-
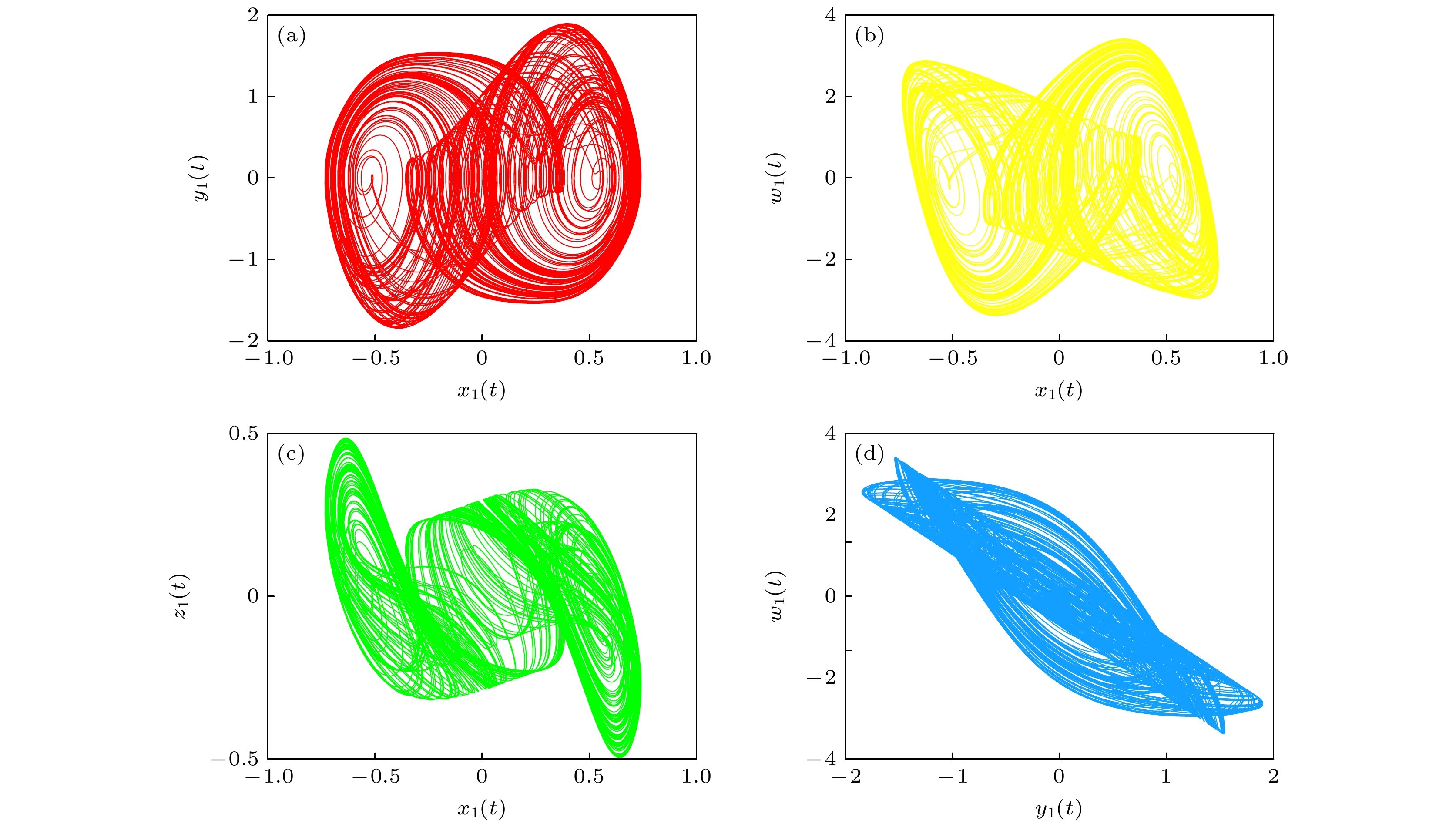
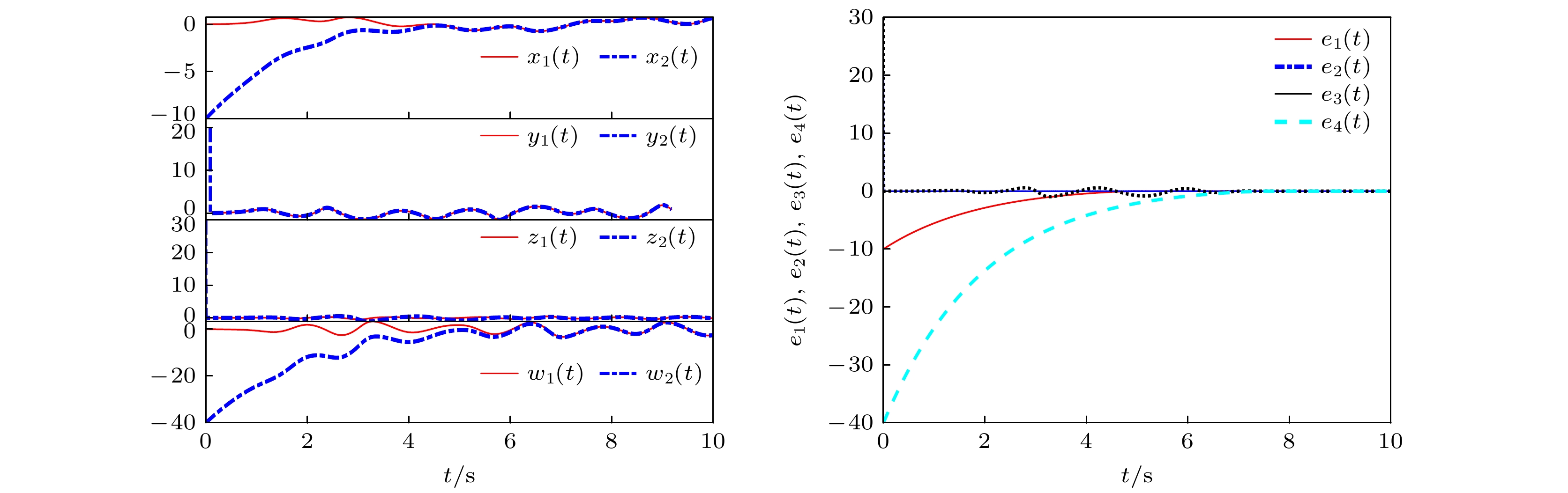
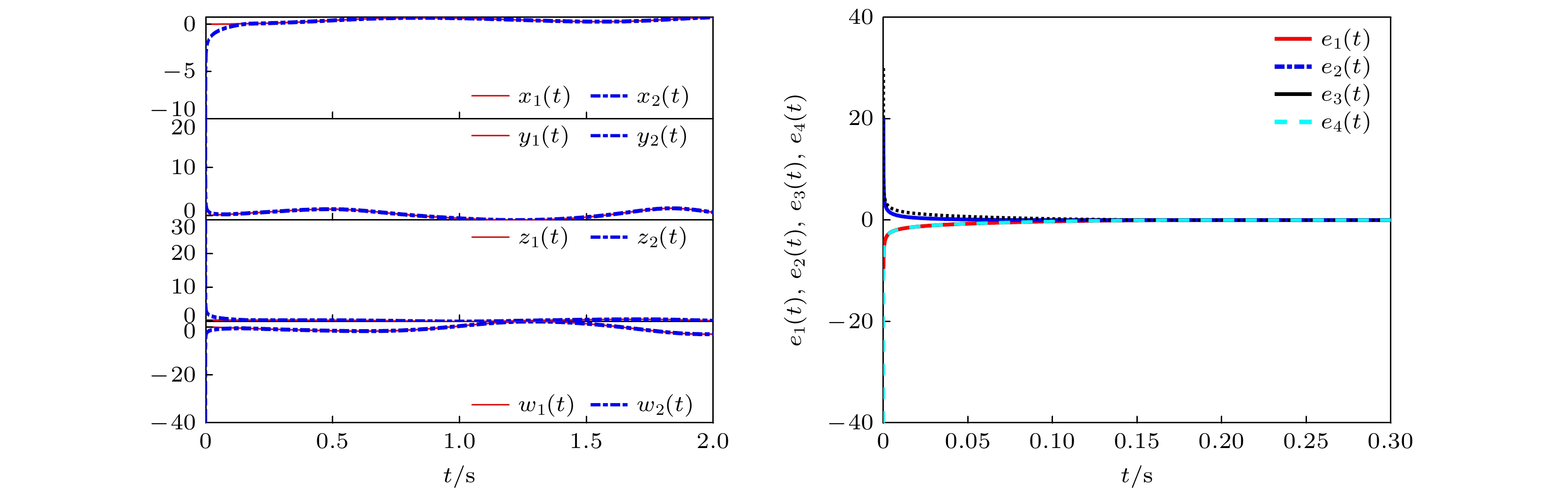
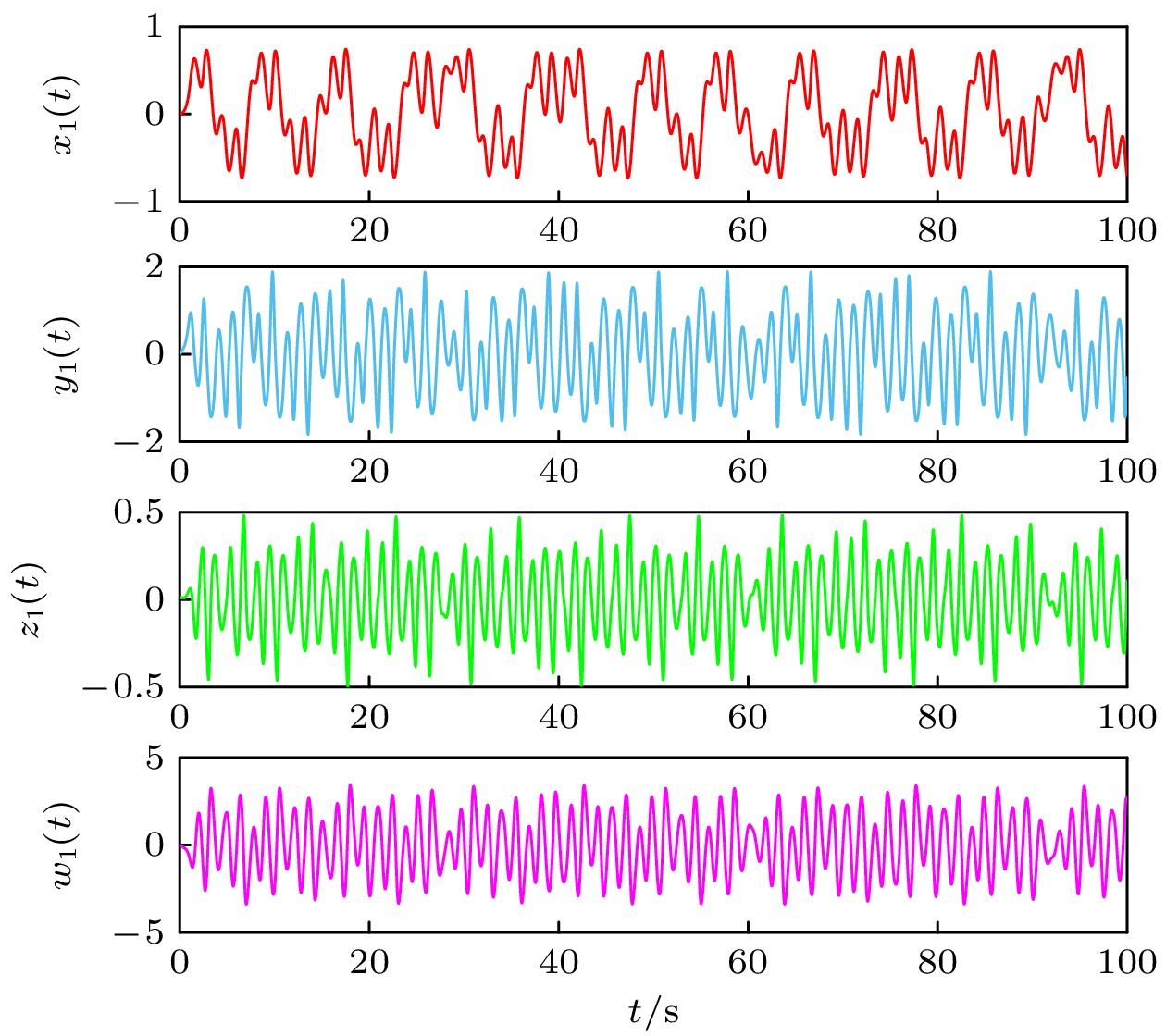
针对一类具有更复杂动力学行为的忆阻混沌系统, 本文基于新型幂次趋近律设计两种滑模控制协议分别实现了系统的有限时间、固定时间同步. 首先对于有限时间同步问题, 基于Lyapunov稳定性理论和有限时间稳定性理论, 推导了实现全局有限时间同步的充分条件, 得到了与系统初始条件有关的稳定时间上限, 并证明了系统的稳定性. 对于固定时间同步问题, 利用固定时间稳定性理论, 推导得到不随系统初始值变化的收敛时间上确界. 最后, 通过设置两组对照实验, 比较了两种滑模控制律对系统同步状态的影响, 其仿真结果与数值分析相符, 从而验证了本文的有效性和可行性.Two innovative sliding mode control laws based on the convergence principle of reaching law are presented in this work. These control laws are used to achieve both finite-time and fixed-time synchronization for a specific class of memristive chaotic system, which are known for their intricate and complex dynamical behaviors. By utilizing these control strategies, we can effectively manage the synchronization process and ensure rapid convergence. Firstly, for the finite-time synchronization issue, a novel power reaching law is derived. Compared with the conventional reaching law, the reaching law presented in this work has a prominent advantage that the chattering of the sliding mode control is reduced to a lesser extent and the speed of reaching the sliding surface is quicker. An upper bound of the stabilization time, which is dependent on the initial conditions of the system, is obtained and the system is proved stable. For the fixed time synchronization problem, a new double power reaching law is put forward to minimize the chattering and accelerate the convergence. Then, by utilizing the fixed time stability theory, the upper bound of the convergence time that remains invariant with the initial value of the system is derived. Finally, in order to verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the theoretical derivation in this paper, two sets of control experiments are set up and the influences of the two control laws on the system synchronization state are compared. The experimental phenomenon strongly proves the accuracy of the proposed theorem.
-
Keywords:
- finite-time synchronization /
- fixed-time synchronization /
- new power reaching law /
- memristive chaotic systems
[1] An X L, Liu S Y, Xiong L, Zhang J G, Li X Y 2024 Expert Syst. Appl. 243 122899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lai Q, Yang L, Hu G W, Guan Z H, Iu H H C 2024 IEEE Trans. Cybern. 54 4039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lai Q, Yang L, Chen G R 2024 IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 71 7819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ji X Y, Dong Z K, Han Y F, Lai C S, Qi D L 2023 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33 7928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ji X Y, Dong Z K, Han Y F, Lai C S, Zhou G D, Qi D L 2023 IEEE Trans. Consum. Electr. 69 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Babanli K M, Kabaoglu R O 2024 Inf. Sci 657 119988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王国超, 李星辉, 颜树华, 谭立龙, 管文良 2021 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Li X H, Yan S H, Tan L L, Guan W L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zheng H, Zhu W, Li X 2024 Chaos Soliton Fract. 180 114496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王栋梁, 史卓, 王井上, 吴洪悦, 张晓辉, 常国庆 2024 73 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D L, Shi Z, Wang J S, Wu H Y, Zhang X H, Chang G Q 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lai Q, Chen Z J 2023 Chaos Soliton Fract. 176 114118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张骁骏, 袁夏明, 王向阳, 朱纪洪, 李春文 2022 自动化学报 48 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X J, Yuan X M, Wang X Y, Zhu J H, Li C W 2022 Acta Autom. Sin. 48 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Mobayen S 2018 ISA T 77 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 吴朝俊, 方礼熠, 杨宁宁 2024 73 010501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu C J, Fang L Y, Yang N N 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 010501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Junejo A K, Xu W, Mu C, Ismail M M, Liu Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 12110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 王宇娟, 涂俐兰, 宋帅, 李宽洋 2018 67 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y J, Tu L L, Song S, Li K Y, 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lai Q, Yang L 2023 Chaos Soliton Fract. 174 113807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hao Y, Fang Z, Liu H 2024 Inf. Sci. 666 120423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bhat S P, Bernstein D S 2000 SIAM J. Control Optim. 38 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dong H L, Cao J D, Liu H 2023 Chaos 33 043113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fu H, Kao Y G 2023 Chaos 33 043136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Polyakov A 2011 IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 57 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ullah S, Khan Q, Zaidi M M, Hua L G 2024 Inf. Sci. 659 120087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zheng C C, Hu C, Yu J, Wen S P 2024 Neural Netw. 169 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu X, Wang L, Zhang C K, He Y 2024 IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 32 2307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang L, Dong T, Ge M F 2019 Appl. Math. Comput. 347 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fallaha C J, Saad M, Kanaan H Y, Haddad K A 2010 IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58 600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang L, Jiang S, Ge M F, Hu C, Hu J H 2021 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 68 4957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] An X L, Liu S Y, Xiong L, Zhang J G, Li X Y 2024 Expert Syst. Appl. 243 122899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lai Q, Yang L, Hu G W, Guan Z H, Iu H H C 2024 IEEE Trans. Cybern. 54 4039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lai Q, Yang L, Chen G R 2024 IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 71 7819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ji X Y, Dong Z K, Han Y F, Lai C S, Qi D L 2023 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33 7928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ji X Y, Dong Z K, Han Y F, Lai C S, Zhou G D, Qi D L 2023 IEEE Trans. Consum. Electr. 69 1005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Babanli K M, Kabaoglu R O 2024 Inf. Sci 657 119988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王国超, 李星辉, 颜树华, 谭立龙, 管文良 2021 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Li X H, Yan S H, Tan L L, Guan W L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zheng H, Zhu W, Li X 2024 Chaos Soliton Fract. 180 114496
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王栋梁, 史卓, 王井上, 吴洪悦, 张晓辉, 常国庆 2024 73 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D L, Shi Z, Wang J S, Wu H Y, Zhang X H, Chang G Q 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lai Q, Chen Z J 2023 Chaos Soliton Fract. 176 114118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张骁骏, 袁夏明, 王向阳, 朱纪洪, 李春文 2022 自动化学报 48 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X J, Yuan X M, Wang X Y, Zhu J H, Li C W 2022 Acta Autom. Sin. 48 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Mobayen S 2018 ISA T 77 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 吴朝俊, 方礼熠, 杨宁宁 2024 73 010501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu C J, Fang L Y, Yang N N 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 010501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Junejo A K, Xu W, Mu C, Ismail M M, Liu Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 12110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 王宇娟, 涂俐兰, 宋帅, 李宽洋 2018 67 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y J, Tu L L, Song S, Li K Y, 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 050504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lai Q, Yang L 2023 Chaos Soliton Fract. 174 113807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hao Y, Fang Z, Liu H 2024 Inf. Sci. 666 120423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bhat S P, Bernstein D S 2000 SIAM J. Control Optim. 38 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Dong H L, Cao J D, Liu H 2023 Chaos 33 043113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fu H, Kao Y G 2023 Chaos 33 043136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Polyakov A 2011 IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 57 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ullah S, Khan Q, Zaidi M M, Hua L G 2024 Inf. Sci. 659 120087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zheng C C, Hu C, Yu J, Wen S P 2024 Neural Netw. 169 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hu X, Wang L, Zhang C K, He Y 2024 IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 32 2307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang L, Dong T, Ge M F 2019 Appl. Math. Comput. 347 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fallaha C J, Saad M, Kanaan H Y, Haddad K A 2010 IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58 600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang L, Jiang S, Ge M F, Hu C, Hu J H 2021 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 68 4957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3626
- PDF下载量: 87
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: