-
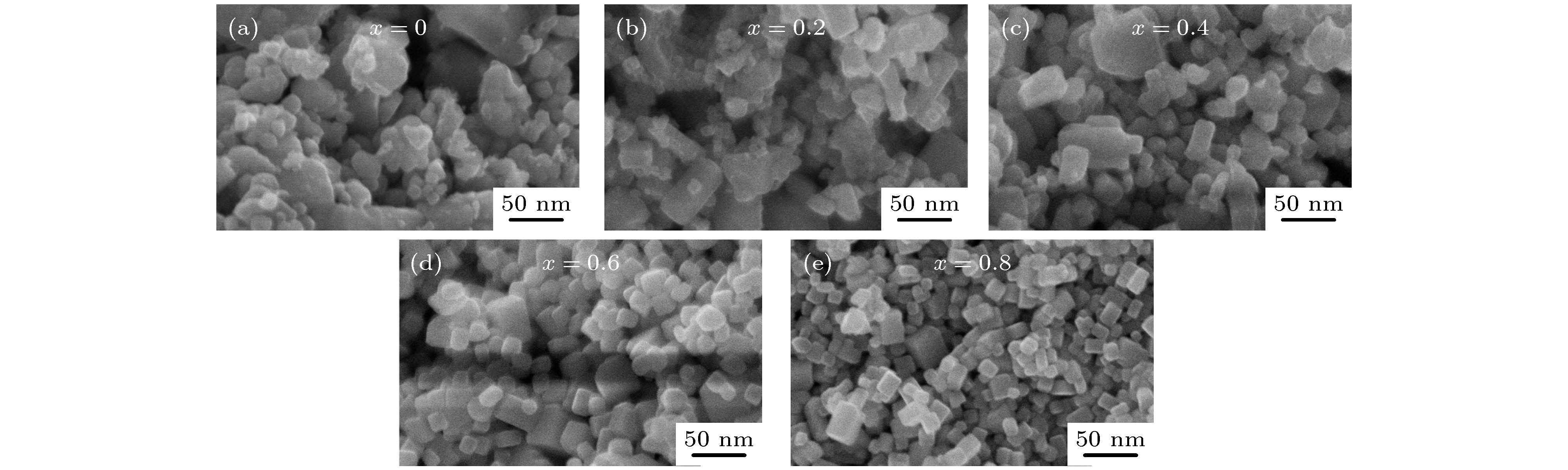
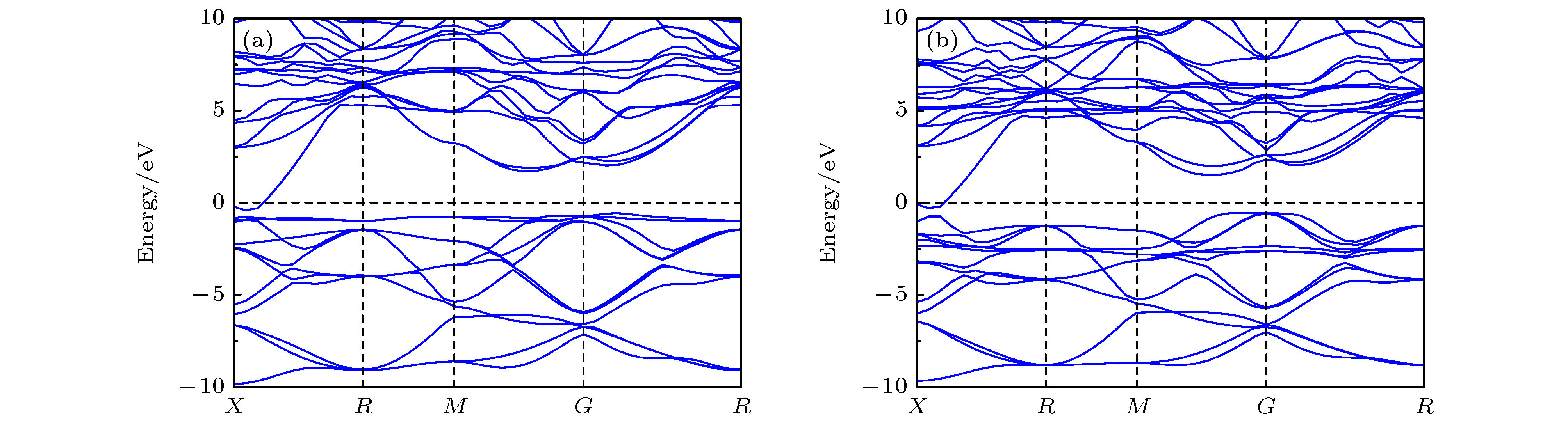
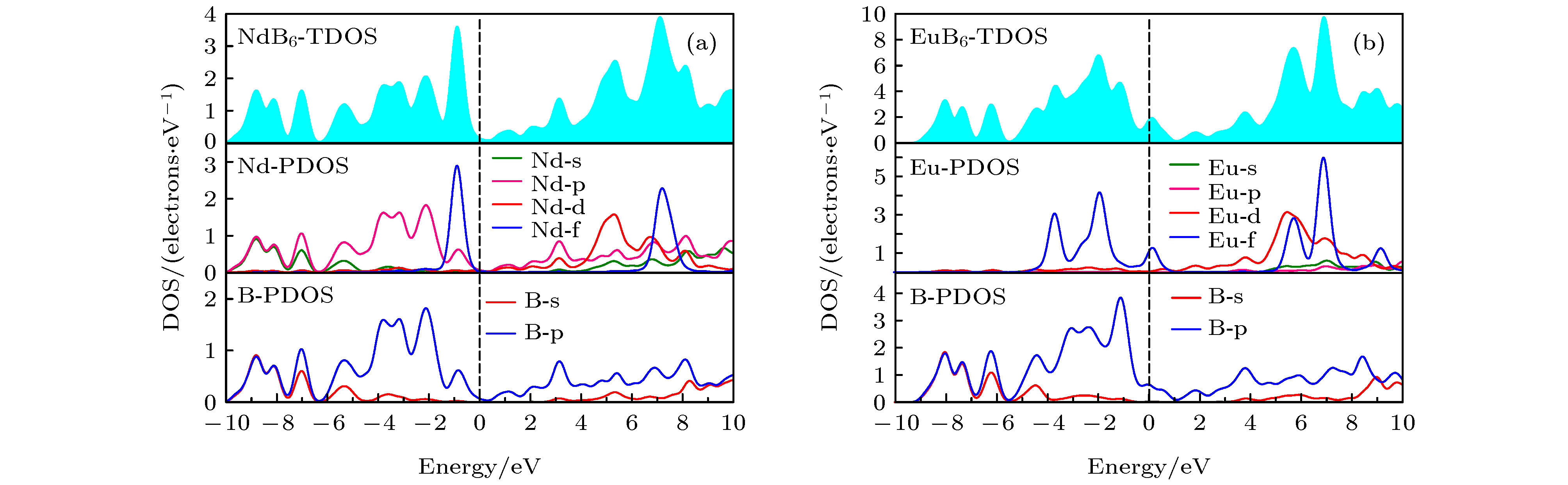
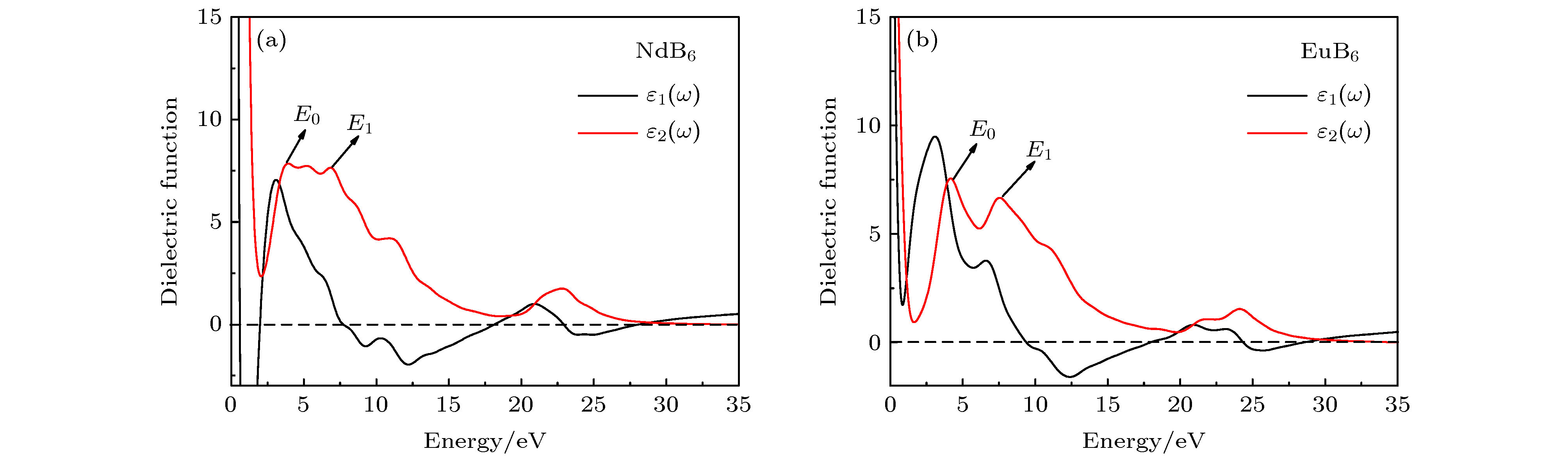
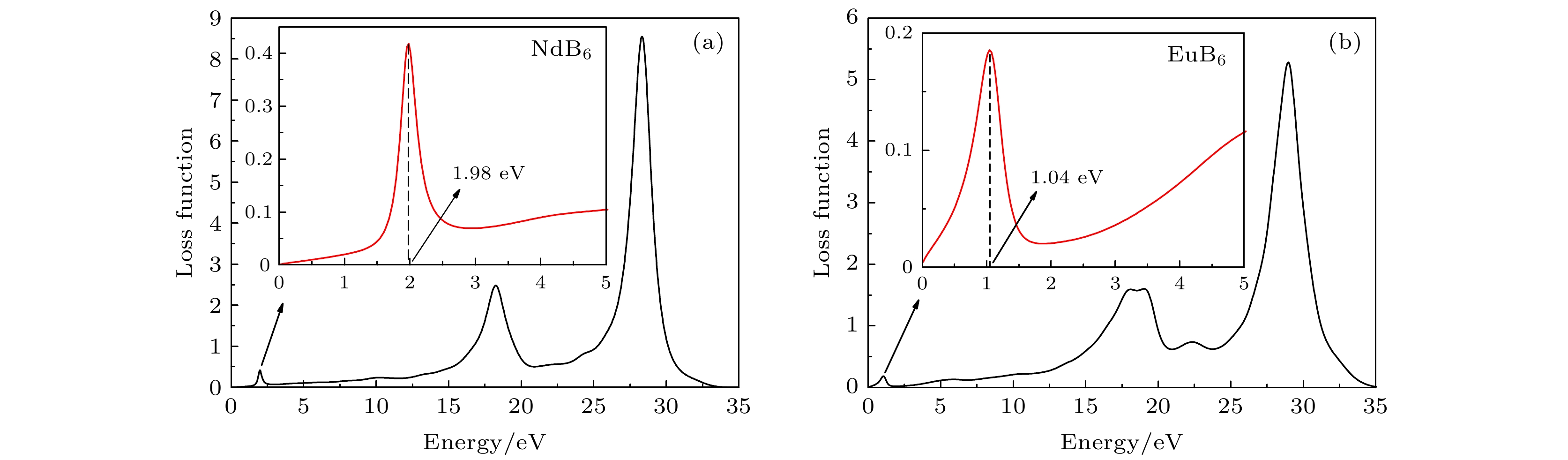
在真空环境中采用固相烧结法成功制备出了多元稀土六硼化物Nd1–xEuxB6纳米粉末. 系统研究了Eu掺杂对纳米NdB6物相、形貌及光吸收性能的影响规律. 结果表明, 所有合成的纳米粉末物相均为单相的CsCl型晶体结构, 具有立方形貌, 平均晶粒尺度为30 nm. 光吸收实验结果表明, 随着Eu掺杂量的增加, 纳米NdB6透射光波长从629 nm红移至1000 nm以上, 表现出了透射光波长的可调特性. 此外, NdB6和EuB6同步辐射吸收图谱表明, Nd和Eu原子分别以Nd3+和Eu2+形式存在于纳米NdB6和EuB6中, 充分说明了Eu掺杂使NdB6传导电子数量减少, 从而导致其等离子共振频率能量的降低. 采用第一性原理计算了NdB6和EuB6的能带结构、态密度、介电函数以及等离子共振频率能量, 从而定性解释了Eu掺杂使NdB6透射光波长红移的特性.Nanocrystalline rare earth hexaborides Nd1–xEuxB6 powders are successfully synthesized by the simple solid-state reaction in vacuum condition for the first time. The effect of Eu doping on the crystal structure, grain morphology, microstructure and optical absorption properties of nanocrystalline NdB6 are investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope (SEM), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and optical absorption measurements. The results show that all the synthesized samples have a single-phase CsCl-type cubic structure with space group of Pm-3m. The SEM results show that the average grain size of the synthesized Nd1–xEuxB6 powders is 50 nm. The HRTEM results show that nanocrystalline Nd1–xEuxB6 has good crystallinity. The results of optical absorption show that the absorption valley of nanocrystalline Nd1–xEuxB6 is redshifted from 629 nm to higher than 1000 nm with the increase of Eu doping, indicating that the transparency of NdB6 is tunable. Additionally, the X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectra μ(E) around the Nd and Eu L3 edges for nanocrystalline NdB6 and EuB6 show that total valence of Nd ion is estimated at +3 in nanocrystalline NdB6 and total valence of Eu ion in nanocrystalline EuB6 is +2. Therefore, the Eu-doping into NdB6 effectively reduces the electron conduction number and it leads the plasma resonance frequency energy to decrease. In order to further qualitatively explain the influence of Eu doping on the optical absorption mechanism, the first principle calculations are used to calculate the band structure, density of states, dielectric function and plasma resonance frequency energy. The calculation results show that the electron band of NdB6 and EuB6 cross the Fermi energy, indicating that they are typical conductors. In addition, the plasmon resonance frequency can be described in the electron energy loss function. The plasmon resonance frequency energy of NdB6 and EuB6 are 1.98 and 1.04 eV, which are corresponding to the absorption valley of 626.26 and 1192.31 nm, respectively. This confirms that the first principle calculation results are in good consistence with the experimental optical absorption valley. Therefore, as an efficient optical absorption material, nanocrystalline Nd1–xEuxB6 powders can expand the optical application scope of rare earth hexaborides.
-
Keywords:
- rare earth hexaboride /
- nanocrystalline material /
- optical absorption
[1] Muz I, Kurban M 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 842 155983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen X B, Mao S S 2007 Chem. Rev. 107 2891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang X B, Ji F 2020 J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20 7464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xiao Q F, Zheng X P, Bu W B, Ge W Q, Zhang S J, Chen F, Xing H Y, Ren Q G, Fan W P, Zhao K L, Hua Y Q, Shi J L 2013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 13041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lv R C, Yang P P, He F, Gai S, Li C X, Dai Y L, Yang G X, Lin J 2015 ACS Nano 9 1630
[6] Yuan Y F, Zhang L, Hu L J, Wang W, Min G H 2011 J. Solid State Chem. 184 3364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Takeda H, Kuno H, Adachi K 2008 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91 2897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Schelm S, Smith G B 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 4346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lai B H, Chen D H 2013 Acta Biomater. 9 7556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen M C, Lin Z W, Ling M H 2016 ACS Nano 10 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Y, Fang C, Li X, Li Z P, Liu B H 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 803 757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xiao L H, Su Y C, Zhou X Z, Chen H Y, Tan J, Hu T, Yan J, Peng P 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 041913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 肖立华, 伏云昌, 苏玉长, 张鹏飞, 彭平 2011 原子与分子 28 0176
Xiao L H, Fu Y C, Su Y C, Zhang P F, Peng P 2011 J. At. Mol. Phys. 28 0176
[14] Xiao L H, Su Y C, Chen H Y, Jiang M, Liu S N, Hu Z X, Liu R F, Peng P, Mu Y L, Zhu D Y 2011 AIP Adv. 1 022140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bao L H, Qi X P, Tana, Chao L M, Tegus O 2016 CrystEngComm 18 1223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bao L H, Qi X P, Tana, Chao L M, Tegus O 2016 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18 19165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bao L H, Chao L M, Li Y J, Ming M, Yibole B, Tegus O 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 651 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bao L H, Chao L M, Wei W, Tegus O 2015 Mater. Lett. 139 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bao L H, Wurentuya B, Wei W, Li Y J, Tegus O 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 617 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang X J, Tsai Y T, Wu S M, Lin Y C, Lee J F, Sheu H S, Cheng B M, Liu R S 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 19612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kerisit S N, Prange M P 2020 Chem. Geol. 534 119460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Qi X P, Bao L H, Chao L M, Tegus O 2018 Physica B 530 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kimura S, Nanba T, Tomikawa M, Kunii S, Kasuya T 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 12196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Choi Y G, Lee K A, Lee K S 2007 Met. Mater. Int. 13 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hernandez R E R, Marcos F R, Serrano A, Salas E, Hussainova I, Fernandez J F 2019 Nanomaterials 9 1473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 4 (a) 纳米Nd0.4Eu0.6B6的TEM照片; (b) HRTEM照片和快速傅里叶变换照片; (c) 纳米Nd0.4Eu0.6B6的HAADF照片; (d)−(f) Nd0.4Eu0.6B6中的Nd, Eu和B元素分布
Fig. 4. (a) TEM image of nanocrystalline Nd0.4Eu0.6B6; (b) HRTEM image and fast Fourier transform pattern; (c) HAADF image of Nd0.4Eu0.6B6; (d)−(f) elemental distribution of Nd, Eu and B for nanocrystalline Nd0.4Eu0.6B6.
-
[1] Muz I, Kurban M 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 842 155983
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen X B, Mao S S 2007 Chem. Rev. 107 2891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang X B, Ji F 2020 J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20 7464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xiao Q F, Zheng X P, Bu W B, Ge W Q, Zhang S J, Chen F, Xing H Y, Ren Q G, Fan W P, Zhao K L, Hua Y Q, Shi J L 2013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 13041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lv R C, Yang P P, He F, Gai S, Li C X, Dai Y L, Yang G X, Lin J 2015 ACS Nano 9 1630
[6] Yuan Y F, Zhang L, Hu L J, Wang W, Min G H 2011 J. Solid State Chem. 184 3364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Takeda H, Kuno H, Adachi K 2008 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91 2897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Schelm S, Smith G B 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 4346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lai B H, Chen D H 2013 Acta Biomater. 9 7556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen M C, Lin Z W, Ling M H 2016 ACS Nano 10 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Y, Fang C, Li X, Li Z P, Liu B H 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 803 757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xiao L H, Su Y C, Zhou X Z, Chen H Y, Tan J, Hu T, Yan J, Peng P 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 041913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 肖立华, 伏云昌, 苏玉长, 张鹏飞, 彭平 2011 原子与分子 28 0176
Xiao L H, Fu Y C, Su Y C, Zhang P F, Peng P 2011 J. At. Mol. Phys. 28 0176
[14] Xiao L H, Su Y C, Chen H Y, Jiang M, Liu S N, Hu Z X, Liu R F, Peng P, Mu Y L, Zhu D Y 2011 AIP Adv. 1 022140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bao L H, Qi X P, Tana, Chao L M, Tegus O 2016 CrystEngComm 18 1223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bao L H, Qi X P, Tana, Chao L M, Tegus O 2016 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18 19165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bao L H, Chao L M, Li Y J, Ming M, Yibole B, Tegus O 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 651 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bao L H, Chao L M, Wei W, Tegus O 2015 Mater. Lett. 139 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bao L H, Wurentuya B, Wei W, Li Y J, Tegus O 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 617 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang X J, Tsai Y T, Wu S M, Lin Y C, Lee J F, Sheu H S, Cheng B M, Liu R S 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 19612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kerisit S N, Prange M P 2020 Chem. Geol. 534 119460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Qi X P, Bao L H, Chao L M, Tegus O 2018 Physica B 530 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kimura S, Nanba T, Tomikawa M, Kunii S, Kasuya T 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 12196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Choi Y G, Lee K A, Lee K S 2007 Met. Mater. Int. 13 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hernandez R E R, Marcos F R, Serrano A, Salas E, Hussainova I, Fernandez J F 2019 Nanomaterials 9 1473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9268
- PDF下载量: 107
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: