-
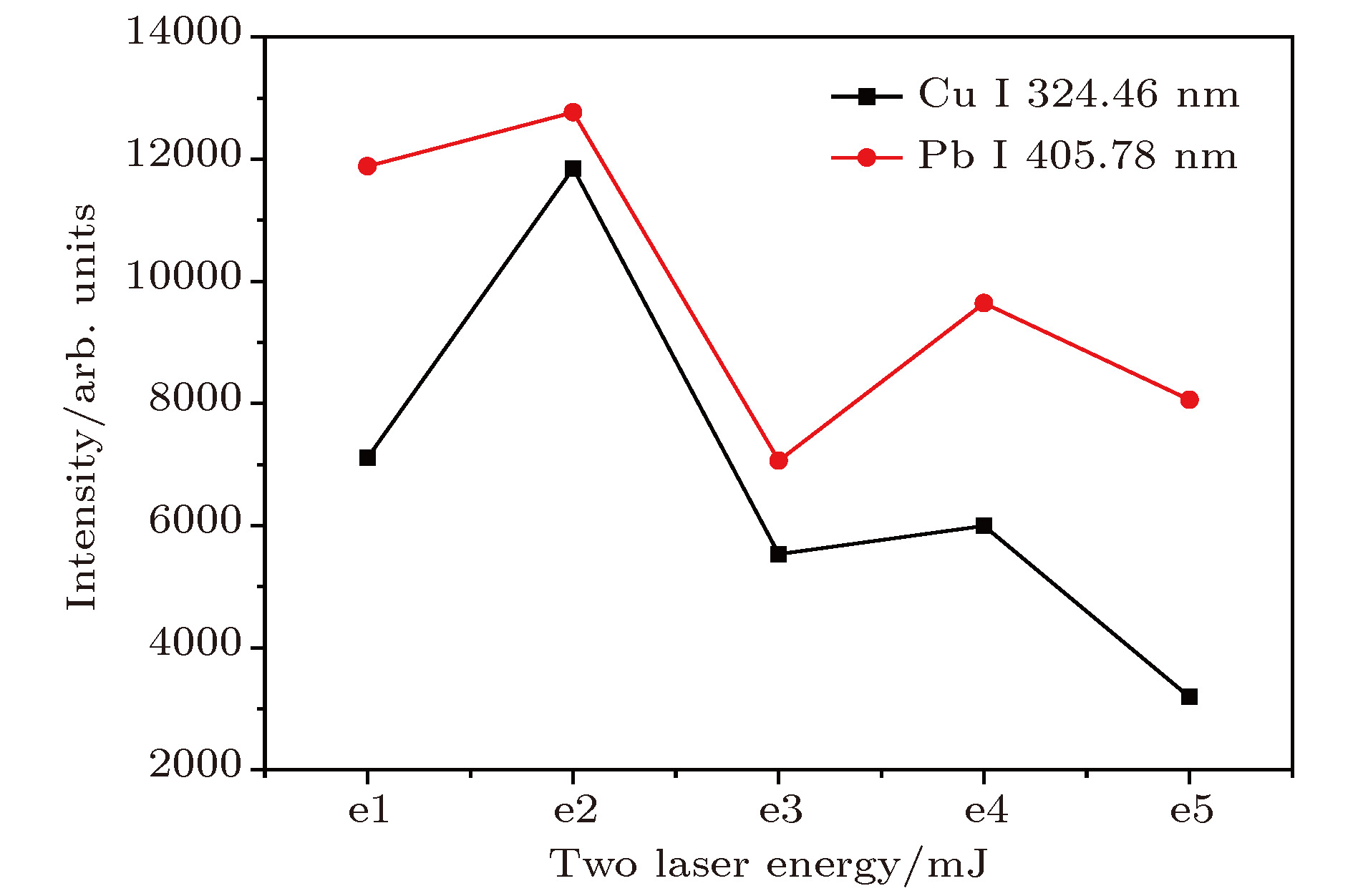
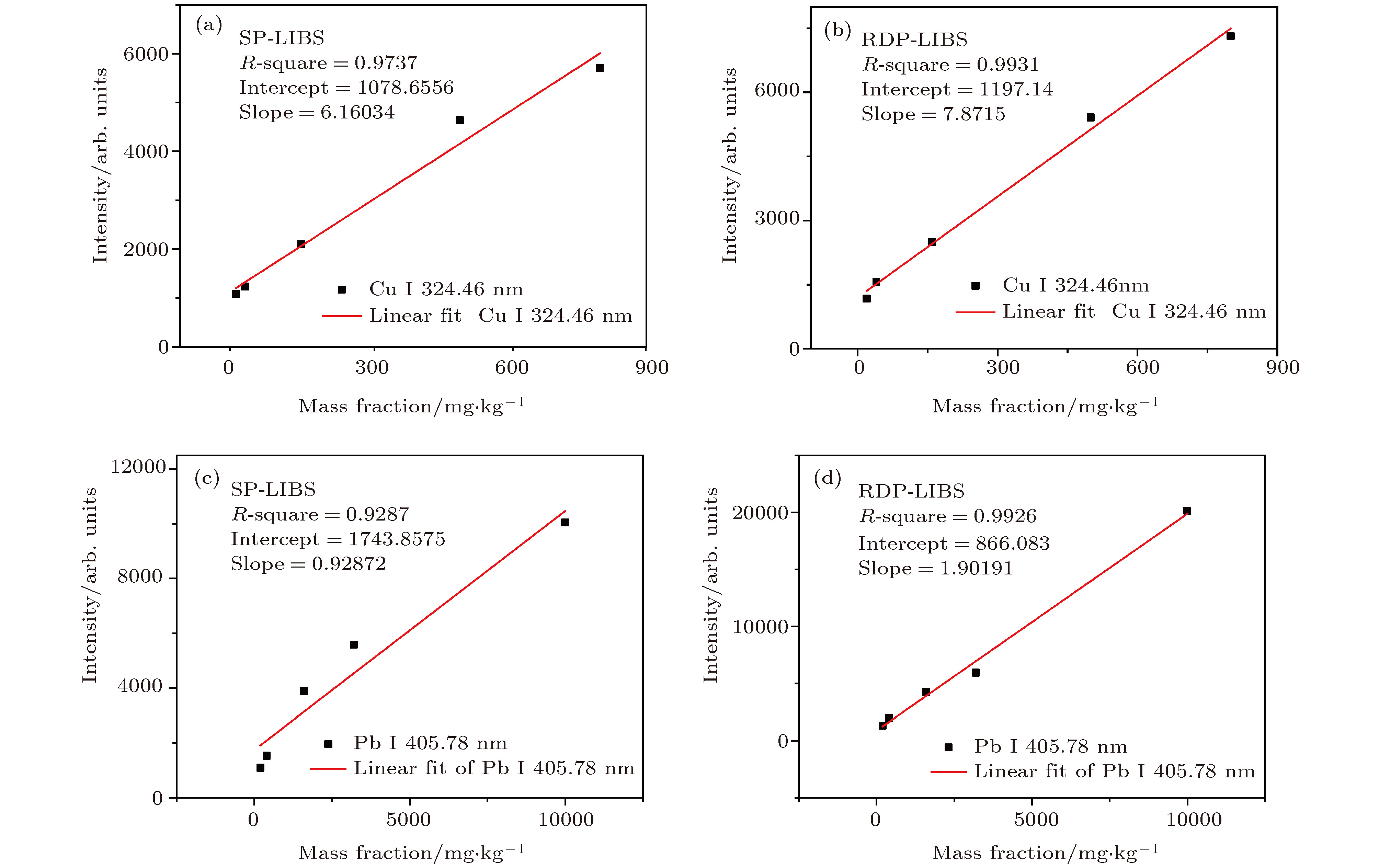
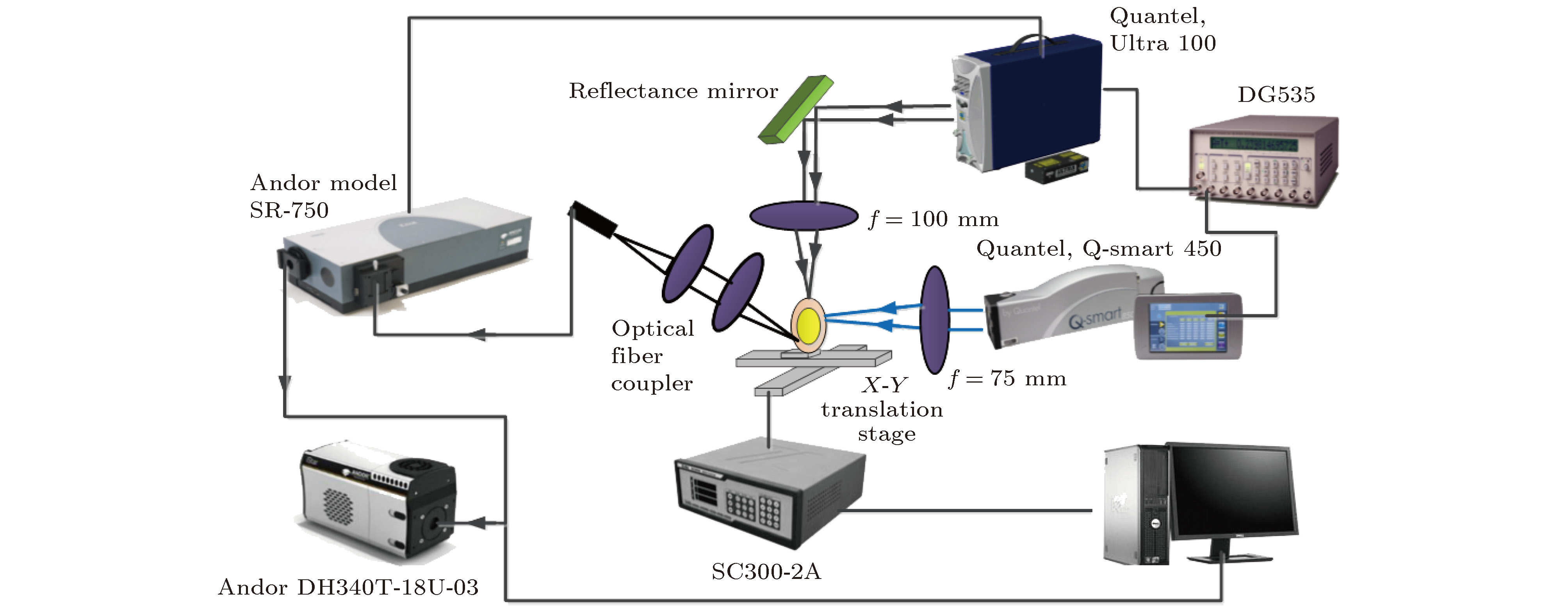
基于单脉冲激光诱导击穿光谱(single pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, SP-LIBS)实验装置, 搭建了再加热双脉冲激光诱导击穿光谱(re-heating double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, RDP-LIBS)系统, 实现了黄连中重金属元素Cu和Pb的检测. 固定激光脉冲频率为4 Hz, 两束激光的总能量为50 mJ, 实验优化了增强电荷耦合器件探测延时、脉冲间隔和双激光脉冲能量组合等参数对Cu I (324.46 nm)和Pb I (405.78 nm)光谱强度的影响, 得特征谱线Cu I (324.46 nm)的最佳激光能量组为(E1 = 15 mJ, E2 = 35 mJ), 脉冲间隔和探测延时分别为1.4 μs和1.5 μs; Pb I (405.78 nm)的激光能量组也为(E1 = 15 mJ, E2 = 35 mJ), 脉冲间隔和探测延时分别为1.6 μs和1.7 μs. 为实现RDP-LIBS技术对中药材重金属元素检测性能的评估, 在最佳实验参数下, 分别对Cu和Pb进行SP-LIBS技术和RDP-LIBS技术定量分析, 检测限分别为1.91 mg/kg和3.03 mg/kg, 较SP-LIBS技术, 检测限均有所降低, 满足《药用植物进出口绿色行业标准》的要求, 且RDP-LIBS的线性曲线拟合度都优于SP-LIBS, 说明RDP-LIBS技术在中药材检测中具有更佳的检测性能.Coptidis plays an important role in the field of traditional Chinese medicine. However, it is easily polluted by heavy metals in environment (water and soil), and thus can affect human health. In order to detect the heavy metal elements Cu and Pb in Coptidis, which was purchased from the Chinese herbal medicine market in Chongqing, the reheated double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (RDP-LIBS) is investigated. In order to reduce the experimental error caused by the irregular shape, it is necessary to pretreat the Coptidis samples prior to the determination step. The Coptidis samples are dried, milled, and sieved to form thin cylindrical tablets each with a diameter of 13 mm and thickness of 2 mm, which are formed under a mechanical press of 10 MPa for 2 min. The influences of the main experimental parameters, such as double-pulse LIBS detection delay, double-pulse LIBS laser energy, and double-pulse LIBS pulse interval are optimized. According to the LIBS signal intensity and signal-to-background ratio, the optimal laser energy set of the characteristic line Cu I (324.46 nm) covers E1 = 15 mJ and E2 = 35 mJ, and the pulse interval and detection delay time are 1.4 μs and 1.5 μs respectively; the laser energy set of Pb I (405.78 nm) also covers E1 = 15 mJ and E2 = 35 mJ, and the pulse interval and detection delay time are 1.6 μs and 1.7 μs, respectively. Comparing with the scenarios of single-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, it can be seen that the spectral intensity of Cu I (324.46 nm) increases from 5779 counts to 12749 counts, i.e. it increases about 2.2 times; the spectral intensity of Pb I (405.78 nm) characteristic line increases from 4703 counts to 15838 counts, i.e. it increases about 3.3 times. It is shown that the second laser pulse re-excites the plasma which is generated by the first laser pulse, thus making the plasma emission spectrum stronger. The detection performances of heavy metal elements in Chinese medicinal materials are evaluated by RDP-LIBS and SP-LIBS. The results show that the detection limit of Cu decreases from 5.13 mg/kg to 1.91 mg/kg, and the detection limit of Pb decreases from 10.87 mg/kg to 3.03 mg/kg. There was observed a noticeable difference in the limit of detection between Cu and Pb, which meets the requirements of the Green Industry Standard for Import and Export of Medicinal Plants. Moreover, the linear curve fitting degree of RDP-LIBS is higher than that of SP-LIBS, which indicates that the RDP-LIBS technology has better detection performance in Chinese herbal medicine.
-
Keywords:
- reheat double pulse /
- Coptidis /
- spectral enhancement /
- limit of detection
[1] Yuan X D, Ling K W, Keuing C W 2009 Phytochem. Anal. 20 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Arpadjan S, Celik G, Taşkesen S, Gucer S 2008 Food Chem. Toxicol. 46 2871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang X H, Li H, Qin K M, Cai H, Liu X, Zheng L J, Gu J, Cai B C 2014 Anal. Lett. 47 1589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Guo Y M, Deng L M, Yang X Y, Li J M 2017 J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 32 2401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhu Z H, Li J M, Guo Y M, Cheng X, Tang Y, Guo L B, Li, X Y, Li, X Y, Lu Y F, Zeng, X Y, 2017 J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 32 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zheng P C, Liu H D, Wang J M, Shi M J, Wang X M, Zhang B, Yang R 2015 J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 30 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 赵法刚, 张宇, 张雷, 尹王保, 董磊, 马维光, 肖连团, 贾锁堂 2018 67 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao F G, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yin W B, Dong L, Ma W G, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang J M, Shi M J, Zheng P C 2017 J. Appl. Spectrosc. 84 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang J M, Xue S W, Zheng P C, Chen Y Y, Peng R 2017 Anal. Lett. 50 2000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 吴宜青, 刘津, 莫欣欣, 孙通, 刘木华 2017 66 054206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y Q, Liu J, Mo X X, Sun T, Liu M H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Q Q, Liu K, Zhao H 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 044206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘晓娜, 史新元, 贾帅芸, 赵娜, 吴志生, 乔延江 2015 中国中药杂志 40 2239
Liu X N, Shi X Y, Jia S Y, Zhao N, Wu Z S, Qiao Y J 2015 China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 40 2239
[13] 李占锋, 王芮雯, 邓琥, 尚丽平 2016 红外与激光工程 45 1006003
Li Z F, Wang R W, Deng H 2016 Infrared Laser Eng. 45 1006003
[14] 李占锋, 王芮雯, 邓琥, 尚丽平 2016 发光学报 37 100
Li Z F, Wang R W, Deng H, Shang L P 2016 Chin. J. Lumin. 37 100
[15] Wang J M, Liao X Y, Zheng P C, Xue S W, Peng R 2018 Anal. Lett. 51 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Skrodzki P J, Becker J R, Diwakar P K, Harilal S S, Hassanein A 2016 Appl. Spectrosc. 70 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lei W Q, Motto-Ros V, Boueri M, Ma Q L, Zheng L J, Zeng H P, Yu J 2009 Spectrochim. Acta B 64 891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Z Z, Deguchi Y, Liu R W, Ikutomo A, Zhang Z Z, Chong D T, Yan J P, Shiou F J 2017 Appl. Spectrosc. 71 2187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] St-Onge L, Detalle V, Sabsabi M 2002 Spectrochim. Acta B 57 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ahmed R, Iqbal J, Baig M A 2015 Laser Phys. Lett. 12 066102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王金梅, 郑慧娟, 郑培超, 谭癸宁 2018 中国激光 45 0702006
Wang J M, Zheng H J, Zheng P C, Tan G N 2018 Chin. J. Lasers 45 0702006
[22] Yu J, Ma Q, Mottoros V, Lei W Q, Wang X C, Bai X S 2012 Front Phys.-Beijing 7 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 余洋, 赵南京, 方丽, 孟德硕, 谷艳红, 王园园, 贾尧, 马明俊, 刘建国, 刘文清 2017 光谱学与光谱分析 37 588
Yu Y, Zhao N J, Fang L, Meng D S, Gu Y H, Wang Y Y, Jia Y, Ma M J, Liu J G, Liu W Q 2017 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 37 588
[24] de Giacomo A, Dell'Aglio M, Bruno D, Gaudiuso R, de Pascale O 2008 Spectrochim. Acta B 63 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Song C, Gao X, Shao Y 2016 Optik 127 3979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 特征谱线的检测限(LOD)和线性拟合度(R2)对比
Table 1. Comparison of detection limits and relative standard deviations of characteristic lines.
特征谱线 Cu I 324.46 nm Pb I 405.78 nm LOD/mg·kg–1 SP-LIBS 5.13 10.87 RDP-LIBS 1.91 3.03 GB/T 5009 20 5 R2 SP-LIBS 0.9738 0.9287 RDP-LIBS 0.9931 0.9926 表 2 Cu和Pb检测能力对比
Table 2. Comparison of detection ability between Cu and Pb.
元素 误差分析 Cu Pb 实际值/mg·kg–1 测量值/mg·kg–1 相对误差/% 精密度/% 实际值/mg·kg–1 测量值/mg·kg–1 相对误差/% 精密度/% SP-LIBS 80 67.7 15.4 9.8 800 638.3 20.2 5.4 300 244.4 18.5 7.6 6400 7163.5 11.9 4.2 RDP-LIBS 80 69.5 13.1 7.8 800 693.9 13.2 3.6 300 323.5 7.7 3.1 6400 5936.4 7.2 3.8 -
[1] Yuan X D, Ling K W, Keuing C W 2009 Phytochem. Anal. 20 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Arpadjan S, Celik G, Taşkesen S, Gucer S 2008 Food Chem. Toxicol. 46 2871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang X H, Li H, Qin K M, Cai H, Liu X, Zheng L J, Gu J, Cai B C 2014 Anal. Lett. 47 1589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Guo Y M, Deng L M, Yang X Y, Li J M 2017 J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 32 2401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhu Z H, Li J M, Guo Y M, Cheng X, Tang Y, Guo L B, Li, X Y, Li, X Y, Lu Y F, Zeng, X Y, 2017 J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 32 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zheng P C, Liu H D, Wang J M, Shi M J, Wang X M, Zhang B, Yang R 2015 J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 30 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 赵法刚, 张宇, 张雷, 尹王保, 董磊, 马维光, 肖连团, 贾锁堂 2018 67 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao F G, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yin W B, Dong L, Ma W G, Xiao L T, Jia S T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang J M, Shi M J, Zheng P C 2017 J. Appl. Spectrosc. 84 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang J M, Xue S W, Zheng P C, Chen Y Y, Peng R 2017 Anal. Lett. 50 2000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 吴宜青, 刘津, 莫欣欣, 孙通, 刘木华 2017 66 054206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y Q, Liu J, Mo X X, Sun T, Liu M H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Q Q, Liu K, Zhao H 2012 Chin. Phys. Lett. 29 044206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘晓娜, 史新元, 贾帅芸, 赵娜, 吴志生, 乔延江 2015 中国中药杂志 40 2239
Liu X N, Shi X Y, Jia S Y, Zhao N, Wu Z S, Qiao Y J 2015 China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 40 2239
[13] 李占锋, 王芮雯, 邓琥, 尚丽平 2016 红外与激光工程 45 1006003
Li Z F, Wang R W, Deng H 2016 Infrared Laser Eng. 45 1006003
[14] 李占锋, 王芮雯, 邓琥, 尚丽平 2016 发光学报 37 100
Li Z F, Wang R W, Deng H, Shang L P 2016 Chin. J. Lumin. 37 100
[15] Wang J M, Liao X Y, Zheng P C, Xue S W, Peng R 2018 Anal. Lett. 51 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Skrodzki P J, Becker J R, Diwakar P K, Harilal S S, Hassanein A 2016 Appl. Spectrosc. 70 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lei W Q, Motto-Ros V, Boueri M, Ma Q L, Zheng L J, Zeng H P, Yu J 2009 Spectrochim. Acta B 64 891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang Z Z, Deguchi Y, Liu R W, Ikutomo A, Zhang Z Z, Chong D T, Yan J P, Shiou F J 2017 Appl. Spectrosc. 71 2187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] St-Onge L, Detalle V, Sabsabi M 2002 Spectrochim. Acta B 57 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ahmed R, Iqbal J, Baig M A 2015 Laser Phys. Lett. 12 066102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王金梅, 郑慧娟, 郑培超, 谭癸宁 2018 中国激光 45 0702006
Wang J M, Zheng H J, Zheng P C, Tan G N 2018 Chin. J. Lasers 45 0702006
[22] Yu J, Ma Q, Mottoros V, Lei W Q, Wang X C, Bai X S 2012 Front Phys.-Beijing 7 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 余洋, 赵南京, 方丽, 孟德硕, 谷艳红, 王园园, 贾尧, 马明俊, 刘建国, 刘文清 2017 光谱学与光谱分析 37 588
Yu Y, Zhao N J, Fang L, Meng D S, Gu Y H, Wang Y Y, Jia Y, Ma M J, Liu J G, Liu W Q 2017 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 37 588
[24] de Giacomo A, Dell'Aglio M, Bruno D, Gaudiuso R, de Pascale O 2008 Spectrochim. Acta B 63 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Song C, Gao X, Shao Y 2016 Optik 127 3979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 18711
- PDF下载量: 91
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: