-
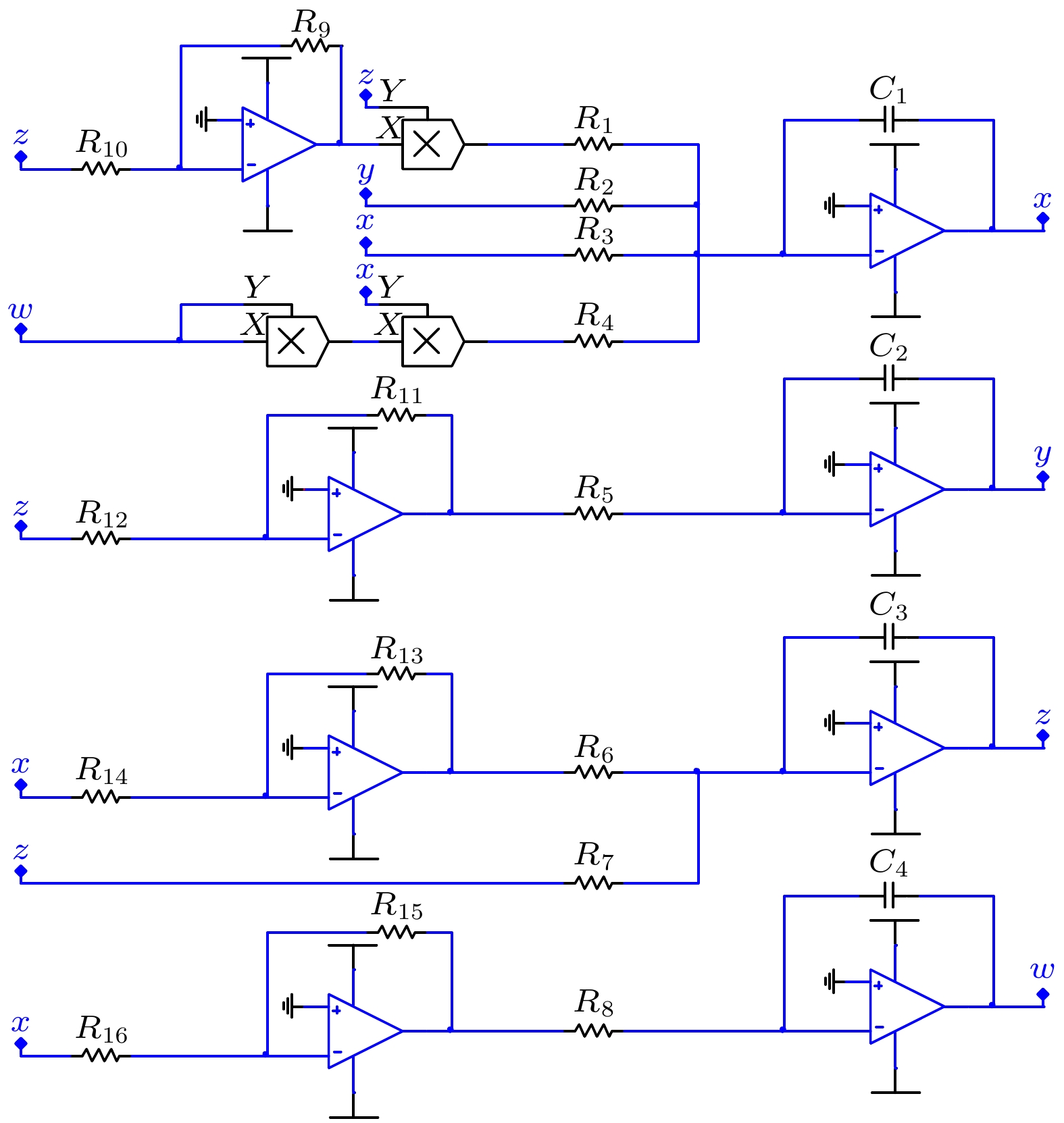
Using memristors to construct special chaotic systems is highly interesting and meaningful. A simple four-dimensional memristive chaotic system with an infinite number of coexisting attractors is proposed in this paper, which has a relatively simple form but demonstrates complex dynamical behavior. Here, we use digital simulations to further investigate the system and utilize the bifurcation diagrams to describe the evolution of the dynamical behavior of the system with the influence of parameters. We find that the system can generate an abundance of chaotic and periodic attractors under different parameters. The amplitudes of the oscillations of the state variables of the system are closely dependent on the initial values. In addition, the experimental results of the circuit are consistent with the digital simulations, proving the existence and feasibility of this memristive chaotic system.
-
Keywords:
- memristive chaotic system /
- coexisting attractors /
- dynamic behaviors /
- circuit realization
[1] Chua L O 1971 IEEE Trans. Circuits Theor. 18 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li C B, Sprott J C 2014 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 24 1450131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 鲜永菊, 夏诚, 钟德, 徐昌彪 2019 控制理论与应用 36 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xian Y J, Xia C, Zhong D, Xu C B 2019 Control Theory Appl. 36 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li C B, Lu T N, Chen G R, Xing H Y 2019 Chaos 29 051102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lai Q, Wan Z Q, Kuate P D K 2020 Electron. Lett. 56 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 颜闽秀, 徐辉 2021 计算物理 38 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan M X, Xu H 2021 Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 38 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lai Q, Kuate P D K, Liu F, Liu F, Iu H H C 2019 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 67 1129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lai Q 2021 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 31 2150013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 耿睿, 李中奇, 杨辉 2021 华东交通大学学报 38 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng R, Li Z Q, Yang H 2021 J. East China Jiaotong Univ. 38 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, Williams R S 2008 Nature 453 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Itoh M, Chua L O 2008 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 18 3183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Muthuswamy B, Kokate P P 2009 IETE Tech. Rev. 26 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z J, Zeng Y C 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 040502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C H, Liu X M, Xia H 2017 Chaos 27 033114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lai Q, Wan Z Q, Kengne L K, Kuate P D K, Chen C Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 68 2197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李晓霞, 郑驰, 王雪, 曹樱子, 徐桂芝 2022 哈尔滨工业大学学报 54 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X X, Zheng C, Wang X, Cao Y Z, Xu G Z 2022 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 54 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lai Q, Lai C, Kuate P D K, Li C B, He S B 2022 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 32 2250042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lai Q, Wan Z Q, Zhang H, Chen G R 2022 IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lai Q, Lai C, Zhang H, Li C B 2022 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 158 112017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 包伯成, 胡文, 许建平, 刘中, 邹凌 2011 60 120502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao B C, Hu W, Xu J P, Liu Z, Zou L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 120502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li C B, Sprott J C 2016 Optik 127 10389
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 孙佳钰 2021 硕士学位论文 (南京: 南京信息工程大学)
Sun J Y 2021 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[23] Huang L L, Wang Y L, Jiang Y C, Lei T F 2021 Math. Prob. Eng. 2021 7457220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang X, Li C B, Chen Y D, Iu H H C Lei T F 2020 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 139 110000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Carr J 1981 Applications of Centre Manifold Theory (New York: Springer) pp1–50
[26] 史传宝, 王光义, 臧寿池 2017 杭州电子科技大学学报(自然科学版) 37 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi C B, Wang G Y, Zang S C 2017 J. Hangzhou Dianzi Univ. (Nat. Sci. ) 37 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 王伟, 曾以成, 陈争, 孙睿婷 2017 计算物理 34 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W, Zeng Y C, Chen Z, Sun R T 2017 Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 34 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 参数
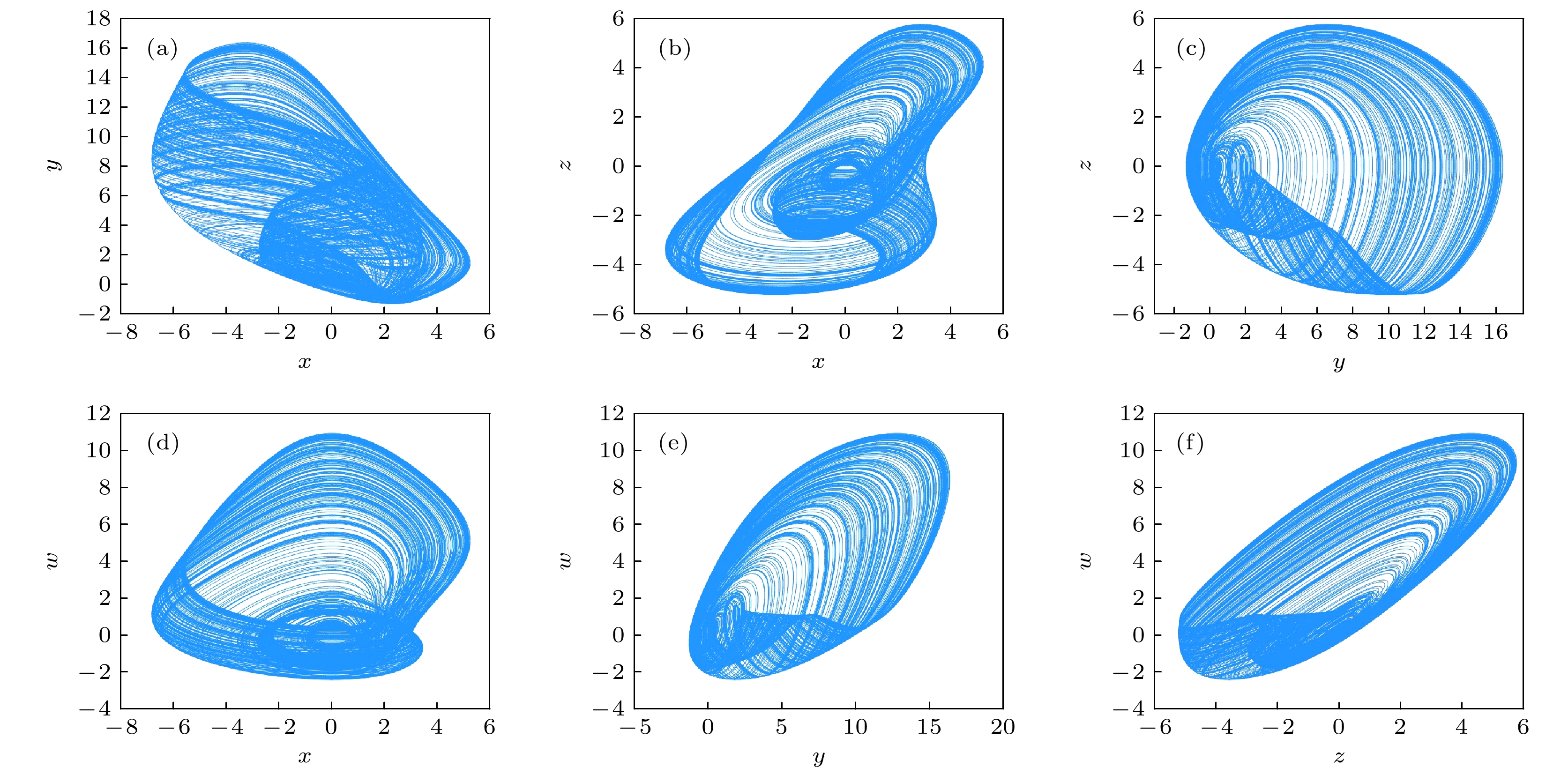
$ a=1.6, b=0.5, p=0.2, q=0.1 $ 和初值$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ 时系统的相平面图 (a)$ x \text- y $ 平面; (b)$ x\text- z $ 平面; (c)$ y \text- z $ 平面; (d)$ x \text- w $ 平面; (e)$ y \text- w $ 平面; (f)$ z \text- w $ 平面Fig. 2. Phase portraits of the system with parameters
$ a = 1.6, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ and initial values$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ : (a)$ x \text- y $ plane; (b)$ x \text- z $ plane; (c)$ y \text- z $ plane; (d)$ x \text- w $ plane; (e)$ y \text- w $ plane; (f)$ z \text- w $ plane.图 3 参数
$ b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ 和初值$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ 时系统随参数$ a \in [0, 10] $ 的分岔图(a)与Lyapunov指数谱(b)Fig. 3. Bifurcation diagram (a) and Lyapunov exponent spectrum (b) for system parameters
$ a \in [0, 10] $ with$b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, $ $ {\text{ }}q = 0.1$ and initial values of$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ .图 4 系统参数为
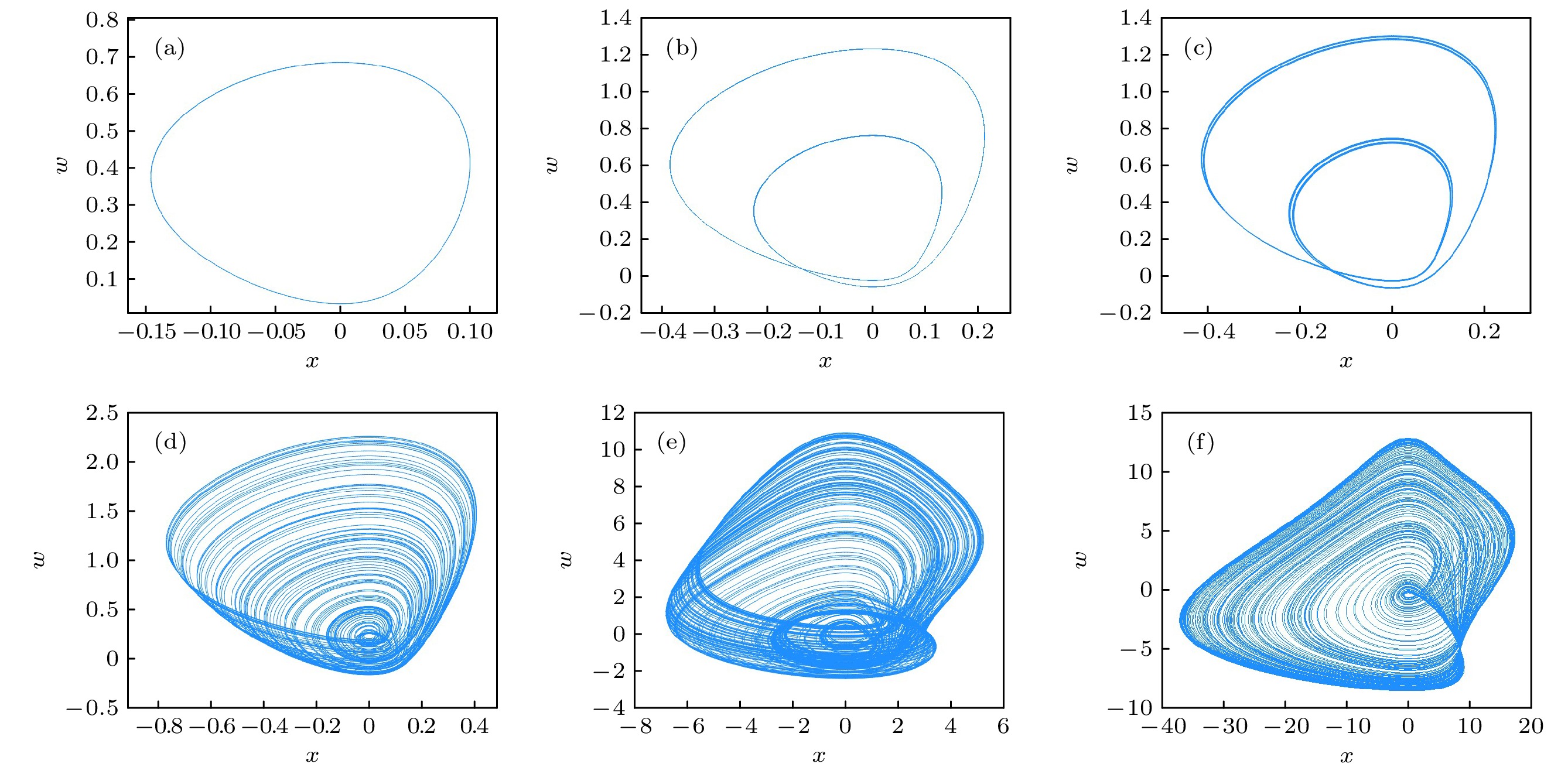
$ b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ , 初值为$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ 时, 表2中不同$ a $ 值对应的$x \text- w$ 相平面图 (a) a = 0.1; (b) a = 0.15; (c) a = 0.155; (d) a = 0.2; (e) a = 1.6; (f) a = 9.1Fig. 4.
$x \text- w$ phase plane diagrams corresponding to different$ a $ values in Table 2 for system parameter$ b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ and an initial value of$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ : (a) a = 0.1; (b) a = 0.15; (c) a = 0.155; (d) a = 0.2; (e) a = 1.6; (f) a = 9.1.图 5 系统参数为
$a \;=\; 1.6, {\text{ }}b\; =\; 0.5, {\text{ }}q\; =\; 0.1$ , 初值为$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ 时, 系统参数$ p \in (0, 0.52] $ 的分岔图(a)与Lyapunov指数谱(b)Fig. 5. Bifurcation diagram (a) with Lyapunov exponent spectrum (b) for system parameters
$ p \in (0, 0.52] $ for$a = 1.6, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, $ $ {\text{ }}q = 0.1$ and initial values of$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ .图 6 系统参数为
$ a = 1.6, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2 $ , 初值为$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ 时, 系统参数$ q \in [0.1, 0.16] $ 的分岔图(a)与Lyapunov指数谱(b)Fig. 6. Bifurcation diagram (a) with Lyapunov exponent spectrum (b) for system parameters
$ q \in [0.1, 0.16] $ with$a = 1.6, $ $ {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2$ and initial values of$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ .图 7 表3中的不同系统参数下的共存吸引子的
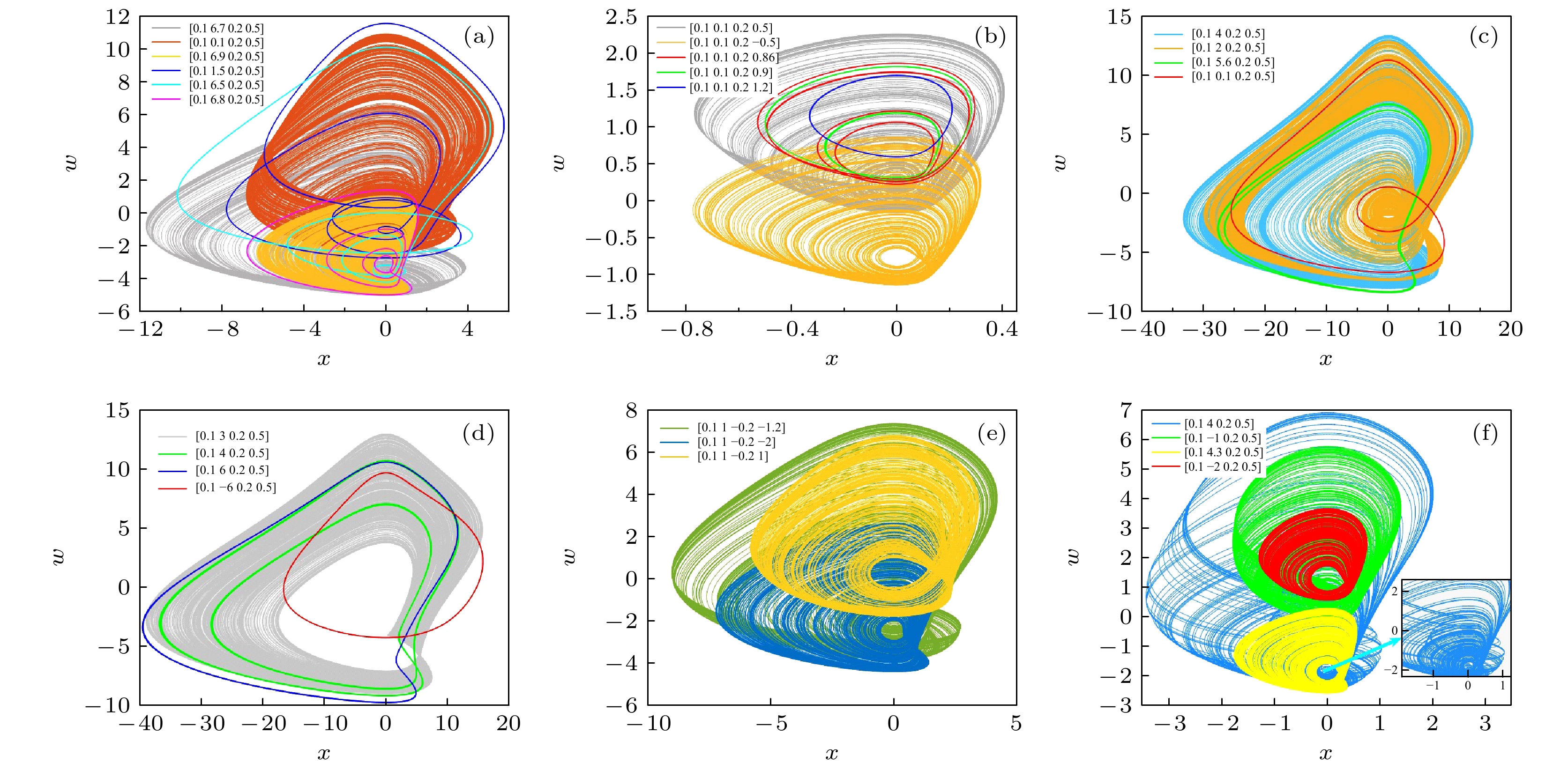
$x {\text{-}} w$ 相平面图 (a) a = 1.6, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (b) a = 0.2, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (c) a = 6, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (d) a = 8, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (e) a = 2, b = 0.6, p = 0.5, q = 0.1; (f) a = 0.5, b = 0.5, p = 0.5, q = 0.1Fig. 7.
$x {\text{-}} w$ phase plane plots of coexisting attractors for different system parameters in Table 3: (a) a = 1.6, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (b) a = 0.2, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (c) a = 6, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (d) a = 8, b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1; (e) a = 2, b = 0.6, p = 0.5, q = 0.1; (f) a = 0.5, b = 0.5, p = 0.5, q = 0.1.图 8 参数
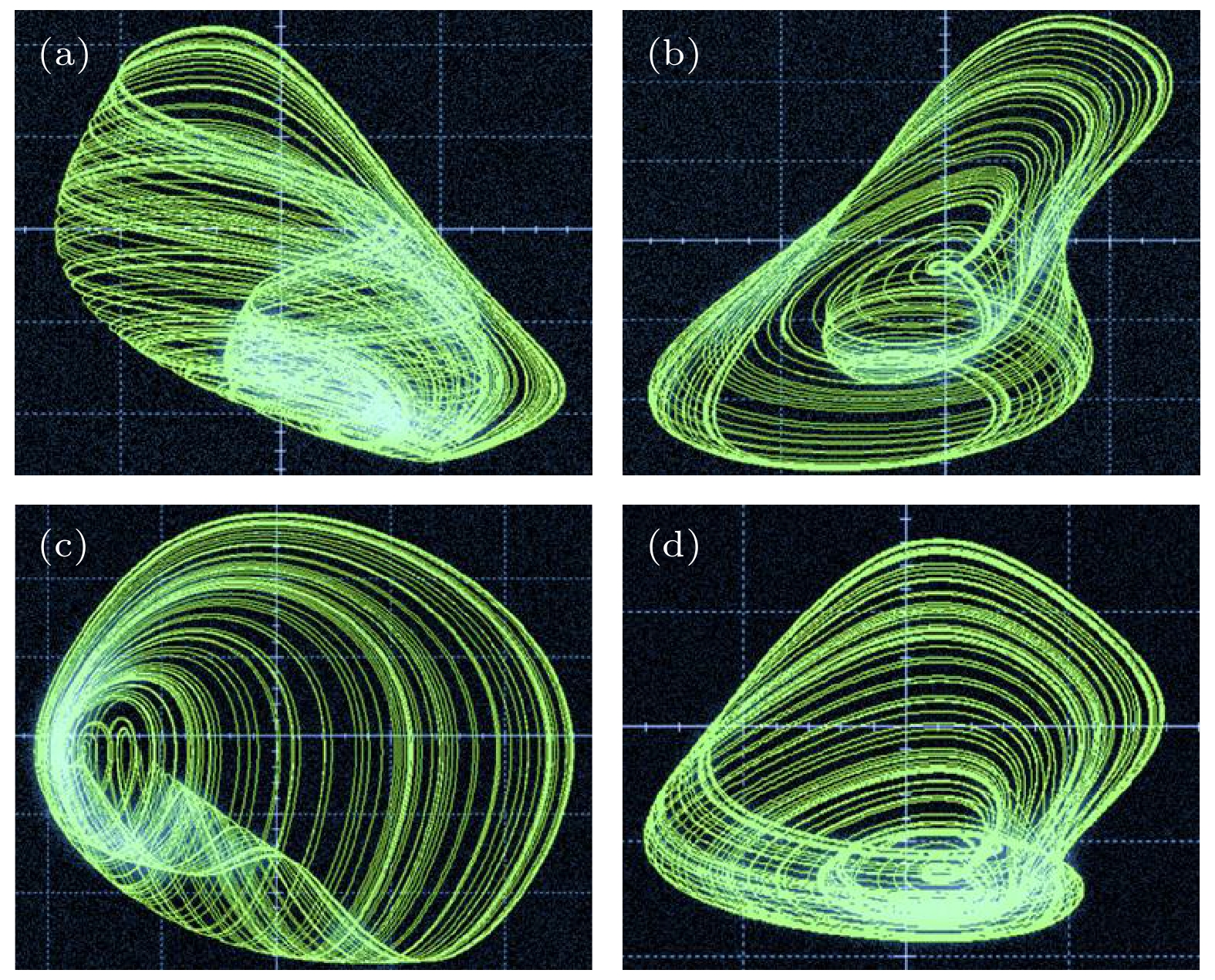
$a = 1.6, \;b = 0.5, \;p = 0.2, \;q = 0.1$ 时, 系统(3)在不同初始条件条件下的A, B系列多共存引子: (a)共存周期吸引子A1—A9; (b)共存混沌吸引子B1—B6Fig. 8. The system (3) with parameters
$a = 1.6, \;b = 0.5, \;p = 0.2, \;q = 0.1$ has multiple coexisting chaotic attractors of series A and B under different initial conditions: (a) Coexisting periodic attractors A1–A9; (b) coexisting chaotic attractors B1–B6.图 9 参数
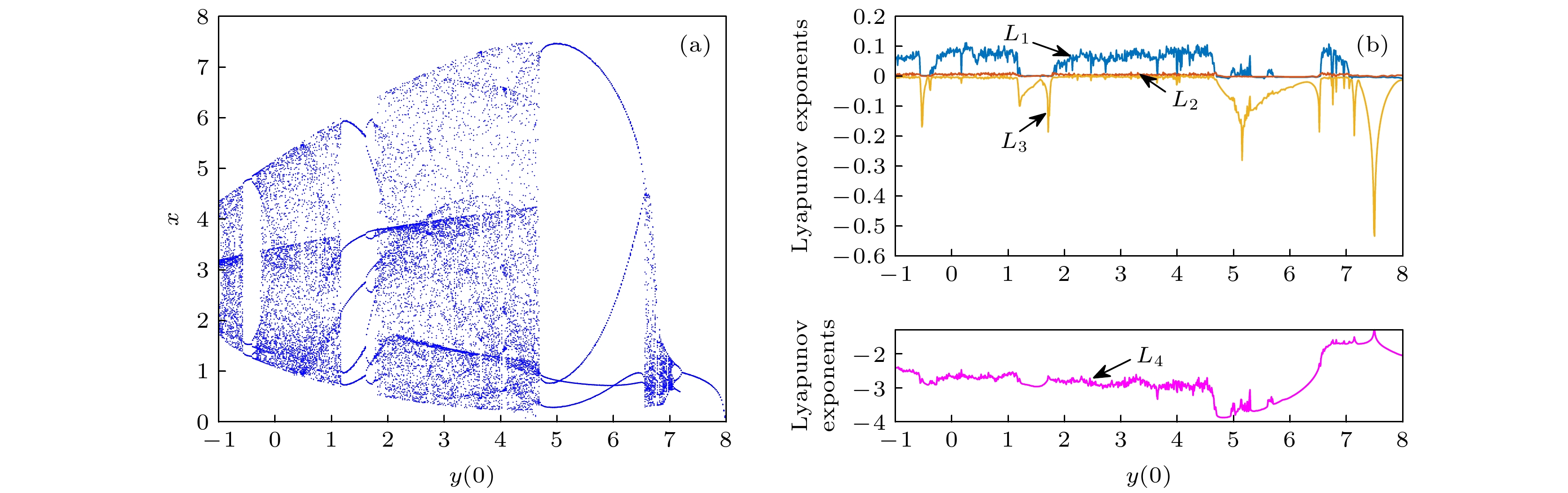
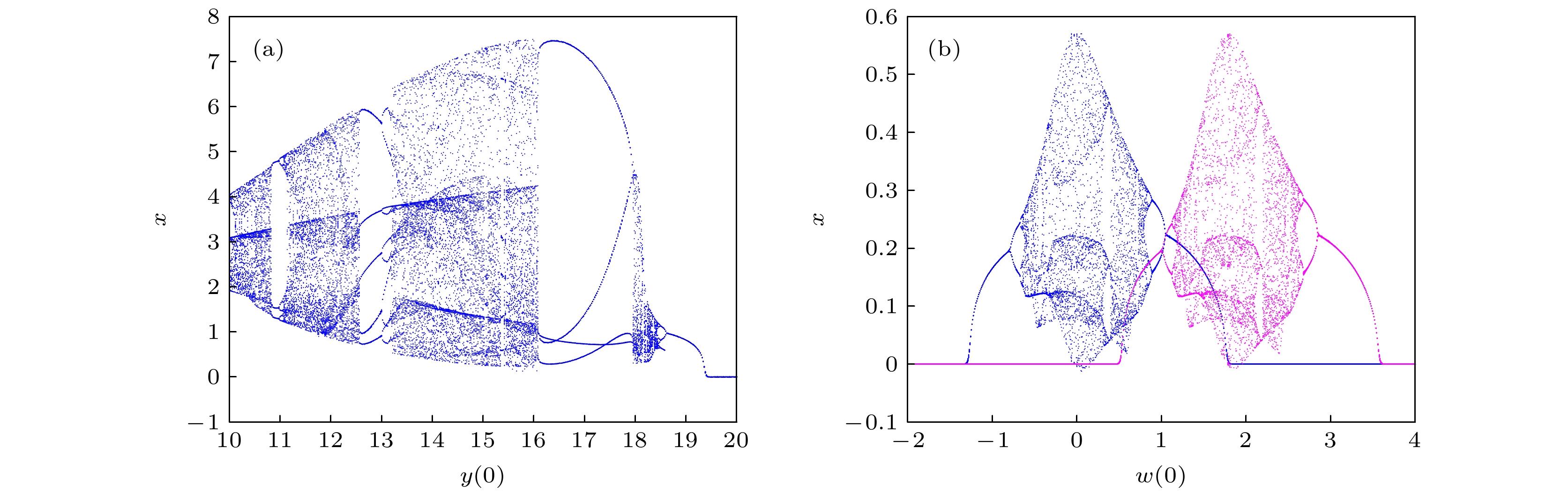
$ a = 1.6, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ 和初始值$ [0.1, y(0), 0.2, 0.5] $ 时, 系统(3)随初始值$ y(0) \in [ - 1, 8] $ 的分岔图(a)与Lyapunov指数谱(b)Fig. 9. Bifurcation diagram (a) of system (3) initial condition
$ y(0) \in [ - 1, 8] $ for parameter$ a = 1.6, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ and initial value$ [0.1, y(0), 0.2, 0.5] $ with Lyapunov exponential spectrum (b).图 10 系统(3)随初始值变化的分岔图 (a)参数
$ a = 1.6, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ 且初值为$ [0.1, y(0), 1, 7] $ 时, 系统初始条件$ y(0) \in [10,20] $ 的分岔图; (b)参数为$ a = 0.2, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ 和初值为$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, w(0)] $ (蓝色),$ [0.1, 0.1, 2, w(0)] $ (紫色)时, 系统初始条件$ w(0) \in [ - 2, 4] $ 的分岔图Fig. 10. Bifurcation diagram of system (3) with initial values: (a) Bifurcation diagram of system initial condition
$ y(0) \in [10,20] $ for parameter$ a = 1.6, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ with initial value$ [0.1, y(0), 1, 7] $ ; (b) bifurcation diagram of system initial condition$ w(0) \in [ - 2, 4] $ for parameter$ a = 0.2, {\text{ }}b = 0.5, {\text{ }}p = 0.2, {\text{ }}q = 0.1 $ and initial values$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, w(0)] $ (blue) and$ [0.1, 0.1, 2, w(0)] $ (purple).表 2 系统参数为
$ b = 0.5, p = 0.2, q = 0.1 $ , 初值为$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ 时, 不同$ a $ 值下吸引子类型及图像编号Table 2. Attractor types and image numbers for different
$ a $ values with system parameter$b = 0.5, p = 0.2, $ $ q = 0.1$ and initial values$ [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5] $ .表 3 不同系统参数下系统共存吸引子类型与图像编号
Table 3. Coexistence of attractor types and image numbers for different system parameters.
系统参数 初始值 吸引子类型 图像编号 a = 1.6, b = 0.5,
p = 0.2, q = 0.1[0.1 0.1 0.2 0.5], [0.1 6.7 0.2 0.5]
[0.1 6.9 0.2 0.5], [0.1 1.5 0.2 0.5]
[0.1 6.5 0.2 0.5], [0.1 6.8 0.2 0.5]三个混沌吸引子与三个周期吸引子 图7(a) a = 0.2, b = 0.5,
p = 0.2, q = 0.1[0.1 0.1 0.2 1.2], [0.1 0.1 0.2 –0.5]
[0.1 0.1 0.2 0.86], [0.1 0.1 0.2 0.5]
[0.1 0.1 0.2 0.9]三个周期吸引子与两个混沌吸引子 图7(b) a = 6, b = 0.5,
p = 0.2, q = 0.1[0.1 0.1 0.2 0.5], [0.1 5.6 0.2 0.5]
[0.1 2 0.2 0.5], [0.1 4 0.2 0.5]两个周期吸引子与两个混沌吸引子 图7(c) a = 8, b = 0.5,
p = 0.2, q = 0.1[0.1 –6 0.2 0.5], [0.1 6 0.2 0.5]
[0.1 4 0.2 0.5], [0.1 3 0.2 0.5]三个周期吸引子与一个混沌吸引子 图7(d) a = 2, b = 0.6,
p = 0.5, q = 0.1[0.1 1 –0.2 1], [0.1 1 –0.2 –2]
[0.1 1 –0.2 –1.2]三个混沌吸引子 图7(e) a = 0.5, b = 0.5,
p = 0.5, q = 0.1[0.1, 4, 0.2, 0.5], [0.1, –1, 0.2, 0.5]
[0.1, 4.3, 0.2, 0.5], [0.1, –2, 0.2, 0.5]四个混沌吸引子 图7(f) -
[1] Chua L O 1971 IEEE Trans. Circuits Theor. 18 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li C B, Sprott J C 2014 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 24 1450131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 鲜永菊, 夏诚, 钟德, 徐昌彪 2019 控制理论与应用 36 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xian Y J, Xia C, Zhong D, Xu C B 2019 Control Theory Appl. 36 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li C B, Lu T N, Chen G R, Xing H Y 2019 Chaos 29 051102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lai Q, Wan Z Q, Kuate P D K 2020 Electron. Lett. 56 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 颜闽秀, 徐辉 2021 计算物理 38 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan M X, Xu H 2021 Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 38 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lai Q, Kuate P D K, Liu F, Liu F, Iu H H C 2019 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 67 1129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lai Q 2021 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 31 2150013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 耿睿, 李中奇, 杨辉 2021 华东交通大学学报 38 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng R, Li Z Q, Yang H 2021 J. East China Jiaotong Univ. 38 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, Williams R S 2008 Nature 453 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Itoh M, Chua L O 2008 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 18 3183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Muthuswamy B, Kokate P P 2009 IETE Tech. Rev. 26 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z J, Zeng Y C 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 040502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C H, Liu X M, Xia H 2017 Chaos 27 033114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lai Q, Wan Z Q, Kengne L K, Kuate P D K, Chen C Y 2020 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 68 2197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李晓霞, 郑驰, 王雪, 曹樱子, 徐桂芝 2022 哈尔滨工业大学学报 54 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X X, Zheng C, Wang X, Cao Y Z, Xu G Z 2022 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 54 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lai Q, Lai C, Kuate P D K, Li C B, He S B 2022 Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 32 2250042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lai Q, Wan Z Q, Zhang H, Chen G R 2022 IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lai Q, Lai C, Zhang H, Li C B 2022 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 158 112017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 包伯成, 胡文, 许建平, 刘中, 邹凌 2011 60 120502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao B C, Hu W, Xu J P, Liu Z, Zou L 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 120502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li C B, Sprott J C 2016 Optik 127 10389
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 孙佳钰 2021 硕士学位论文 (南京: 南京信息工程大学)
Sun J Y 2021 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[23] Huang L L, Wang Y L, Jiang Y C, Lei T F 2021 Math. Prob. Eng. 2021 7457220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang X, Li C B, Chen Y D, Iu H H C Lei T F 2020 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 139 110000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Carr J 1981 Applications of Centre Manifold Theory (New York: Springer) pp1–50
[26] 史传宝, 王光义, 臧寿池 2017 杭州电子科技大学学报(自然科学版) 37 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi C B, Wang G Y, Zang S C 2017 J. Hangzhou Dianzi Univ. (Nat. Sci. ) 37 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 王伟, 曾以成, 陈争, 孙睿婷 2017 计算物理 34 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang W, Zeng Y C, Chen Z, Sun R T 2017 Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 34 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7104
- PDF下载量: 209
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: