-
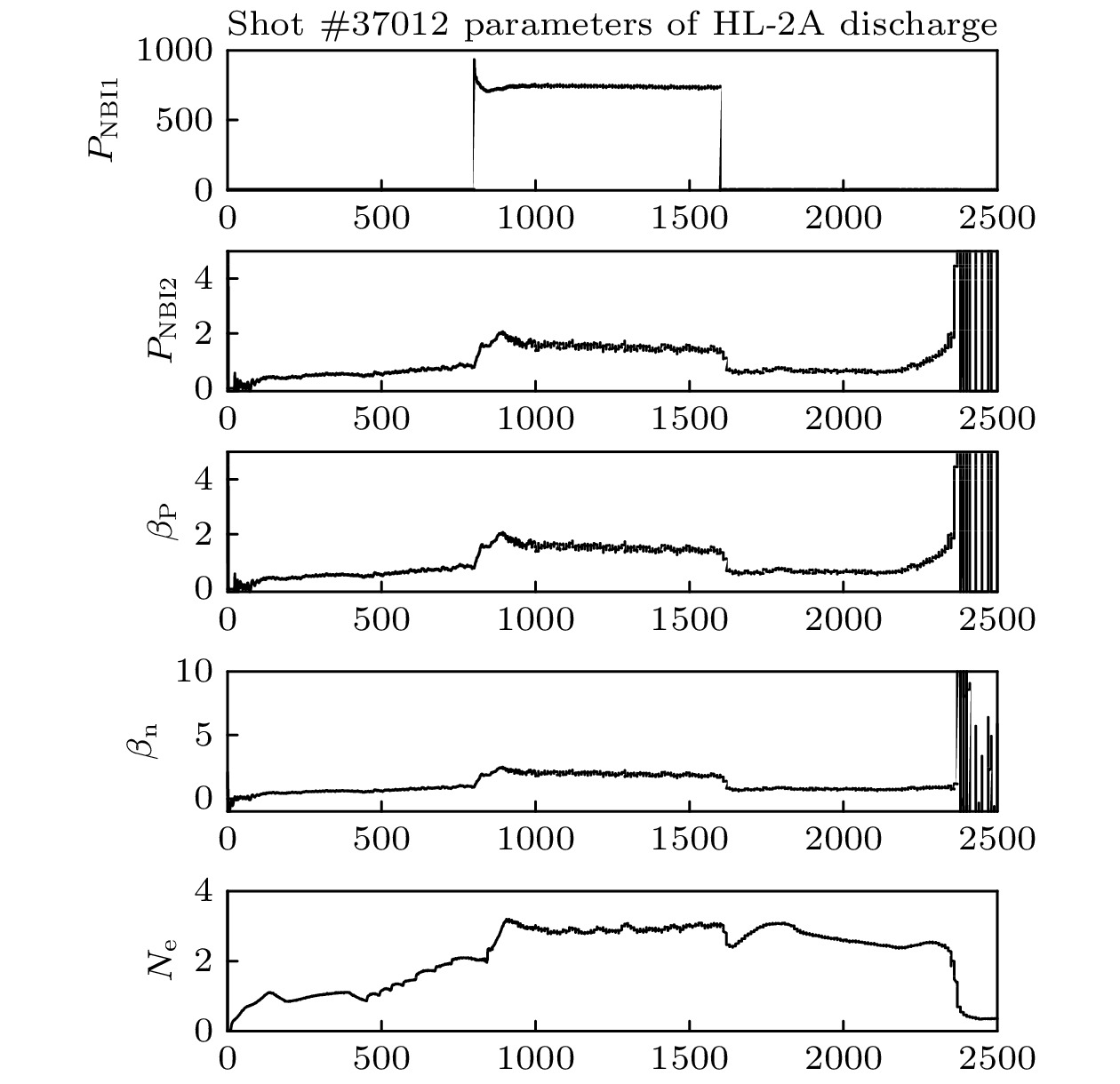
磁约束托卡马克装置等离子体物理参数, 如等离子体电流、约束磁场、安全因子的实时监测对高约束模式(H模)的稳态运行至关重要. 本文介绍了基于HL-2A实验数据和集成建模手段, 重建先进高约束运行模式(H模)下等离子体位形, 电流密度和安全因子参数剖面. 通过搭建动力学平衡位形集成模拟平台, 结合工作流快速处理手段, 采用真实实验数据和集成模拟模型, 得到了HL-2A高约束模式放电条件的离子和电子温度、密度, 电流密度和安全因子q剖面, 重建了高约束模式放电物理图像和托卡马克内部磁面位形和等离子体边界参数连续分布, 计算了等离子体欧姆电流、自举电流和射频电流等剖面及各自份额, 给出了先进运行模式下安全因子q径向分布. 通过集成模拟, 发现HL-2A该炮号参数条件下台基宽度约7.52 cm, 压强梯度的方向在
ρ(r/a) = 0.1改变, 在ρ = 0.7附近数值达到最大, 可能是负剪切产生的内部输运垒位形(ITB)引起的. 通过等离子体磁场和电流等剖面重建和实时监测, 可以评估HL-2A高约束放电实验的品质, 为HL-2M高比压(βn)先进模式的稳态运行提供参考. The plasma current (Ip), magnetic field (B), and safety factor distribution (q profile) of the HL-2A tokamak device are crucial to monitoring the steady-state operational scenarios (in high confinement mode, H mode). Based on real experimental data and integrated modeling simulation method (OMFIT), the plasma parameters’ profiles such as magnetic field configuration and current density profiles in H mode were reconstructed. By building up an integrated simulation platform for dynamic equilibrium configuration, and combining the rapid workflow processing method and experimental data with integrated simulation models, the ion and electron temperature, density, and current density profiles were obtained. The integration simulation platform was established to reconstruct the internal magnetic surface configuration, the plasma boundary parameter distribution, the ion/electron temperature, current density, and the q profile. The Ohmic current, bootstrap current, and radio-frequency current profiles with its fractions were calculated. The width of the pedestal region was about 7.52 cm according to our simulation results. It was found that the pressure gradient changes its direction at radial coordinate ρ(r/a) = 0.1 and reaches its maximum value near ρ = 0.7, which may be the internal transport barrier (ITB) configuration caused by negative shear. The profile reconstruction and real-time monitoring of the physical parameters are conducive to evaluating the quality of H mode discharge experiment and can assist in the steady-state operation of advanced operating modes such as HL-2M high normalized beta (βn) discharge. -
Keywords:
- HL-2A /
- OMFIT platform /
- integrated modeling framework
[1] Wagner F 1982 Phys. Re. Lett. 49 1408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李凯 2020 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Li K 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[3] 钟武律, 段旭如 2020 原子核物理评论 37 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong W L, Duan X R 2020 Nucl. Phys. Re. 37 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Snyder P B, Aiba N, Beurskens M 2009 Nucl. Fusion 49 085035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stacey W M, Groebner R J 2003 Phys. Plasm. 10 2412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lao L L, Ferron J R, Groebner R J, et al. 1990 Nucl. Fusion 30 103549
[7] Fellinger P, Marklein R, Langenberg K J, Klaholz S 1995 Wave Motion 21 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 陈文锦, 何小雪, 刘亮, 魏彦玲, 马倩, 余德良 2016 核聚变与等离子体物理 36 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W J, He X X, Liu L, Wei Y L, Ma Q, Yu D L 2016 Nucl. Fusion Plasma Phys. 36 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Logan N C, Grierson, B A, Haskey S R, Smith S P, Meneghini O, Eldon D 2018 Nucl. Fusion 74 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Meneghini O, Lao L 2013 Plasma Fusion Res. 8 2403009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Meneghini O, Smith S P, Lao L L, Izacard O, et al. 2015 Nucl. Fusion 55 083008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴木泉 2020 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Wu M Q 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[13] 李强 2009 原子能科学技术 S2 204
Li Q 2009 Atomic Energy Sci. Technol. S2 204 (in Chinese)
[14] 饶军, 陆志鸿, 张劲松等 2009 核聚变与等离子体物理 29 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rao J, Lu Z H, Zhang J S, et al. 2009 Nucl. Fusion Plasma Phys. 29 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Owen L W, Canik J M, Groebner R J, et al. 2010 Nucl. Fusion 50 64017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Beurskens M N A, Giudicotti L, Kempenaarsl M, et al. 2008 Re. Scient. Instrum. 79 10.1063
[17] Candy J, Holland C, Waltz R E, et al. 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 2137
[18] Staebler G M, Belli E A, Candy J, Kinsey J E, Dudding H, Patel B 2021 Nuclear Fusion 61 116007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Staebler G M, Kinsey J E, Belli E A, et al. 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 1596
[20] Belli E A, Candy J, Angioni C 2014 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 56 124002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shaing K C, Lai A L 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 122504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hubbard A E, Boivin R L, Granetz R S, et al. 1998 Phys. Plasmas 5 1744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Belli E A, Candy J 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 062301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Staebler G M, Candy J, Belli E A, Kinsey J E, Bonanomi N, Patel B 2021 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 63 015013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Snyder P B, Groebner R J, Hughes J W, et al. 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 103016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gao X, Zhang T, Han X, et al. 2015 Nucl. Fusion 55 083015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Groebner R J, Baker D R, Burrell K H, et al. 2001 Nucl. Fusion 41 1789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Groebner R J, Osborne T H 1998 Phys. Plasmas 5 1800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kinsey J E, Staebler G M, Candy J, et al. 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 83001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] McDonald D C, Cordey J G, Thomsen K, 2007 Nucl. Fusion 47 147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Saibene G, Sartori R, Loarte A, et al. 2002 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 44 1769
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 HL-2A托卡马克平衡物理参数实验数据 (a)等离子体中离子温度Ti径向分布; (b)电子温度Te径向分布; (c)电子密度ne径向分布
Fig. 3. (a) Radial distribution profile of ion temperature Ti in HL-2A Tokamak plasma; (b) radial distribution profile of electron temperature Te in HL-2A Tokamak plasma; (c) radial distribution profile of electron density ne in HL-2A tokamak plasma.
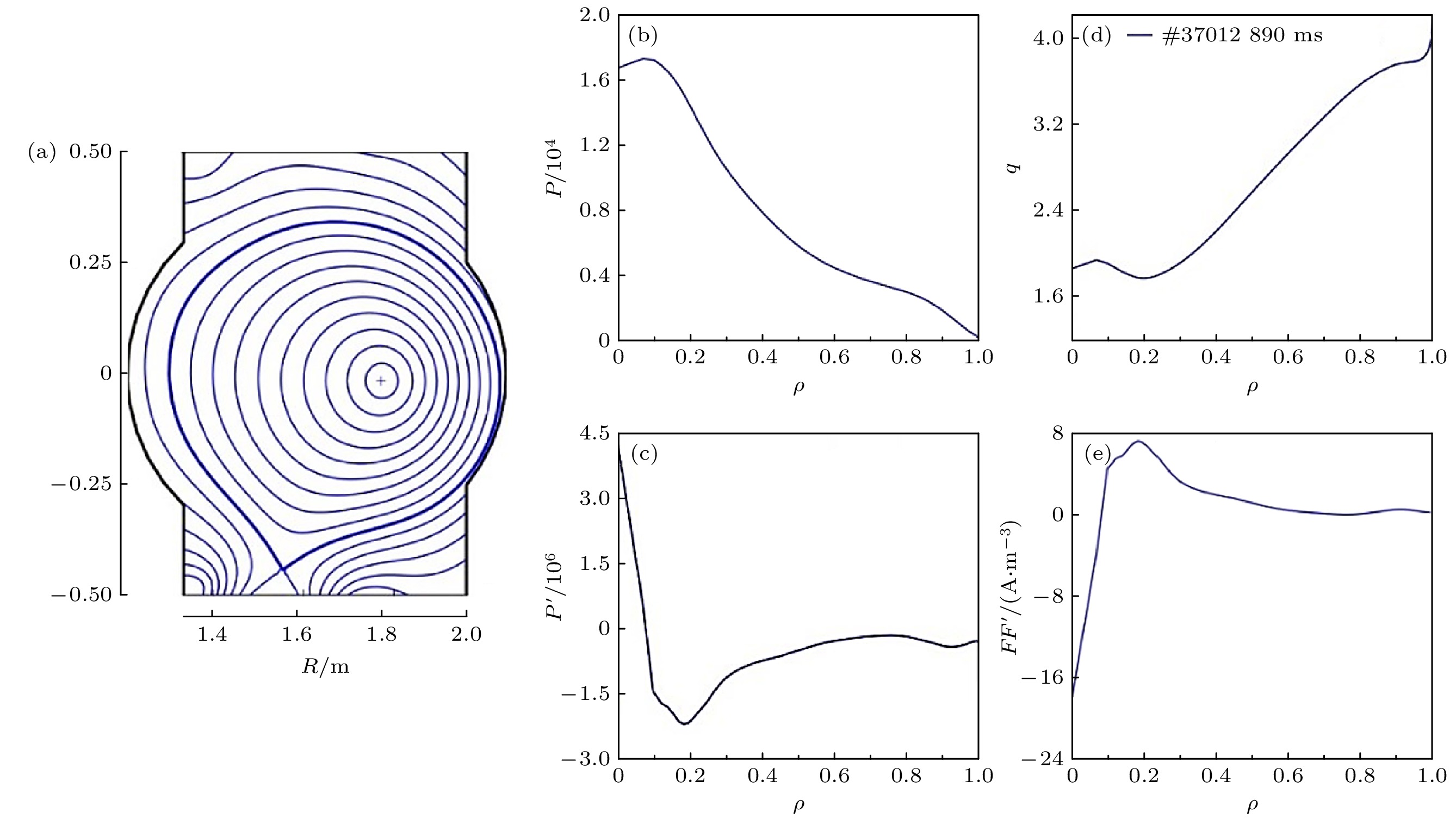
图 7 集成模拟程序OMFIT得到的HL-2A托卡马克等离子体磁场位形结构图 (a); 等离子体压强(单位Pa)径向剖面分布(b); 压强梯度P’(无量纲)径向分布(c); 安全因子q(无量纲)随着径向变化分布剖面(d); 极向电流梯度FF'(A/m3)径向分布剖面(e)
Fig. 7. HL-2A Tokamak plasma magnetic field configuration obtained by integrated simulation code OMFIT (a); pressure profile(unit Pa) (b); profile distribution of the pressure gradient(Dimensionless quantity) (c); profile distribution of safety factor q (Dimensionless quantity) obtained (d); profile distribution of the polar current gradient FF' (unit A/m3)
(e). 图 8 (a)磁约束托卡马克装置shot #37012由集成模拟程序OMFIT计算的整体电流密度、包含中性束电流密度、自举电流密度、欧姆电流密度和射频电流密度及份额分布曲线; (b)OMFIT程序和平衡反演程序EFIT计算的安全因子q剖面对比图
Fig. 8. (a) Magnetic confinement Tokamak device shot #37012 total current densities calculated by the integrated simulation program OMFIT, including neutral beam current density, bootstrap current density, Ohmic current density, and RF current density with percentages of respective current densities in total current densities; (b) comparison of the safety factor q profiles calculated by the OMFIT program and the balance inversion code EFIT.
-
[1] Wagner F 1982 Phys. Re. Lett. 49 1408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 李凯 2020 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Li K 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[3] 钟武律, 段旭如 2020 原子核物理评论 37 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong W L, Duan X R 2020 Nucl. Phys. Re. 37 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Snyder P B, Aiba N, Beurskens M 2009 Nucl. Fusion 49 085035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Stacey W M, Groebner R J 2003 Phys. Plasm. 10 2412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lao L L, Ferron J R, Groebner R J, et al. 1990 Nucl. Fusion 30 103549
[7] Fellinger P, Marklein R, Langenberg K J, Klaholz S 1995 Wave Motion 21 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 陈文锦, 何小雪, 刘亮, 魏彦玲, 马倩, 余德良 2016 核聚变与等离子体物理 36 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W J, He X X, Liu L, Wei Y L, Ma Q, Yu D L 2016 Nucl. Fusion Plasma Phys. 36 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Logan N C, Grierson, B A, Haskey S R, Smith S P, Meneghini O, Eldon D 2018 Nucl. Fusion 74 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Meneghini O, Lao L 2013 Plasma Fusion Res. 8 2403009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Meneghini O, Smith S P, Lao L L, Izacard O, et al. 2015 Nucl. Fusion 55 083008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴木泉 2020 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Wu M Q 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[13] 李强 2009 原子能科学技术 S2 204
Li Q 2009 Atomic Energy Sci. Technol. S2 204 (in Chinese)
[14] 饶军, 陆志鸿, 张劲松等 2009 核聚变与等离子体物理 29 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rao J, Lu Z H, Zhang J S, et al. 2009 Nucl. Fusion Plasma Phys. 29 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Owen L W, Canik J M, Groebner R J, et al. 2010 Nucl. Fusion 50 64017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Beurskens M N A, Giudicotti L, Kempenaarsl M, et al. 2008 Re. Scient. Instrum. 79 10.1063
[17] Candy J, Holland C, Waltz R E, et al. 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 2137
[18] Staebler G M, Belli E A, Candy J, Kinsey J E, Dudding H, Patel B 2021 Nuclear Fusion 61 116007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Staebler G M, Kinsey J E, Belli E A, et al. 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 1596
[20] Belli E A, Candy J, Angioni C 2014 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 56 124002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shaing K C, Lai A L 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 122504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hubbard A E, Boivin R L, Granetz R S, et al. 1998 Phys. Plasmas 5 1744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Belli E A, Candy J 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 062301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Staebler G M, Candy J, Belli E A, Kinsey J E, Bonanomi N, Patel B 2021 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 63 015013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Snyder P B, Groebner R J, Hughes J W, et al. 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 103016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gao X, Zhang T, Han X, et al. 2015 Nucl. Fusion 55 083015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Groebner R J, Baker D R, Burrell K H, et al. 2001 Nucl. Fusion 41 1789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Groebner R J, Osborne T H 1998 Phys. Plasmas 5 1800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kinsey J E, Staebler G M, Candy J, et al. 2011 Nucl. Fusion 51 83001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] McDonald D C, Cordey J G, Thomsen K, 2007 Nucl. Fusion 47 147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Saibene G, Sartori R, Loarte A, et al. 2002 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 44 1769
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9637
- PDF下载量: 149
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: