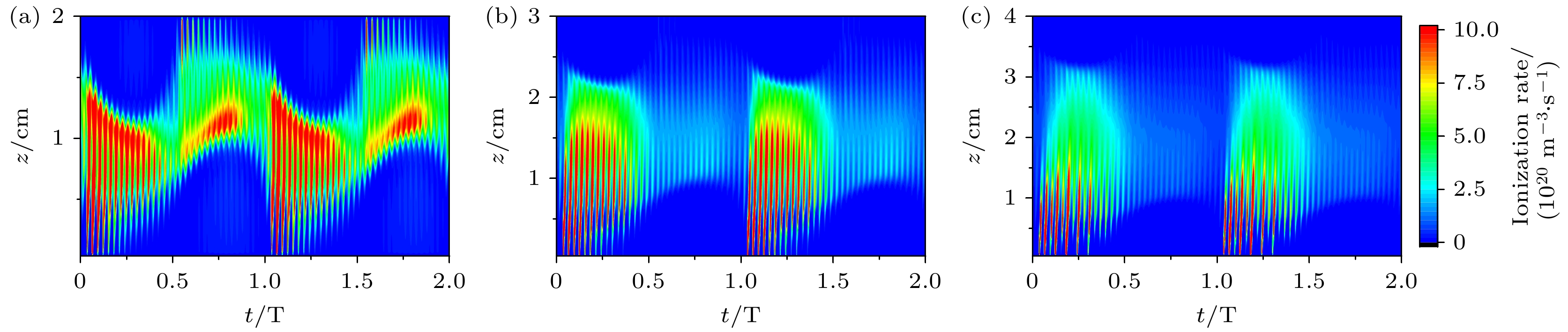
图 3 超低频电压不同时, 采用经验公式计算二次电子发射系数下, 腔室中心r = 0 cm处电离率的时空分布 (a) 100 V; (b) 400 V; (c) 700 V; (d) 1000 V
Fig. 3. Using empirical formula to calculate the temporal and spatial distribution of ionization rate at r = 0 cm in the center of the chamber under the secondary electron emission coefficient, ultra-low frequency: (a) 100 V; (b) 400 V; (c) 700 V; (d) 1000 V.
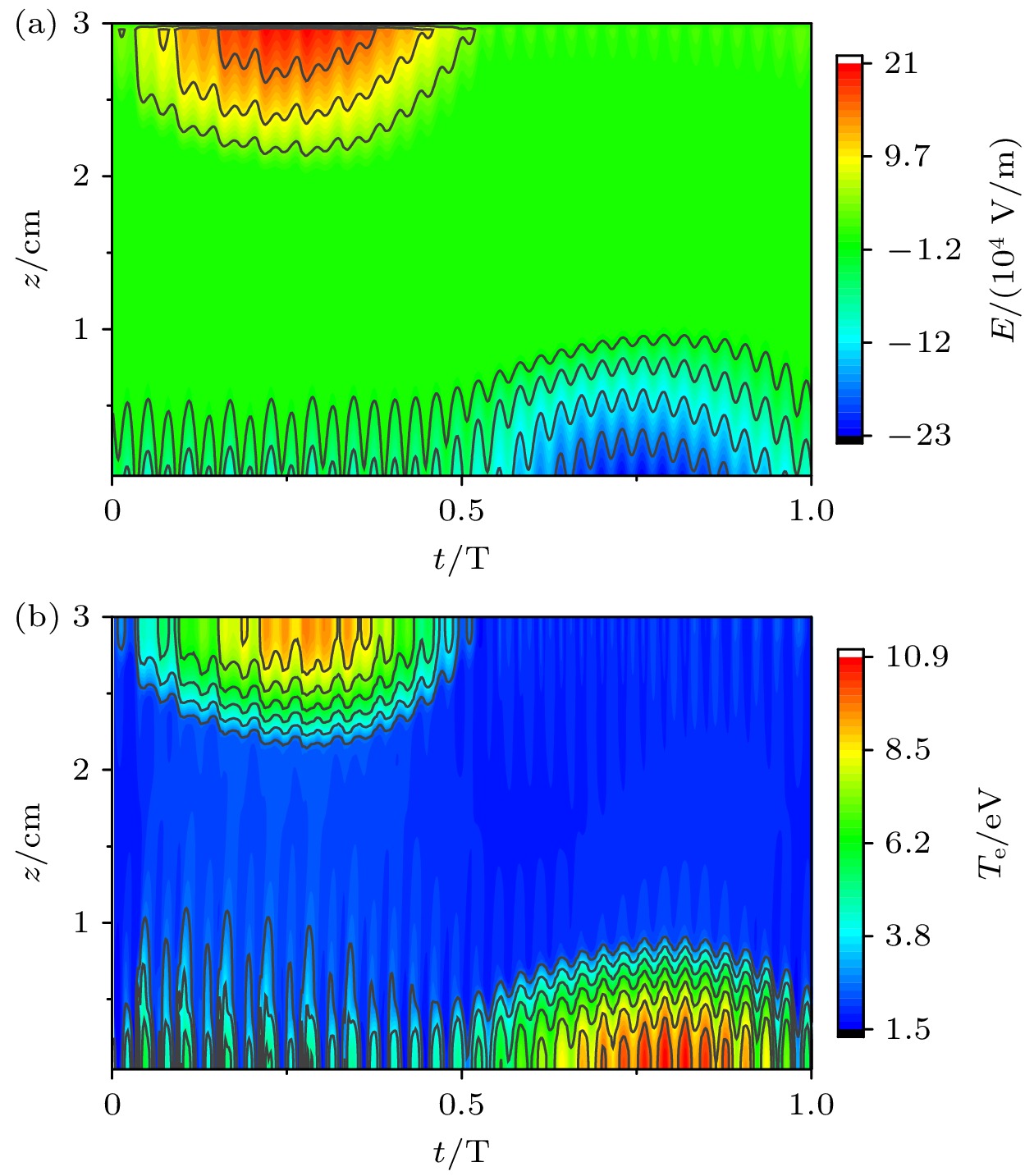
图 4 采用经验公式计算二次电子发射系数下, 超低频电压1000 V时, 腔室中心r = 0 cm处的(a)轴向电场和(b)电子温度的时空分布
Fig. 4. Using empirical formula to calculate the temporal and spatial distribution of (a) axial electric field and (b) electron temperature at the center of the chamber r = 0 cm at ultra-low frequency voltage of 1000 V under the secondary electron emission coefficient.
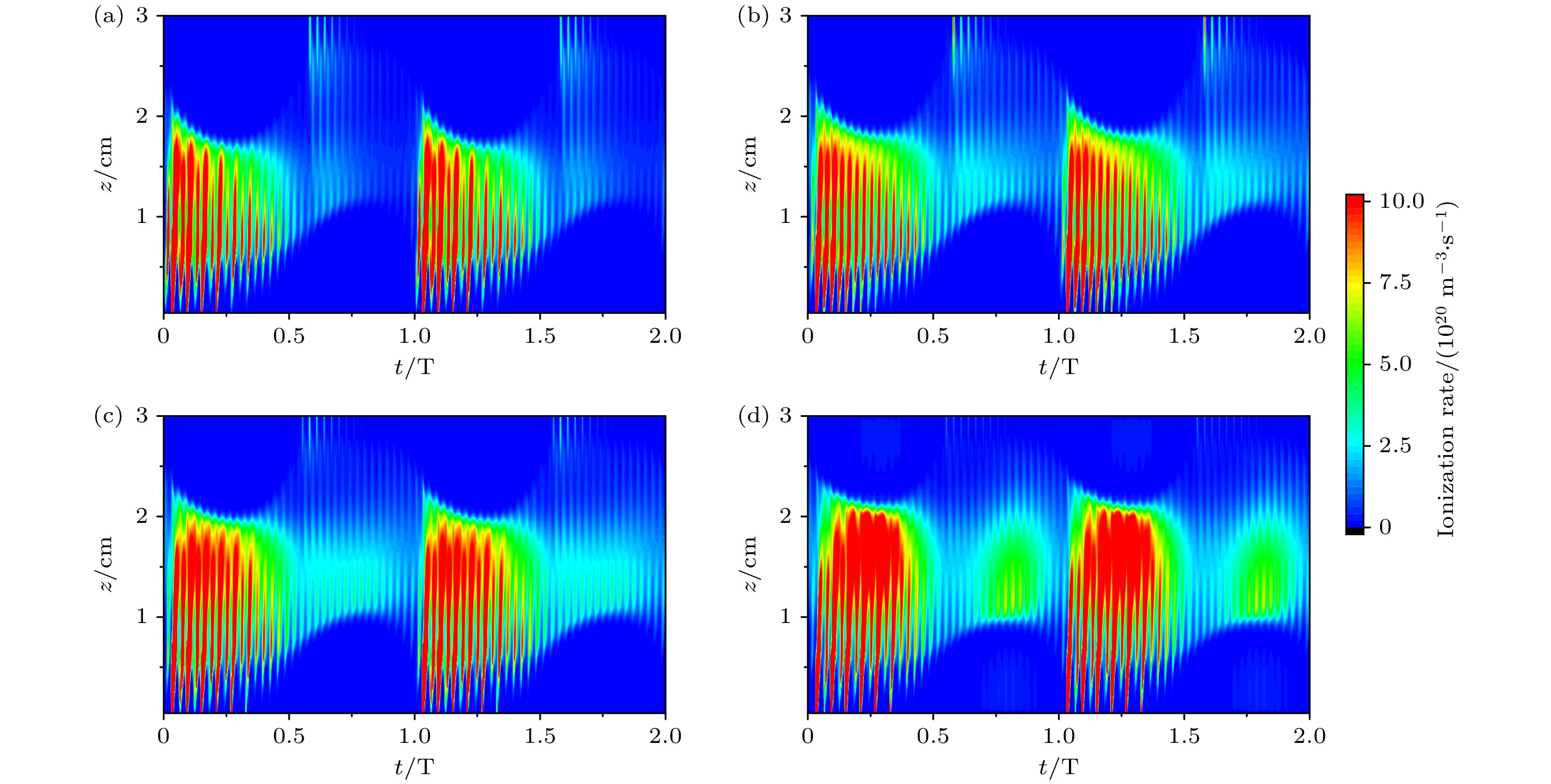
图 6 超低频电压为200 V时, 不同二次电子发射系数下, 电离率的时空分布 (a) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0; (b) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.1; (c) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.2; (d)采用经验公式计算$ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $
Fig. 6. Time and space distribution of ionization rate under different secondary electron emission coefficients at ultra-low frequency voltage of 200 V: (a) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0; (b) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.1; (c) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.2; (d) ${\gamma _{\mathrm{i}}} $ calculated by empirical formula.
图 7 超低频电压为1000 V时, 不同二次电子发射系数下, 电离率的时空分布 (a) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0; (b) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.1; (c) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.2; (d)采用经验公式计算$ {\gamma _{\mathrm{i}}} $
Fig. 7. Time and space distribution of ionization rate under different secondary electron emission coefficients at ultra-low frequency voltage of 1000 V: (a) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0; (b) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.1; (c) $ {\gamma _{\text{i}}} $ = 0.2; (d) $ {\gamma _{\mathrm{i}}}$ calculated by empirical formula.
表 1 Ar等离子体中的电子碰撞反应
Table 1. Electron collision reactions in Ar plasma.
-
[1] 戴忠玲, 毛明, 王友年 2006 物理 35 693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai Z L, Mao M, Wang Y N 2006 Physics 35 693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kim S S, Hamaguchi S, Yoon N S, Chang C S, Lee Y D, Ku S H 2001 Phys. Plasmas 8 1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 谭毅成, 伍尚华, 朱佐祥, 向其军, 朱祖云, 田卓 2018 人工晶体学报 47 1272
Tan Y C, Wu S H, Zhu Z X, Xiang Q J, Zhu Z Y, Tian Z 2018 J. Synth. Cryst. 47 1272
[4] Lieberman M A, Lichtenberg A J 2008 Principles of Plasma Discharges & Materials Processing 11 800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chabert P, Braithwaite N 2011 Physics of Radio-Frequency Plasmas (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[6] Lee J K, Manuilenko O V, Babaeva N Y, Kim H C, Shon J W 2005 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Han L, Kenney J, Rauf S, Korolov I, Schulze J 2023 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 32 115018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim H H, Shin J H, Lee H J 2023 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. , A 41 023004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y, Zhao K, Ma F F, Liu Y X, Gao F, Julian Schulze, Wang Y N 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 124 064102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Y, Zhao K, Ma F F, Sun J Y, Liu Y X, Gao F, Zhang Y R, Wang Y N 2025 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 34 035016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang J C, Tian P, Kenney J, Rauf S, Korolov I, Schulze J 2021 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30 075031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu J, Zhang Q Z, Liu Y X, Gao F, Wang Y N 2013 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46 235202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hartmann P, Korolov I, Escandon L J, Gennip W V, Buskes K, Schulze J 2022 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 31 055017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hartmann P, Wang L, Nosges K, Berger B, Wilczek S, Brinkmann R P, Mussenbrock T, Juhasz Z, Donko Z, Derzsi A, Lee E, Schulze J 2020 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 29 075014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu G H, Wang X Y, Liu Y X, Sun J Y, Wang Y N 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 064004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schulze J, Donko Z, Luggenholscher D, Czarnetzki U 2009 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18 034011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Takagi S, Chikata T, Sekine M 2021 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 60 SAAB07
[18] Donko Z, Schulze J, Hartmann P, Korolov I, Czarnetzki U, Schungel E 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 081501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schulze J, Donko Z, Schuengel E, Czarnetzki U 2011 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 20 045007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Saikia P, Bhuyan H, Yap S L, Escalona M, Favre M, Wyndham E, Schulze J 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 083505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张钰如, 高飞, 王友年 2021 70 095206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y R, Gao F, Wang Y N 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 095206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang Y R, Xiang X, Zhao S X, Bogaerts A, Wang Y N 2010 Phys. Plasma 17 113512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kurokawa M, Kitajima M, Toyoshima K, Kishino T 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 062717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] De Heer F J, Jansen R H J, Van Der Kaay W 1979 J. Phys. B: Atom. Mol. Phys. 12 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Tachibana K 1986 Phys. Rev. A 34 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rejoub R, Lindsay B G, Stebbings R F 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 042713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ali M A, Stone P M 2008 Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 271 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Phelps A V, Pitchford L C, Pedoussat C, Donko Z 1999 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 8 B1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Brinkmann R P 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 102 093303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Horvath B, Daksha M, Korolov I, Derzsi A, Schulze J 2017 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26 124001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Campanell M D, Khrabrov A V, Kaganovich I D 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 255001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Campanell M D 2013 Phys. Rev. E 88 033103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 798
- PDF下载量: 40
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: