-
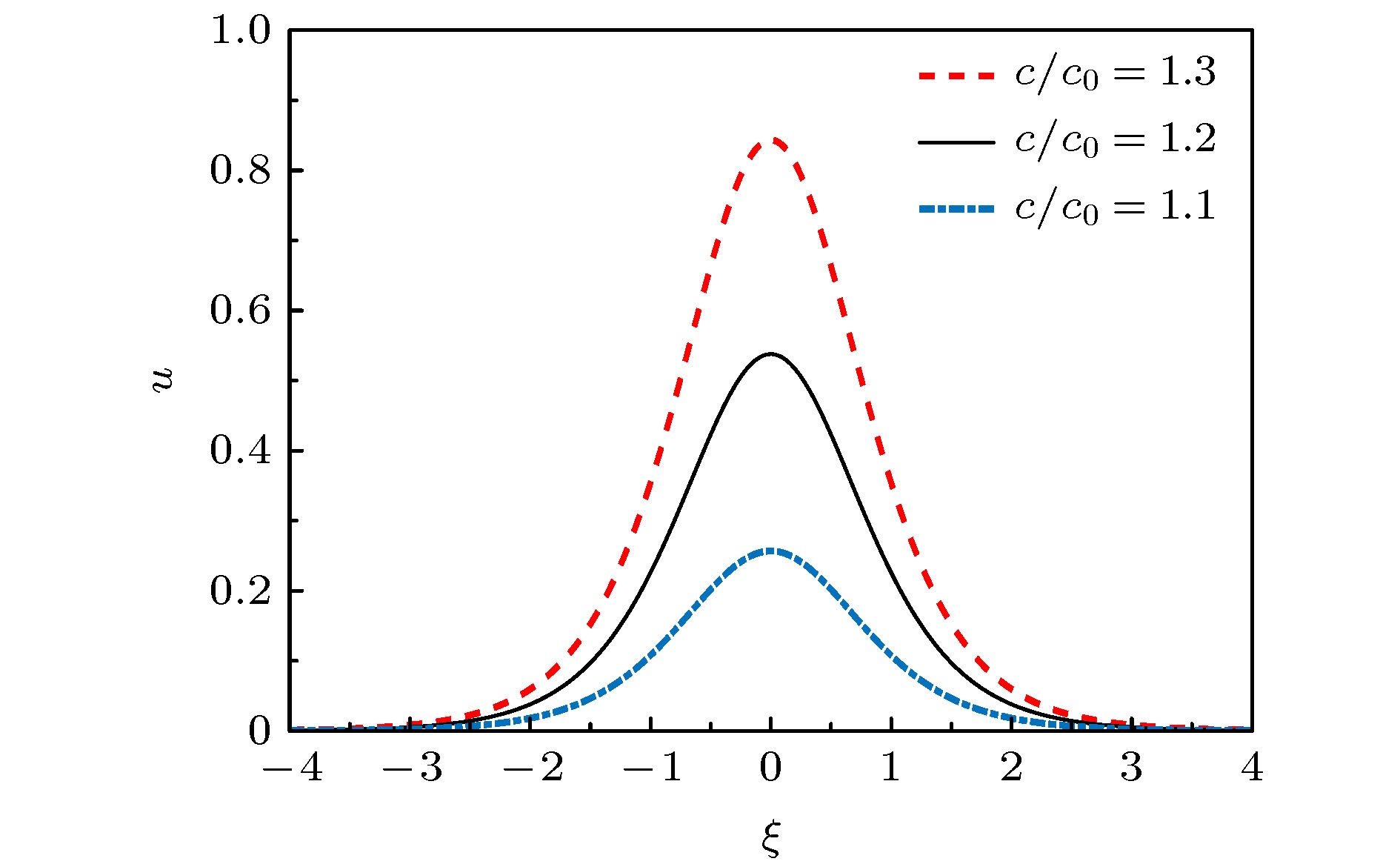
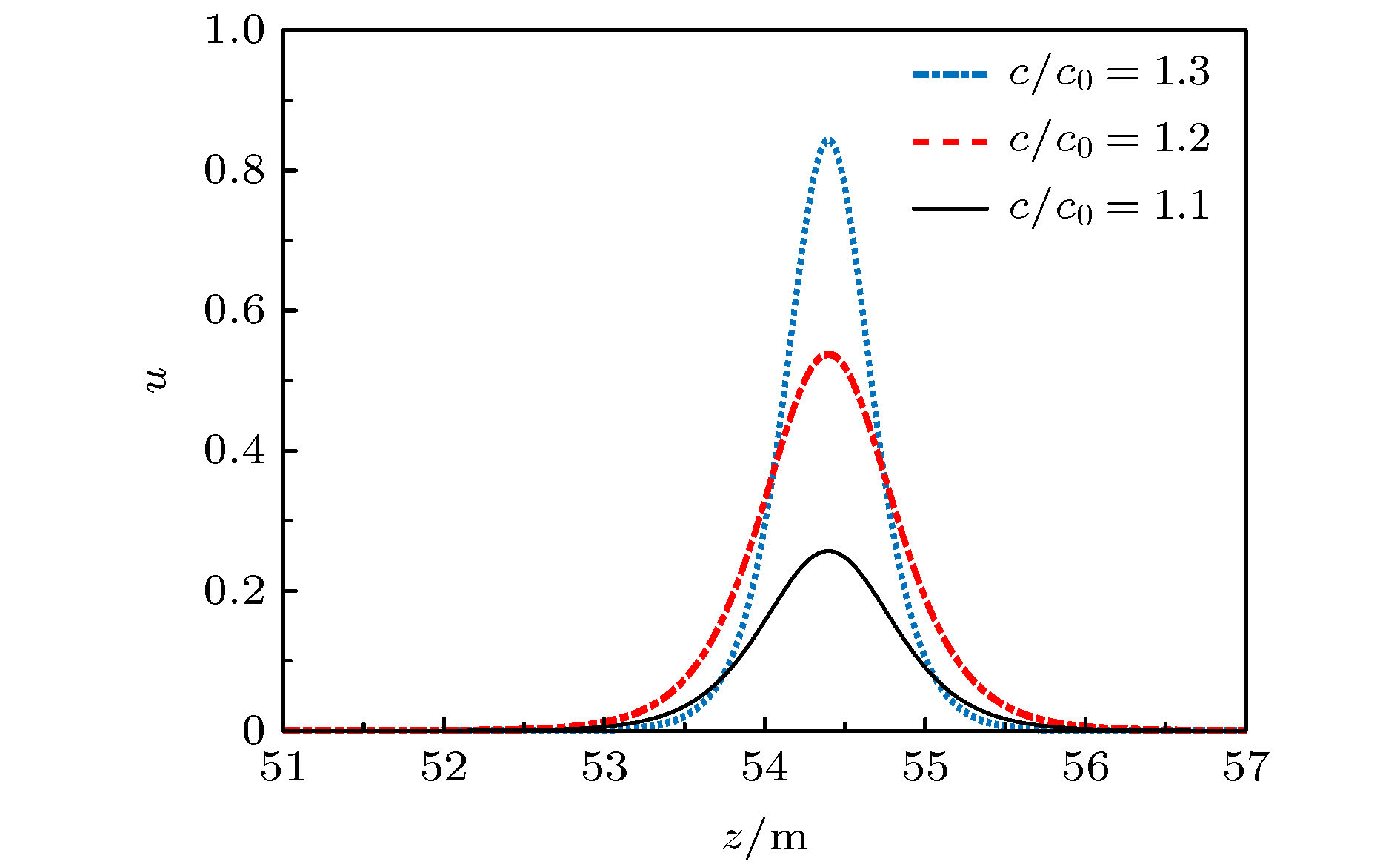
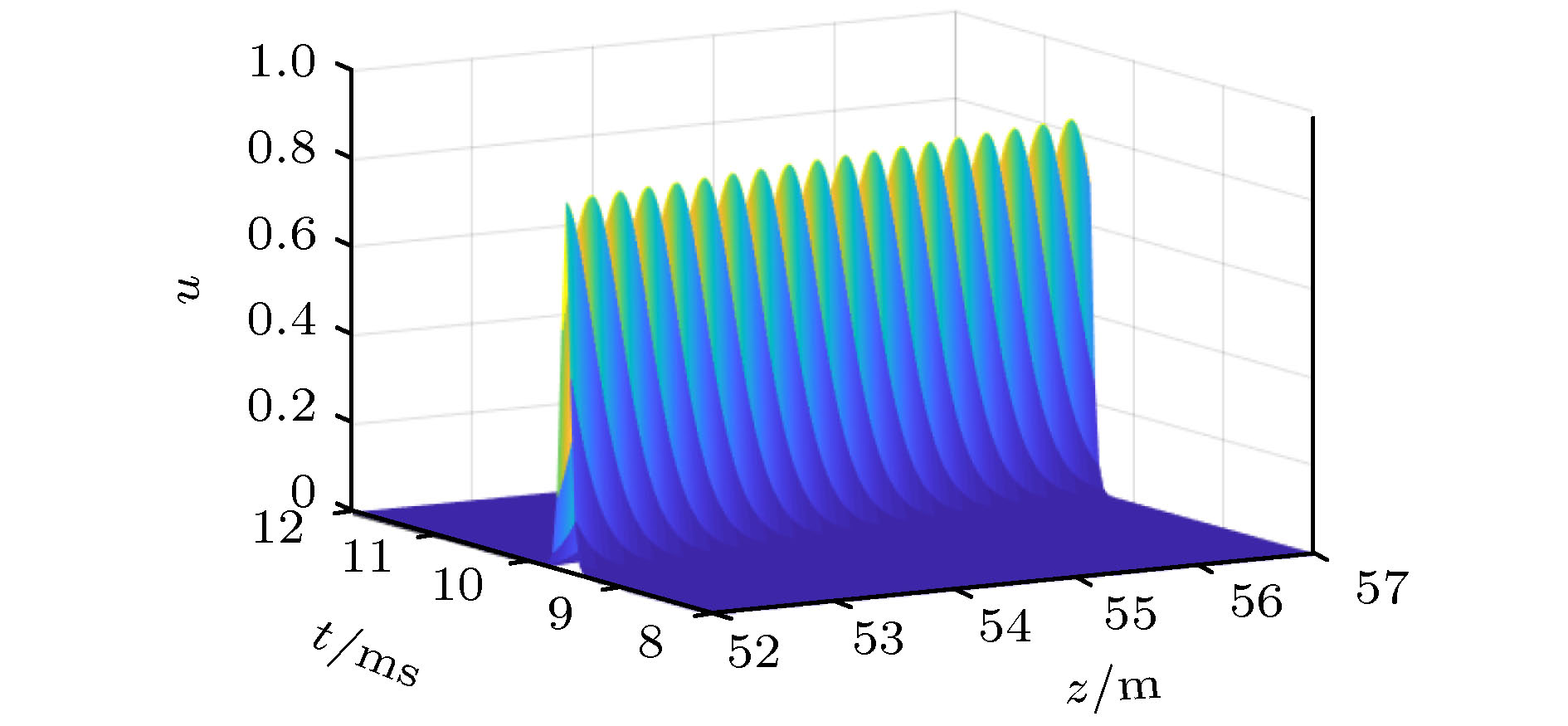
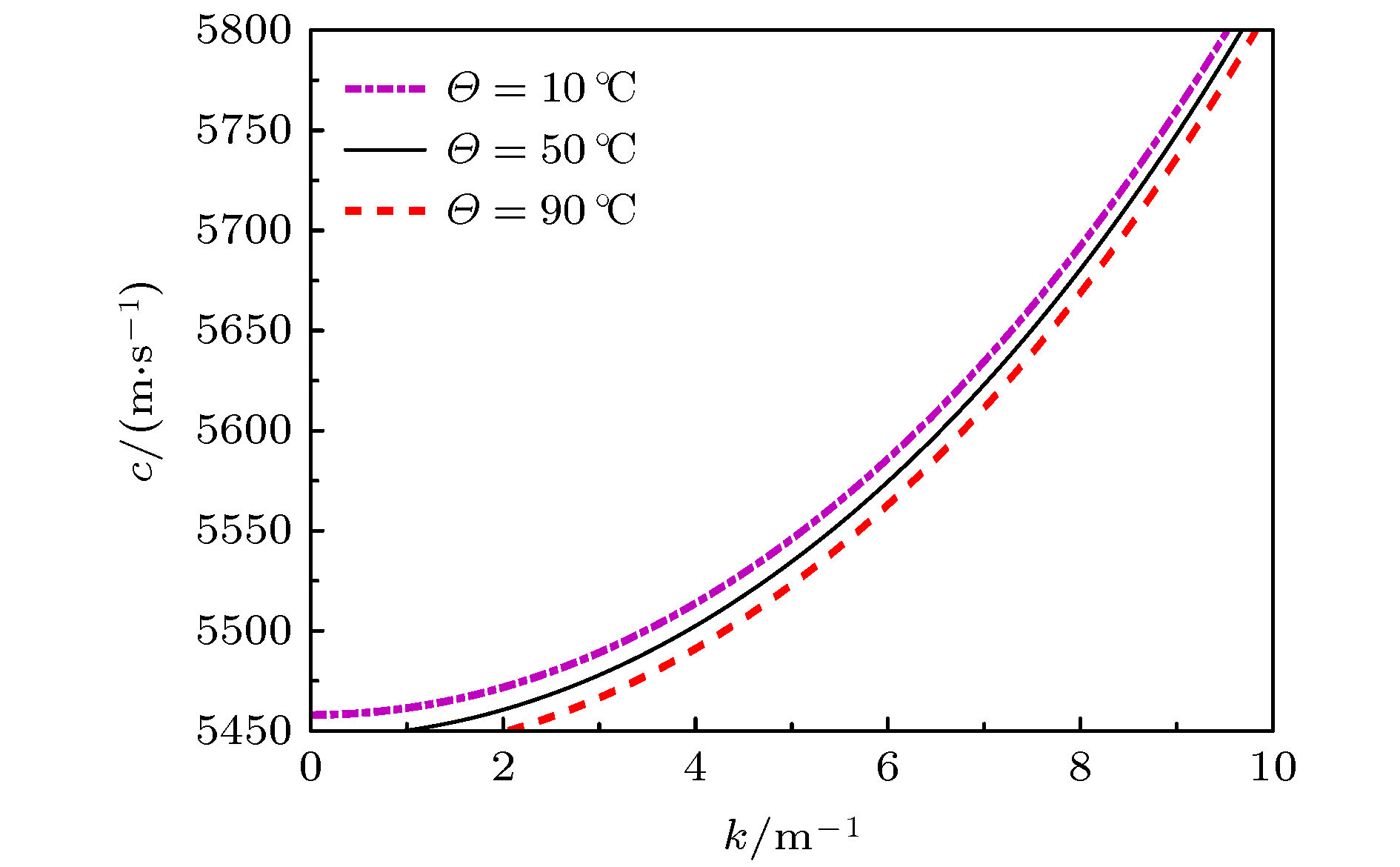
利用有限变形理论, 以无限长压电圆杆为研究对象, 考虑了在横向惯性、等效泊松比效应以及在热电弹耦合共同作用下, 基于Hamilton原理, 并引入Euler方程推导出压电圆杆的纵向波动方程. 采用Jacobi椭圆函数展开法, 求解压电圆杆的波动方程和对应的解. 最后, 通过Matlab软件得到不同波速比下的色散曲线, 以及温度场对压电圆杆的波形、波幅和波数的影响曲线. 数值分析结果表明: 随着温度的升高, 波速逐渐降低, 温度场的改变可影响和控制孤立波的传播特性.
-
关键词:
- 压电圆杆 /
- Hamilton原理 /
- 温度效应 /
- 孤波
Piezoelectric elements have been commonly used because of their wide applications in sensors, transducers, and some micro intelligent structures. However, in the fields of aviation, aerospace, and automation, some relevant equipment works in a harsh environment and is susceptible to the temperature change, thereby leading its performances to be greatly affected. Therefore, the problem of nonlinear wave relating to piezoelectric circular rods in different temperature fields is studied by modeling and numerical analysis. Firstly, based on the theory of finite deformation, we take infinite piezoelectric circular rod as a research object and consider the effects of transverse inertia and equivalent Poisson's ratio under the thermoelectric coupling action. Using the Hamilton principle and introducing the Euler equation, the longitudinal wave equation of piezoelectric circular rod is obtained. Secondly, Jacobi elliptic cosine function and Jacobi elliptic sine function expansion method are used to solve the wave equation of the piezoelectric circular rod, and the solitary wave solution and the exact periodic solution of the wave equation are obtained. It is found that the periodic solution can be reduced into a solitary wave solution under certain conditions, and it is proved theoretically that there may be solitary wave stably propagating in a piezoelectric circular rod. Finally, the dispersion curves of different wave velocity ratios and the curves about influences of temperature field on the waveform, amplitude and wave number of the piezoelectric rod are obtained by Matlab. The numerical results show that the wave velocity decreases with the increase of temperature when the wave velocity ratio is constant. Given the temperature is constant, it can be found that with the increase of the ratio, the amplitude of solitary wave gradually increases while the wavelength gradually decreases. In addition, the images obtained show that although temperature change can cause the characteristics of solitary waves to change, the solitary waves are always symmetrical bell shaped waves in the propagation process, reflecting the stability characteristics under the combined action of nonlinear and dispersion effects. Therefore, the variation of temperature field can influence and control some propagation characteristics of solitary waves. Moreover, the wave theory has been widely used in the nondestructive testing of structures and the improving of information transmission quality due to its special stability.-
Keywords:
- piezoelectric rod /
- Hamilton principle /
- temperature effect /
- solitary wave
[1] Janshoff A, Steinem C, Galla H J 2000 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39 4004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘延柱, 薛纭, 陈立群 2004 53 2424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y Z, Xue Y, Chen L Q 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 2424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] He T H, Tian X G, Shen Y P 2002 Int. J. Eng. Sci. 40 1081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 范恩贵 2000 49 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan E G 2000 Acta Phys. Sin. 49 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李向正, 张卫国, 原三领 2010 59 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X Z, Zhang W G, Yuan S L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 冯依虎 2019 应用力学与数学 40 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y H 2019 Appl. Math. Mech. 40 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guo J G, Zhou L J, Zhang S Y 2005 Appl. Math. Mech. 26 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李敏, 王博婷, 许韬, 水涓涓 2020 69 010502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M, Wang B T, Xu T, Shui J J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 010502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 李志斌, 潘素起 2004 50 402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z B, Pan S Q 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 50 402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xia T C, Li B, Zhang H Q 2001 Appl. Math. E-Notes 1 139
[11] 钱存, 王亮亮, 张解放 2011 60 064214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qian C, Wang L L, Zhang J F 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 064214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘式达, 傅遵涛, 刘式适, 赵强 2002 51 718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S D, Fu Z T, Liu S K, Zhao Q 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang S Y, Zhang W 1987 Acta Mech. Sin. 3 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘志芳, 张善元 2007 固体力学学报 28 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z F, Zhang S Y 2007 Acta Mech. Solid. Sin. 28 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘志芳, 张善元 2006 55 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z F, Zhang S Y 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Z F, Zhang S Y 2006 Appl. Math. Mech. 27 1431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 邓庆田, 罗松南, 彭亮 2009 应用力学学报 26 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng Q T, Luo S N, Peng L 2009 Chin. J. Appl. Mech. 26 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Seadawy A R, Manafian J 2018 Results Phys. 8 1158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Baskonus H M, Bulut H, Atangana A 2016 Smart Mater. Struct. 25 035022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bulut H, Sulaiman T A, Baskonus H M 2018 Opt. Quantum. Electron. 50 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang Q 2001 Int. J. Solids. Struct. 38 8207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xue C X, Pan E 2013 Int. J. Eng. Sci. 62 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Samsonov A M 2001 Strain Solitons in Solids and How to Construct Them (New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC) p111
[24] Toffoli T, Fernandez L, Monbaliu J, Benoit M, Gagnaire-Renou E, Lefèvre J M, Cavaleri L, Proment D, Pakozdi C, Stansberg C T, Waseda T, Onorato M 2013 Phys. Fluids 25 091701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ansari R, Oskouie F M, Gholami R, Sadeghi F 2016 Compos. Part B-Eng. 89 316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ootao Y, Tanigawa Y 2000 Int. J. Eng. Sci. 38 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shiv P J 1992 Smart Mater. Struct. 1 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xue C X, Pan E, Zhang S Y 2011 Smart Mater. Struct. 20 105010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 常瑞鼎 2014 硕士学位论文 (湘潭: 湘潭大学)
Chang R D 2014 M. S. Thesis (Hunan: Xiangtan University) (in Chinese)
[30] 贾菲B 著 (林声和 译) 1976 压电陶瓷 (北京: 科学出版社)第125−145页
Jaffe B (translated by Lin S H) 1976 Piezoelectric Ceramics (Beijing: Science Press) pp125−145 (in Chinese)
-
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 c11/(N·m–2) 166 × 109 e15/(C·m–2) 11.6 c12/(N·m–2) 77 × 109 ε11/(C2·N–2·m–1) 11.2 × 10–9 c13/(N·m–2) 78 × 109 ε33/(C2·N-2·m–1) 12.9 × 10–9 c33/(N·m–2) 162 × 109 d1/(C·km–2) –5.4831 × 10–6 c44/(N·m–2) 43 × 109 d3/(C·km–2) –5.4831 × 10–6 e31/(C·m–2) –4.4 α1 = 0.5α3 10 × 10–6 e33/(C·m–2) 18.6 β1/m2 0.5278 × 10–4 β2/m2 2.112 × 10–4 β3/m2 4.7502 × 10–4 α/(N·m·kg–1) 3.5561 × 107 veff 0.2906 ρ/(kg·m-3) 5.8 × 103 表 2 不同温度下波速比较
Table 2. Comparison of the wave velocities at different temperature.
Θ/℃ c0/(103 m·s–1) 10 5.4482 50 5.4367 90 5.4251 表 3 R = 0.05 m时不同波速比下参数比较
Table 3. Comparison of parameters under different wave velocity ratios when R = 0.05 m.
c/c0 A/m Λ/m k 1.1 0.2567 0.5429 11.5675 1.2 0.5378 0.4092 15.3470 1.3 0.8434 0.3540 17.740 表 4 波速比c/c0 = 1.1时不同半径下参数比较
Table 4. Comparison of parameters under different radii when c/c0 = 1.1.
R/m Λ/m k 0.025 0.2705 23.2162 0.050 0.5429 11.5675 0.075 0.8116 7.7375 -
[1] Janshoff A, Steinem C, Galla H J 2000 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39 4004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘延柱, 薛纭, 陈立群 2004 53 2424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y Z, Xue Y, Chen L Q 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 2424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] He T H, Tian X G, Shen Y P 2002 Int. J. Eng. Sci. 40 1081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 范恩贵 2000 49 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan E G 2000 Acta Phys. Sin. 49 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李向正, 张卫国, 原三领 2010 59 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X Z, Zhang W G, Yuan S L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 冯依虎 2019 应用力学与数学 40 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y H 2019 Appl. Math. Mech. 40 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guo J G, Zhou L J, Zhang S Y 2005 Appl. Math. Mech. 26 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李敏, 王博婷, 许韬, 水涓涓 2020 69 010502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M, Wang B T, Xu T, Shui J J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 010502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 李志斌, 潘素起 2004 50 402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z B, Pan S Q 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 50 402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xia T C, Li B, Zhang H Q 2001 Appl. Math. E-Notes 1 139
[11] 钱存, 王亮亮, 张解放 2011 60 064214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qian C, Wang L L, Zhang J F 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 064214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘式达, 傅遵涛, 刘式适, 赵强 2002 51 718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S D, Fu Z T, Liu S K, Zhao Q 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang S Y, Zhang W 1987 Acta Mech. Sin. 3 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘志芳, 张善元 2007 固体力学学报 28 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z F, Zhang S Y 2007 Acta Mech. Solid. Sin. 28 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘志芳, 张善元 2006 55 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z F, Zhang S Y 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Z F, Zhang S Y 2006 Appl. Math. Mech. 27 1431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 邓庆田, 罗松南, 彭亮 2009 应用力学学报 26 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng Q T, Luo S N, Peng L 2009 Chin. J. Appl. Mech. 26 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Seadawy A R, Manafian J 2018 Results Phys. 8 1158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Baskonus H M, Bulut H, Atangana A 2016 Smart Mater. Struct. 25 035022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Bulut H, Sulaiman T A, Baskonus H M 2018 Opt. Quantum. Electron. 50 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang Q 2001 Int. J. Solids. Struct. 38 8207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xue C X, Pan E 2013 Int. J. Eng. Sci. 62 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Samsonov A M 2001 Strain Solitons in Solids and How to Construct Them (New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC) p111
[24] Toffoli T, Fernandez L, Monbaliu J, Benoit M, Gagnaire-Renou E, Lefèvre J M, Cavaleri L, Proment D, Pakozdi C, Stansberg C T, Waseda T, Onorato M 2013 Phys. Fluids 25 091701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ansari R, Oskouie F M, Gholami R, Sadeghi F 2016 Compos. Part B-Eng. 89 316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ootao Y, Tanigawa Y 2000 Int. J. Eng. Sci. 38 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shiv P J 1992 Smart Mater. Struct. 1 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xue C X, Pan E, Zhang S Y 2011 Smart Mater. Struct. 20 105010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 常瑞鼎 2014 硕士学位论文 (湘潭: 湘潭大学)
Chang R D 2014 M. S. Thesis (Hunan: Xiangtan University) (in Chinese)
[30] 贾菲B 著 (林声和 译) 1976 压电陶瓷 (北京: 科学出版社)第125−145页
Jaffe B (translated by Lin S H) 1976 Piezoelectric Ceramics (Beijing: Science Press) pp125−145 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 6688
- PDF下载量: 97
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: