-
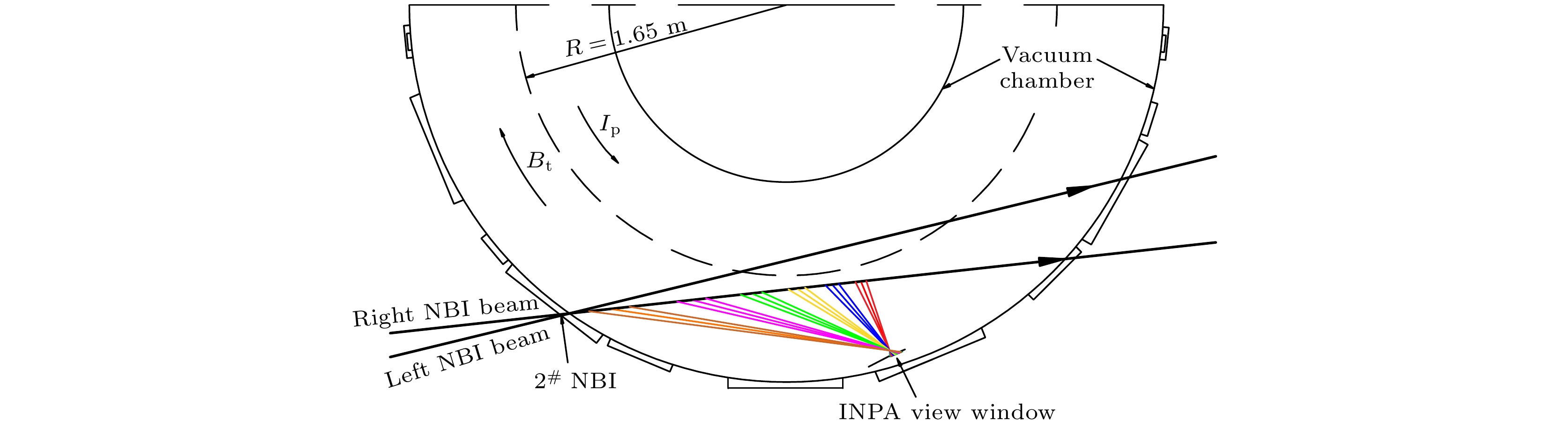
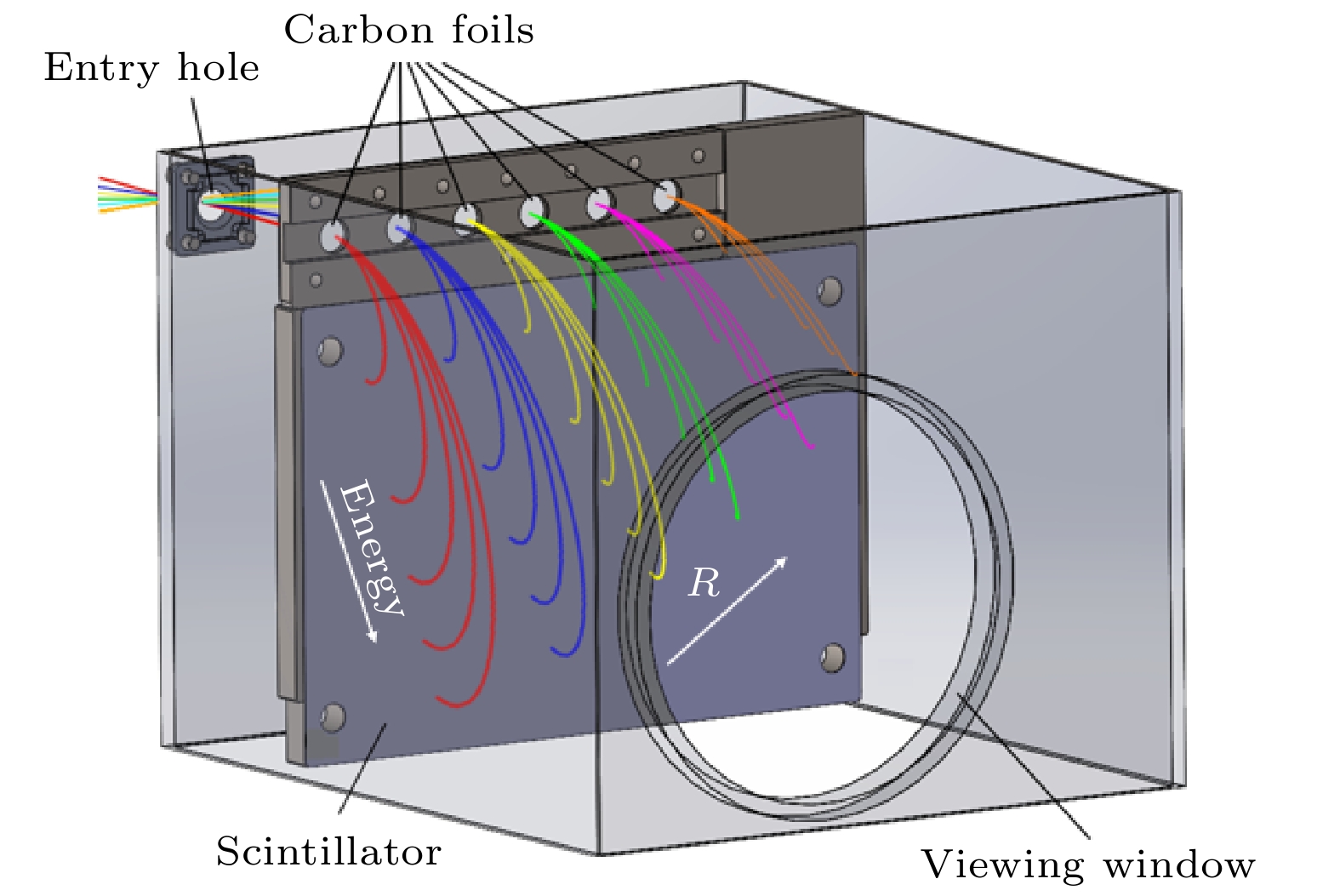
在HL-2A装置上发展了基于硫化锌银闪烁体的成像型中性粒子分析器, 对磁约束聚变等离子体中高能量粒子(EP)的分布、能量和螺距角等关键信息, 以及EP与磁流体不稳定性之间的相互作用等物理问题进行了研究. 在中性束注入路径上逃逸出的具有等离子体中快离子能量和螺距角信息的中性粒子, 通过由入射孔和碳微晶体膜片组成的准直系统后转化为离子, 在装置边缘磁场中受洛伦兹力偏转而撞击到闪烁体屏上. 通过分析发光点的位置和光强度, 可以推断出装置中快离子的位置、能量和螺距角等关键信息. 在HL-2A装置高能量粒子物理实验中, 通过该诊断和理论计算初步证实了长寿模不稳定性是由能量、螺距角和位置分别为E = 12.5—32 keV,
$\theta \sim$ 149.2° ($v_{//}/v\sim$ 0.86)和R = 170.5—171.5 cm的芯部快离子激发.-
关键词:
- 快离子 /
- 成像型中性粒子分析器 /
- 长寿模不稳定性
The imaging neutral particle analyzer (INPA) based on scintillator (ZnS(Ag)) is designed and used on HL-2A tokamak to investigate the distribution of energetic particles (EPs) and even their interactions with magnetohydrodynamic instabilities. The collimation system is composed of a pinhole of 3 mm in diameter and six circular carbon microcrystal diaphragms each with a thickness of 10 nm. The neutral particles escape from six definite positions in the neutral beam injection path and pass through the collimator system at a certain pitch angle, and the neutral particles become fast ions after passing through the carbon microcrystal diaphragm. The fast ions will hit the scintillator after a 180° deflection by the edge magnetic field. The energy, pitch angle and birthplace can be calculated by the position and light intensity of the impact spots. The images of impact spots caused by long-lived mode are recorded by a high-speed camera through the fiber optic bundle. The long-lived mode instabilities approve to be excited by the core EPs with energy value in a range of$E\sim $ 12.5-32 keV, pitch angle of$v_{//}/v\sim$ 0.86, and the birthplace in a range of$R\sim $ 170.5-171.5 cm.[1] Heidbrink W W 2002 Phys. Plasmas 9 2113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen L, Zonca F 2016 Rev. Mod. Phys. 88 015008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ding X T, Chen W 2018 Plasma Sci. Technol. 20 094008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shi P W, Chen W, Duan X R 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett 38 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen W, Wang Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 125001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Fasoli A, Gormenzano C, Berk H L, Breizman B, Briguglio S, Darrow D S, Gorelenkov N, Heidbrink W W, Jaun A, Konovalov S V 2007 Nucl. Fusion 47 S264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Afanasyev V I, Chernyshev F V, Kozlovsky S S, et al. 2022 JINST 17 C07001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kocan M, Garcia-Munoz M, Ayllon-Guerola J, et al. 2017 JINST 12 C12027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang J, Huang J, Chang J F, Wu C R, Heidbrink W W, Salewski M, Madsen B, Zhu Y B, von Hellermann M G, Gao W, Xu Z, Wan B 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10D121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Saquilayan G M Q, Wada M 2018 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57 01AA01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 商洁, 黄渊, 杨凯, 陈宝维, 刘春华, 杨屹 2021 光谱学与光谱分析 41 333
Shang J, Huang Y, Yang K, Chen B W, Liu C H, Yang Y 2021 Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 41 333
[12] Berezovsky E L, Efremov S L, Izvozchikov A B, Petrov, M P, Petrov S Y 1981 10th European Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics Moscow, Russian Republic, September 14–19, 1981 p67
[13] Medlley S S, Donne A J H, Kaita R, Kislyakov A I, Petrov M P, Roquemore A L 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 011101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Medlley S S, Bell R E, Petrov M P, Roquemore A L, Suvorkin E V 2003 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74 1896
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bracco G, Betello G, Mantovani S, Moleti A, Tilia B, Zanza V 1992 Rev.Sci.Instrum. 63 5685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Karpushov A N, Duval B P, Schlatter C 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 033504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chernyshev F V, Afanasyev V I, Dech A V, Kick M, Kislyakov A I, Kozlovskii S S, Kreter A, Mironov M I, Petrov M P, Petrov S Y 2004 Instr. Exp. Tech. 47 214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhu Y B, Bortolon A, Heidbrink W W, Celle S L, Roquemore A L 2012 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83 10D304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Afanasiev V I, Gondhalekar A, Babenko P Y, et al. 2003 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74 2338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Stott P E, Gorini G, Prandoni P, Sindoni E 2012 Diagnostics for Experimental Thermonuclear Fusion Reactors 2 (New York: Springer
[21] Xia Z W, Li W, Yang Q W, Lu J, Yi P, Gao J M 2013 Plasma Sci. Technol. 15 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Du X D, Van Zeeland M A, Heidbrink W W, Su D 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 082006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Van Zeeland M A, Du X D, Heidbrink W W, Stagner L, Su D 2019 JINST 14 C09027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rueda-Rueda J, Garcia-Munoz M, Viezzer E, Schneider P A, Garcia-Dominguez J, Ayllon-Guerola J, Galdon-Quiroga J, Herrmann A, Du X D, Van Zeeland M A, Oyola P, Rodriguez-Ramos M, ASDEX Upgrade team 2021 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92 043554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 刘洋, 徐明, 蔡辉山, 等 2023 第八届等离子体诊断会议 中国珠海, 2023年5月25−27日
Liu Y, Xu M, Cai H S, et al. 2023 The 8th Conference on Fusion Plasma Diagnostics Zhuhai China, March 25−27, 2023
[26] 颜筱宇, 何小斐, 于利明, 等 2023 第八届等离子体诊断会议 中国珠海, 2023年5月25—27日
Yan X Y, He X F, Yu L M, et al. 2023 The 8th Conference on Fusion Plasma Diagnostics Zhu Hai, China, March 25−27, 2023
[27] Zhang R B, Wang X Q, Xiao C J, Wang X G, Liu Y, Deng W, Chen W, Ding X T, Duan X R, HL-2A Team 2014 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 56 095007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang X Q, Zhang R B, Qin L, Wang X G 2014 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 56 095013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Peeters A 1994 Ph. D. Dissertation (Eindhoven: Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
-
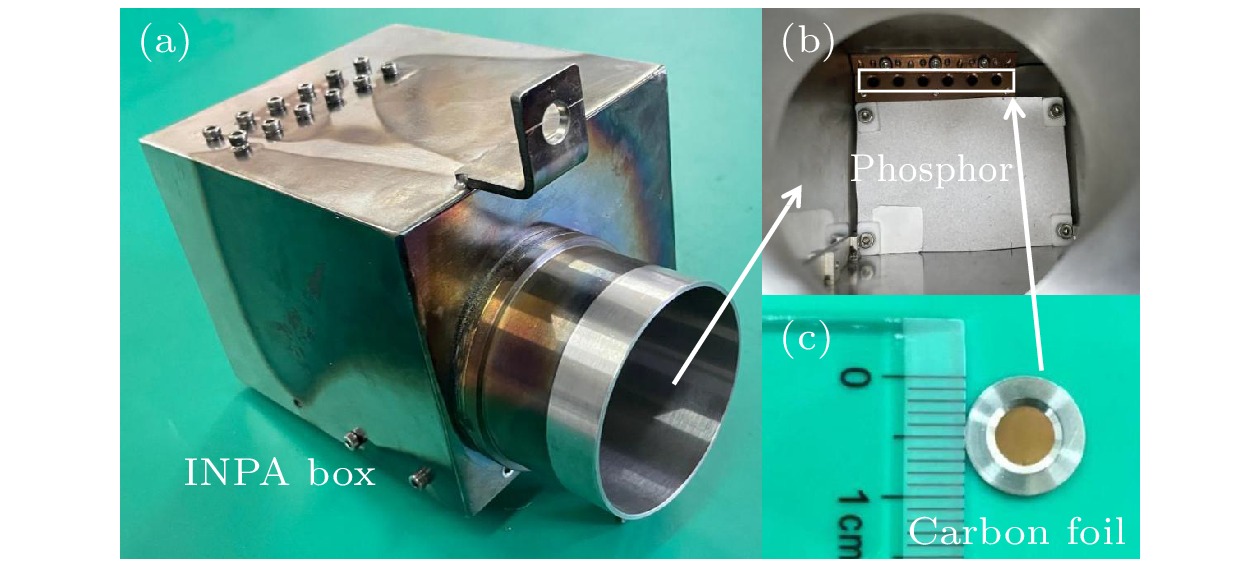
图 4 HL-2A装置上INPA诊断系统主要部件的实物及内部布置图 (a) INPA的外观图; (b)内部剥离膜片和闪烁体的布局图; (c)碳微晶体膜片尺寸和结构
Fig. 4. External figure and arrangement inside the chamber of INPA diagnostics on HL-2A: (a) External figure; (b) arrangement of carbon microcrystal diaphragm and scintillator inside the chamber: (c) detail structure of carbon microcrystal diaphragm
图 5 INPA诊断系统中几何机构引起的误差分析 (a)粒子束在磁场中的偏转及在闪烁体上的轰击斑; (b) INPA诊断系统6个测量通道的粒子在闪烁体上的落点; (c)粒子在闪烁体上的落点位置和入射能量的关系; (d)能量分辨率与粒子能量的关系
Fig. 5. Analysis of errors caused by geometric mechanisms of diagnostic systems: (a) Flight orbits and impact spots of the measured particles on scintillator; (b) positions of impact spots from the particles from 6 channels in INPA; (c) relationship between the position of the particle’s landing point on the scintillator and the incident energy; (d) relationship between energy of particles and energy resolution
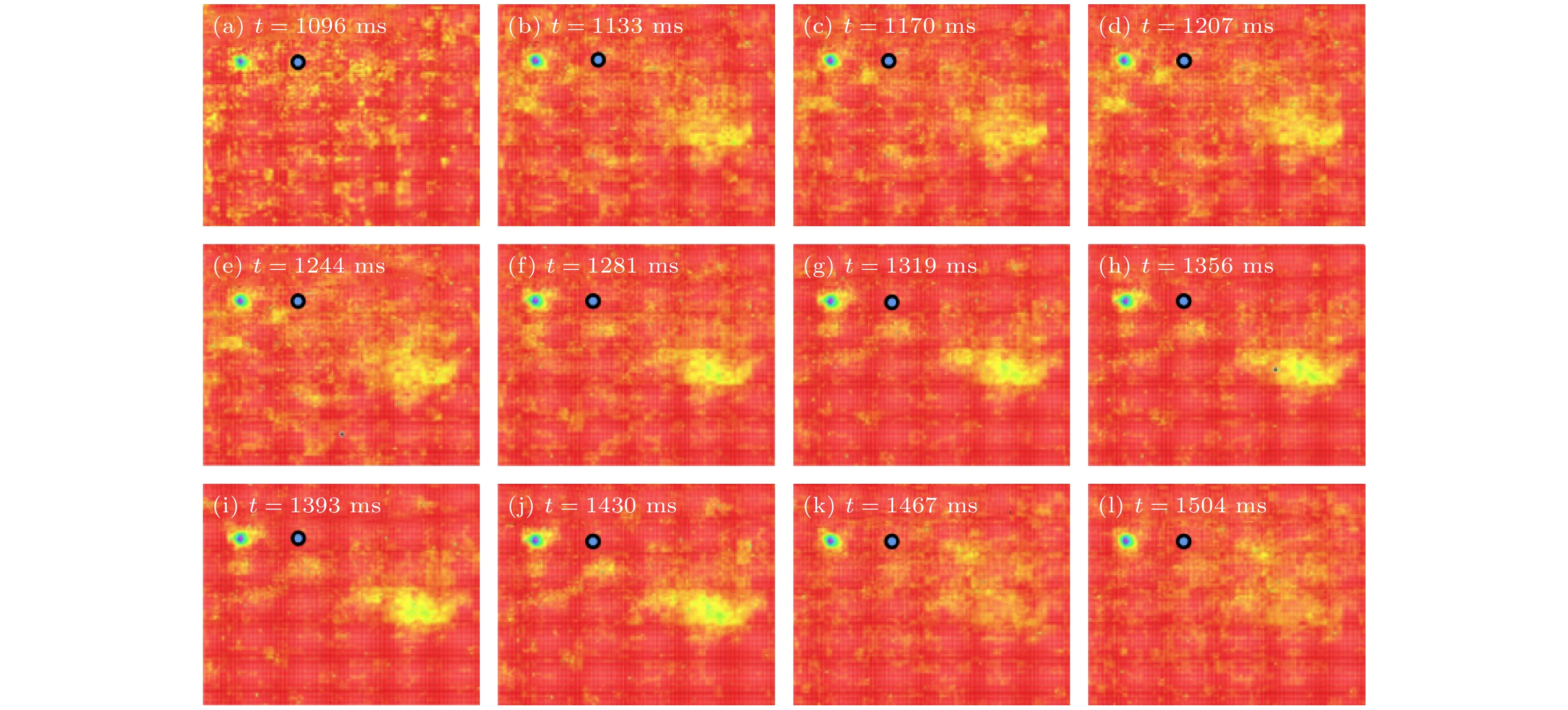
图 7 HL-2A装置上第38140次放电的实验参数及观测到的LLM不稳定性 (a) 等离子体主要放电参数, 即
$I_{\rm{p}}$ 、等离子体平均密度$n_{\rm{e}}$ 和$B_{\rm{t}}$ ; (b)$1^\#$ 和$2^\#$ NBI束线的加热功率和时序; (c)氘$\alpha$ (${{D}}_\alpha$ )辐射信号; (d) Mirnov磁探针信号及(e)频率谱图Fig. 7. Discharge parameters and the observed LLM instabilities in shot 38140 on HL-2A: (a) Main discharge parameters,
$I_{\rm{p}}$ , line-averaged electron density$n_{\rm{e}}$ and$B_{\rm{t}}$ ; (b) heating power of$1^\#$ and$2^\#$ NBI systems and evolution; (c)${{D}}_\alpha$ signal; (d) Mirnov signal and (e) its spectrogram表 1 INPA诊断系统的6个测量通道所观测粒子的位置和粒子特征信息
Table 1. Observed positions and characteristic information of particles from the 6 channels of the INPA system
测量通道(No.) 1 2 3 4 5 6 R/cm 172.6 170.6 170.9 175.8 180.5 211.8 Z/cm –10.5 –10.5 –10.5 –10.5 –10.5 –10.5 $\theta$/(°) 90.0 121.9 149.2 170.9 172.0 158.4 $v_{/ /}/v$ 0 0.53 0.86 0.98 0.99 0.93 表 2 INPA诊断系统的6个通道对应的测量范围
Table 2. Measurement ranges corresponding to the 6 channels of the INPA diagnostic system
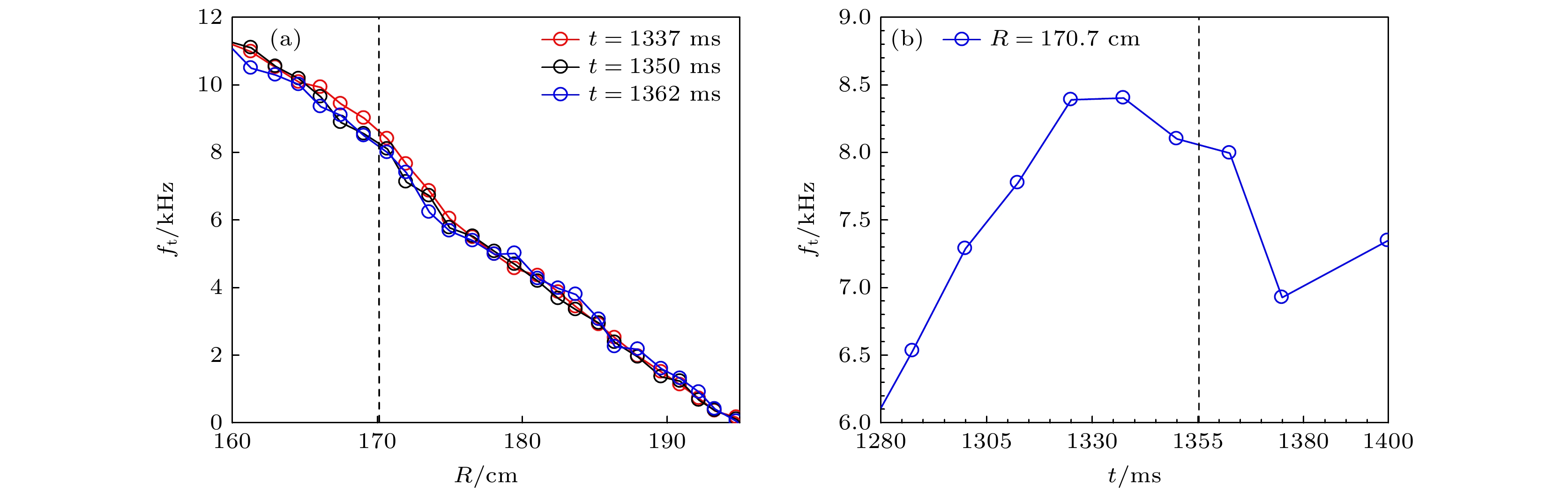
测量通道(No.) 1 2 3 4 5 6 $ R_{{\rm{min}}} $/cm 172.1 170.4 170.6 174.3 185.5 201.5 $R_{{\rm{max}}}$/cm 173.2 170.9 171.5 177.8 194.1 219.1 $\phi$/(°) 1.25 1.00 0.59 0.33 0.19 0.11 表 3 通行快离子的理论计算频率值与实验观测LLM不稳定性频率对比
Table 3. Comparisons between the calculated frequency of EIs and
$f_{{\rm{LLM}}}$ E/keV $f_{\rm{p}}$/kHz $f_{\rm{t}}$/kHz $f_{{\rm{Lab}}} = f_{\rm{p}}+f_{{\rm{t}}}$/kHz $f_{{\rm{LLM}}}$/kHz 12.5 2.4 8.1 2.4 + 8.1 = 10.5 13.4 32 6.2 8.1 6.2 + 8.1 = 14.3 13.4 -
[1] Heidbrink W W 2002 Phys. Plasmas 9 2113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen L, Zonca F 2016 Rev. Mod. Phys. 88 015008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ding X T, Chen W 2018 Plasma Sci. Technol. 20 094008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Shi P W, Chen W, Duan X R 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett 38 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen W, Wang Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 125001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Fasoli A, Gormenzano C, Berk H L, Breizman B, Briguglio S, Darrow D S, Gorelenkov N, Heidbrink W W, Jaun A, Konovalov S V 2007 Nucl. Fusion 47 S264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Afanasyev V I, Chernyshev F V, Kozlovsky S S, et al. 2022 JINST 17 C07001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kocan M, Garcia-Munoz M, Ayllon-Guerola J, et al. 2017 JINST 12 C12027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang J, Huang J, Chang J F, Wu C R, Heidbrink W W, Salewski M, Madsen B, Zhu Y B, von Hellermann M G, Gao W, Xu Z, Wan B 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10D121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Saquilayan G M Q, Wada M 2018 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 57 01AA01
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 商洁, 黄渊, 杨凯, 陈宝维, 刘春华, 杨屹 2021 光谱学与光谱分析 41 333
Shang J, Huang Y, Yang K, Chen B W, Liu C H, Yang Y 2021 Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 41 333
[12] Berezovsky E L, Efremov S L, Izvozchikov A B, Petrov, M P, Petrov S Y 1981 10th European Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics Moscow, Russian Republic, September 14–19, 1981 p67
[13] Medlley S S, Donne A J H, Kaita R, Kislyakov A I, Petrov M P, Roquemore A L 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 011101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Medlley S S, Bell R E, Petrov M P, Roquemore A L, Suvorkin E V 2003 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74 1896
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bracco G, Betello G, Mantovani S, Moleti A, Tilia B, Zanza V 1992 Rev.Sci.Instrum. 63 5685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Karpushov A N, Duval B P, Schlatter C 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 033504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chernyshev F V, Afanasyev V I, Dech A V, Kick M, Kislyakov A I, Kozlovskii S S, Kreter A, Mironov M I, Petrov M P, Petrov S Y 2004 Instr. Exp. Tech. 47 214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhu Y B, Bortolon A, Heidbrink W W, Celle S L, Roquemore A L 2012 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83 10D304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Afanasiev V I, Gondhalekar A, Babenko P Y, et al. 2003 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74 2338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Stott P E, Gorini G, Prandoni P, Sindoni E 2012 Diagnostics for Experimental Thermonuclear Fusion Reactors 2 (New York: Springer
[21] Xia Z W, Li W, Yang Q W, Lu J, Yi P, Gao J M 2013 Plasma Sci. Technol. 15 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Du X D, Van Zeeland M A, Heidbrink W W, Su D 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 082006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Van Zeeland M A, Du X D, Heidbrink W W, Stagner L, Su D 2019 JINST 14 C09027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rueda-Rueda J, Garcia-Munoz M, Viezzer E, Schneider P A, Garcia-Dominguez J, Ayllon-Guerola J, Galdon-Quiroga J, Herrmann A, Du X D, Van Zeeland M A, Oyola P, Rodriguez-Ramos M, ASDEX Upgrade team 2021 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92 043554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 刘洋, 徐明, 蔡辉山, 等 2023 第八届等离子体诊断会议 中国珠海, 2023年5月25−27日
Liu Y, Xu M, Cai H S, et al. 2023 The 8th Conference on Fusion Plasma Diagnostics Zhuhai China, March 25−27, 2023
[26] 颜筱宇, 何小斐, 于利明, 等 2023 第八届等离子体诊断会议 中国珠海, 2023年5月25—27日
Yan X Y, He X F, Yu L M, et al. 2023 The 8th Conference on Fusion Plasma Diagnostics Zhu Hai, China, March 25−27, 2023
[27] Zhang R B, Wang X Q, Xiao C J, Wang X G, Liu Y, Deng W, Chen W, Ding X T, Duan X R, HL-2A Team 2014 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 56 095007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang X Q, Zhang R B, Qin L, Wang X G 2014 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 56 095013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Peeters A 1994 Ph. D. Dissertation (Eindhoven: Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
计量
- 文章访问数: 5224
- PDF下载量: 145
- 被引次数: 0


















 下载:
下载: