-
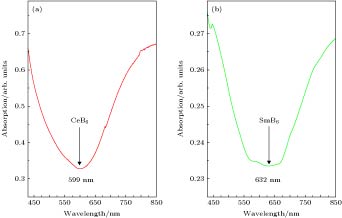
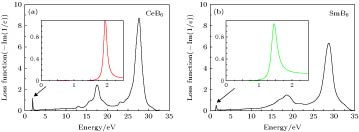
采用蒸发冷凝法成功制备出了纳米稀土六硼化物CeB6和SmB6超细粉末. 对所制备粉末物相、晶粒形貌、微观结构及光吸收性能进行了系统研究. 结果表明, 纳米CeB6和SmB6粉末主相为CaB6-型立方晶体结构, 球型形貌, 平均晶粒尺度为50 nm. 高分辨透射电镜观察结果表明, 在冷凝(结晶)过程中由于稀土元素Sm具有易挥发特性导致纳米SmB6结晶过程中存在大量的晶体缺陷. 光吸收结果表明, 纳米CeB6透射光波长为599 nm, 纳米SmB6透射光波长为632 nm, 均表现出了可见光穿透的特点. 为进一步定性解释光吸收机理, 采用第一性原理计算了能带、态密度及等离子共振频率能量.In the present work, the nanocrystalline CeB6 and SmB6 powder are successfully prepared by evaporative condensation method. The phase composition, grain morphology, microstructure and optical absorption properties for each of the prepared powders are studied systematically. The results show that the main phase of nanocrystalline CeB6 powder and SmB6 powder are both composed of CaB6-type cubic structure with space group of Pm-3m. The scanning electron microscope results show that the synthesized CeB6 and SmB6 nanoparticles display an spherical morphology with an average grain size of 50 nm. The high resolution transmission electron microscopy observation results show that there exist many intrinsic crystal defects in nanocrystalline SmB6, such as lattice distortions or edge dislocations, due to the high volatility characteristic of Sm atom in the condensation (crystallization) process. The optical absorption results show that the absorption valley of nanocrystalline CeB6 and SmB6 are respectively located at 599 nm and 632 nm, indicating the high transparency characteristic of visible light. To further qualitatively explain the difference in optical absorption mechanism between CeB6 and SmB6, the first principle calculations are employed to calculate their band structures, densities of states, optical absorption energy, and plasma resonance frequency energy. The calculation results show that there is an electron band crossing the Fermi energy for both CeB6 and SmB6, indicating their typical conductor behaviors. The upmost valence band of CeB6 and SmB6 are composed of B-2p and B-2s states, and their bottommost conduction bands are mainly composed of Ce-4f, Ce-5d, Sm-4f, Sm-5d, B-2p and B-2s states. In addition, the volume plasma of carrier electrons can be described in the electron energy-loss function. The peak position in the low energy region of the loss function corresponds to the relevant plasma frequency. As a result, the calculated low energy loss function of CeB6 and SmB6 are 1.96 eV and 1.5 eV, respectively. Moreover, the calculated absorption valley of CeB6 and SmB6 respectively appear at 639 nm and 800 nm, which are in good accordance with the experimental results. Therefore, as an efficient optical absorption materials, the nanocrystalline CeB6 and SmB6 should open the way to extending the optical applications of rare-earth hexaborides.
-
Keywords:
- evaporative condensation method /
- rare earth hexaboride /
- nanocrystalline material /
- optical absorption
[1] Bao L H, Chao L M, Wei W, Tegus O 2014 Mater. Lett. 139 187
[2] 包黎红, 那仁格日乐, 特古斯, 张忻, 张久兴 2013 62 196105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Narengerile, Tegus O, Zhang X, Zhang J X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 196105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘洪亮, 张忻, 王杨, 肖怡新, 张久兴 2018 67 048101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H L, Zhang X, Wang Y, Xiao Y X, Zhang J X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 048101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王杨, 张忻, 张久兴, 刘洪亮, 江浩, 李录录 2016 无机化学学报 31 797
Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang J X, Liu H L, Jiang H, Li L L 2016 J. Inorg. Mater. 31 797
[5] 包黎红, 张久兴, 周身林, 张宁 2011 60 106501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Zhang J X, Zhou S L, Zhang N 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 106501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 包黎红, 朝洛蒙, 伟伟, 特古斯 2015 64 096104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Chao L M, Wei W, Tegus O 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 096104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 韩伟 2017 博士学位论文 (广州: 华南理工大学)
Han W 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Guangzhou: South China University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[8] 吴锦雷, 刘盛 2003 贵金属 24 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J L, Liu S 2003 Precious Metals 24 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 周爱秋, 许效红, 姚伟峰, 曾凡亮, 宋邦强 2004 化学 3 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou A Q, Xu X H, Yao W F, Zeng F L, Song B Q 2004 Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 3 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chao L M, Bao L H, Shi J J, Wei W, Tegus O, Zhang Z D 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 622 618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen M C, Lin Z W, Ling M H 2016 ACS Nano 10 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bai L, Ma N, Liu F L 2009 Physica B 404 4086
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kim S S, Na S I, Jo J, Kim D Y, Nah Y C 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 073307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nedyalkov N N, Nakajima Y, Takami A, Koleva M, Karashanova D, Terakawa M 2016 Opt. Laser Technol. 79 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Takeda H, Kuno H, Adachi K 2008 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91 2897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sato Y, Terauchi M, Mukai M, Kaneyama T, Adachi K 2011 Ultramicroscopy 111 1381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 肖立华, 苏玉长, 刘仪柯, 冉景榆, 杨涛, 彭平 2017 功能材料信息 3 19
Xiao L H, Su Y C, Liu Y K, Ran J Y, Yang T, Peng P 2017 Func. Mate. Info. 3 19
[18] Zeng X S, Ye Y X, Zou S L, Gou Q D, Wen Y F, Ou P 2017 Crystals 7 320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kimura S, Nanba T, Kunii S, Suzuki T, Kasuya T 1990 Solid State Commun. 75 717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 包黎红, 陶如玉, 特古斯, 黄颖楷, 冷华倩, Anne de Visser 2017 66 186102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Tao R Y, Tegus O, Huang Y K, Leng H Q, Anne de Visser 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 186102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
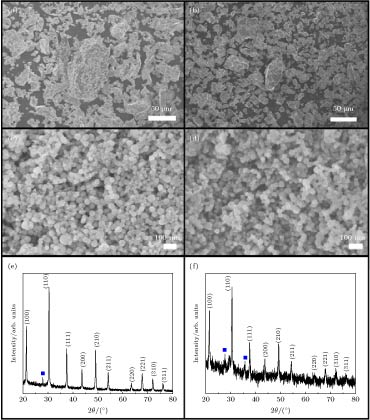
图 2 (a)和(b)原料CeB6和SmB6粗粉的FESEM照片; (c)和(d)蒸发冷凝法制备的纳米CeB6和SmB6的FESEM照片; (e)和(f)为纳米CeB6和SmB6的XRD图谱
Fig. 2. (a), (b) FESEM image of precursor powder CeB6 and SmB6; (c), (d) FESEM image of CeB6 and SmB6 nanocrystals prepared by evaporation condensation; (e), (f) XRD spectra of CeB6 and SmB6 nanocrystals prepared by evaporation condensation.
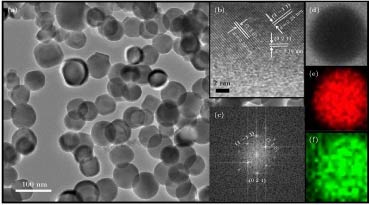
图 3 (a) 纳米CeB6的TEM照片; 单颗粒纳米CeB6的(b) HRTEM照片、(c) 快速傅里叶变换照片、(d) HAADF-STEM分析, 以及相应(e), (f) Ce和B的元素分布照片
Fig. 3. (a) TEM image of nanocrystalline CeB6; (b) HRTEM image, (c) fast Fourier transform pattern, (d) HAADF-STEM, and (e), (f) elemental distribution of Ce and B for single particle of nanocrystalline CeB6.
-
[1] Bao L H, Chao L M, Wei W, Tegus O 2014 Mater. Lett. 139 187
[2] 包黎红, 那仁格日乐, 特古斯, 张忻, 张久兴 2013 62 196105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Narengerile, Tegus O, Zhang X, Zhang J X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 196105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘洪亮, 张忻, 王杨, 肖怡新, 张久兴 2018 67 048101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H L, Zhang X, Wang Y, Xiao Y X, Zhang J X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 048101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王杨, 张忻, 张久兴, 刘洪亮, 江浩, 李录录 2016 无机化学学报 31 797
Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang J X, Liu H L, Jiang H, Li L L 2016 J. Inorg. Mater. 31 797
[5] 包黎红, 张久兴, 周身林, 张宁 2011 60 106501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Zhang J X, Zhou S L, Zhang N 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 106501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 包黎红, 朝洛蒙, 伟伟, 特古斯 2015 64 096104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Chao L M, Wei W, Tegus O 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 096104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 韩伟 2017 博士学位论文 (广州: 华南理工大学)
Han W 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Guangzhou: South China University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[8] 吴锦雷, 刘盛 2003 贵金属 24 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J L, Liu S 2003 Precious Metals 24 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 周爱秋, 许效红, 姚伟峰, 曾凡亮, 宋邦强 2004 化学 3 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou A Q, Xu X H, Yao W F, Zeng F L, Song B Q 2004 Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 3 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chao L M, Bao L H, Shi J J, Wei W, Tegus O, Zhang Z D 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 622 618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen M C, Lin Z W, Ling M H 2016 ACS Nano 10 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bai L, Ma N, Liu F L 2009 Physica B 404 4086
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kim S S, Na S I, Jo J, Kim D Y, Nah Y C 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 073307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nedyalkov N N, Nakajima Y, Takami A, Koleva M, Karashanova D, Terakawa M 2016 Opt. Laser Technol. 79 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Takeda H, Kuno H, Adachi K 2008 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91 2897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sato Y, Terauchi M, Mukai M, Kaneyama T, Adachi K 2011 Ultramicroscopy 111 1381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 肖立华, 苏玉长, 刘仪柯, 冉景榆, 杨涛, 彭平 2017 功能材料信息 3 19
Xiao L H, Su Y C, Liu Y K, Ran J Y, Yang T, Peng P 2017 Func. Mate. Info. 3 19
[18] Zeng X S, Ye Y X, Zou S L, Gou Q D, Wen Y F, Ou P 2017 Crystals 7 320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kimura S, Nanba T, Kunii S, Suzuki T, Kasuya T 1990 Solid State Commun. 75 717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 包黎红, 陶如玉, 特古斯, 黄颖楷, 冷华倩, Anne de Visser 2017 66 186102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L H, Tao R Y, Tegus O, Huang Y K, Leng H Q, Anne de Visser 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 186102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11489
- PDF下载量: 91
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: