-
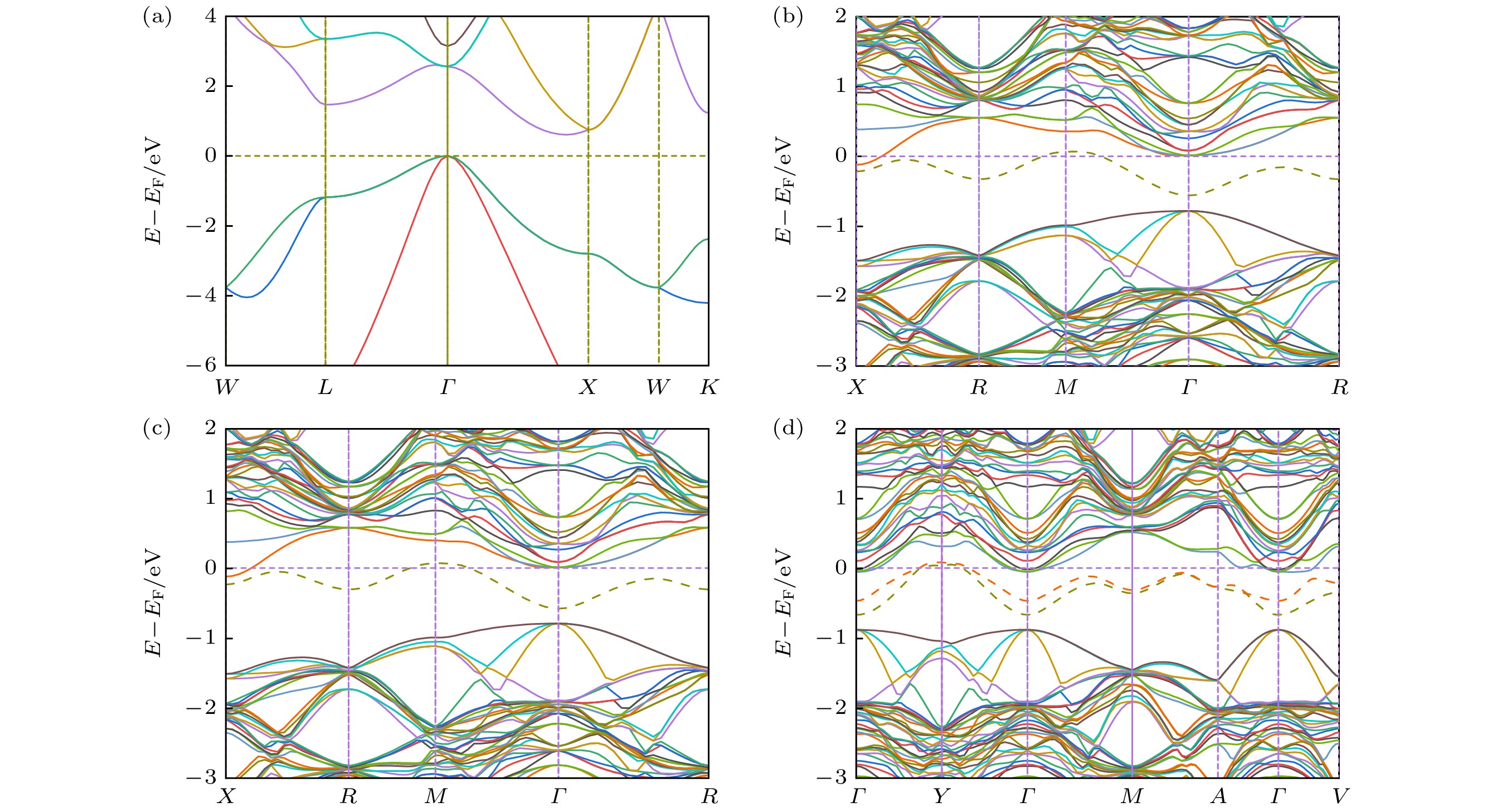
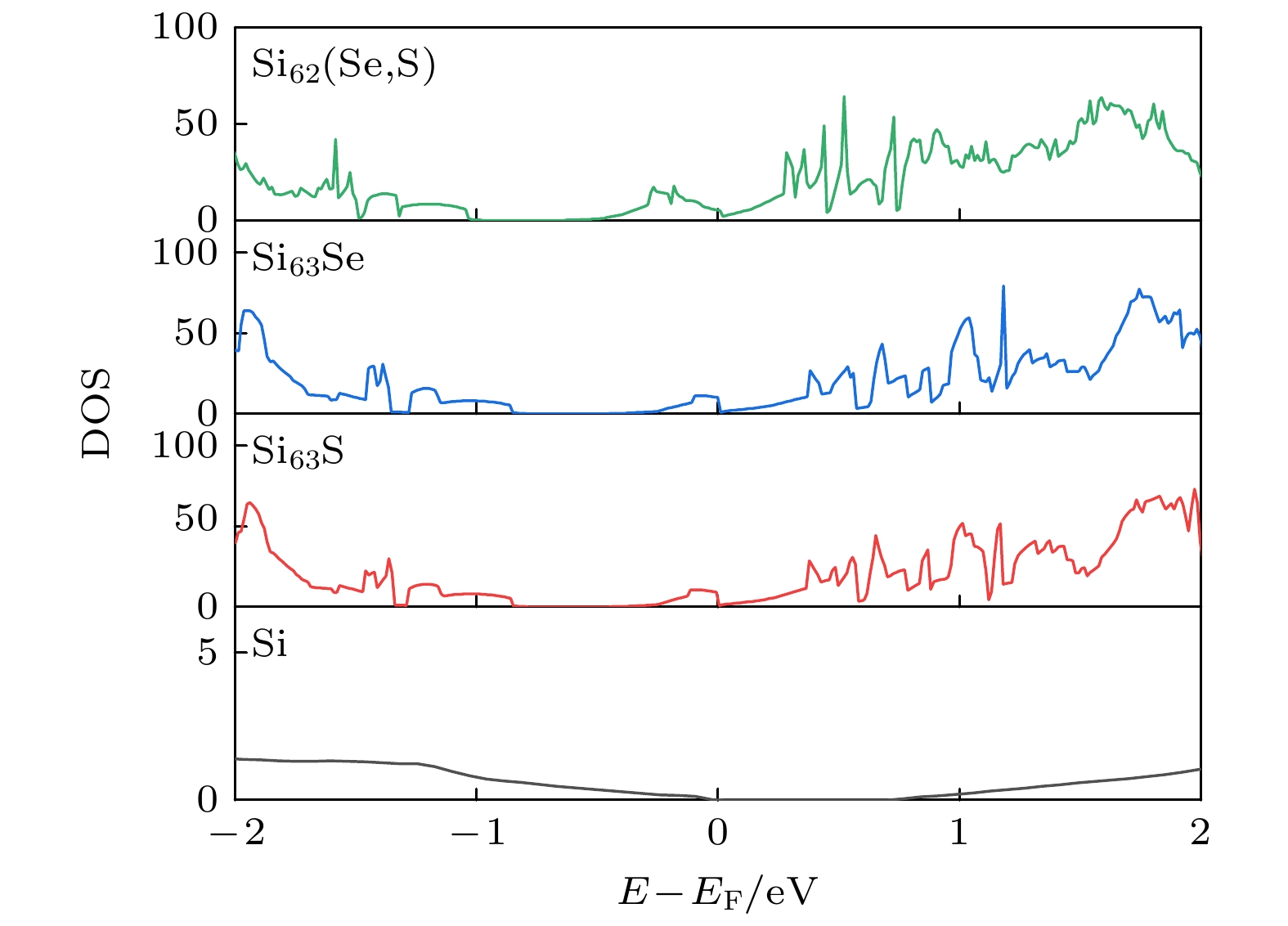
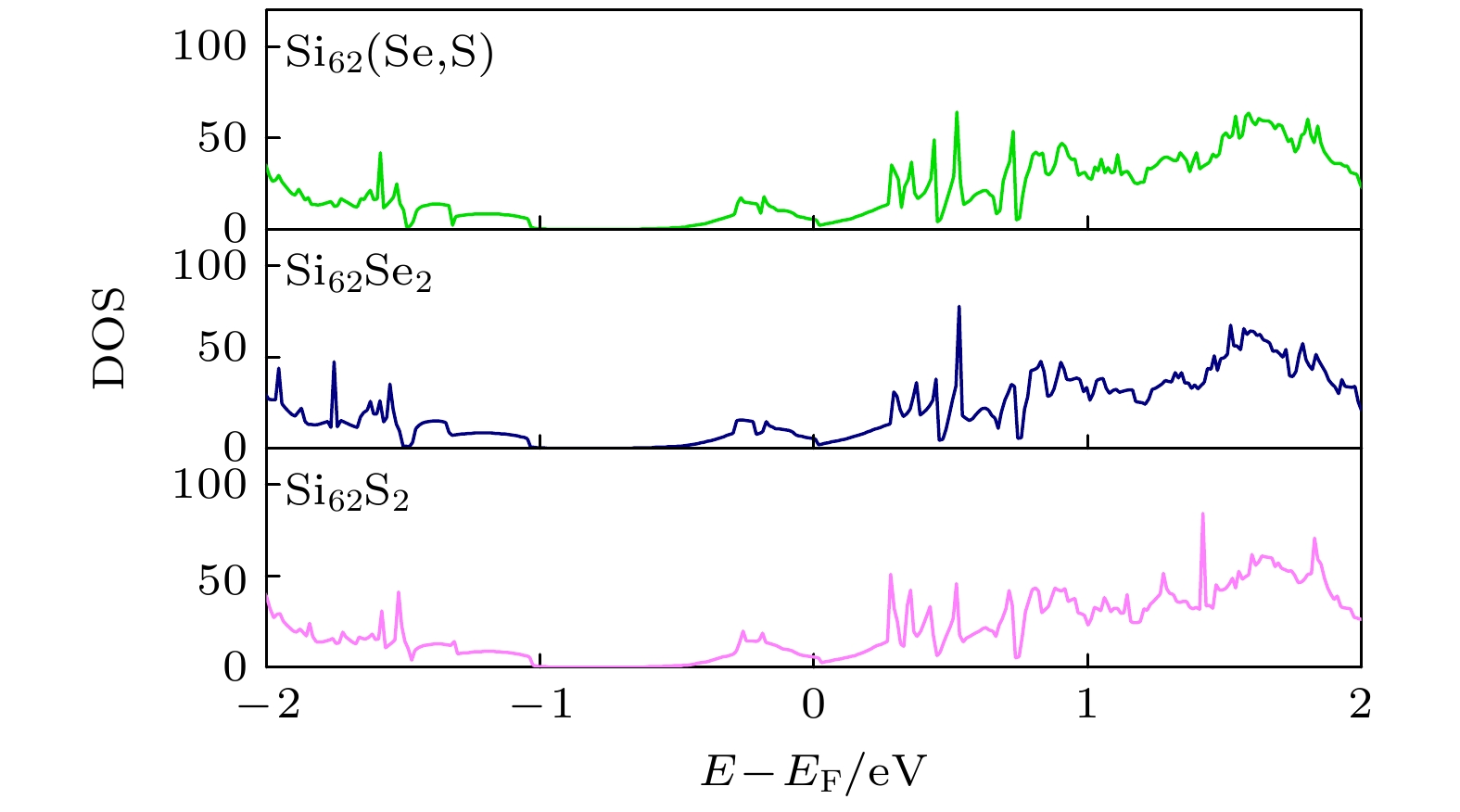
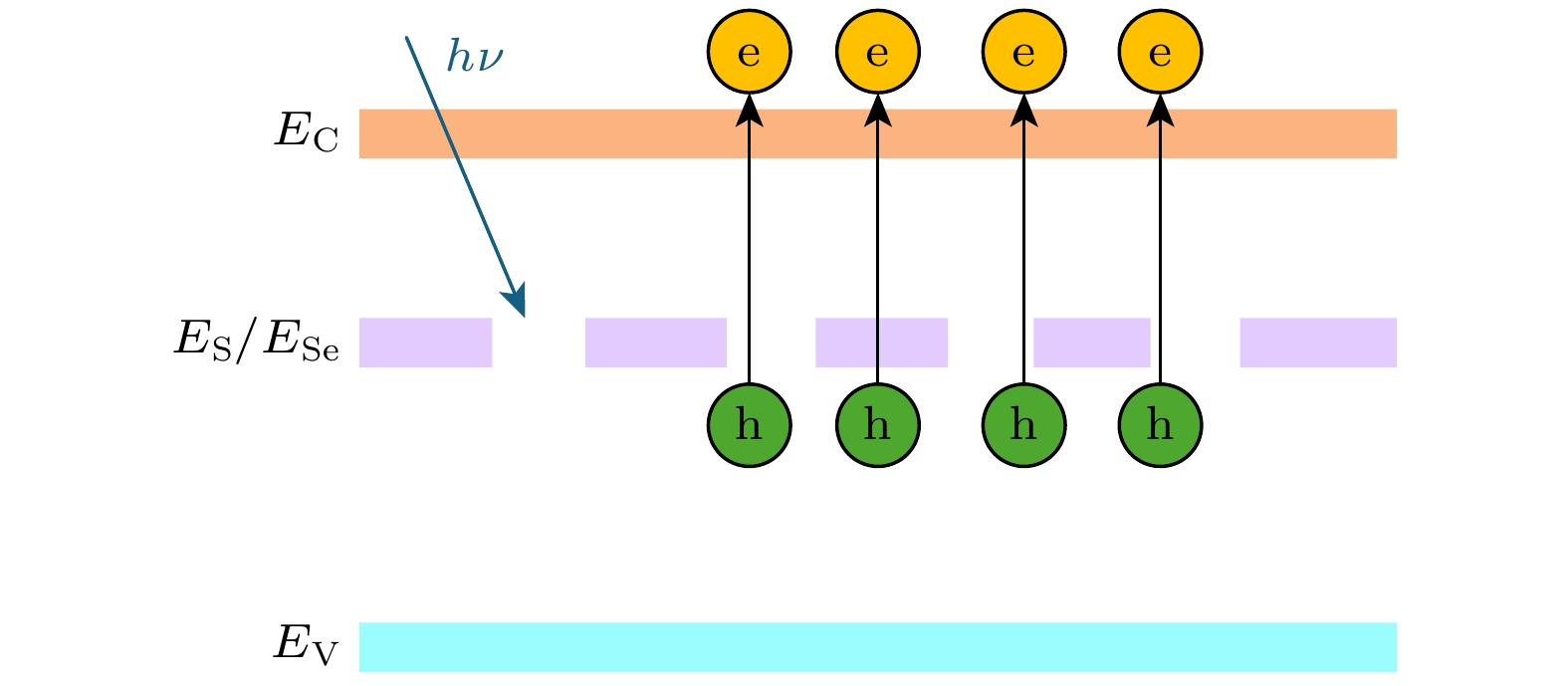
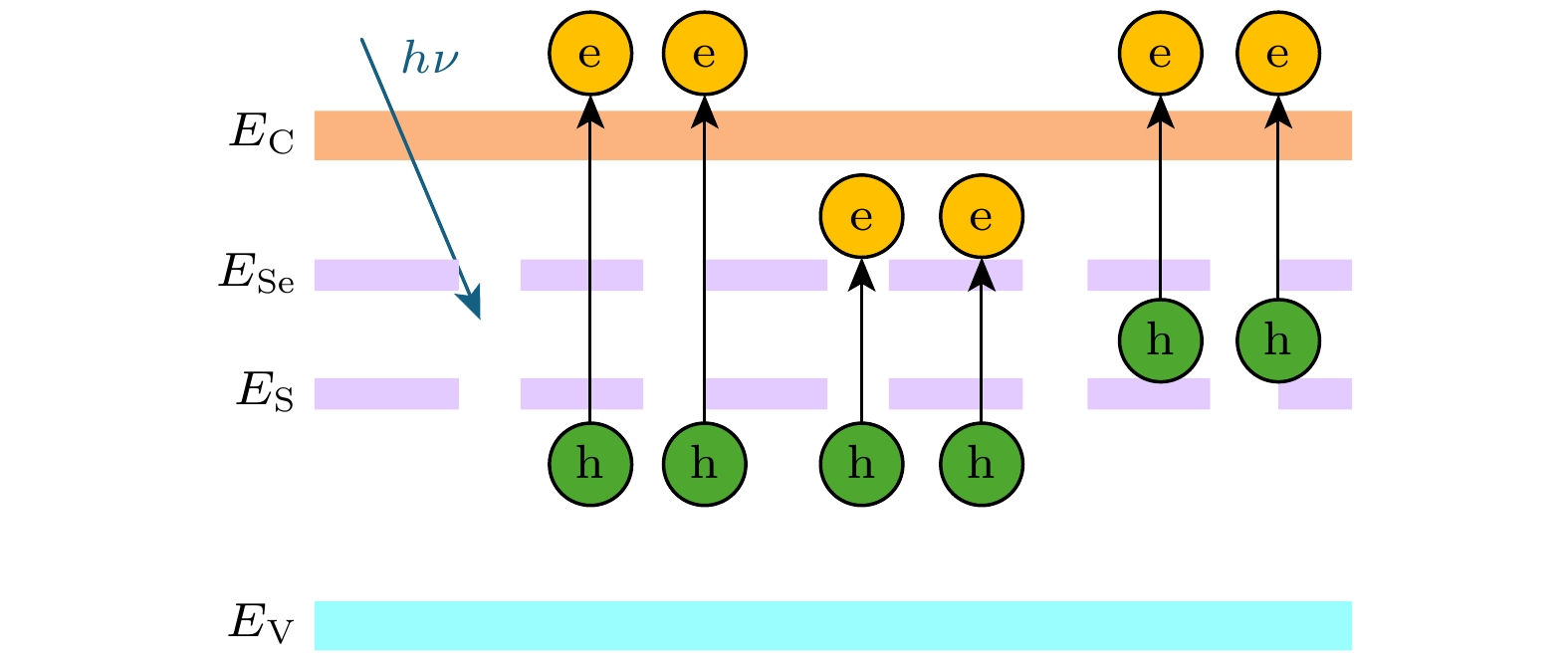
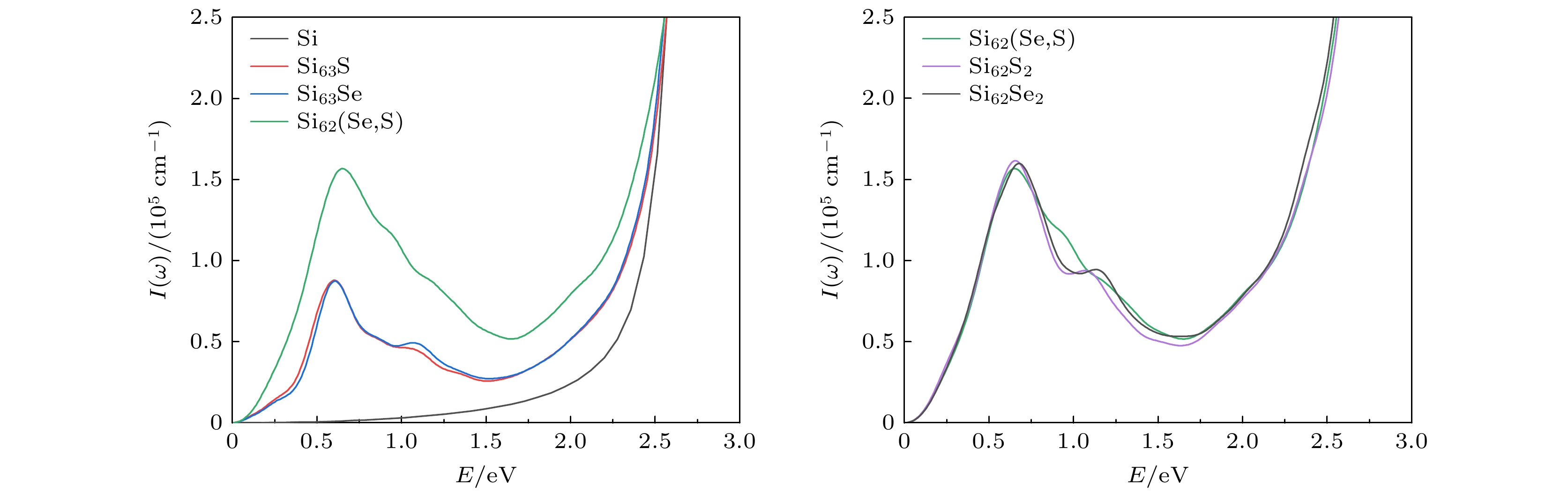
基于第一性原理研究了S, Se单掺杂以及共掺杂Si的光电特性, 对掺杂前后晶体的几何结构、稳定性、能带结构和电子态密度以及光学性质进行比较分析. 计算结果表明, S掺杂Si与Se掺杂Si的光电特性极其相似, 其禁带中均出现一条新的杂质能级, 主要由S的3s态与Se的4s态电子形成, 杂质能级的形成促进低能光子的吸收, 增大了掺杂Si材料在近红外波段的光吸收率; 与单晶硅相比, S掺杂Si与Se掺杂Si的光吸收谱, 在0.6 eV处出现了一个新的峰值, 该峰值正是由电子从杂质能级向导带跃迁产生. S, Se共掺杂Si在工作温度下表现出良好的稳定性; 价带与导带之间出现两条杂质能级, 分别由S的3s态与Se的4s态电子形成; S, Se共掺杂Si的光吸收率在低能区较单掺杂Si有较大提升, 新增吸收峰出现在0.65 eV处, 形成原因与单掺杂相似. 然而, 由于两条杂质能带间的间接跃迁过程, 共掺杂Si在低能区的吸收峰更大. 且与相同浓度的单掺杂Si相比, S, Se共掺杂Si的光吸收率在0.81—1.06 eV范围内明显提高.In order to provide more accurate theoretical guidance for improving photoelectric properties of chalcogens doped silicon, the lattice structure, stability, band structure, density of state and optical properties of (S, Se) co-doped silicon are systematically investigated based on the first principles, and the related properties are compared with those of S-doped and Se-doped silicon. The calculated results show that the photoelectric characteristics of S-doped Si and Se-doped Si are extremely similar to each other, with a new impurity band appearing in their bandgap. This new impurity band primarily results from the contributions of the 3s state electrons of S and the 4s state electrons of Se, promoting the absorption of low-energy photons and increasing the optical absorptivity of doped Si in the near infrared region. Compared with monocrystalline silicon, the S-doped Si and Se-doped Si have the optical absorption spectra, each with a new peak at 0.6 eV, which is caused by the transition of electrons from the impurity band to the conduction band. The (S, Se) co-doped Si exhibits good stability at operating temperature, and two impurity bands appear between the valence band and conduction band, which are formed by electrons from the 3s state of S and the 4s state of Se, respectively. The optical absorptivity of (S, Se) co-doped Si is greatly improved in the low energy region compared with that of single doped Si, with a new absorption peak appearing at 0.65 eV, similar to the formation observed in singly doped Si. However, due to the indirect transition process between two impurity energy bands, the absorption peak of (S, Se) co-doped Si is larger in the low energy region. Compared with S-doped silicon and Se-doped silicon with the same concentration, the (S, Se) co-doped Si has optical absorptivity that is significantly improved in the range from 0.81 eV to 1.06 eV. This study provides theoretical guidance for applying the (S, Se) co-doped Si to the field of photoelectron such as infrared photodetectors and solar cells.
-
Keywords:
- doped Si /
- first principles /
- photoelectric characteristic
[1] 周治平 2014 武汉光电论坛论文集 (武汉: 华中科技大学出版社) 第249页
Zhou Z P 2014 Proceedings of Wuhan Opto-Electronic Forum (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology Press) p249
[2] Michael O, Mathias K, Steffen E, Maurice W, Zili Y, Daniel S, Köllner A C, Joachim N B, Jörg S 2021 IEEE Sens. J. 20 18696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yang J J, Jurczak P, Cui F, Li K S, Tang M C, Billiald L, Beanland R 2019 J. Cryst. Growth 514 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Her T H, Finlay R J, Mazur E, Wu C, Deliwala S 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 1673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu C, Crouch C H, Zhao L, Carey J E, Younkin R, Levinson J A, Mazur E, Farrell R M, Gothoskar P, Karger A 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 1850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tansel T, Aydin O 2024 J. Phys. D 57 295103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhao X N, Lin K, Zhao B, Du W H, Nivas J J, Amoruso S, Wang X 2023 Appl. Surf. Sci. 619 156624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 钟豪 2019 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Zhong H 2019 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[9] Du L Y, Yin J, Zeng W, Pang S Z, Yi H 2023 Mater. Lett. 331 133463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 高宇辰 2022 硕士学位论文 (吉林: 吉林大学)
Gao Y C 2022 M. S. Thesis (Jilin: Jilin University
[11] Yang Y, Yi Z R, Chao L, Zhao J H 2023 Opt. Quantum Electron. 55 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 任哲毅 2024 硕士学位论文 (吉林: 吉林大学)
Ren Z Y 2024 M. S. Thesis (Jilin: Jilin University
[13] Zhu J, Gandi N A, Schwingenschlögl U 2018 Adv. Theor. Simul. 1 1800017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang X Y, Wang T, Ren Q, Xu J T, Cui Y A 2023 Micro Nanostruct. 184 207695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 薛晓晚 2018 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Xue X W 2018 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology
[16] 梁伟华, 丁学成, 褚立志, 邓泽超, 郭建新, 吴转花, 王英龙 2010 59 8071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang W H, Ding X C, Chu L Z, Deng Z C, Guo J X, Wu Z H, Wang Y L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 8071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tang X, Li W, Xu W, Ren Q Y, Chen Q Y 2024 Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 184 108797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu M, Cai G K, Li Z, Ye L, Wang C 2024 Vacuum 225 113222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li J Y, Zhao C L, Li W, Ren Q Y, Xu J, Xu W 2023 Phys. Scr. 98 115408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Sharif M N, Yang J S, Zhang X K, Tang Y H, Yang G, Wang K F 2024 Vacuum 219 112714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Comput. Mater. Sci. 6 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shuichi N 1984 J. Chem. Phys. 81 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 关丽, 李强, 赵庆勋, 郭建新, 周阳, 金利涛, 耿波, 刘保亭 2009 58 5624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan L, Li Q, Zhao Q X, Guo J X, Zhou Y, Jin L T, Geng B, Liu B T 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 5624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kumaravelu G, Alkaisi M M, Bittar A 2002 29th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference New Orleans, LA, USA, May 19–24, 2002 p258
[26] 杜玲艳 2018 博士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Du L Y 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[27] 宣曜宇 2017 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Xuan Y Y 2017 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[28] Khan M, Xu J N, Chen N, Cao W B 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 513 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Feng J, Xiao B, Chen C J, Zhou C T, Du Y P, Zhou R 2009 Solid State Commun. 149 1569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
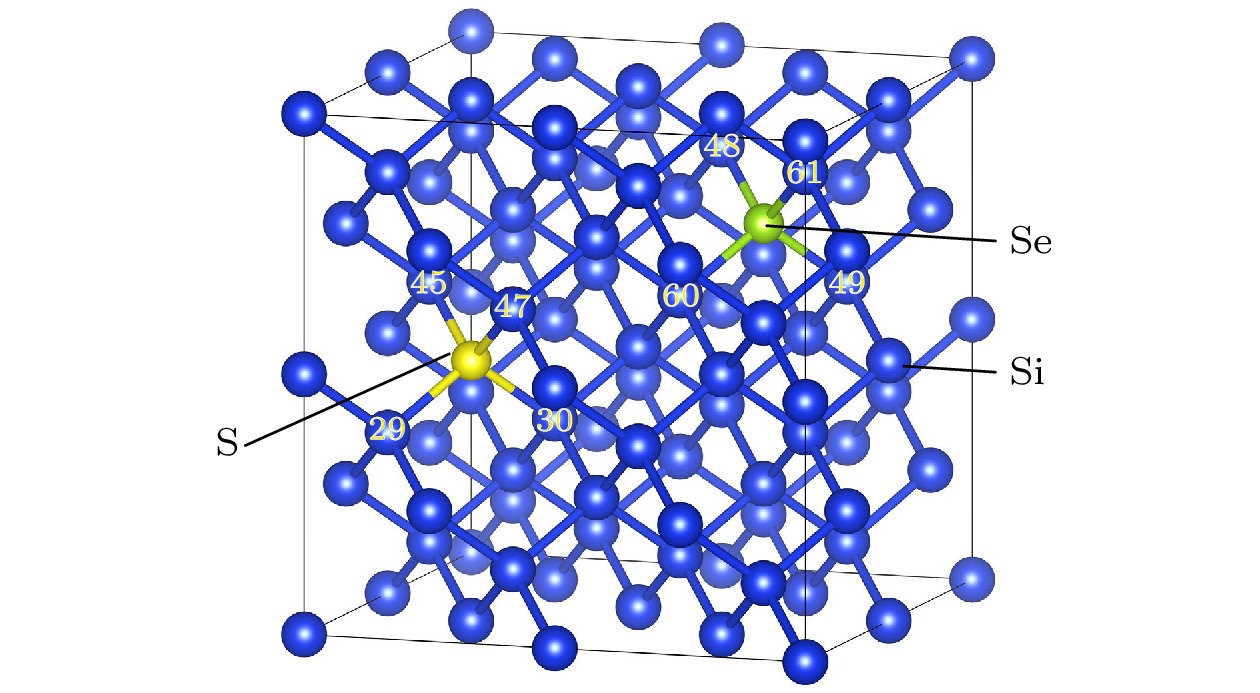
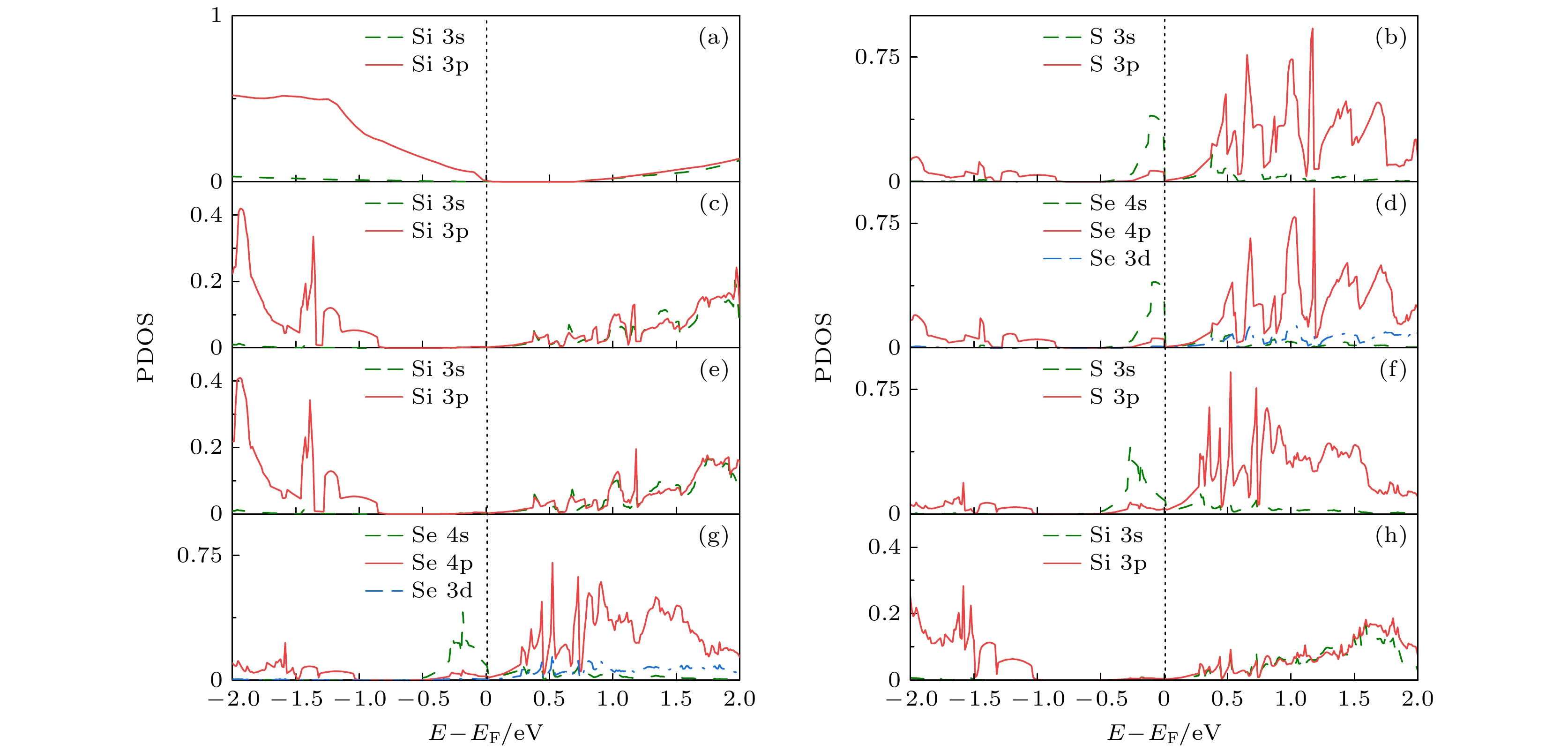
图 8 纯Si与掺杂Si的分态密度 (a)纯Si中的Si; (b) Si63S中的S; (c) Si63S中的Si; (d) Si63Se中的Se; (e) Si63Se中的Si; (f) Si62(Se, S)中的S; (g) Si62(Se, S)中的Se; (h) Si62(Se, S)中的Si
Fig. 8. Partial density of state of pure Si and doped Si: (a) Si in pure Si; (b) S in Si63S; (c) Si in Si63S; (d) Se in Si63Se; (e) Si in Si63Se; (f) S in Si62(Se, S); (g) Se in Si62(Se, S); (h) Si in Si62(Se, S).
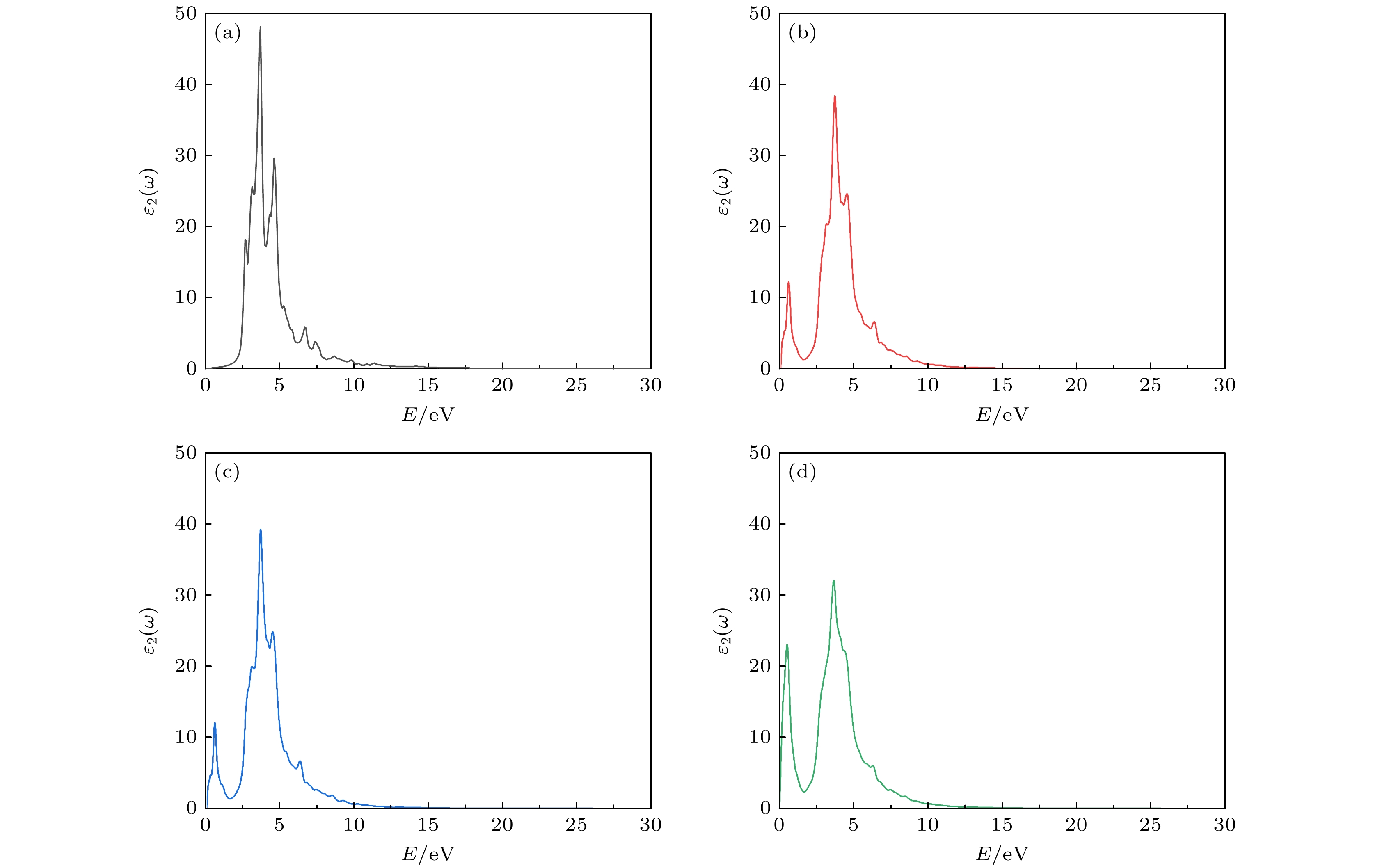
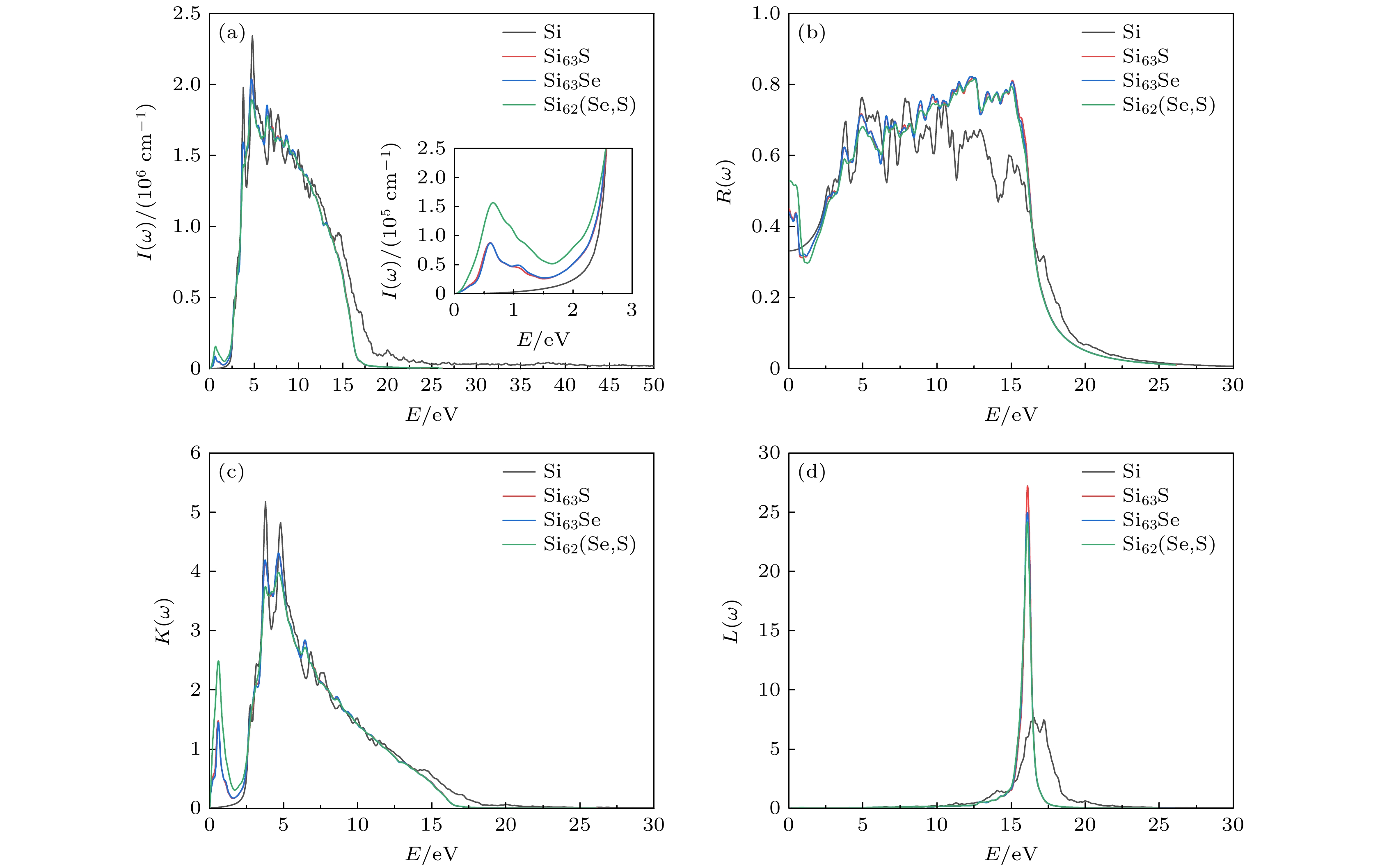
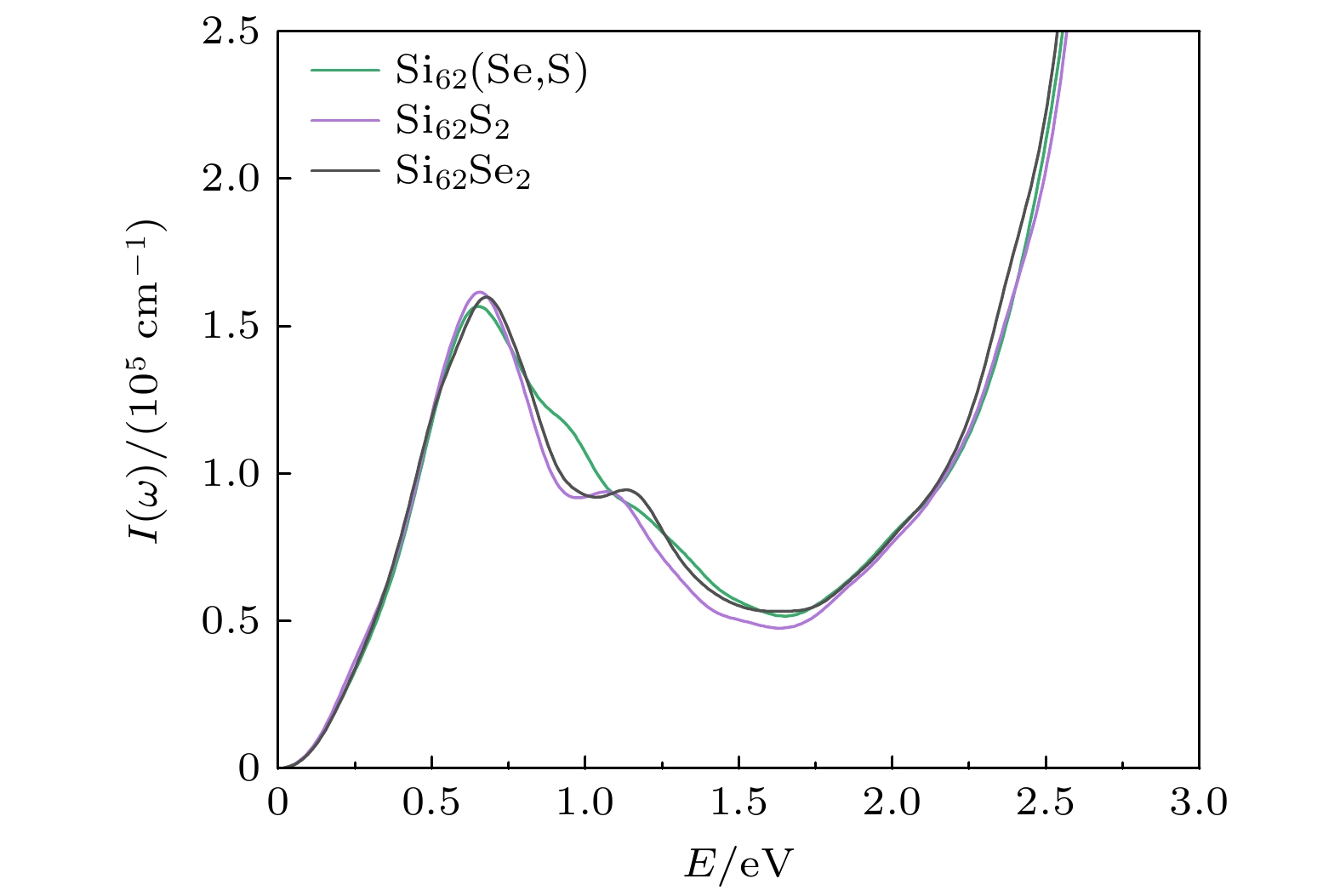
图 10 纯Si与掺杂Si的光吸收谱(a)、反射谱(b)、消光系数谱(c)和能量损失谱(d), 其中图(a)中插图为纯Si与掺杂Si的光吸收谱在0—3 eV部分的放大
Fig. 10. Optical absorption spectrum (a), reflection spectrum (b), extinction coefficient spectrum (c) and energy loss spectrum (d) of pure Si and doped Si, the inset in panel (a) shows the amplification of the optical absorption spectrum of pure Si and doped Si at 0–3 eV.
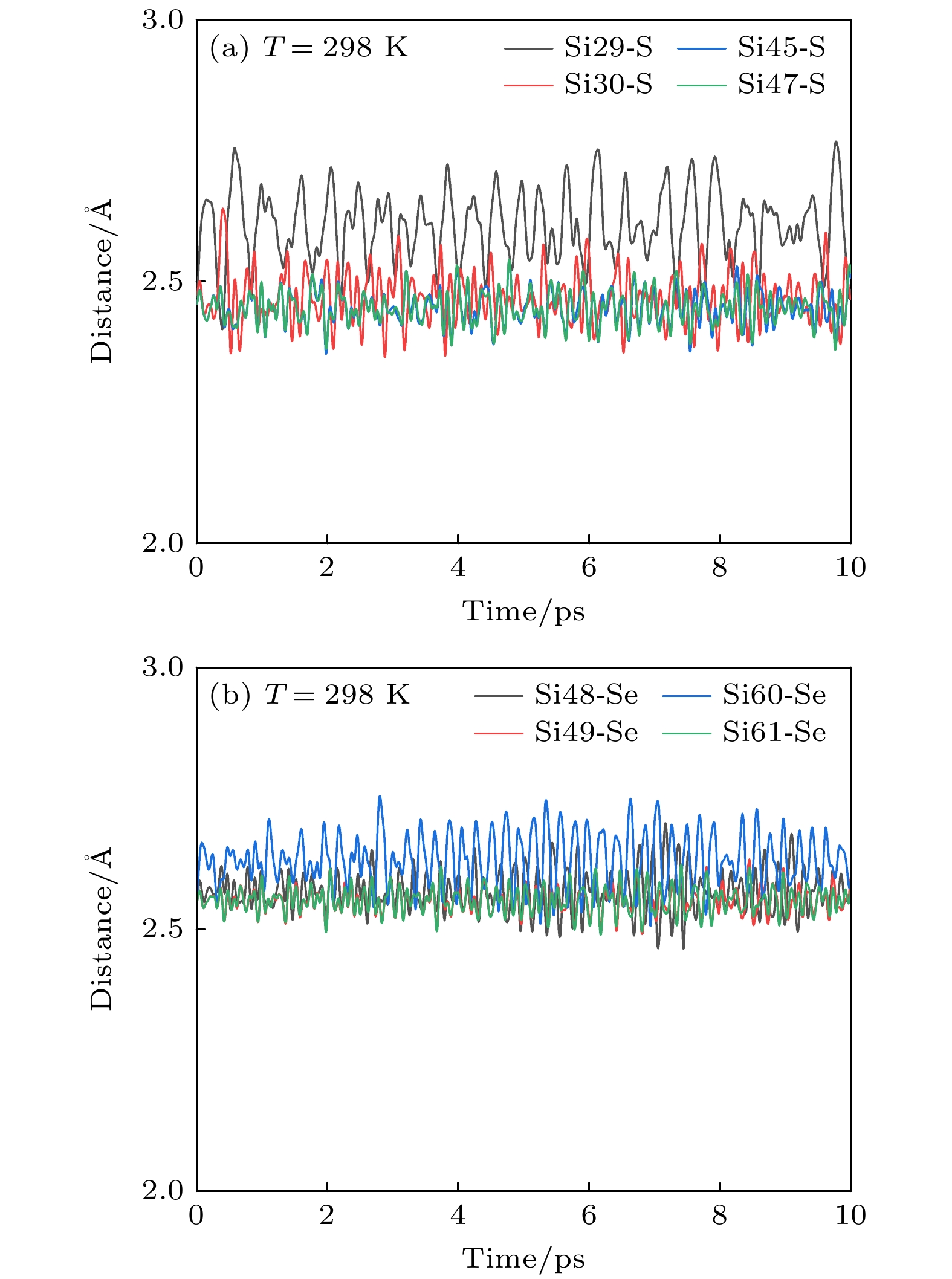
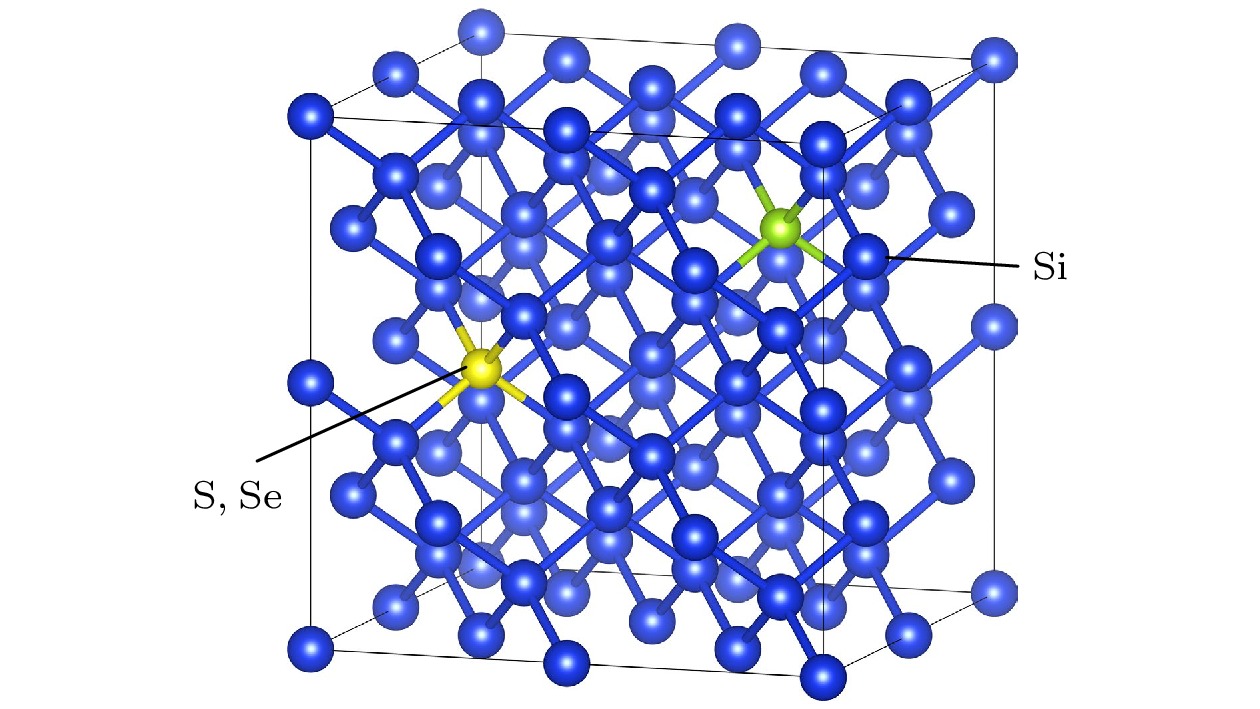
表 1 结构优化后单晶硅、Si超晶胞、S, Se单掺杂及共掺杂硅的晶格常数及键长
Table 1. Lattice constants and bond lengths of single crystal silicon, Si supercell, S, Se single doping and co-doping silicon after structure optimization.
Compound Lattice
constant/ÅBond length/Å ${E^{\text{f}}}$/eV Si—X Si—Si Si单晶胞 5.467 — 2.367 — Si(2×2×2) 10.934 — 2.367 — ${\text{S}}{{\text{i}}_{{63}}}{{\text{S}}_{}}$ 10.928 2.463 2.365 1.24 ${\text{S}}{{\text{i}}_{{63}}}{\text{Se}}$ 10.946 2.558 2.368 1.27 $ {\text{S}}{{\text{i}}_{{62}}}{\text{(Se, S)}} $ 10.944 2.457
(Si—S)2.364 2.54 2.552
(Si—Se)2.367 -
[1] 周治平 2014 武汉光电论坛论文集 (武汉: 华中科技大学出版社) 第249页
Zhou Z P 2014 Proceedings of Wuhan Opto-Electronic Forum (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology Press) p249
[2] Michael O, Mathias K, Steffen E, Maurice W, Zili Y, Daniel S, Köllner A C, Joachim N B, Jörg S 2021 IEEE Sens. J. 20 18696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yang J J, Jurczak P, Cui F, Li K S, Tang M C, Billiald L, Beanland R 2019 J. Cryst. Growth 514 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Her T H, Finlay R J, Mazur E, Wu C, Deliwala S 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 1673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu C, Crouch C H, Zhao L, Carey J E, Younkin R, Levinson J A, Mazur E, Farrell R M, Gothoskar P, Karger A 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 1850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tansel T, Aydin O 2024 J. Phys. D 57 295103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhao X N, Lin K, Zhao B, Du W H, Nivas J J, Amoruso S, Wang X 2023 Appl. Surf. Sci. 619 156624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 钟豪 2019 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Zhong H 2019 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[9] Du L Y, Yin J, Zeng W, Pang S Z, Yi H 2023 Mater. Lett. 331 133463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 高宇辰 2022 硕士学位论文 (吉林: 吉林大学)
Gao Y C 2022 M. S. Thesis (Jilin: Jilin University
[11] Yang Y, Yi Z R, Chao L, Zhao J H 2023 Opt. Quantum Electron. 55 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 任哲毅 2024 硕士学位论文 (吉林: 吉林大学)
Ren Z Y 2024 M. S. Thesis (Jilin: Jilin University
[13] Zhu J, Gandi N A, Schwingenschlögl U 2018 Adv. Theor. Simul. 1 1800017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang X Y, Wang T, Ren Q, Xu J T, Cui Y A 2023 Micro Nanostruct. 184 207695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 薛晓晚 2018 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Xue X W 2018 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology
[16] 梁伟华, 丁学成, 褚立志, 邓泽超, 郭建新, 吴转花, 王英龙 2010 59 8071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang W H, Ding X C, Chu L Z, Deng Z C, Guo J X, Wu Z H, Wang Y L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 8071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tang X, Li W, Xu W, Ren Q Y, Chen Q Y 2024 Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 184 108797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu M, Cai G K, Li Z, Ye L, Wang C 2024 Vacuum 225 113222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li J Y, Zhao C L, Li W, Ren Q Y, Xu J, Xu W 2023 Phys. Scr. 98 115408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Sharif M N, Yang J S, Zhang X K, Tang Y H, Yang G, Wang K F 2024 Vacuum 219 112714
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Comput. Mater. Sci. 6 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shuichi N 1984 J. Chem. Phys. 81 511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 关丽, 李强, 赵庆勋, 郭建新, 周阳, 金利涛, 耿波, 刘保亭 2009 58 5624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guan L, Li Q, Zhao Q X, Guo J X, Zhou Y, Jin L T, Geng B, Liu B T 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 5624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kumaravelu G, Alkaisi M M, Bittar A 2002 29th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference New Orleans, LA, USA, May 19–24, 2002 p258
[26] 杜玲艳 2018 博士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Du L Y 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[27] 宣曜宇 2017 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Xuan Y Y 2017 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
[28] Khan M, Xu J N, Chen N, Cao W B 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 513 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Feng J, Xiao B, Chen C J, Zhou C T, Du Y P, Zhou R 2009 Solid State Commun. 149 1569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3266
- PDF下载量: 103
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: