-
在自制直线式飞行时间质谱仪上进行了双色共振增强双光子电离实验, 获得了振动分辨的邻羟基苯腈的共振增强多光子电离(resonance enhanced multiphoton ionization, REMPI)光谱, 结合高精度密度泛函理论计算和Franck-Condon光谱模拟, 详细分析了光谱特征, 发现了大量基频、泛频和组合振动, 并进行了光谱归属. 大部分苯环的基频振动归属为环在平面内的畸变或平面内的摇摆, 这与分子激发过程中苯环的扩张有关. 理论和实验结果都表明, REMPI光谱的低频段信号强, 背景低, 谱带少, 分辨率好. 随着振动频率的增加, 信号向相反的方向变化. 这是由于低频段光谱主要来自于低频的基频振动、少量泛频的贡献. 随着振动频率增加, 泛频和各种模的组合振动逐渐增多, 导致了高频区谱带稠密, 分辨率变差. 高阶振动和多模的组合振动通常有较低的Franck-Condon因子, 因此信号随频率增大逐渐变弱, 信噪比变差.
-
关键词:
- 邻羟基苯腈 /
- 双色共振增强多光子电离 /
- 光谱模拟 /
- 振动光谱
The cyano group is a typical electron-withdrawing group, which has aroused the interest of relevant researchers. Many papers reported the dispersed fluorescence spectra of o-hydroxybenzonitrile, its dimers, and complexes with small molecules, aiming to study the intermolecule hydrogen bond and the vibration features of the electronic ground state. There are also reports on using fluorescence excitation spectra to study excited state vibrations, but no report on the systematical analyzing of the vibration features of excited state spectra. Compared with fluorescence spectroscopy, resonance enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI) spectroscopy detects ions to obtain excited state energy level data, which has mass-resolution capability, and eliminates the interference of impurities with different charge-to-mass ratios. The strong electron-withdrawing ability of cyano group results in higher ionization energy for molecules containing cyano groups. Many REMPI experiments on benzonitrile derivatives require two-color lasers. In this paper, two-color resonance enhanced two-photon ionization experiment is performed by using a home-made linear time-of-flight mass spectrometer, and the vibration-resolved REMPI spectrum of o-hydroxybenzonitrile is obtained for the first time. Combining the high-precision density functional theory calculations with the Franck-Condon spectral simulations, the spectral characteristics are analyzed in detail, and a large number of fundamental, overtone and combined vibrations are found. The spectral assignment is carried out as accurately as possible. Most of the fundamental vibrations located at ring are assigned to the in-plane distortion or swing of the ring, which is related to the expansion of the ring during the molecular excitation. Theoretical and experimental results show that the low-frequency signal of REMPI spectrum is strong, the background is low, the band is less, and the resolution is good. As the vibration frequency increases, the signal changes in the worse direction. This is because the low-frequency spectrum mainly comes from the low-frequency fundamental vibrations and a little contribution from overtones. As the vibration frequency increases, the contributions from overtone and combined vibrations gradually increase, resulting in dense bands and low resolution. Theoretical calculations show that the high-order vibration and combination of multi-mode vibrations usually have a lower Franck-Condon factor, so the signal gradually becomes weak as the frequency increases, and the signal-to-noise ratio becomes worse.-
Keywords:
- o-hydroxybenzonitrile /
- two-color resonance enhanced multiphoton ionization /
- spectral simulation /
- vibrational spectroscopy
[1] Roth W, Imhof P, Kleinermanns K 2001 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 3 1806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li C, Pradhan M, Tzeng W B 2005 Chem. Phys. Lett. 411 506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Küpper J, Schmitt M, Kleinermanns K 2002 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 4 4634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Jacoby C, Böhm M, Vu C, Ratzer C, Schmitt M 2006 ChemPhysChem 7 448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Georgieva M K, Angelova P N, Binev I G 2004 J. Mol. Struct. 692 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Biswas N, Wategaonkar S, Watanabe T, Ebata T, Mikami N 2004 Chem. Phys. Lett. 394 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Broquier M, Lahmani F, Zehnacker-Rentien A, Brenner V, Millié P, Peremans A 2001 J. Phys. Chem. A 105 6841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le Barbu-Debus K, Broquier M, Lahmani F, Zehnacker-Rentien A 2005 Mol. Phys. 103 1655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lahmani F, Zehnacker-Rentien A, Broquier M 2002 J. Photoch. Photobio. A 154 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lahmani F, Broquier M, Zehnacker-Rentien A 2002 Chem. Phys. Lett. 354 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kopec S, Ottiger P, Leutwyler S, Köppel H 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 142 84308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Imhof P, Kleinermanns K 2001 J. Phys. Chem. A 105 8922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhao Y, Jin Y, Li C, Jia S 2019 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 363 111182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hao J, Duan C, Yang Y, Li C, Jia S 2020 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 369 111258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 段春泱, 李娜, 赵岩, 李昌勇 2021 70 53301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan C Y, Li N, Zhao Y, Li C Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 53301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李鑫, 赵岩, 靳颖辉, 王晓锐, 余谢秋, 武媚, 韩昱行, 杨勇刚, 李昌勇, 贾锁堂 2017 66 93301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X, Zhao Y, Jin Y H, Wang X R, Yu X Q, Wu M, Han Y X, Yang Y G, Li C Y, Jia S T 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 93301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Frisch M J, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, Scuseria G E, Robb M A, et al. 2009 Gaussian 09 (Pittsburgh: Gaussian Inc. )
[18] Santoro F, Lami A, Improta R, Bloino J, Barone V 2008 J. Chem. Phys. 128 224311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo M, He R, Dai Y, Shen W, Li M, Zhu C, Lin S H. 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 136 144313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li C, Lin J L, Tzeng W B 2005 J. Chem. Phys. 122 44311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ullrich S, Geppert W D, Dessent C E H, Müller-Dethlefs K 2000 J. Phys. Chem. A 104 11864
[22] Schneider M, Wilke M, Hebestreit ML, Ruiz-Santoyo J A, Álvarez-Valtierra L, Yi J T, Meerts W L, Pratt D W, Schmitt M 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 21364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Qin C, TzengS Y, Zhang B, Tzeng W B 2014 Acta Phys-Chim. Sin. 30 1416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Huang H C, Shiung K S, Jin B Y, Tzeng W B 2013 Chem. Phys. 425 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xu Y, Tzeng S Y, Shivatare V, Takahashi K, Zhang B, Tzeng W B 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 142 124314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Isozaki T, Sakeda K, Suzuki T, Ichimura T 2010 J. Chem. Phys. 132 214308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Huang H C, Jin B Y, Tzeng W B 2012 J. Photoch. and Photobio. A 243 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wu P Y, Tzeng S Y, Hsu Y C, Tzeng W B 2017 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 332 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yang S C, Huang S W, Tzeng W B 2010 J. Phys. Chem. A 114 11144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qin C, Tzeng S Y, Zhang B, Tzeng W B 2019 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 355 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wilson E B 1934 Phys. Rev. A 45 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hollas J M 2004 Modern Spectroscopy (WEST SUSSEX: J. Wiley & Sons) p249
[33] Zhao Y, Jin Y, Hao J, Yang Y, Li C, Jia S 2018 Chem. Phys. Lett. 711 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 实验发现的激发态S1较强的振动模及其频率, 括号内数字是理论计算的频率. 实心黑色圆点代表各原子振动到达的最远点位, 空心圆圈代表C原子平衡点位, H原子用小点表示, 平衡点的O和N分别用红色和粉色表示
Fig. 3. Strong vibration modes of the excited state S1 and their vibration frequencies found in the experiment. The numbers in parentheses are the theoretically calculated frequencies. The solid black dot represents the biggest displacement, the open circle represents the equilibrium point of the C atom. The H atom is represented by a small dot, and the O and N of the equilibrium point are represented by red and pink dots, respectively.
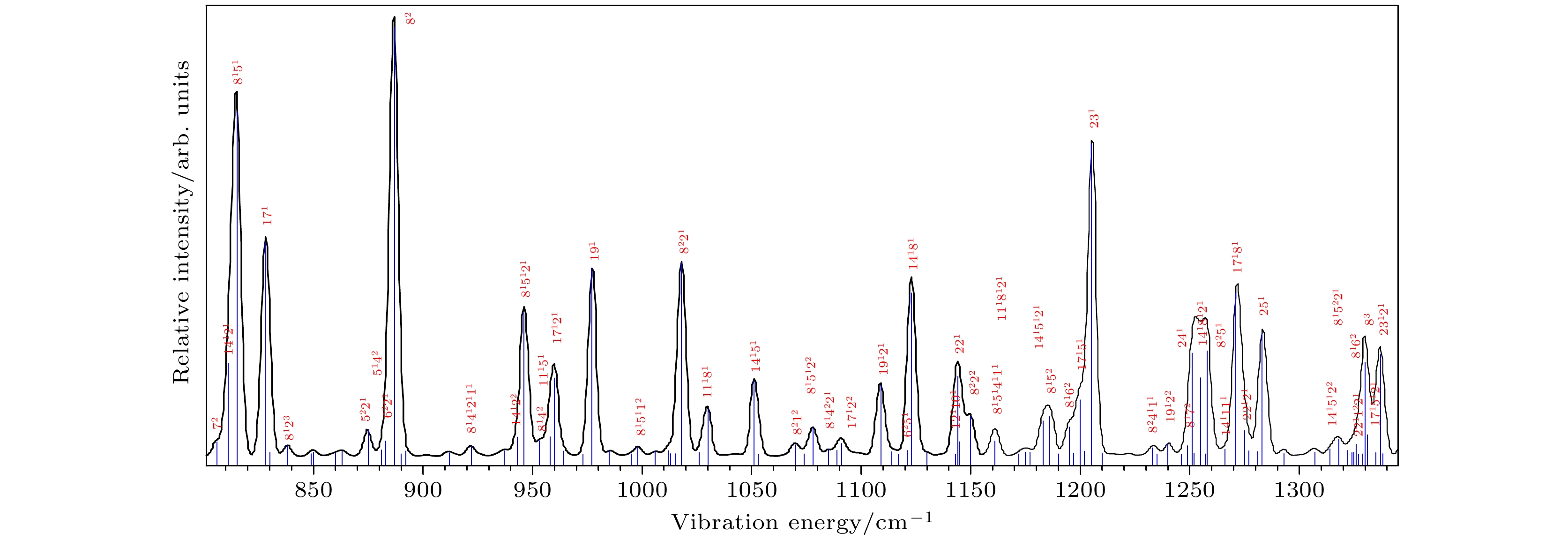
图 4 基于B3 LYP/aug-cc-pvtz计算的Franck-Condon光谱及其谱带的归属, 蓝色竖线代表振动模, 线的高度代表了振动模的强度. 大的红色数字代表了计算的所有振动频率按升序排定的序号, 上标数字代表了振动模的泛频次数
Fig. 4. Franck-Condon simulation and the assignment of its bands calculated based on B3 LYP/aug-cc-pvtz. The blue vertical line represents the vibration mode, and its height represents the strength of the vibration mode. The big red number represents the sequence number of all calculated vibration frequencies in ascending order, and the superscript number represents the vibrational quantum number of overtone.
表 1 双色REMPI测量的电子振动跃迁能、振动频率和相对强度、密度泛函理论(B3LYP/6-311++G(d, p))计算的激发态振动频率(修正因子为0.971)及光谱归属(单位: cm–1)
Table 1. Measured electronic vibration transition energy, vibration frequency, and relative intensity by two-color REMPI, excited state vibration frequency calculated by density functional theory of B3LYP/6-311++G(d, p) level (scaler factor: 0.971), and spectral assignment (in cm–1).
跃迁能 测量频率 相对强度 计算频率 归属a 跃迁能 测量频率 相对强度 计算频率 归属a 33973 0 100 $0^0_0 $ 34715 742 20 9b${}^2_0 $ 34102 129 80 131 $15^1_0 $ 34751 778 5 6b${}^1_0 $10a${}^1_0 $γCN${}^1_0 $ 34152 179 17 γCN${}^2_0 $ 34781 808 18 9b${}^1_0 $${15}^2_0 $γCN${}^2_0 $ 34231 258 23 $15^2_0 $ 34787 814 39 9b${}^1_0 $6b${}^1_0 $/${1}^1_0 $${15}^1_0 $ 34243 270 17 γCN${}^3_0 $ 34795 822 10 10a${}^3_0 $γCN${}^1_0 $ 34279 306 4 $15^1_0 $γCN${}^2_0 $ 34803 830 37 827 ${12}^1_0 $ 34306 333 9 10a${}^1_0 $γCN${}^1_0 $ 34844 871 14 9b${}^2_0 $${15}^1_0 $ 34344 371 64 371 9b${}^1_0 $ 34859 886 20 6b${}^2_0 $ 34361 388 3 $15^3_0 $ 34916 943 34 6b${}^1_0 $9b${}^1_0 $${15}^1_0 $/${1}^1_0 $${15}^2_0 $ 34370 397 2 $15^1_0 $γCN${}^3_0 $ 34935 961 72 12b${}^1_0 $${15}^1_0 $/9b${}^1_0 $βCN${}^1_0 $ 34397 424 7 10a${}^1_0 $γCN${}^2_0 $ 34981 1008 13 6b${}^1_0 $${15}^1_0 $ 34416 443 42 443 6b${}^1_0 $ 35024 1051 35 ${1}^1_0 $9b${}^1_0 $ 34436 463 3 10a${}^1_0 $$15^1_0 $γCN${}^1_0 $ 35062 1089 33 ${12}^1_0 $${15}^2_0 $/6b${}^1_0 $9b${}^1_0 $${15}^2_0 $ 34464 491 8 10a${}^2_0 $ 35094 1121 32 ${1}^1_0 $6b${}^1_0 $ 34473 500 30 9b${}^1_0 $$15^1_0 $ 35130 1156 34 ${4}^1_0 $6b${}^1_0 $${15}^1_0 $ 34485 512 5 10a${}^1_0 $γCN${}^3_0 $ 35174 1201 19 1204 ${13}^1_0 $ 34494 521 5 520 6a${}^1_0 $ 35201 1227 29 6b${}^1_0 $10a${}^1_0 $γCN${}^1_0 $ 34523 549 5 9b${}^1_0 $γCN${}^2_0 $ 35230 1257 27 6b${}^2_0 $9b${}^1_0 $ 34545 572 25 6b${}^1_0 $${15}^1_0 $ 35247 1274 43 ${12}^1_0 $6b${}^1_0 $ 34557 582 8 586 βCN${}^1_0 $ 35292 1319 29 6b${}^3_0 $ 34594 621 7 6b${}^1_0 $γCN${}^2_0 $ 35298 1325 24 ${13}^1_0 $${15}^1_0 $ 34603 630 14 9b${}^1_0 $${15}^2_0 $ 35306 1333 21 18b${}^1_0 $6b${}^1_0 $ 34651 679 51 679 ${1}^1_0 $ 35328 1355 12 6b${}^1_0 $16b${}^2_0 $ 34675 702 7 6b${}^1_0 $${15}^2_0 $ 注: a β, 平面内的摇摆; γ, 垂直于环平面的振动. 表 2 B3LYP/aug-cc-pvtz理论计算的邻羟基苯腈的电子基态S0和激发态S1的键长和键角
Table 2. Bond lengths and bond angles of o-hydroxybenzonitrile in S0 and S1 states calculated with B3LYP/aug-cc-pvtz level.
S1 S0 Δ(S1–S0) 键长/Å C1—C2 1.454 1.407 0.047 C2—C3 1.411 1.401 0.010 C3—C4 1.419 1.382 0.037 C4—C5 1.399 1.395 0.004 C5—C6 1.414 1.385 0.029 C6—C1 1.399 1.393 0.006 C1—O11 1.333 1.352 –0.019 O11—H12 0.976 0.967 0.009 C2—C13 1.395 1.424 –0.029 C13—N14 1.171 1.154 0.017 C4—H8 1.082 1.080 0.002 C3—H7 1.079 1.081 –0.002 C6—H10 1.080 1.080 0 C5—H9 1.078 1.081 –0.003 键角/(°) C1—O11—H12 109.995 110.823 –0.828 C2—C13—N14 174.683 175.853 –1.170 -
[1] Roth W, Imhof P, Kleinermanns K 2001 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 3 1806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li C, Pradhan M, Tzeng W B 2005 Chem. Phys. Lett. 411 506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Küpper J, Schmitt M, Kleinermanns K 2002 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 4 4634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Jacoby C, Böhm M, Vu C, Ratzer C, Schmitt M 2006 ChemPhysChem 7 448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Georgieva M K, Angelova P N, Binev I G 2004 J. Mol. Struct. 692 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Biswas N, Wategaonkar S, Watanabe T, Ebata T, Mikami N 2004 Chem. Phys. Lett. 394 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Broquier M, Lahmani F, Zehnacker-Rentien A, Brenner V, Millié P, Peremans A 2001 J. Phys. Chem. A 105 6841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Le Barbu-Debus K, Broquier M, Lahmani F, Zehnacker-Rentien A 2005 Mol. Phys. 103 1655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lahmani F, Zehnacker-Rentien A, Broquier M 2002 J. Photoch. Photobio. A 154 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lahmani F, Broquier M, Zehnacker-Rentien A 2002 Chem. Phys. Lett. 354 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kopec S, Ottiger P, Leutwyler S, Köppel H 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 142 84308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Imhof P, Kleinermanns K 2001 J. Phys. Chem. A 105 8922
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhao Y, Jin Y, Li C, Jia S 2019 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 363 111182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hao J, Duan C, Yang Y, Li C, Jia S 2020 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 369 111258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 段春泱, 李娜, 赵岩, 李昌勇 2021 70 53301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan C Y, Li N, Zhao Y, Li C Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 53301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李鑫, 赵岩, 靳颖辉, 王晓锐, 余谢秋, 武媚, 韩昱行, 杨勇刚, 李昌勇, 贾锁堂 2017 66 93301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X, Zhao Y, Jin Y H, Wang X R, Yu X Q, Wu M, Han Y X, Yang Y G, Li C Y, Jia S T 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 93301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Frisch M J, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, Scuseria G E, Robb M A, et al. 2009 Gaussian 09 (Pittsburgh: Gaussian Inc. )
[18] Santoro F, Lami A, Improta R, Bloino J, Barone V 2008 J. Chem. Phys. 128 224311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo M, He R, Dai Y, Shen W, Li M, Zhu C, Lin S H. 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 136 144313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li C, Lin J L, Tzeng W B 2005 J. Chem. Phys. 122 44311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ullrich S, Geppert W D, Dessent C E H, Müller-Dethlefs K 2000 J. Phys. Chem. A 104 11864
[22] Schneider M, Wilke M, Hebestreit ML, Ruiz-Santoyo J A, Álvarez-Valtierra L, Yi J T, Meerts W L, Pratt D W, Schmitt M 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 21364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Qin C, TzengS Y, Zhang B, Tzeng W B 2014 Acta Phys-Chim. Sin. 30 1416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Huang H C, Shiung K S, Jin B Y, Tzeng W B 2013 Chem. Phys. 425 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xu Y, Tzeng S Y, Shivatare V, Takahashi K, Zhang B, Tzeng W B 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 142 124314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Isozaki T, Sakeda K, Suzuki T, Ichimura T 2010 J. Chem. Phys. 132 214308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Huang H C, Jin B Y, Tzeng W B 2012 J. Photoch. and Photobio. A 243 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wu P Y, Tzeng S Y, Hsu Y C, Tzeng W B 2017 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 332 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yang S C, Huang S W, Tzeng W B 2010 J. Phys. Chem. A 114 11144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Qin C, Tzeng S Y, Zhang B, Tzeng W B 2019 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 355 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wilson E B 1934 Phys. Rev. A 45 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hollas J M 2004 Modern Spectroscopy (WEST SUSSEX: J. Wiley & Sons) p249
[33] Zhao Y, Jin Y, Hao J, Yang Y, Li C, Jia S 2018 Chem. Phys. Lett. 711 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5516
- PDF下载量: 83
- 被引次数: 0
















 下载:
下载: