-
以钙钛矿为顶、晶硅为底的钙钛矿/硅叠层电池可以提高太阳光谱的利用率, 突破单结电池中的肖克利极限(SQ极限), 是实现更高光电转换效率的有效途径之一. 如何降低光子在电池表面和界面的传输损失, 最大化响应层的吸收效率是其中的关键. 本文通过时域有限差分法和严格耦合波分析, 系统研究了不同种类金属纳米球对钙钛矿/硅叠层电池的光谱响应和能量转换效率的增强机制. 结果表明, 由于表面电子云对光波的共振增强, 金属纳米结构的引入显著提升了光子进入到电池响应层的透射率, 电池总的吸收光谱和量子响应效率因而得到明显提升. 对于最优的Al纳米球, 观察到的加权平均透射率从73.16%提升到79.15%, 电池能量转换效率从23.09%提高到24.97%, 效率相对提高了8.14%.Perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells, by combining perovskite as a top absorber material and crystalline silicon as a bottom absorber material, can expand and enhance the utilization of solar spectrum. Therefore, such a tandem structure shows great potential to break through the Shockley-Queisser (SQ) limit of 31%-33% for single-junction (SJ) solar cells and is considered as one of the most promising approaches to achieving the higher performance in photoelectric conversion of solar cells. Reducing the optical losses from the surface and interfaces of cell device and making more photons propagate into the active layers are the key factors for achieving the goal. In this paper, the enhancement of spectral response and energy conversion efficiency of perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells depending on Au, Ag, Cu, Al nanosphere are studied by using the finite difference time domain method and rigorous coupled-wave analysis. The results show that owing to the introduction of metal nanosphere, the transmittance of photons propagating into the active material is promoted significantly. Therefore, the cell device achieves an apparent increase both in total absorbance and in quantum efficiency. The observed weighted average transmittance and energy conversion efficiency are increased from 73.16% and 23.09% to 79.15% and 24.97%, respectively, with an 8.14% improvement for the perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells coated with the optimized Al nanospheres.
-
Keywords:
- metal nanostructure /
- optical properties /
- plasmon /
- tandem cell
[1] Masuko K, Shigematsu M, Hashiguchi T 2014 IEEE J. Photovolt. 4 1433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yoshikawa K, Kawasaki H, Yoshida W 2017 Nat. Energy 2 17032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Richter A, Hermle M, Glunz S W 2013 IEEE J. Photovolt. 3 1184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu X, Jiang J, Wang F, et al. 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 46894
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kojima A, Teshima K, Shirai Y, Miyasaka T 2009 Am. Chem. Soc. 131 6050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) 2021 https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/pdfs/best-research-cell-efficiencies.
[7] Jeong M, Choi I W, Go E M 2020 Science 369 1615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jeong J, Kim M, Seo J 2021 Nature 592 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 姚鑫, 丁艳丽, 张晓丹 2015 64 038805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao X, Ding Y L, Zhang X D 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 038805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 李春静, 杨瑞霞, 田汉民 2018 物理 47 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C J, Yang R X, Tian H M 2018 Physics 47 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang R, Huang T, Xue J 2021 Nat. Photonics 15 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao J, Wang A, Green M A 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 1991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Eperon G E, Leijtens T, Bush K A 2016 Science 354 861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Eperon G E, Stranks S D, Menelaou C 2014 Energ Environ. Sci. 7 982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hao F, Stoumpos C C, Chang R P H 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 8094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Unger E L, Kegelmann L, Suchan K 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 11401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Green M A 2013 Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A 371 20110413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ba L, Liu H, Shen W 2018 Prog. Photovolt. 26 924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sahli F, Werner J, Kamino B A 2018 Nat. Mater. 17 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen B, Yu Z, Liu K 2019 Joule 3 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hou Y, Aydin E, De Bastiani M 2020 Science 367 1135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 宫步青, 陈小雨, 王伟鹏, 王治业, 周华, 沈向前 2020 69 188801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong B Q, Chen X Y, Wang W P, Wang Z Y, Zhou H, Shen X Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 188801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 姜悦, 王淑英, 王治业, 周华, 卡马勒, 赵颂, 沈向前 2021 70 218801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang Y, Wang S Y, Wang Z Y, Zhou H, Ka M L, Zhao S, Shen X Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 218801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ferry V E 2011 Light Trapping in Plasmonic Solar Cells (Los Angeles: California Institute of Technology)
[25] Saliba M, Zhang W, Burlakov V M, et al. 2015 Adv. Funct. Mater. 25 5038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Santbergen R, Mishima R, Meguro T, et al. 2016 Opt. Express 24 A1288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Edward D P 1998 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (San Diego: Academic Press) p519
[28] William R E, Holly F. Z, Eric M T, Rizia B, 2016 Energ Environ. Sci. 9 1577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Xu Q, Liu F, Liu Y X, Meng W S, Cui K Y, Feng X, Zhang W, Huang Y D, 2014 Opt. Express 22 A301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
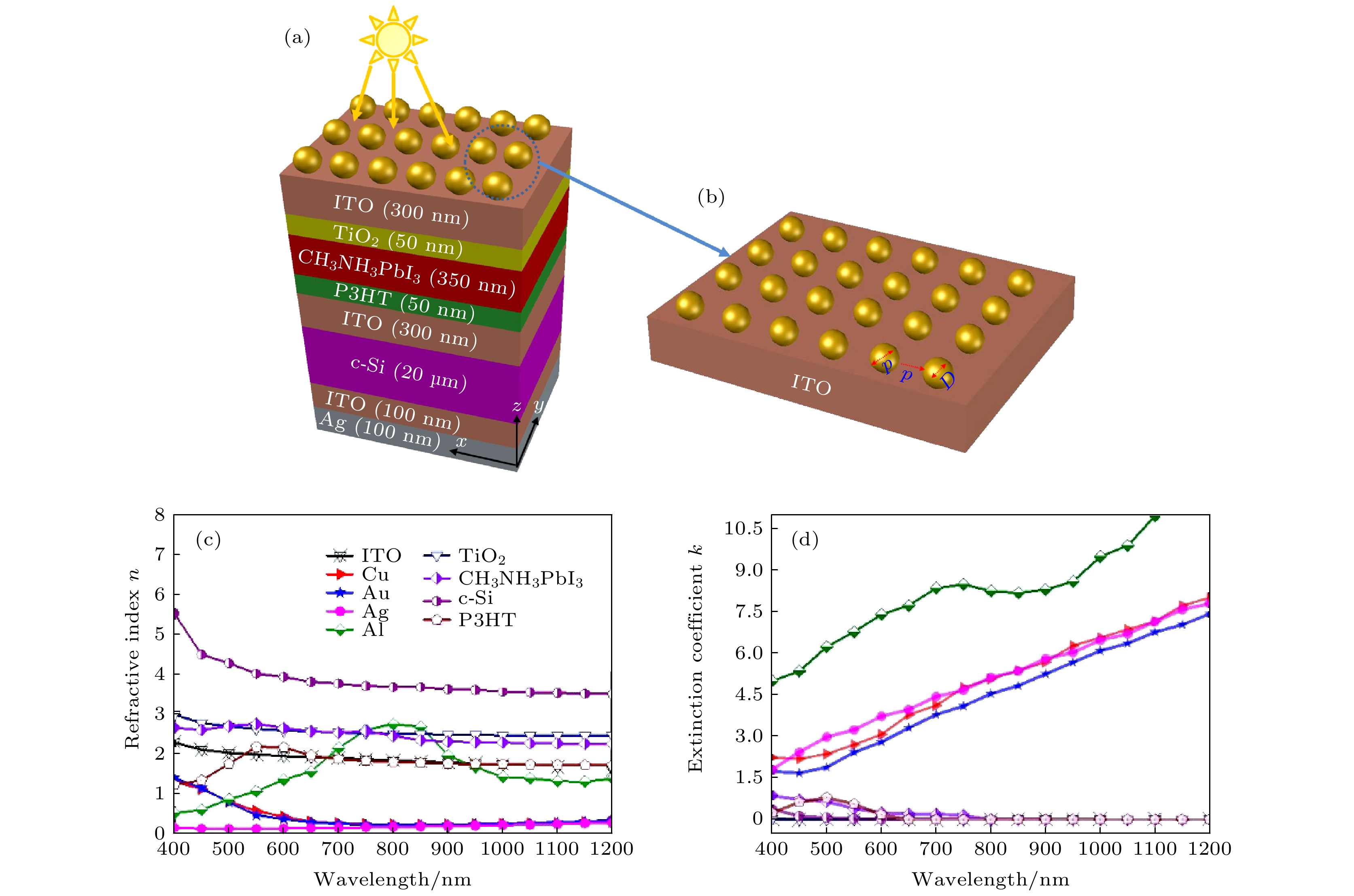
图 1 钙钛矿/硅叠层电池的仿真模型及结构参数 (a)电池模型; (b)金属纳米球的直径及周期示意图; (c)折射率; (d)消光参数
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of perovskite/silicon tandem solar cell with metal nanospheres and structural parameters for simulation: (a) Cell model; (b) schematic diagram of diameter and period of metal nanospheres; (c) refractive index; (d) extinction parameter.
图 4 不同金属纳米球调控的电池光谱响应特性和光电转换效率 (a)电池吸收光谱; (b)量子响应效率; (c)短路电流密度; (d) I-V特性曲线
Fig. 4. Spectral response characteristics and photoelectric conversion performance of solar cell with different metal nanospheres: (a) Total absorption of cell devices; (b) external quantum efficiency; (c) short-circuit current density; (d) current-voltage characteristics.
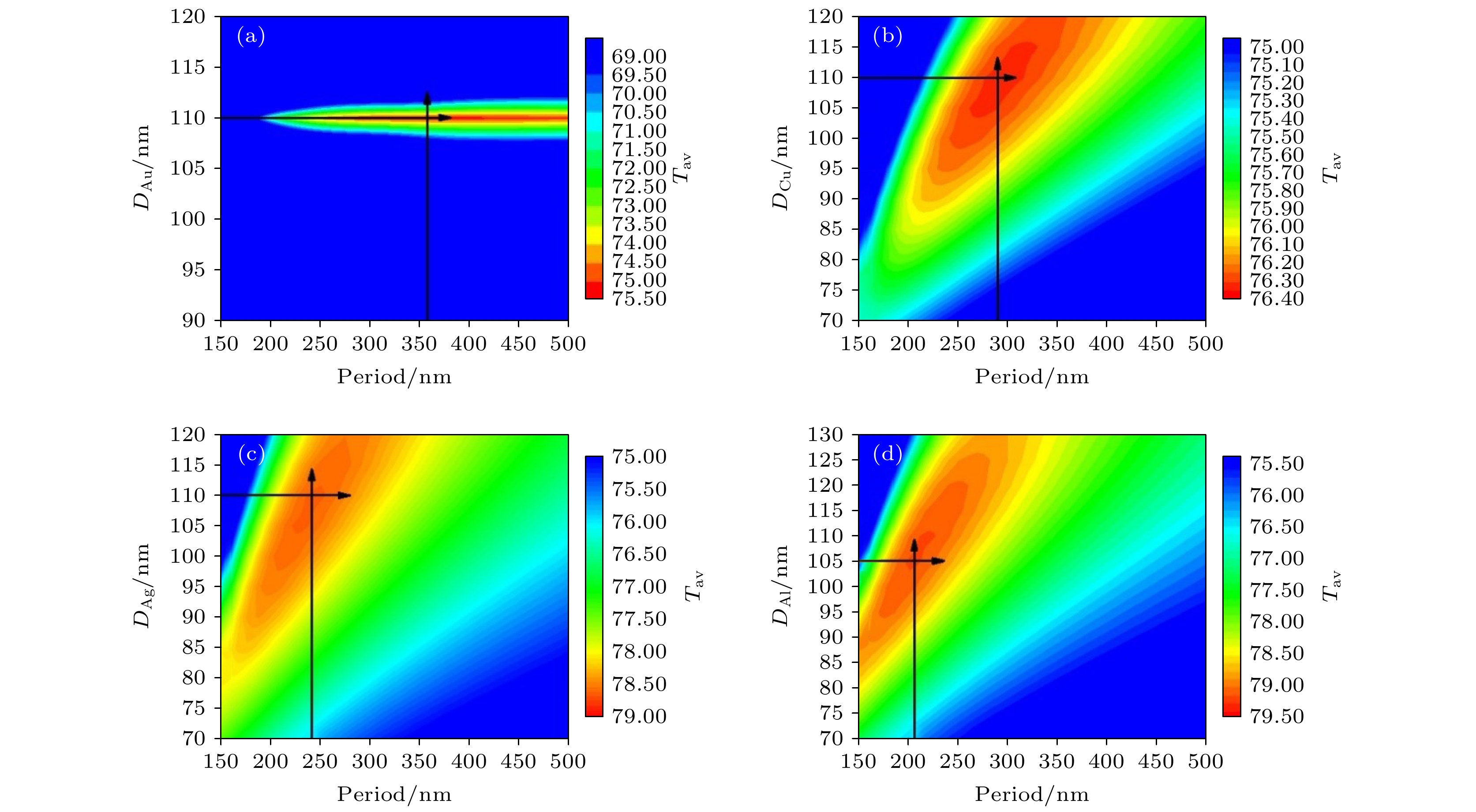
表 1 不同金属纳米球的最优结构参数及相应的光学特性
Table 1. Optimized structural parameters and corresponding optical properties of different metal nanospheres.
D/nm P/nm Tav/% Aav/% Flat — — 73.16 76.83 Au 110 355 75.28 82.78 Cu 110 295 76.33 83.10 Ag 110 245 78.59 83.61 Al 105 205 79.15 83.84 -
[1] Masuko K, Shigematsu M, Hashiguchi T 2014 IEEE J. Photovolt. 4 1433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yoshikawa K, Kawasaki H, Yoshida W 2017 Nat. Energy 2 17032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Richter A, Hermle M, Glunz S W 2013 IEEE J. Photovolt. 3 1184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu X, Jiang J, Wang F, et al. 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 46894
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kojima A, Teshima K, Shirai Y, Miyasaka T 2009 Am. Chem. Soc. 131 6050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) 2021 https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/pdfs/best-research-cell-efficiencies.
[7] Jeong M, Choi I W, Go E M 2020 Science 369 1615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jeong J, Kim M, Seo J 2021 Nature 592 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 姚鑫, 丁艳丽, 张晓丹 2015 64 038805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao X, Ding Y L, Zhang X D 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 038805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 李春静, 杨瑞霞, 田汉民 2018 物理 47 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C J, Yang R X, Tian H M 2018 Physics 47 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang R, Huang T, Xue J 2021 Nat. Photonics 15 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao J, Wang A, Green M A 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 1991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Eperon G E, Leijtens T, Bush K A 2016 Science 354 861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Eperon G E, Stranks S D, Menelaou C 2014 Energ Environ. Sci. 7 982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hao F, Stoumpos C C, Chang R P H 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 8094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Unger E L, Kegelmann L, Suchan K 2017 J. Mater. Chem. A 5 11401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Green M A 2013 Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. A 371 20110413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ba L, Liu H, Shen W 2018 Prog. Photovolt. 26 924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sahli F, Werner J, Kamino B A 2018 Nat. Mater. 17 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen B, Yu Z, Liu K 2019 Joule 3 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hou Y, Aydin E, De Bastiani M 2020 Science 367 1135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 宫步青, 陈小雨, 王伟鹏, 王治业, 周华, 沈向前 2020 69 188801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong B Q, Chen X Y, Wang W P, Wang Z Y, Zhou H, Shen X Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 188801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 姜悦, 王淑英, 王治业, 周华, 卡马勒, 赵颂, 沈向前 2021 70 218801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang Y, Wang S Y, Wang Z Y, Zhou H, Ka M L, Zhao S, Shen X Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 218801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ferry V E 2011 Light Trapping in Plasmonic Solar Cells (Los Angeles: California Institute of Technology)
[25] Saliba M, Zhang W, Burlakov V M, et al. 2015 Adv. Funct. Mater. 25 5038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Santbergen R, Mishima R, Meguro T, et al. 2016 Opt. Express 24 A1288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Edward D P 1998 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (San Diego: Academic Press) p519
[28] William R E, Holly F. Z, Eric M T, Rizia B, 2016 Energ Environ. Sci. 9 1577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Xu Q, Liu F, Liu Y X, Meng W S, Cui K Y, Feng X, Zhang W, Huang Y D, 2014 Opt. Express 22 A301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8158
- PDF下载量: 168
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: