-
基于自旋-轨道耦合玻色凝聚体, 提出了一种凝聚体的自旋频谱对外场调控参数的动力学响应效应. 该效应由对凝聚体的快速晃动和外加的迅变塞曼场来驱动. 研究发现, 自旋频谱的谱峰对外场驱动参数呈现出简单的线性关系. 通过对模型作适当近似和简化, 本文给出了该线性关系的解析关系式. 同时, 基于Gross-Pitaevskii方程对系统的动力学演化做了数值计算, 数值结果与解析表达式符合得很好. 另外, 本文还进一步探究了自旋频谱对外场驱动响应的物理本质, 发现该效应来源于不同自旋-轨道态之间的量子干涉, 可以利用量子多臂干涉仪的图像来理解其内涵. 文章的最后对方案的实验可行性及相关参数进行了讨论与估计. 本文的结果在量子控制和量子计量学等领域有潜在价值.Dynamical characteristics of internal and external states of a Bose-Einstein condensate are generally different and independent, thus requiring different experimental manipulation techniques. The spin-orbit coupling recently achieved in Bose-Einstein condensates essentially connects spin and motion degree of freedom, endowing spin states with the ability to respond to orbital manipulation, and vice versa. In this work, a dynamical response effect, induced by simultaneously manipulating the internal and external states of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensate, is predicted. Here, the “simultaneously manipulating the internal and external states” means that the driving field combines the Zeeman field applied to the internal state of the atom and the orbital potential affecting the external states of the atom. Specifically, the Bose-Einstein condensate is assumed to be activated by an abruptly applied Zeeman field and a sudden shake of the trapping potential. After some reasonable simplification and approximation of the model (i.e. neglecting the inter-atomic interactions and modelling the shake of the trapping potential by a short time-dependent pulse), an analytical relationship connecting spin frequency spectrum and the parameters of the driving fields is derived. The numerical calculations based on directly integrating the Gross-Pitaevskii equation are in good agreement with the results from the analytical relationship. The physical origin of the predicted spin dynamical response can be traced back to the quantum interference among different spin-orbit states. Due to the fact that a series of characteristic parameters of the condensate can be manifested in the spin frequency spectrum, the dynamical response effect predicted here provides a candidate method for determining and calibrating various system parameters by measuring the spin frequency spectrum.
-
Keywords:
- Bose-Einstein condensate /
- spin-orbit coupling /
- ultracold quantum gases /
- spin frequency spectrum
[1] Chu S 1998 Rev. Mod. Phys. 70 685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bloch I, Dalibard J, Zwerger W 2008 Rev. Mod. Phys. 80 885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dalibard J, Gerbier F, Juzeliūnas G, Öhberg P 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 1523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qiu X Z, Zoller P, Li X P 2020 PRX Quantum 1 020311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jayaseelan M, Manikandan S K, Jordan A N, Bigelow N P 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 1847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kaufman A M, Ni K K 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 1324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Davis K B, Mewes M O, Andrews M R, van Druten N J, Durfee D S, Kurn D M, Ketterle W 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 3969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Anderson M H, Ensher J R, Matthewa M R, Wieman C E, Cornell E A 1995 Science 269 198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Pitaevskii L, Stringari S 2016 Bose-Einstein Condensation and Superfluidity (Oxford: Oxford University Press
[10] Jie J W, Guan Q, Blume D 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 043606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jie J W, Guan Q, Zhong S, Schwettmann A, Blume D 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 023324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jie J W, Zhong S, Zhang Q, Morgenstern I, Ooi H G, Guan Q, Bhagat A, Nematollahi D, Schwettmann A, and Blume D 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 053309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang Y X, Zhang Y B, Lu R, Wang X G, Yi S 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 043625
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xing H, Wang A, Tan Q S, Zhang W, Yi S 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 043615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lewenstein M, Sanpera A, Ahufinger V 2012 Ultracold Atoms in Optical Lattices: Simulating Quantum Many-body Systems (Oxford: Oxford University Press
[16] Lin Y J, Jiménez-García K, Spielman I B 2011 Nature 471 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang C, Gao C, Jian C M, Zhai H 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 160403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sinha S, Nath R, Santos L 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 270401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu H, Ramachandhran B, Pu H, Liu X J 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 010402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pan J S, Zhang W, Yi W, Guo G C 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 043619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li J R, Lee J, Huang W, Burchesky S, Shteynas B, Top F C, Jamison A O, and Ketterle W 2017 Nature 543 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liao R Y 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 140403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Campbell D L, Price R M, Putra A, Valdés-Curiel A, Trypogeorgos D, Spielman I B 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Vaishnav J Y, Clark C W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 153002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang Y P, Mao L, Zhang C W 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 035302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang Y P, Chen G, Zhang C W 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 1937
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang J Y, Ji S C, Chen Z, Zhang L, Du Z D, Yan B, Pan G S, Zhao B, Deng Y J, Zhai H, Chen S, Pan J W 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 115301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Qu C L, Hamner C, Gong M, Zhang C W, Engels P 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 021604(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hamner C, Qu C, Zhang Y, Chang J, Gong M, Zhang C, Engels P 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Khamehchi M A, Hossain K, Mossman M E, Zhang Y, Busch T, Forbes M M, Engels P 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 155301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wu C H, Fan J T, Chen J, Jia S T 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 013617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fan G, Chen X L, Zou P 2022 Front. Phys. 17 52502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Bednarek S, Szumniak P, Szafran B 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 235319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Pawlowski J, Szumniak P, Skubis A, Bednarek S 2014 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 26 345302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Golovach V N, Borhani M, Loss D 2006 Phys. Rev. B 74 165319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Li R, You J Q, Sun C P, Nori F 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 086805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Widera A, Gerbier F, Fölling S, Gericke T, Mandel O, Bloch I 2006 New. J. Phys. 8 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Ho T L 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 742
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Grossmann F 2008 Theoretical Femtosecond Physics: Atoms and Molecules in Strong Laser Fields (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer
[40] Baudon J, Mathevet R, Robert J 1999 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 32 R173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Shevchenko S N, Ashhab S, Nori F 2010 Phys. Rep. 492 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Li Y Q, Feng G S, Xu R D, Wang X F, Wu J Z, Chen G, Dai X C, Ma J, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 053604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
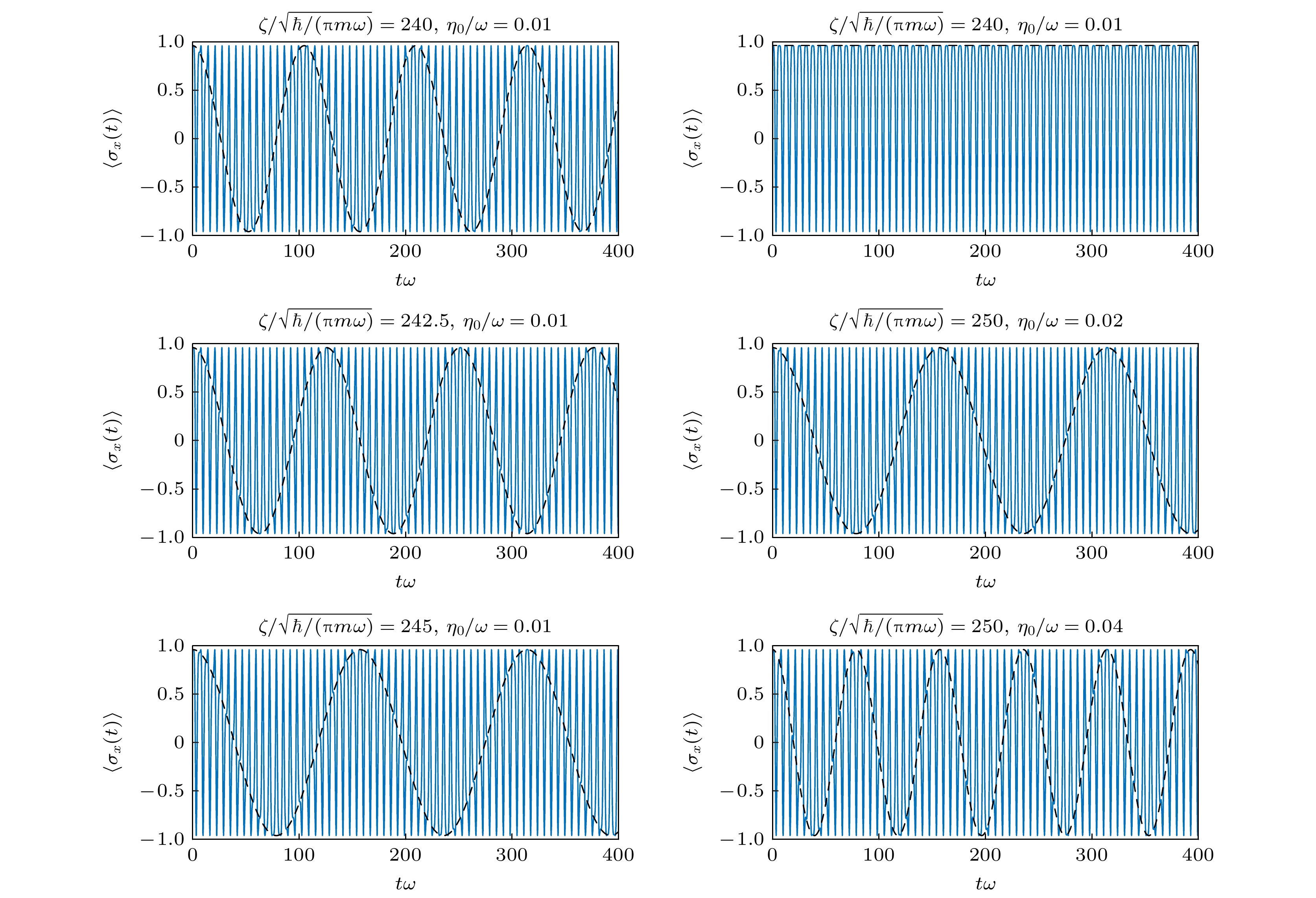
图 2 $ \left\langle {{\sigma _x}(t)} \right\rangle $在不同驱动参数下以$ \left| {\varPsi (0)} \right\rangle = \left( {\left| {{\chi _ + }(0)} \right\rangle \left| + \right\rangle + \left| {{\chi _ - }(0)} \right\rangle \left| - \right\rangle } \right)/\sqrt 2 $为初态随时间的演化, 其他参数固定为$ \alpha = 0.2\sqrt {\hbar \omega /m} , $$ \tau = 0.01/\omega , \;\;\varOmega = 0 $
Fig. 2. Time evolution of $ \left\langle {{\sigma _x}(t)} \right\rangle $ under the initial state $ \left| {\varPsi (0)} \right\rangle = \left( {\left| {{\chi _ + }(0)} \right\rangle \left| + \right\rangle + \left| {{\chi _ - }(0)} \right\rangle \left| - \right\rangle } \right)/\sqrt 2 $ for different driving parameters. The other parameters are set by $ \alpha = 0.2\sqrt {\hbar \omega /m} , \, \, \tau = 0.01/\omega , \;\;\varOmega = 0 $.
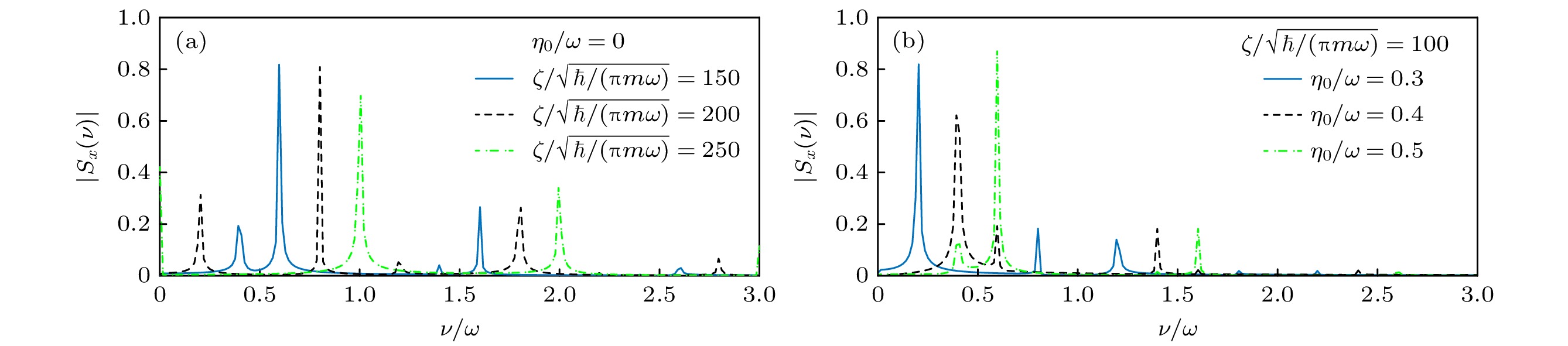
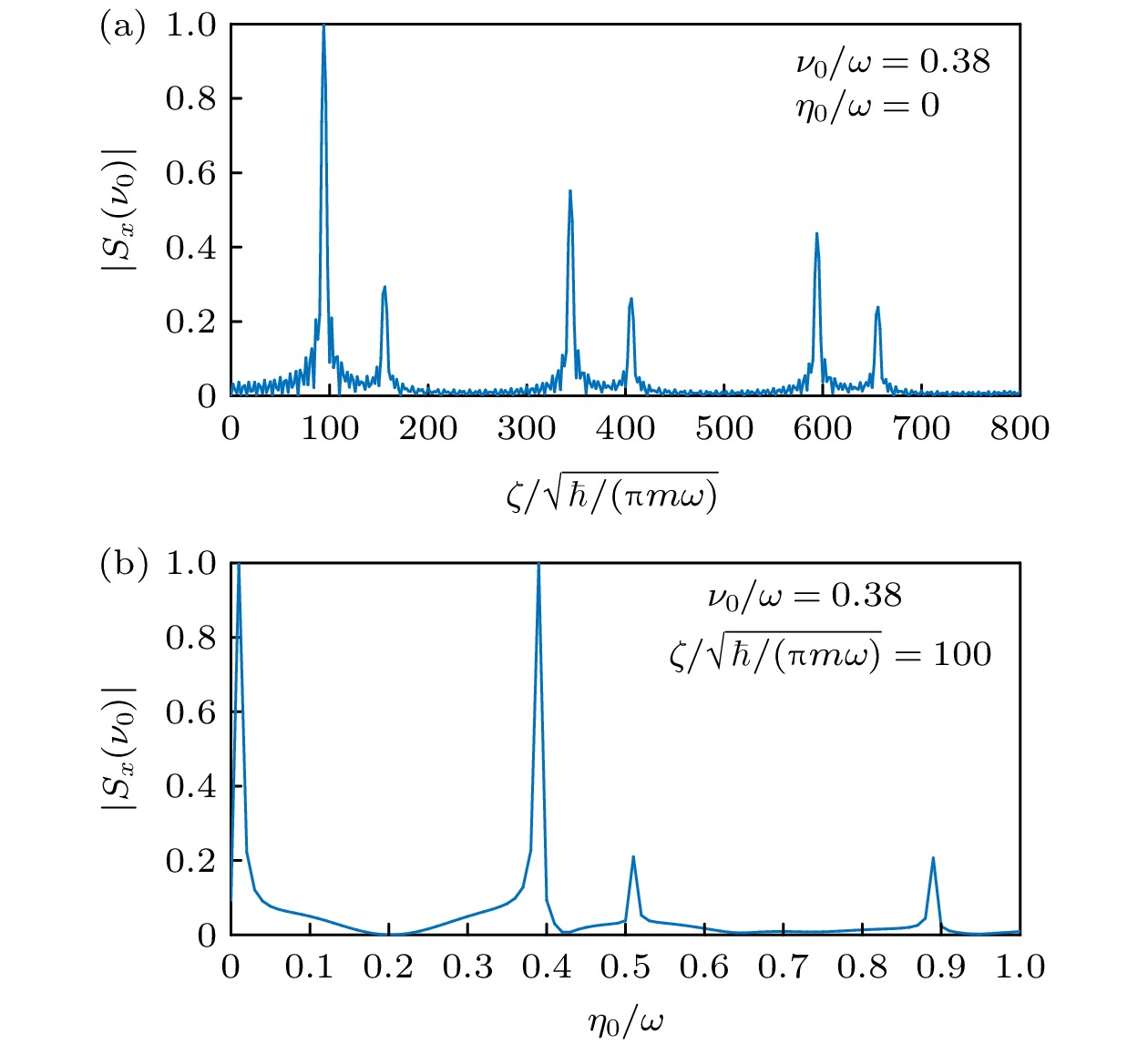
图 3 固定其余参数, 变化$ \zeta $ (a)和$ {\eta _0} $ (b)时自旋频谱$ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $的取值, 其他参数固定为$ \alpha = 0.2\sqrt {\hbar \omega /m} $, $ \tau = 0.01/\omega $, $ {T_{\text{L}}} = $$ 400/\omega $, $ \varOmega = 0 $, 初态选择为$ \left| {\varPsi (0)} \right\rangle = \left( {\left| {{\chi _ + }(0)} \right\rangle \left| + \right\rangle + \left| {{\chi _ - }(0)} \right\rangle \left| - \right\rangle } \right)/\sqrt 2 $
Fig. 3. Spin frequency spectrum $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $ for varying $ \zeta $ (a) and $ {\eta _0} $ (b). The other parameters are set by $ \alpha = 0.2\sqrt {\hbar \omega /m} $, $ \tau = 0.01/\omega $, $ {T_{\text{L}}} = 400/\omega $, and $ \varOmega = 0 $. The initial state is chosen as $ \left| {\varPsi (0)} \right\rangle = ( \left| {{\chi _ + }(0)} \right\rangle \left| + \right\rangle + \left| {{\chi _ - }(0)} \right\rangle \left| - \right\rangle )/\sqrt 2 $.
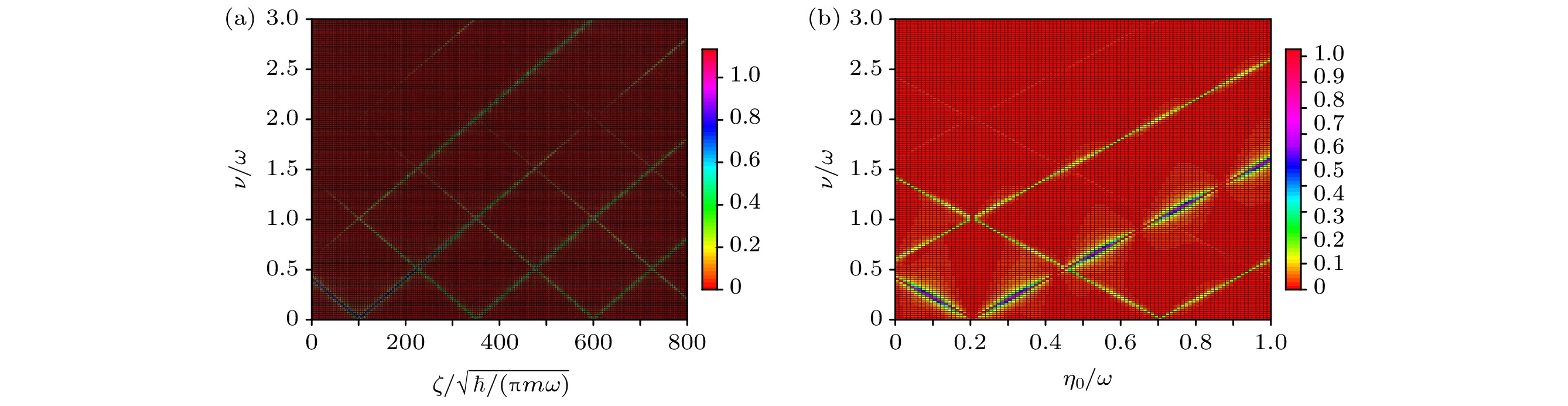
图 4 自旋频谱$ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $在(a) $ \zeta {\text{ - }}\nu $和(b) $ {\eta _0}{\text{ - }}\nu $ 平面上的取值 (a) $ {\eta _0} = 0.2\omega $; (b) $ \zeta = 100\sqrt {\hbar /\left( {{\text{π}}m\omega } \right)} $; 其他参数以及初态选择与图3一致
Fig. 4. Spin frequency spectrum $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $ in the (a) $ \zeta {\text{ - }}\nu $ plane and the (b) $ {\eta _0}{\text{ - }}\nu $ plane: (a) $ {\eta _0} = 0.2\omega $; (b) $ \zeta = 100\sqrt {\hbar /\left( {{\text{π}}m\omega } \right)} $. The other parameters and the initial state are the same as those in Fig. 3.
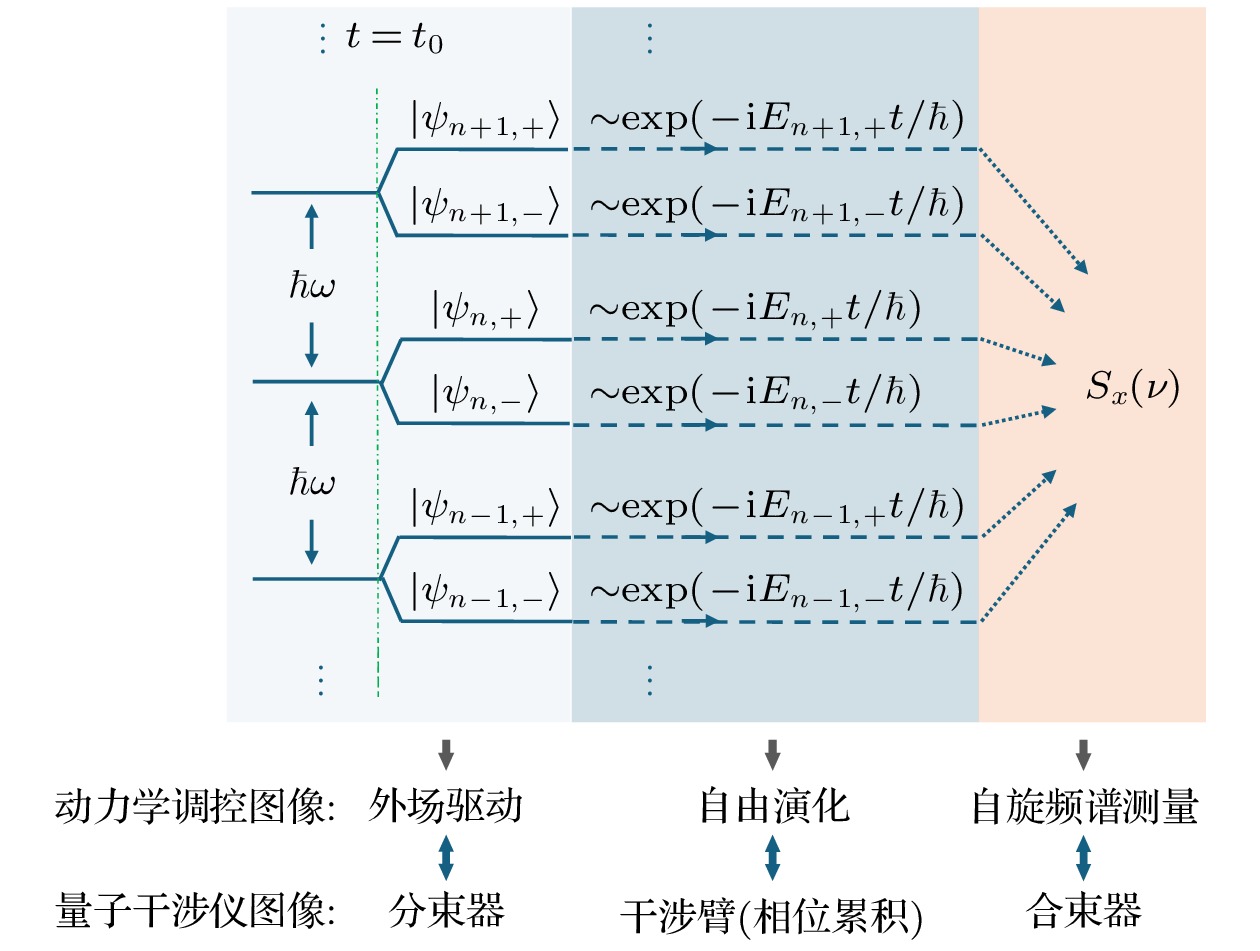
图 5 多自旋-轨道态量子干涉的示意图, 动力学调控图像与量子干涉图像具有对应关系, 图中不同颜色的模块表示干涉过程的不同组成部分
Fig. 5. Schematic description of the multiple spin-orbit-states interference. The dynamical control image corresponds to the quantum interference image, where different colored modules in the diagram represent different components of the interference process.
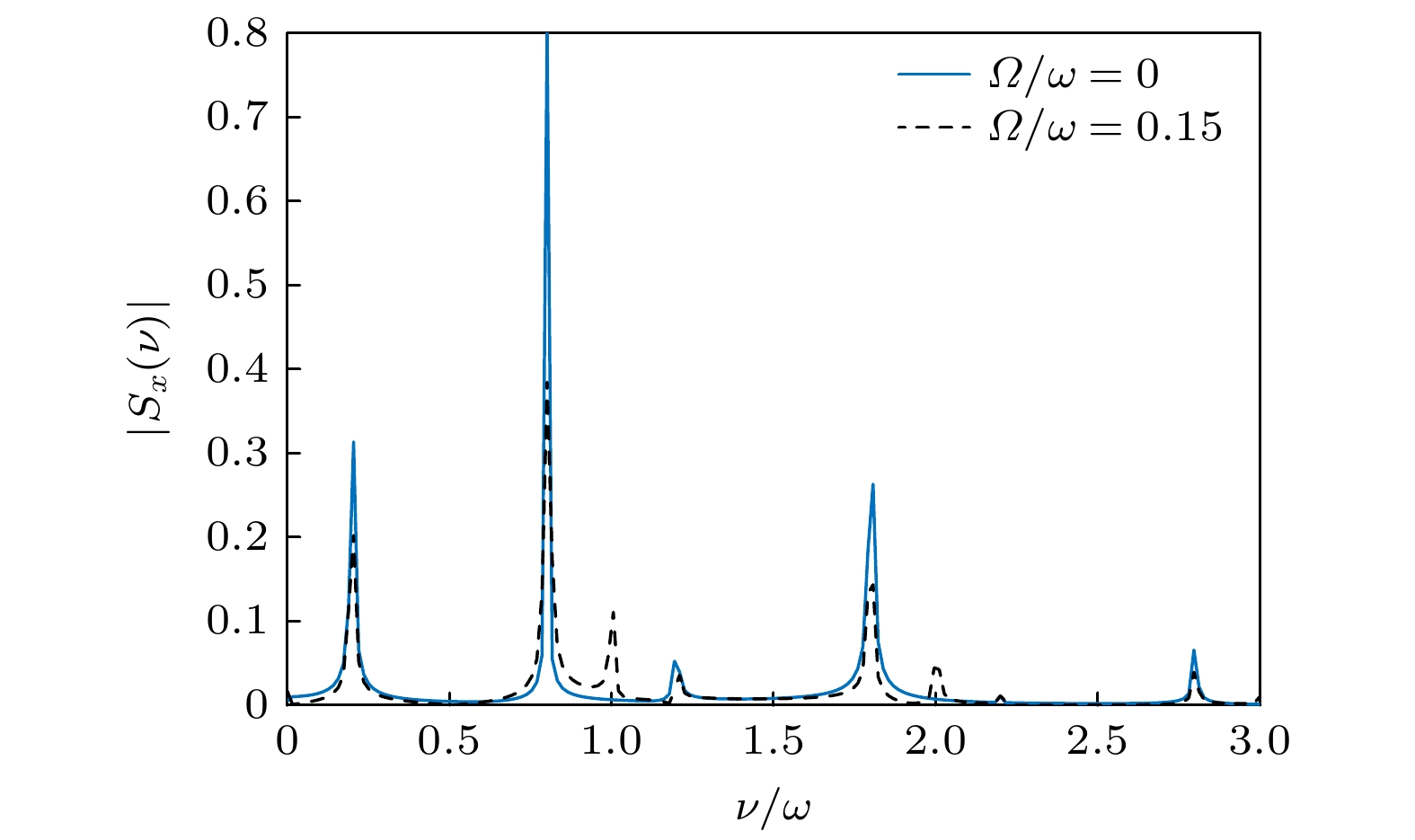
图 6 $ \varOmega = 0 $(蓝色实线)和$ \varOmega = 0.15\omega $(黑色虚线)时自旋频谱$ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $的取值, 驱动参数固定为$ \zeta = 100\sqrt {\hbar /({\text{π}}m\omega )} , $$ \eta = 0 $, 其他参数以及初态选择与图3一致
Fig. 6. Spin frequency spectrum $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $ for $ \varOmega = 0 $ (blue solid curve) and $ \varOmega = 0.15\omega $ (green dashed curve). The driving parameters are set by $ \zeta = 100\sqrt {\hbar /({\text{π}}m\omega )} , \;\eta = 0 $. The other parameters and the initial state are the same as those in Fig. 3.
图 7 自旋频谱$ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $在$ \nu = \tilde \nu = 0.38\omega $处随驱动参数(a) $ \zeta $和(b) $ {\eta _0} $的变化, 其他参数以及初态选择与图3一致
Fig. 7. Value of spin frequency spectrum $ | {{S_x}(\nu )} | $ at $ \nu = $$ \tilde \nu = 0.38\omega $ as a function of (a) $ \zeta $ and (b) $ {\eta _0} $. The other parameters and the initial state are the same as those in Fig. 3.
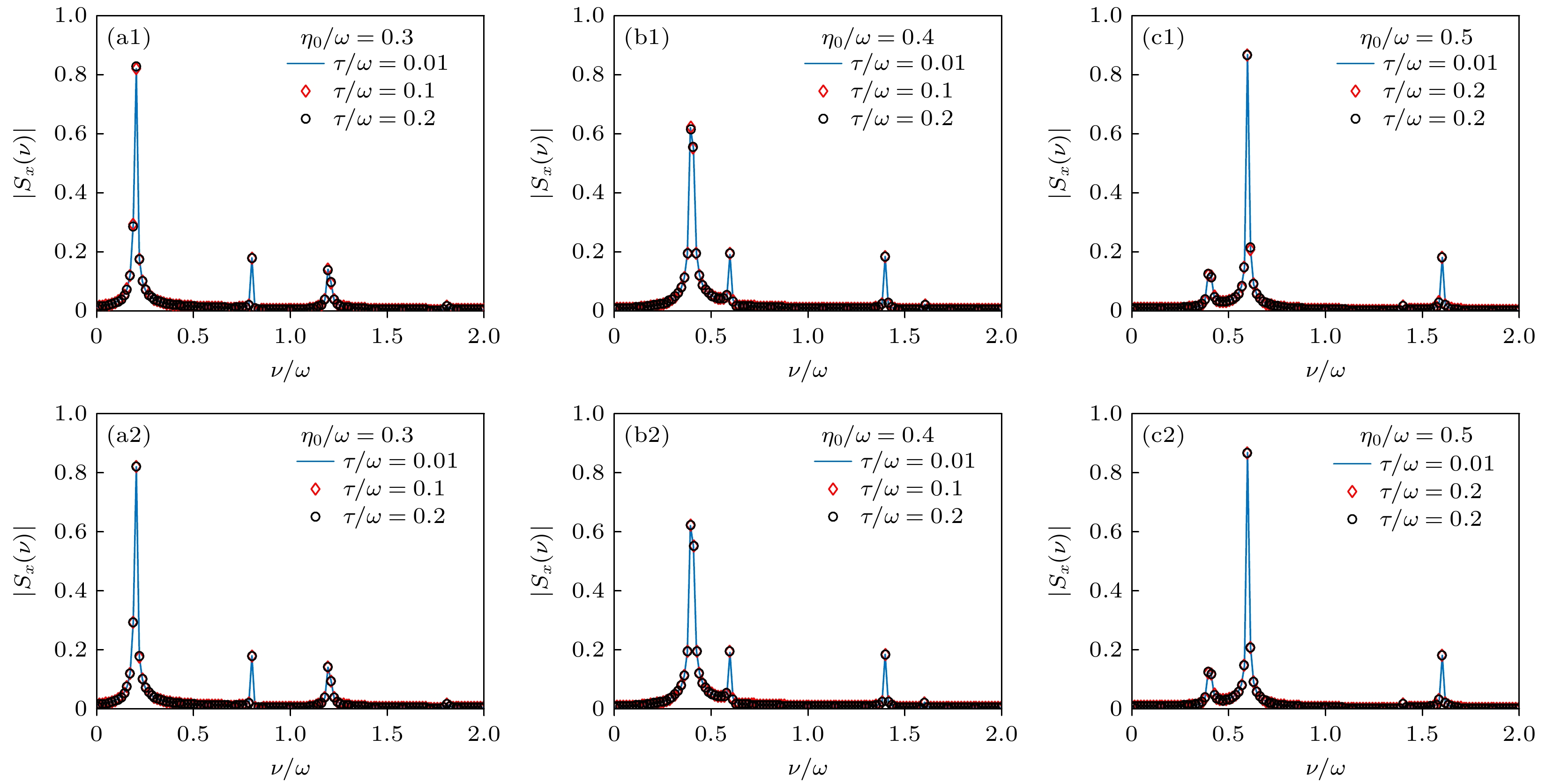
图 8 $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $对于不同脉冲宽度$ \tau $的取值 (a1)—(c1)对应于(3)式描述的高斯型脉冲; (a2)—(c2)对应于(21)式描述的方波型脉冲; $ \zeta = 100\sqrt {\hbar /\left( {\varGamma m\omega } \right)} $, 其中$ \varGamma = \sqrt {\text{π}} $对应于高斯型脉冲, $ \varGamma = 1 $对应于方波型脉冲, 其他参数以及初态选择与图3一致
Fig. 8. Value of spin frequency spectrum $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $ for different $ \tau $: (a1)–(c1) correspond to the Gaussian pulse defined in Eq. (3); (a2)–(c2) correspond to the square pulse defined in Eq. (21). In these figures, $ \zeta = 100\sqrt {\hbar /\left( {\varGamma m\omega } \right)} $ , where $ \varGamma = \sqrt {\text{π}} $ for the Gaussian pulse and $ \varGamma = 1 $ for the square pulse. The other parameters and the initial state are the same as those in Fig. 3.
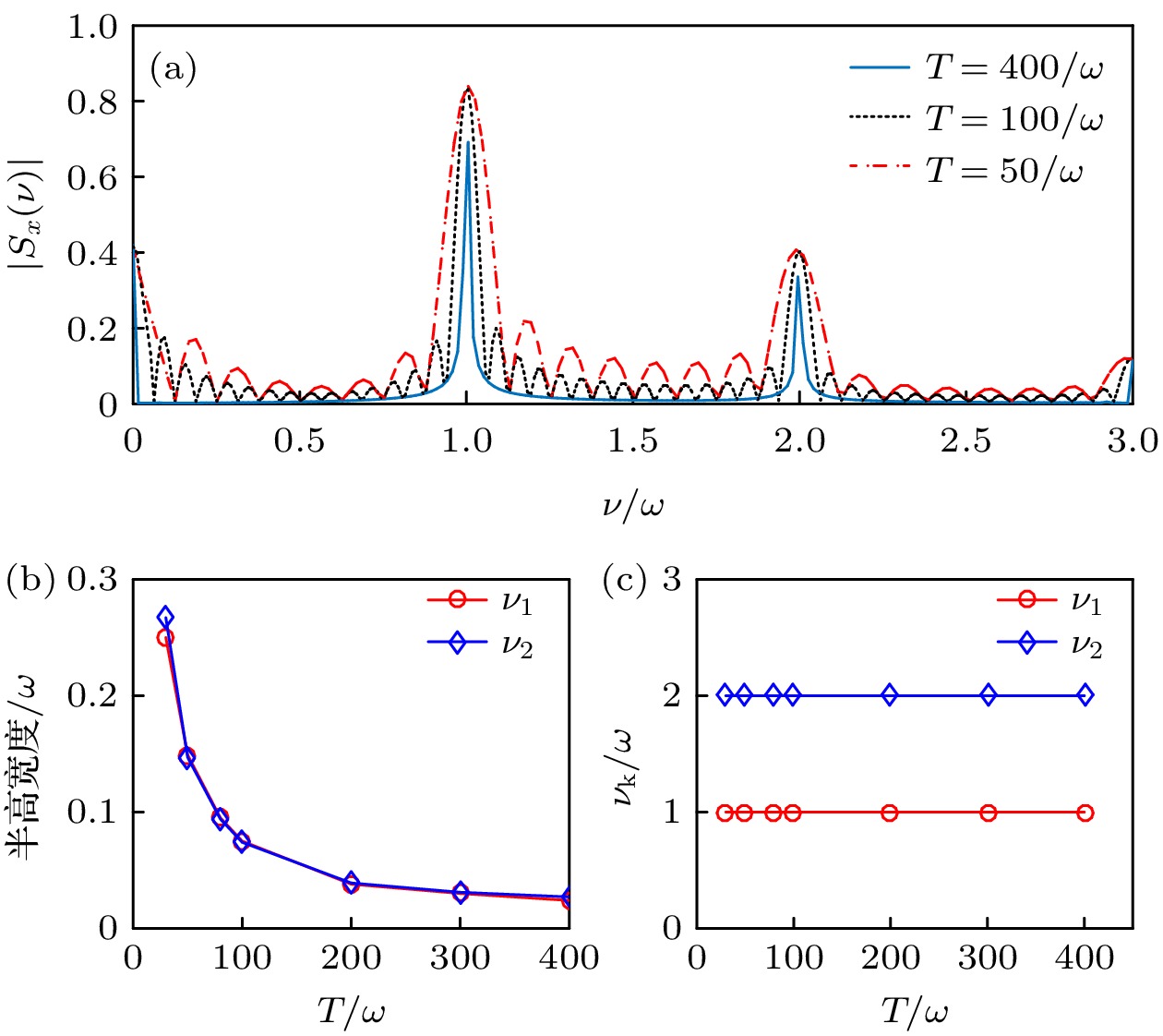
图 9 (a) $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $在不同积分时间$ T $下的取值; (b)图(a)中两个谱峰$ {\nu _1} $和$ {\nu _2} $的半高宽度随积分时间$ T $的变化; (c)图(a)中两个谱峰$ {\nu _1} $和$ {\nu _2} $的峰值位置随积分时间$ T $的变化; 所有图中$ \zeta = 250\sqrt {\hbar /\left( {{\text{π}}m\omega } \right)} $, $ {\eta _0}/\omega = 0 $, 其他参数以及初态选择与图3一致
Fig. 9. (a) Value of spin frequency spectrum $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $ for different $ T $; (b) the half-height width of the spectrum peak $ {\nu _1} $ and $ {\nu _2} $ appearing in panel (a) as a function of $ T $; (c) the peak position of $ {\nu _1} $ and $ {\nu _2} $ appearing in panel (a) as a function of $ T $. In these figures, $ \zeta = 250\sqrt {\hbar /\left( {{\text{π}}m\omega } \right)} $ and $ {\eta _0}/\omega = 0 $. The other parameters and the initial state are the same as those in Fig. 3.
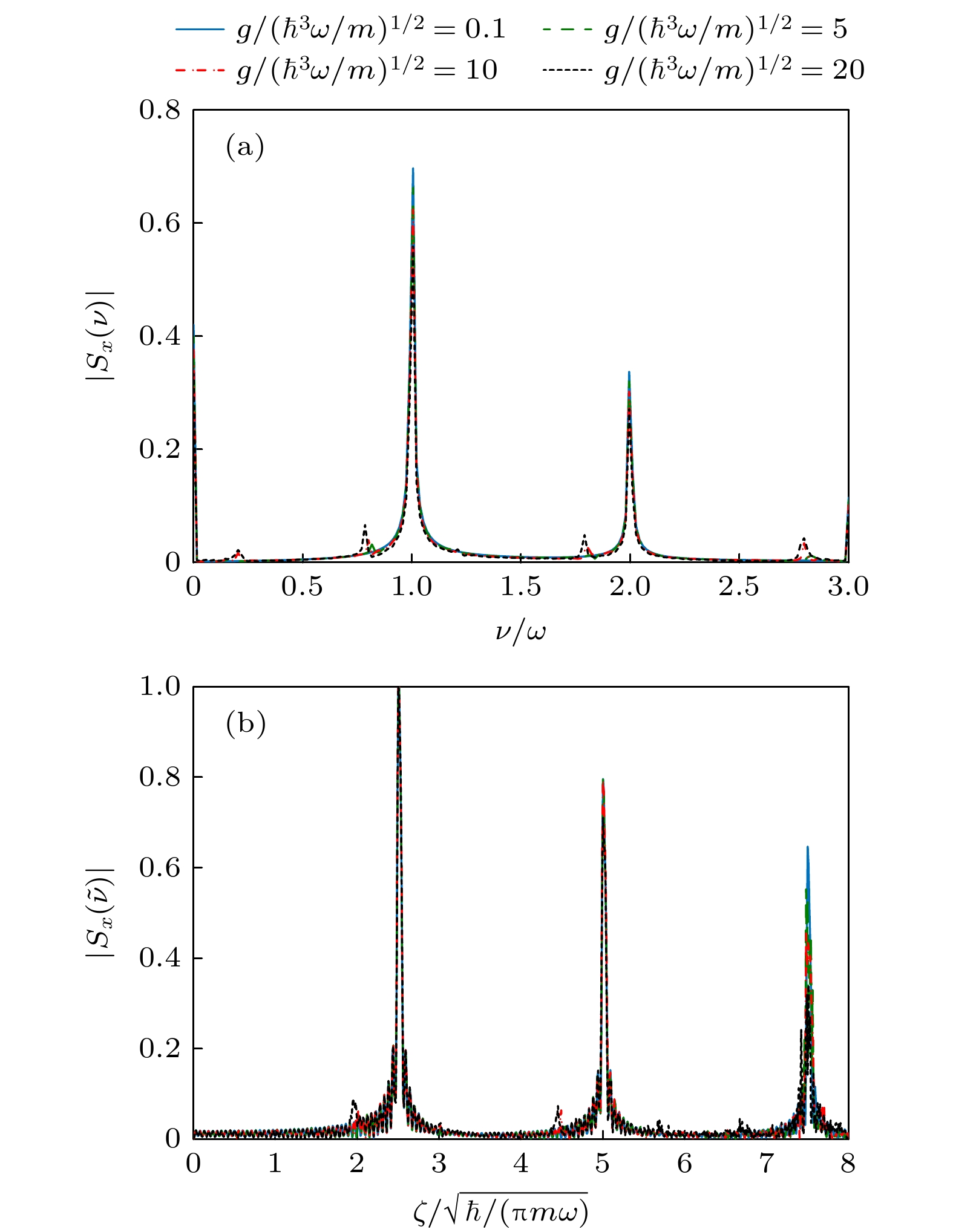
图 10 (a)相互作用$ g $不同时, 自旋频谱$ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $的取值; (b)自旋频谱$ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $在$ \nu = \tilde \nu = \omega $处随驱动参数$ \zeta $的变化, 不同相互作用$ g $用不同线型表示; 其他参数以及初态选择与图3一致
Fig. 10. (a) Value of spin frequency spectrum $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $ for different interaction coefficient $ g $; (b) the value of spin frequency spectrum $ \left| {{S_x}(\nu )} \right| $ at $ \nu = \tilde \nu = \omega $ as a function of $ \zeta $, and the results of different $ g $ are labelled by different linetypes. The other parameters and the initial state are the same as those in Fig. 3.
-
[1] Chu S 1998 Rev. Mod. Phys. 70 685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bloch I, Dalibard J, Zwerger W 2008 Rev. Mod. Phys. 80 885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dalibard J, Gerbier F, Juzeliūnas G, Öhberg P 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 1523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qiu X Z, Zoller P, Li X P 2020 PRX Quantum 1 020311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jayaseelan M, Manikandan S K, Jordan A N, Bigelow N P 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 1847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Kaufman A M, Ni K K 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 1324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Davis K B, Mewes M O, Andrews M R, van Druten N J, Durfee D S, Kurn D M, Ketterle W 1995 Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 3969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Anderson M H, Ensher J R, Matthewa M R, Wieman C E, Cornell E A 1995 Science 269 198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Pitaevskii L, Stringari S 2016 Bose-Einstein Condensation and Superfluidity (Oxford: Oxford University Press
[10] Jie J W, Guan Q, Blume D 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 043606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jie J W, Guan Q, Zhong S, Schwettmann A, Blume D 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 023324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jie J W, Zhong S, Zhang Q, Morgenstern I, Ooi H G, Guan Q, Bhagat A, Nematollahi D, Schwettmann A, and Blume D 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 053309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang Y X, Zhang Y B, Lu R, Wang X G, Yi S 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 043625
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xing H, Wang A, Tan Q S, Zhang W, Yi S 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 043615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lewenstein M, Sanpera A, Ahufinger V 2012 Ultracold Atoms in Optical Lattices: Simulating Quantum Many-body Systems (Oxford: Oxford University Press
[16] Lin Y J, Jiménez-García K, Spielman I B 2011 Nature 471 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang C, Gao C, Jian C M, Zhai H 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 160403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sinha S, Nath R, Santos L 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 270401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu H, Ramachandhran B, Pu H, Liu X J 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 010402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pan J S, Zhang W, Yi W, Guo G C 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 043619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li J R, Lee J, Huang W, Burchesky S, Shteynas B, Top F C, Jamison A O, and Ketterle W 2017 Nature 543 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liao R Y 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 140403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Campbell D L, Price R M, Putra A, Valdés-Curiel A, Trypogeorgos D, Spielman I B 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Vaishnav J Y, Clark C W 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 153002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang Y P, Mao L, Zhang C W 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 035302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang Y P, Chen G, Zhang C W 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 1937
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang J Y, Ji S C, Chen Z, Zhang L, Du Z D, Yan B, Pan G S, Zhao B, Deng Y J, Zhai H, Chen S, Pan J W 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 115301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Qu C L, Hamner C, Gong M, Zhang C W, Engels P 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 021604(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hamner C, Qu C, Zhang Y, Chang J, Gong M, Zhang C, Engels P 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 4023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Khamehchi M A, Hossain K, Mossman M E, Zhang Y, Busch T, Forbes M M, Engels P 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 155301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wu C H, Fan J T, Chen J, Jia S T 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 013617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Fan G, Chen X L, Zou P 2022 Front. Phys. 17 52502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Bednarek S, Szumniak P, Szafran B 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 235319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Pawlowski J, Szumniak P, Skubis A, Bednarek S 2014 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 26 345302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Golovach V N, Borhani M, Loss D 2006 Phys. Rev. B 74 165319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Li R, You J Q, Sun C P, Nori F 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 086805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Widera A, Gerbier F, Fölling S, Gericke T, Mandel O, Bloch I 2006 New. J. Phys. 8 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Ho T L 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 742
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Grossmann F 2008 Theoretical Femtosecond Physics: Atoms and Molecules in Strong Laser Fields (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer
[40] Baudon J, Mathevet R, Robert J 1999 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 32 R173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Shevchenko S N, Ashhab S, Nori F 2010 Phys. Rep. 492 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Li Y Q, Feng G S, Xu R D, Wang X F, Wu J Z, Chen G, Dai X C, Ma J, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 053604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1714
- PDF下载量: 46
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: